教科書
重要箇所穴埋め問題(64題)
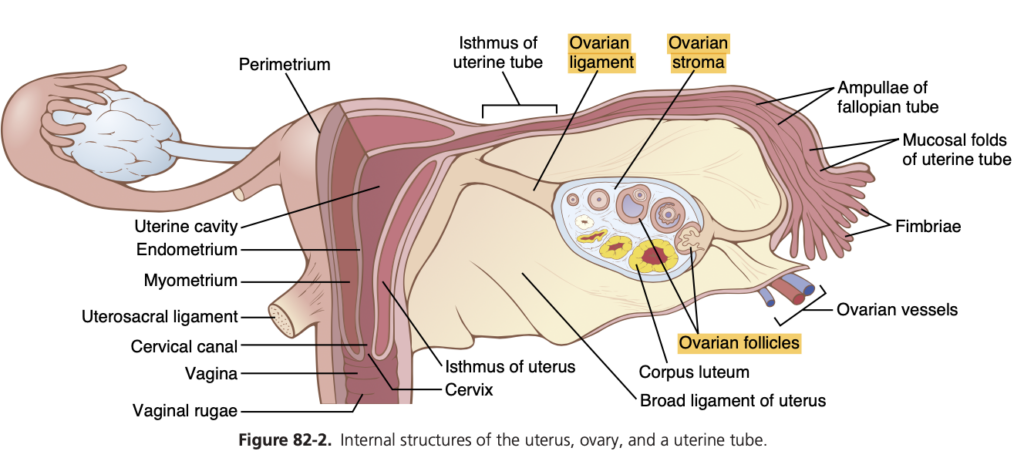
Question 1: Female Reproductive System (女性生殖器系)
Q: The female reproductive system consists of the _______, _______ , and _______, which are essential for reproduction.
Answer: ovaries / fallopian tubes / uterus
Explanation:
女性の生殖器系は卵巣 (ovaries)、卵管 (fallopian tubes)、および子宮 (uterus) で構成されており、これらはすべて妊娠に重要な役割を果たします。卵巣は卵子 (ova) を生産し、卵管は卵子を子宮へと輸送します。子宮は受精卵が着床して成長する場所です。
Question 2: Oogenesis (卵子形成)
Q: During oogenesis, primordial germ cells migrate from the _______ to the _______, where they differentiate into _______.
Answer: yolk sac / ovarian cortex / oogonia
Explanation:
卵子形成 (oogenesis) の過程では、原始生殖細胞 (primordial germ cells) は卵黄嚢 (yolk sac) から卵巣の皮質 (ovarian cortex) へ移動し、卵母細胞 (oogonia) に分化します。この移動と分化は、卵巣の発生の重要な部分です。
Question 3: Follicular Development (卵胞の発達)
Q: A primordial follicle consists of a _______ surrounded by a single layer of _______ cells, which originate from the _______.
Answer: primary oocyte / granulosa / ovarian stroma
Explanation:
原始卵胞 (primordial follicle) は、1つの一次卵母細胞 (primary oocyte) と、それを取り囲む1層の顆粒膜細胞 (granulosa cells) から構成されます。顆粒膜細胞は卵巣の間質 (ovarian stroma) に由来します。
Question 4: Meiosis of Oocytes (卵母細胞の減数分裂)
Q: The first stage of meiosis begins during _______ development, is arrested in _______ I, and resumes after _______.
Answer: fetal / prophase / puberty
Explanation:
卵母細胞の減数分裂 (meiosis) は胎児期 (fetal development) に始まり、第一分裂前期 (prophase I) で一時的に停止します。その後、思春期 (puberty) 以降に再開されます。これは、卵子の成熟過程の一部です。
Question 5: Hormonal Regulation (ホルモン調節)
Q: The ovarian hormones _______ and _______ are secreted in response to the anterior pituitary hormones _______.
Answer: estrogen / progesterone / FSH and LH
Explanation:
卵巣ホルモンであるエストロゲン (estrogen) とプロゲステロン (progesterone) は、下垂体前葉から分泌される卵胞刺激ホルモン (FSH) と黄体形成ホルモン (LH) の刺激に応答して分泌されます。これらのホルモンは、月経周期の調節に重要な役割を果たします。
Question 6: Ovulation Process (排卵の過程)
Q: Ovulation occurs when an _______ is released from the _______ into the _______.
Answer: ovum / ovarian follicle / abdominal cavity
Explanation:
排卵 (ovulation) は、卵胞 (ovarian follicle) から卵子 (ovum) が腹腔 (abdominal cavity) に放出される過程です。その後、卵子は卵管 (fallopian tube) に移動し、受精が可能な状態になります。
Question 7: Role of Gonadotropic Hormones (性腺刺激ホルモンの役割)
Q: The gonadotropic hormones _______ and _______ are secreted by the _______ gland to regulate ovarian function.
Answer: FSH / LH / anterior pituitary
Explanation:
卵巣機能は、下垂体前葉 (anterior pituitary) から分泌される卵胞刺激ホルモン (FSH) と黄体形成ホルモン (LH) によって調節されます。これらのホルモンは、卵胞の成長や排卵を促進する重要な役割を果たします。
Question 8: Menstrual Cycle (月経周期)
Q: The menstrual cycle is regulated by fluctuations in _______ and _______, which cause cyclical changes in the _______.
Answer: estrogen / progesterone / endometrium
Explanation:
月経周期 (menstrual cycle) は、エストロゲン (estrogen) とプロゲステロン (progesterone) の変動により調節されます。これらのホルモンは、子宮内膜 (endometrium) に周期的な変化を引き起こし、受精卵の着床をサポートします。
Question 9: Puberty and Menarche (思春期と初経)
Q: Puberty begins with increased secretion of _______ and _______, leading to the first menstrual cycle, known as _______.
Answer: FSH / LH / menarche
Explanation:
思春期 (puberty) では、卵胞刺激ホルモン (FSH) と黄体形成ホルモン (LH) の分泌が増加します。これにより、最初の月経 (menarche) が始まります。思春期のこの変化は、女性の生殖能力の開始を示しています。
Question 10: Female Sexual Cycle (女性の性周期)
Q: The female sexual cycle lasts for an average of _______ days and is characterized by the release of _______ and the preparation of the _______ for implantation.
Answer: 28 / a single ovum / endometrium
Explanation:
女性の性周期 (female sexual cycle) は平均して28日間続き、卵巣から1つの卵子 (single ovum) が排出され、子宮内膜 (endometrium) が受精卵の着床に備えるという特徴があります。この周期は月経周期 (menstrual cycle) とも呼ばれます。
Question 11: Hormonal Pulsatile Secretion (ホルモンのパルス分泌)
Q: The hypothalamus secretes _______ in short pulses every _______ minutes, which stimulates the release of _______ from the anterior pituitary.
Answer: GnRH / 90 / FSH and LH
Explanation:
視床下部 (hypothalamus) は、性腺刺激ホルモン放出ホルモン (GnRH) を90分ごとの短いパルス (pulses) で分泌します。これにより、下垂体前葉 (anterior pituitary) から卵胞刺激ホルモン (FSH) と黄体形成ホルモン (LH) の分泌が促進され、卵巣の機能が調節されます。
Question 12: Corpus Luteum Fate (黄体の運命)
Q: The corpus luteum is formed after _______ and secretes _______ and _______ to maintain the endometrium.
Answer: ovulation / estrogen / progesterone
Explanation:
排卵 (ovulation) 後、卵胞は黄体 (corpus luteum) に変わります。黄体は、子宮内膜 (endometrium) を維持するためにエストロゲン (estrogen) とプロゲステロン (progesterone) を分泌します。妊娠が成立しない場合、黄体は退行して黄体退行 (luteolysis) が起こります。
Question 13: Embryo Implantation (胚の着床)
Q: Embryo implantation occurs in the _______ when the _______ attaches to the _______ prepared during the menstrual cycle.
Answer: uterus / blastocyst / endometrium
Explanation:
胚の着床 (embryo implantation) は、受精卵が子宮 (uterus) の内膜 (endometrium) に付着することで起こります。この受精卵は胚盤胞 (blastocyst) にまで発達しており、月経周期 (menstrual cycle) によって準備された内膜に結合します。この過程は、妊娠の開始において重要な役割を果たします。
Question 14: Menstrual Cycle Irregularities (月経周期の異常)
Q: Menstrual cycle irregularities may be caused by abnormal fluctuations in _______ , _______ , and _______ levels.
Answer: FSH / LH / estrogen
Explanation:
月経周期の異常 (menstrual cycle irregularities) は、卵胞刺激ホルモン (FSH)、黄体形成ホルモン (LH)、およびエストロゲン (estrogen) の異常な変動が原因となる可能性があります。これらのホルモンのバランスが崩れると、排卵の失敗、無月経 (amenorrhea)、および不規則な月経周期が引き起こされることがあります。
Question 1: Ovarian Follicle Growth (卵胞の成長)
Q: The growth of ovarian follicles begins with the development of _______ follicles, followed by the formation of _______ follicles, and finally the development of _______ follicles.
Answer: primordial / primary / vesicular
Explanation:
卵胞の成長 (follicular growth) は、原始卵胞 (primordial follicle) の発達から始まり、次に一次卵胞 (primary follicle) へと進み、最終的に胞状卵胞 (vesicular follicle) へと発達します。これは月経周期の一部であり、排卵に向けた重要なプロセスです。
Question 2: Role of Theca Cells (内卵胞膜細胞の役割)
Q: The theca layer of the follicle is divided into the _______ and _______, with the former secreting _______ hormones.
Answer: theca interna / theca externa / steroid
Explanation:
卵胞の卵胞膜 (theca) は、内卵胞膜 (theca interna) と外卵胞膜 (theca externa) に分けられます。内卵胞膜 (theca interna) は、ステロイドホルモン (steroid hormones) の分泌を担い、卵胞の発達に重要な役割を果たします。
Question 3: Role of FSH and LH (FSHとLHの役割)
Q: The growth of primary follicles is stimulated by _______ alone, but later growth of vesicular follicles requires the addition of _______ and _______.
Answer: FSH / LH / estrogen
Explanation:
一次卵胞 (primary follicles) の成長は、卵胞刺激ホルモン (FSH) のみによって促進されますが、胞状卵胞 (vesicular follicles) へのさらなる成長には、黄体形成ホルモン (LH) とエストロゲン (estrogen) の追加的な刺激が必要です。これにより、卵胞の発達が加速されます。
Question 4: Ovulation Mechanism (排卵のメカニズム)
Q: Ovulation occurs when a surge of _______ causes the _______ to release proteolytic enzymes, leading to the rupture of the _______.
Answer: LH / theca externa / follicular wall
Explanation:
排卵 (ovulation) は、黄体形成ホルモン (LH) の急激な増加によって引き起こされます。このホルモンは、外卵胞膜 (theca externa) にリソソーム由来のプロテアーゼ (proteolytic enzymes) を放出させ、卵胞壁 (follicular wall) の崩壊と卵子の放出を促します。
Question 5: Follicular Atresia (卵胞の閉鎖)
Q: Follicular atresia occurs when _______ levels decrease due to _______ secretion from the dominant follicle, leading to the degeneration of _______ follicles.
Answer: FSH / estrogen / smaller
Explanation:
卵胞の閉鎖 (follicular atresia) は、優勢な卵胞 (dominant follicle) からのエストロゲン (estrogen) 分泌によって、卵胞刺激ホルモン (FSH) の分泌が低下することで起こります。この結果、成長が不十分な小さな卵胞 (smaller follicles) が退行してしまいます。
Question 6: Follicular Fluid (卵胞液)
Q: Follicular fluid is secreted by _______ cells and contains a high concentration of _______, which stimulates the growth of more _______ receptors on these cells.
Answer: granulosa / estrogen / FSH
Explanation:
卵胞液 (follicular fluid) は顆粒膜細胞 (granulosa cells) によって分泌され、その中にはエストロゲン (estrogen) が高濃度で含まれています。このエストロゲンは、顆粒膜細胞にさらに多くの卵胞刺激ホルモン受容体 (FSH receptors) を生成させ、フィードバック効果を引き起こします。
Question 7: Dominant Follicle Selection (優勢卵胞の選択)
Q: The dominant follicle is selected because it has a higher concentration of _______, which inhibits the secretion of _______ from the pituitary, causing the regression of _______ follicles.
Answer: estrogen / FSH / smaller
Explanation:
優勢卵胞 (dominant follicle) は、より高い濃度のエストロゲン (estrogen) を分泌するため、下垂体 (pituitary) からの卵胞刺激ホルモン (FSH) の分泌を抑制します。この抑制により、他の成長中の小さな卵胞 (smaller follicles) は退行してしまいます。
Question 8: Ovulation Timing (排卵のタイミング)
Q: Ovulation occurs approximately _______ days after the onset of menstruation, triggered by a surge in _______ secretion, which peaks _______ hours before ovulation.
Answer: 14 / LH / 16
Explanation:
排卵 (ovulation) は、月経 (menstruation) の開始から約14日後に起こります。排卵の約16時間前に黄体形成ホルモン (LH) の急増 (surge) が見られ、これが排卵の引き金となります。
Question 9: Role of Proteolytic Enzymes (プロテアーゼの役割)
Q: Proteolytic enzymes are released by _______ cells, causing the weakening of the _______ and leading to the release of the _______.
Answer: theca externa / follicular wall / ovum
Explanation:
プロテアーゼ (proteolytic enzymes) は、外卵胞膜 (theca externa) の細胞から放出されます。これにより、卵胞壁 (follicular wall) が弱体化し、卵子 (ovum) が放出される排卵 (ovulation) が引き起こされます。
Question 10: Corona Radiata (放線冠)
Q: The corona radiata is composed of _______ cells that surround the _______ and are released during _______.
Answer: granulosa / ovum / ovulation
Explanation:
放線冠 (corona radiata) は、卵子 (ovum) を取り囲む顆粒膜細胞 (granulosa cells) から構成されています。これらの細胞は、排卵 (ovulation) の過程で卵子とともに放出され、卵子の保護と輸送に関与します。
Question 1: Corpus Luteum Formation (黄体の形成)
Q: The corpus luteum is formed from the _______ and _______ cells after ovulation and is responsible for secreting large amounts of _______ during the luteal phase.
Answer: granulosa / theca interna / progesterone
Explanation:
排卵後、顆粒膜細胞 (granulosa cells) と内卵胞膜細胞 (theca interna cells) が黄体 (corpus luteum) を形成します。黄体は、黄体期 (luteal phase) にプロゲステロン (progesterone) を大量に分泌する役割を担っています。
Question 2: Luteinization Process (黄体化の過程)
Q: Luteinization involves the conversion of _______ and _______ cells into lutein cells, which contain _______ inclusions, giving them a yellowish appearance.
Answer: granulosa / theca interna / lipid
Explanation:
黄体化 (luteinization) とは、顆粒膜細胞 (granulosa cells) と内卵胞膜細胞 (theca interna cells) が黄体細胞 (lutein cells) に変化するプロセスです。これらの細胞は脂質 (lipid) を含むため、黄色っぽい外観を持つようになります。
Question 3: Role of Luteinizing Hormone (黄体形成ホルモンの役割)
Q: The conversion of granulosa and theca interna cells into lutein cells is triggered by _______ secreted from the _______ and is maintained until the production of _______ by the placenta during pregnancy.
Answer: LH / anterior pituitary / chorionic gonadotropin
Explanation:
顆粒膜細胞 (granulosa cells) と内卵胞膜細胞 (theca interna cells) を黄体細胞 (lutein cells) に変化させるのは、下垂体前葉 (anterior pituitary) から分泌される黄体形成ホルモン (LH) です。妊娠が成立すると、胎盤 (placenta) から分泌される絨毛性ゴナドトロピン (chorionic gonadotropin, hCG) によって黄体の機能が維持されます。
Question 4: Hormones Secreted by the Corpus Luteum (黄体が分泌するホルモン)
Q: The corpus luteum secretes _______ and _______, which inhibit the release of _______ from the anterior pituitary gland.
Answer: progesterone / estrogen / FSH
Explanation:
黄体 (corpus luteum) は、プロゲステロン (progesterone) とエストロゲン (estrogen) を分泌します。これらのホルモンは、下垂体前葉 (anterior pituitary) からの卵胞刺激ホルモン (FSH) の分泌を抑制し、新たな卵胞の成長を防ぎます。
Question 5: Corpus Albicans Formation (白体の形成)
Q: The corpus luteum degenerates into the _______ after about _______ days, when the levels of _______ and progesterone drop.
Answer: corpus albicans / 12 / estrogen
Explanation:
黄体 (corpus luteum) は、排卵から約12日後に退行し、白体 (corpus albicans) になります。この時、エストロゲン (estrogen) およびプロゲステロン (progesterone) のレベルが大幅に低下します。この減少は、次の卵胞の成長を開始させる引き金となります。
Question 6: Luteal Phase of the Ovarian Cycle (黄体期の卵巣周期)
Q: During the luteal phase, the corpus luteum secretes _______ and _______, which inhibit the release of _______ from the anterior pituitary, maintaining a low level of gonadotropic hormones.
Answer: progesterone / estrogen / LH
Explanation:
黄体期 (luteal phase) では、黄体 (corpus luteum) からプロゲステロン (progesterone) とエストロゲン (estrogen) が分泌されます。これらのホルモンは、下垂体前葉 (anterior pituitary) からの黄体形成ホルモン (LH) の分泌を抑制し、ゴナドトロピンホルモンのレベルを低く保ちます。
Question 7: Feedback Mechanism of Estrogen and Progesterone (エストロゲンとプロゲステロンのフィードバック機構)
Q: The secretion of estrogen and progesterone from the corpus luteum inhibits the release of _______ and _______ from the anterior pituitary, preventing the development of new _______.
Answer: FSH / LH / follicles
Explanation:
黄体 (corpus luteum) から分泌されるエストロゲン (estrogen) とプロゲステロン (progesterone) は、下垂体前葉 (anterior pituitary) からの卵胞刺激ホルモン (FSH) と黄体形成ホルモン (LH) の分泌を抑制します。この抑制により、新しい卵胞 (follicles) の成長が防がれます。
Question 8: Role of Inhibin (インヒビンの役割)
Q: The hormone _______ is secreted by lutein cells and inhibits the release of _______ from the anterior pituitary, helping to maintain low levels of _______ during the luteal phase.
Answer: inhibin / FSH / gonadotropic hormones
Explanation:
インヒビン (inhibin) は、黄体細胞 (lutein cells) によって分泌され、下垂体前葉 (anterior pituitary) からの卵胞刺激ホルモン (FSH) の分泌を抑制します。このメカニズムにより、黄体期 (luteal phase) におけるゴナドトロピンホルモン (gonadotropic hormones) のレベルが低く保たれます。
Question 9: Estrogen and Progesterone Function (エストロゲンとプロゲステロンの機能)
Q: The two main ovarian hormones are _______ and _______, which promote the growth of the _______ and prepare the uterus for implantation.
Answer: estrogen / progesterone / endometrium
Explanation:
卵巣の2つの主要なホルモンは、エストロゲン (estrogen) とプロゲステロン (progesterone) です。これらのホルモンは、子宮内膜 (endometrium) の成長を促進し、受精卵の着床の準備を行います。
Question 10: Menstrual Cycle Reset (月経周期のリセット)
Q: The decrease in _______ and _______ at the end of the luteal phase causes the degeneration of the _______ and initiates a new menstrual cycle.
Answer: estrogen / progesterone / corpus luteum
Explanation:
黄体期 (luteal phase) の終わりにエストロゲン (estrogen) とプロゲステロン (progesterone) が減少すると、黄体 (corpus luteum) が退行し、月経周期 (menstrual cycle) が再開します。これにより、新しい卵胞の成長が開始されます。
Question 1: Synthesis of Estrogens (エストロゲンの合成)
Q: Estrogens are synthesized in the _______ from _______ with the help of the enzyme _______ in granulosa cells.
Answer: ovaries / androgens / aromatase
Explanation:
エストロゲン (estrogens) は、卵巣 (ovaries) でアンドロゲン (androgens) から合成されます。このプロセスは、顆粒膜細胞 (granulosa cells) に存在するアロマターゼ (aromatase) 酵素によって行われます。
Question 2: Transport of Estrogens (エストロゲンの輸送)
Q: Estrogens are transported in the blood bound to _______ and _______ globulins, and they are released into tissues within _______ minutes.
Answer: albumin / estrogen-binding / 30
Explanation:
エストロゲン (estrogens) は、血漿アルブミン (albumin) およびエストロゲン結合グロブリン (estrogen-binding globulins) に結合して血流内を輸送されます。これらのホルモンは、約30分以内に組織へ放出されます。
Question 3: Degradation of Estrogens (エストロゲンの分解)
Q: Estrogens are conjugated in the _______ to form _______ and sulfates, which are excreted mainly in the _______.
Answer: liver / glucuronides / urine
Explanation:
エストロゲン (estrogens) は、肝臓 (liver) でグルクロン酸抱合 (glucuronides) および硫酸抱合 (sulfates) されます。これらの抱合物は、主に尿 (urine) に排泄されますが、一部は胆汁にも排泄されます。
Question 4: Function of Estrogens (エストロゲンの機能)
Q: Estrogens promote the proliferation and growth of _______ tissues, stimulate the development of _______ characteristics, and support the proliferation of the _______ lining.
Answer: reproductive / secondary sexual / endometrial
Explanation:
エストロゲン (estrogens) は、生殖器組織 (reproductive tissues) の増殖と成長を促進し、女性の二次性徴 (secondary sexual characteristics) の発達を刺激します。また、子宮内膜 (endometrial lining) の増殖をサポートし、妊娠に備えます。
Question 5: Effects of Estrogen on Uterus (エストロゲンの子宮への効果)
Q: Estrogens increase the size of the _______ , cause proliferation of the _______ , and stimulate the development of _______ glands.
Answer: uterus / endometrial stroma / endometrial
Explanation:
エストロゲン (estrogens) は、子宮 (uterus) のサイズを増大させ、子宮内膜基質 (endometrial stroma) の増殖を促進します。また、子宮内膜腺 (endometrial glands) の発達を刺激し、妊娠に備えるための栄養供給をサポートします。
Question 6: Effects of Estrogen on Fallopian Tubes (エストロゲンの卵管への効果)
Q: Estrogens stimulate proliferation of the _______ tissues, increase the number of _______ cells, and enhance the activity of _______ in the fallopian tubes.
Answer: glandular / ciliated / cilia
Explanation:
エストロゲン (estrogens) は、卵管 (fallopian tubes) の腺組織 (glandular tissues) の増殖を促進し、線毛細胞 (ciliated cells) の数を増加させます。これにより、受精卵の子宮への輸送を助ける線毛 (cilia) の活動が促進されます。
Question 7: Effects of Estrogen on Bone (エストロゲンの骨への効果)
Q: Estrogens inhibit _______ activity, promote the production of _______ , and stimulate the closure of _______ in long bones.
Answer: osteoclastic / osteoprotegerin / epiphyses
Explanation:
エストロゲン (estrogens) は、破骨細胞 (osteoclasts) の活動を抑制し、骨吸収を防ぎます。また、オステオプロテゲリン (osteoprotegerin) の生成を促進し、長骨 (long bones) の骨端 (epiphyses) を閉鎖させます。これにより、女性の成長が男性よりも早く止まる理由が説明されます。
Question 8: Function of Progesterone (プロゲステロンの機能)
Q: Progesterone prepares the _______ for implantation, supports the development of the _______ , and promotes the growth of _______ in the breast.
Answer: uterus / endometrium / alveoli
Explanation:
プロゲステロン (progesterone) は、受精卵の着床 (implantation) に備えて子宮 (uterus) を準備し、子宮内膜 (endometrium) の発達をサポートします。また、乳房 (breast) において乳腺胞 (alveoli) の成長を促進します。
Question 9: Degradation of Progesterone (プロゲステロンの分解)
Q: Progesterone is metabolized in the _______ , converted into _______ , and excreted in the _______ as its final metabolic product.
Answer: liver / pregnanediol / urine
Explanation:
プロゲステロン (progesterone) は肝臓 (liver) で代謝され、プレグナンジオール (pregnanediol) に変換されます。最終的な代謝産物は尿 (urine) に排泄され、これによりプロゲステロンの産生量を推定することが可能です。
Question 10: Estrogen and Breast Development (エストロゲンと乳房の発達)
Q: Estrogens promote the growth of _______ tissues, the development of the _______ system, and the deposition of _______ in the breasts.
Answer: stromal / ductile / fat
Explanation:
エストロゲン (estrogens) は、乳房 (breasts) の間質組織 (stromal tissues) の成長、乳管系 (ductile system) の発達、および脂肪 (fat) の沈着を促進します。これにより、思春期の女性の乳房が成長しますが、乳腺小葉や乳腺胞の完全な成長はプロゲステロンとプロラクチンの影響を受けます。
Question 1: Osteoporosis (骨粗鬆症)
Q: Estrogen deficiency after _______ leads to increased _______ activity, decreased bone _______, and decreased calcium deposition.
Answer: menopause / osteoclastic / matrix
Explanation:
閉経 (menopause) 後のエストロゲン (estrogen) 欠乏は、破骨細胞 (osteoclastic) の活動を増加させ、骨基質 (bone matrix) の減少とカルシウムの沈着減少を引き起こします。この影響は、骨粗鬆症 (osteoporosis) の発生に関連しています。
Question 2: Menstrual Phases (月経の段階)
Q: The endometrial cycle includes the _______ phase before ovulation, the _______ phase after ovulation, and the _______ phase when menstruation occurs.
Answer: proliferative / secretory / menstrual
Explanation:
子宮内膜周期 (endometrial cycle) は、排卵前の増殖期 (proliferative phase)、排卵後の分泌期 (secretory phase)、および月経期 (menstrual phase) で構成されます。これらの各段階は、卵巣ホルモン (エストロゲンとプロゲステロン) の変化によって制御されます。
Question 3: Progesterone Functions (プロゲステロンの機能)
Q: Progesterone promotes secretory changes in the _______, decreases the frequency of _______ contractions, and supports the development of breast _______.
Answer: endometrium / uterine / alveoli
Explanation:
プロゲステロン (progesterone) は、子宮内膜 (endometrium) に分泌性変化を引き起こし、子宮 (uterus) の収縮頻度を減少させます。また、乳房 (breast) の乳腺胞 (alveoli) の発達をサポートし、授乳の準備を整えます。
Question 4: Menstrual Flow (月経の流れ)
Q: Menstrual flow contains about _______ mL of blood, _______ mL of serous fluid, and large numbers of _______ for infection resistance.
Answer: 40 / 35 / leukocytes
Explanation:
月経血 (menstrual flow) には、約40mLの血液 (blood)、35mLの漿液 (serous fluid)、および多数の白血球 (leukocytes) が含まれています。これにより、子宮内膜が剥がれ落ちる際の感染に対する抵抗力が高まります。
Question 5: Effect of Estrogens on Skin (エストロゲンの皮膚への効果)
Q: Estrogens make the skin more _______, increase its _______, and make it thicker than the skin of a _______.
Answer: smooth / vascular / child
Explanation:
エストロゲン (estrogens) は、皮膚 (skin) を滑らか (smooth) にし、血管量 (vascularity) を増加させます。その結果、子供 (child) の皮膚よりも女性の皮膚は厚くなります。
Question 6: Proliferative Phase (増殖期)
Q: During the proliferative phase, _______ hormones promote the growth of _______ cells, leading to the re-epithelialization of the _______.
Answer: estrogen / stromal / endometrium
Explanation:
増殖期 (proliferative phase) では、エストロゲン (estrogen) が子宮内膜 (endometrium) の上皮を再生させるため、間質細胞 (stromal cells) の増殖が促進されます。この段階は、月経が終了してから次の排卵までの期間に発生します。
Question 7: Secretory Phase (分泌期)
Q: The secretory phase occurs after _______ and is driven by the hormones _______ and _______, which increase endometrial thickness.
Answer: ovulation / progesterone / estrogen
Explanation:
分泌期 (secretory phase) は、排卵 (ovulation) 後に起こり、プロゲステロン (progesterone) とエストロゲン (estrogen) によって制御されます。この段階では、子宮内膜の厚さが増加し、受精卵の着床が可能な状態になります。
Question 8: Role of Prostaglandins (プロスタグランジンの役割)
Q: During menstruation, _______ release triggers uterine _______, which help to _______ the desquamated endometrium.
Answer: prostaglandins / contractions / expel
Explanation:
月経 (menstruation) では、プロスタグランジン (prostaglandins) の放出が子宮 (uterus) の収縮 (contractions) を引き起こし、剥がれた子宮内膜 (desquamated endometrium) の排出 (expel) を助けます。この作用は、月経血が排出される過程の一部です。
Question 9: Menstrual Onset (月経の開始)
Q: Menstruation begins when _______ and _______ levels drop, leading to the involution of the _______.
Answer: estrogen / progesterone / corpus luteum
Explanation:
月経 (menstruation) は、エストロゲン (estrogen) とプロゲステロン (progesterone) のレベルが低下することで開始されます。このホルモンの低下は、黄体 (corpus luteum) の退行 (involution) に関連しています。
Question 10: Fluid Retention by Estrogen (エストロゲンによる体液貯留)
Q: Estrogens increase the retention of _______ and _______, similar to the action of the hormone _______ on kidney tubules.
Answer: sodium / water / aldosterone
Explanation:
エストロゲン (estrogens) は、腎尿細管 (kidney tubules) に作用して、アルドステロン (aldosterone) に類似した効果を持ち、ナトリウム (sodium) と水 (water) の貯留を引き起こします。この効果は、妊娠中に顕著になることがあります。
Question 1: Pulsatile Secretion of GnRH (GnRHのパルス分泌)
Q: GnRH is released in _______ from the _______ and stimulates the release of _______ from the anterior pituitary.
Answer: pulses / hypothalamus / LH and FSH
Explanation:
ゴナドトロピン放出ホルモン (GnRH) は、視床下部 (hypothalamus) からパルス (pulses) で分泌され、下垂体前葉 (anterior pituitary) から黄体形成ホルモン (LH) と卵胞刺激ホルモン (FSH) の分泌を刺激します。GnRHの連続的な分泌ではなく、間欠的な分泌が必要であることが重要なポイントです。
Question 2: Control of GnRH Release (GnRHの分泌制御)
Q: The release of GnRH occurs primarily in the _______ nuclei of the hypothalamus and is influenced by signals from the _______ system and the _______ area.
Answer: arcuate / limbic / preoptic
Explanation:
GnRHの放出は、主に視床下部の弓状核 (arcuate nuclei) で起こり、大脳辺縁系 (limbic system) と視床下部の視索前野 (preoptic area) からの信号によって制御されます。これにより、精神的な要因が女性の性的機能に影響を与える理由が説明されます。
Question 3: Negative Feedback of Estrogen (エストロゲンの負のフィードバック)
Q: Small amounts of _______ inhibit the secretion of _______ and _______ from the anterior pituitary.
Answer: estrogen / LH / FSH
Explanation:
少量のエストロゲン (estrogen) は、下垂体前葉 (anterior pituitary) からの黄体形成ホルモン (LH) と卵胞刺激ホルモン (FSH) の分泌を抑制します。これにより、卵胞の発達が制御され、月経周期が適切に進行します。
Question 4: Role of Inhibin (インヒビンの役割)
Q: Inhibin is secreted by the _______ cells of the _______ and inhibits the secretion of _______ from the anterior pituitary.
Answer: granulosa / corpus luteum / FSH
Explanation:
インヒビン (inhibin) は、黄体 (corpus luteum) の顆粒膜細胞 (granulosa cells) から分泌され、下垂体前葉 (anterior pituitary) からの卵胞刺激ホルモン (FSH) の分泌を抑制します。これにより、月経周期の後半における卵胞のさらなる成長が抑制されます。
Question 5: LH Surge Before Ovulation (排卵前のLHサージ)
Q: The preovulatory LH surge occurs _______ to _______ hours before ovulation and is caused by a positive feedback effect of _______ on the anterior pituitary.
Answer: 24 / 48 / estrogen
Explanation:
排卵前の黄体形成ホルモン (LH) の急増 (surge) は、排卵の24〜48時間前に発生します。この急増は、エストロゲン (estrogen) が下垂体前葉 (anterior pituitary) に及ぼす正のフィードバック効果によって引き起こされます。
Question 6: Role of Progesterone Before Ovulation (排卵前のプロゲステロンの役割)
Q: Before the preovulatory LH surge, _______ cells secrete small amounts of _______ , which may contribute to the surge in _______ secretion.
Answer: granulosa / progesterone / LH
Explanation:
排卵前の黄体形成ホルモン (LH) の急増の前に、顆粒膜細胞 (granulosa cells) は少量のプロゲステロン (progesterone) を分泌します。このプロゲステロンは、LHの急増を引き起こす要因の1つである可能性があります。
Question 7: Continuous GnRH Release (連続的なGnRH分泌の効果)
Q: Continuous infusion of _______ inhibits the release of _______ and _______ from the anterior pituitary.
Answer: GnRH / LH / FSH
Explanation:
GnRHを連続的 (continuous) に投与すると、下垂体前葉 (anterior pituitary) からの黄体形成ホルモン (LH) および卵胞刺激ホルモン (FSH) の分泌が抑制されます。GnRHは、間欠的な (pulsatile) 分泌が必要であり、これが連続的な投与の影響の理由です。
Question 8: Feedback of Estrogen and Progesterone (エストロゲンとプロゲステロンのフィードバック効果)
Q: The negative feedback effect on the anterior pituitary is strongest when _______ and _______ are both present, causing a decrease in the secretion of _______.
Answer: estrogen / progesterone / LH and FSH
Explanation:
エストロゲン (estrogen) とプロゲステロン (progesterone) が両方存在すると、負のフィードバック (negative feedback) 効果が最大化され、下垂体前葉 (anterior pituitary) からの黄体形成ホルモン (LH) と卵胞刺激ホルモン (FSH) の分泌が抑制されます。
Question 9: Source of LH and FSH (LHとFSHの供給源)
Q: The secretion of _______ and _______ is stimulated by _______ released from the hypothalamus.
Answer: LH / FSH / GnRH
Explanation:
黄体形成ホルモン (LH) と卵胞刺激ホルモン (FSH) の分泌は、視床下部 (hypothalamus) から分泌されるゴナドトロピン放出ホルモン (GnRH) によって刺激されます。この仕組みは、月経周期の調節において重要な役割を果たします。
Question 10: Positive Feedback of Estrogen (エストロゲンの正のフィードバック)
Q: The positive feedback effect of _______ occurs during the late follicular phase, leading to a surge in _______ that triggers _______.
Answer: estrogen / LH / ovulation
Explanation:
エストロゲン (estrogen) の正のフィードバック (positive feedback) 効果は、卵胞期 (follicular phase) の後半に発生します。この効果は、黄体形成ホルモン (LH) の急増 (surge) を引き起こし、排卵 (ovulation) を促進します。
Question 1: Feedback Oscillation (フィードバックの振動)
Q: The feedback oscillation in the female sexual cycle begins with the secretion of _______ and _______ from the corpus luteum, leading to decreased secretion of _______ from the anterior pituitary.
Answer: progesterone / estrogen / FSH and LH
Explanation:
フィードバックの振動 (feedback oscillation) は、黄体 (corpus luteum) からのプロゲステロン (progesterone) およびエストロゲン (estrogen) の分泌から始まります。これにより、下垂体前葉 (anterior pituitary) からの卵胞刺激ホルモン (FSH) および黄体形成ホルモン (LH) の分泌が抑制されます。
Question 2: Follicular Growth (卵胞の成長)
Q: During the follicular growth phase, the secretion of _______ from the corpus luteum decreases, causing the release of _______ from the hypothalamus, which in turn increases secretion of _______ from the anterior pituitary.
Answer: estrogen / GnRH / FSH
Explanation:
卵胞の成長 (follicular growth) 段階では、黄体 (corpus luteum) からのエストロゲン (estrogen) の分泌が減少し、これが視床下部 (hypothalamus) からのGnRH (ゴナドトロピン放出ホルモン) の分泌を促します。これにより、下垂体前葉 (anterior pituitary) からの卵胞刺激ホルモン (FSH) の分泌が増加し、新しい卵胞の成長が促進されます。
Question 3: Preovulatory LH Surge (排卵前のLHサージ)
Q: The preovulatory surge of _______ occurs due to positive feedback from _______ on the anterior pituitary, causing ovulation and formation of the _______.
Answer: LH / estrogen / corpus luteum
Explanation:
排卵前の黄体形成ホルモン (LH) サージは、エストロゲン (estrogen) が下垂体前葉 (anterior pituitary) に及ぼす正のフィードバック効果により引き起こされます。これにより、排卵 (ovulation) が促進され、黄体 (corpus luteum) が形成されます。
Question 4: Anovulatory Cycles (無排卵周期)
Q: Anovulatory cycles occur when the surge of _______ is insufficient to cause _______ , resulting in no development of the _______.
Answer: LH / ovulation / corpus luteum
Explanation:
無排卵周期 (anovulatory cycle) では、黄体形成ホルモン (LH) のサージが不十分なため、排卵 (ovulation) が起こりません。その結果、黄体 (corpus luteum) が形成されず、プロゲステロンの分泌が起こらないため、月経周期が短縮される場合があります。
Question 5: Puberty and Menarche (思春期と初経)
Q: Puberty begins with increased secretion of _______ by the pituitary, leading to higher levels of _______ from the ovaries and the onset of _______.
Answer: gonadotropins / estrogen / menarche
Explanation:
思春期 (puberty) は、下垂体 (pituitary) からのゴナドトロピン (gonadotropins) の分泌が増加することから始まります。これにより、卵巣 (ovaries) からのエストロゲン (estrogen) のレベルが上昇し、初経 (menarche) が発生します。
Question 6: Menopause (閉経)
Q: Menopause occurs due to the depletion of _______ in the ovaries, resulting in a decrease in _______ production and a rise in the secretion of _______ from the anterior pituitary.
Answer: primordial follicles / estrogen / FSH
Explanation:
閉経 (menopause) は、卵巣 (ovaries) における原始卵胞 (primordial follicles) の枯渇が原因です。その結果、エストロゲン (estrogen) の産生が低下し、下垂体前葉 (anterior pituitary) からの卵胞刺激ホルモン (FSH) の分泌が増加します。
Question 7: Symptoms of Menopause (閉経の症状)
Q: Menopause is associated with symptoms such as _______ , loss of _______ , and decreased _______ density.
Answer: hot flashes / estrogen / bone
Explanation:
閉経 (menopause) は、ホットフラッシュ (hot flashes)、エストロゲン (estrogen) の喪失、および骨密度 (bone density) の低下などの症状を引き起こします。これらの症状は、エストロゲンの欠乏によるものです。
Question 8: Female Sexual Response (女性の性的応答)
Q: Female erection is controlled by _______ signals that dilate arteries, while lubrication is produced by _______ glands and the _______ epithelium.
Answer: parasympathetic / Bartholin / vaginal
Explanation:
女性の勃起 (female erection) は、副交感神経 (parasympathetic) 信号によって制御され、動脈の拡張が引き起こされます。潤滑 (lubrication) は、バルトリン腺 (Bartholin glands) と膣上皮 (vaginal epithelium) から分泌される粘液によって提供されます。
Question 9: Role of Oxytocin (オキシトシンの役割)
Q: During orgasm, the release of _______ from the posterior pituitary increases _______ contractions, which helps transport _______ through the uterus.
Answer: oxytocin / uterine / sperm
Explanation:
オキシトシン (oxytocin) は、女性のオルガズム (orgasm) 中に後葉 (posterior pituitary) から分泌され、子宮 (uterine) 収縮を増加させます。これにより、精子 (sperm) が子宮を通過するのを助け、受精の可能性が高まります。
Question 10: Causes of Amenorrhea (無月経の原因)
Q: Amenorrhea can be caused by low levels of _______ from the ovaries, insufficient _______ release from the hypothalamus, or insufficient _______ from the anterior pituitary.
Answer: estrogen / GnRH / LH
Explanation:
無月経 (amenorrhea) は、卵巣 (ovaries) からのエストロゲン (estrogen) 分泌の不足、視床下部 (hypothalamus) からのGnRH (ゴナドトロピン放出ホルモン) の放出不十分、または下垂体前葉 (anterior pituitary) からの黄体形成ホルモン (LH) の不足によって引き起こされる可能性があります。
Question 1: Female Fertility (女性の生殖能力)
Q: The fertile period in the female reproductive cycle lasts about _______ days, during which the ovum remains viable for about _______ hours, while sperm can survive for up to _______ days.
Answer: 4 to 5 / 24 / 5
Explanation:
女性の生殖可能期間 (fertile period) は、4〜5日間続きます。卵子 (ovum) は約24時間生存可能ですが、精子 (sperm) は女性の生殖器内で最大5日間生存する可能性があります。
Question 2: Rhythm Method of Contraception (リズム法による避妊)
Q: The rhythm method of contraception is based on avoiding intercourse around the time of _______, which is typically calculated as _______ days before and _______ days after ovulation.
Answer: ovulation / 4 / 3
Explanation:
リズム法 (rhythm method) による避妊は、排卵 (ovulation) の前4日間と後3日間に性交を避けることで行われます。これは、精子が女性の体内で最大5日間生存できるためです。
Question 3: Hormonal Contraception (ホルモン避妊法)
Q: Hormonal contraception works by preventing the surge of _______ , which is required for _______ to occur, and this is achieved by administering synthetic _______.
Answer: LH / ovulation / estrogens and progestins
Explanation:
ホルモン避妊法 (hormonal contraception) は、黄体形成ホルモン (LH) のサージを抑制することで、排卵 (ovulation) を防ぎます。これには、合成エストロゲン (synthetic estrogens) およびプロゲスチン (progestins) の投与が使用されます。
Question 4: Synthetic Hormones in Contraception (避妊における合成ホルモン)
Q: Synthetic _______ such as ethinyl estradiol and mestranol, and synthetic _______ such as norethindrone, are used in contraceptive pills to prevent _______.
Answer: estrogens / progestins / ovulation
Explanation:
避妊ピル (contraceptive pills) には、エチニルエストラジオール (ethinyl estradiol) やメストラノール (mestranol) などの合成エストロゲン (synthetic estrogens) と、ノルエチンドロン (norethindrone) などの合成プロゲスチン (synthetic progestins) が含まれています。これにより、排卵 (ovulation) が防止されます。
Question 5: Causes of Female Sterility (女性の不妊の原因)
Q: Female sterility can be caused by failure to _______, blockage of the _______, or secretion of abnormal _______ by the cervix.
Answer: ovulate / fallopian tubes / mucus
Explanation:
女性の不妊 (female sterility) は、排卵の失敗 (failure to ovulate)、卵管 (fallopian tubes) の閉塞、または子宮頸部 (cervix) における異常な粘液 (mucus) の分泌が原因となる可能性があります。
Question 6: Ovulation Failure (排卵失敗)
Q: Ovulation failure is often caused by insufficient secretion of _______, thick ovarian _______, or the absence of the _______ surge.
Answer: gonadotropins / capsules / LH
Explanation:
排卵失敗 (ovulation failure) は、ゴナドトロピン (gonadotropins) の分泌不十分、卵巣カプセル (ovarian capsules) の肥厚、またはLH (黄体形成ホルモン) サージの欠如が原因となる場合があります。
Question 7: Endometriosis (子宮内膜症)
Q: Endometriosis occurs when _______ tissue grows outside the uterus, causing _______ in the pelvic cavity and potential blockage of the _______.
Answer: endometrial / fibrosis / fallopian tubes
Explanation:
子宮内膜症 (endometriosis) は、子宮外に子宮内膜組織 (endometrial tissue) が成長し、骨盤腔内で線維化 (fibrosis) を引き起こします。これにより、卵管 (fallopian tubes) の閉塞が発生する可能性があります。
Question 8: Salpingitis (卵管炎)
Q: Salpingitis is the _______ of the fallopian tubes, often caused by _______ infection, which can lead to _______ and infertility.
Answer: inflammation / gonococcal / fibrosis
Explanation:
卵管炎 (salpingitis) は、卵管 (fallopian tubes) の炎症 (inflammation) であり、通常は淋菌感染 (gonococcal infection) によって引き起こされます。この炎症は線維化 (fibrosis) を引き起こし、不妊 (infertility) につながる可能性があります。
Question 9: Cervical Mucus and Fertility (子宮頸管粘液と生殖能力)
Q: Fertility is influenced by cervical mucus, which becomes more _______ during ovulation under the influence of _______, allowing _______ to pass through the cervix.
Answer: fluid / estrogen / sperm
Explanation:
子宮頸管粘液 (cervical mucus) は、エストロゲン (estrogen) の影響下で排卵時に流動的 (fluid) になります。これにより、精子 (sperm) が子宮頸管を通過しやすくなります。
Question 10: Pregnancy Tests (妊娠検査)
Q: A pregnancy test detects the presence of _______ in urine, which is secreted by the _______ and signals successful _______.
Answer: hCG / placenta / implantation
Explanation:
妊娠検査 (pregnancy test) は、尿中のhCG (ヒト絨毛性ゴナドトロピン) を検出します。hCGは、着床 (implantation) が成功したことを示すシグナルであり、胎盤 (placenta) によって分泌されます。
Question 1: Ovum Maturation and Fertilization (卵子の成熟と受精)
Q: Before ovulation, the ovum is in the _______ stage, but after it expels the first _______ body, it becomes a _______ oocyte.
Answer: primary oocyte / polar / secondary
Explanation:
卵子 (ovum) は、排卵 (ovulation) 前は一次卵母細胞 (primary oocyte) の段階にあり、第一極体 (polar body) を放出すると、二次卵母細胞 (secondary oocyte) になります。この段階で、卵子は受精が可能になります。
Question 2: Entry of Ovum Into Fallopian Tube (卵子の卵管への進入)
Q: After ovulation, the ovum enters the _______ cavity and is guided by _______ epithelium into the _______ tube.
Answer: peritoneal / ciliated / fallopian
Explanation:
排卵 (ovulation) 後、卵子 (ovum) は腹腔 (peritoneal cavity) に入り、線毛上皮 (ciliated epithelium) によって卵管 (fallopian tube) に導かれます。この仕組みにより、卵子は子宮に到達します。
Question 3: Fertilization Process (受精のプロセス)
Q: Fertilization occurs in the _______ of the fallopian tube, where the sperm penetrates the _______ and the _______ to reach the ovum.
Answer: ampulla / corona radiata / zona pellucida
Explanation:
受精 (fertilization) は、卵管 (fallopian tube) の膨大部 (ampulla) で行われ、精子 (sperm) は卵子の外側の放線冠 (corona radiata) と透明帯 (zona pellucida) を通過して卵子に到達します。
Question 4: Chromosome Formation After Fertilization (受精後の染色体形成)
Q: After fertilization, the female pronucleus containing _______ chromosomes and the male pronucleus containing _______ chromosomes combine to form a _______ with 46 chromosomes.
Answer: 23 / 23 / zygote
Explanation:
受精 (fertilization) 後、女性の前核 (female pronucleus) は23本の染色体 (chromosomes) を持ち、男性の前核 (male pronucleus) も23本の染色体を持ちます。これらが結合して受精卵 (zygote) を形成し、46本の染色体を持つ細胞が生じます。
Question 5: Determination of Fetal Sex (胎児の性別の決定)
Q: The sex of the fetus is determined by whether the sperm carries an _______ chromosome, which produces a female (XX), or a _______ chromosome, which produces a male (XY), when combined with the ovum’s _______ chromosome.
Answer: X / Y / X
Explanation:
胎児の性別 (fetal sex) は、精子 (sperm) がX染色体 (X chromosome) を持つかY染色体 (Y chromosome) を持つかによって決まります。卵子 (ovum) は常にX染色体 (X chromosome) を持つため、XX は女性、XY は男性を生じます。
Question 6: Transport of Fertilized Ovum (受精卵の輸送)
Q: After fertilization, the zygote travels through the _______ tube, aided by _______ contractions and the action of _______ epithelium.
Answer: fallopian / smooth muscle / ciliated
Explanation:
受精 (fertilization) 後、受精卵 (zygote) は卵管 (fallopian tube) を通過します。輸送は、平滑筋 (smooth muscle) の収縮と線毛上皮 (ciliated epithelium) の協調的な動きによって支援されます。
Question 7: Implantation of the Blastocyst (胚盤胞の着床)
Q: Implantation occurs in the _______, where trophoblast cells secrete _______ enzymes to digest the _______ for implantation.
Answer: uterus / proteolytic / endometrium
Explanation:
着床 (implantation) は子宮 (uterus) で発生します。栄養膜細胞 (trophoblast cells) はプロテアーゼ (proteolytic enzymes) を分泌し、子宮内膜 (endometrium) を消化して、胚盤胞が着床できるようにします。
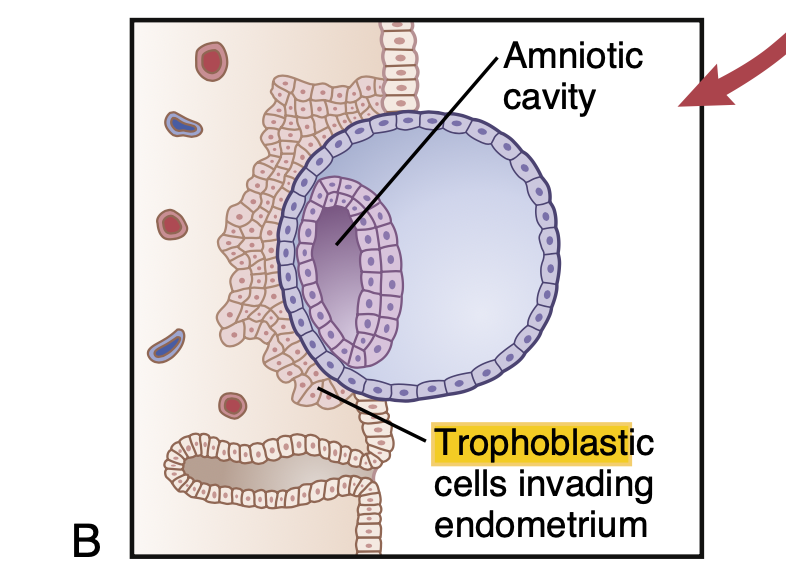
Question 8: Role of Trophoblast (栄養膜の役割)
Q: The trophoblast forms the _______, secretes _______ enzymes, and later contributes to the formation of the _______.
Answer: blastocyst / proteolytic / placenta
Explanation:
栄養膜 (trophoblast) は、胚盤胞 (blastocyst) を形成し、プロテアーゼ (proteolytic enzymes) を分泌します。このプロセスは、胎盤 (placenta) の形成にも関与します。
Question 9: Uterine Changes During Implantation (着床中の子宮の変化)
Q: During implantation, the uterus provides _______ milk, the endometrium becomes _______ , and the blastocyst embeds into the _______.
Answer: uterine / secretory / endometrium
Explanation:
着床 (implantation) 中、子宮 (uterus) は子宮乳 (uterine milk) を分泌し、子宮内膜 (endometrium) は分泌型 (secretory) になり、胚盤胞 (blastocyst) は子宮内膜に埋め込まれます。
Question 10: Development of Zygote (接合子の発育)
Q: The zygote forms after the fusion of male and female _______ , undergoes multiple rounds of _______, and eventually develops into a _______.
Answer: pronuclei / cell division / blastocyst
Explanation:
接合子 (zygote) は、男性および女性の前核 (pronuclei) の融合後に形成されます。その後、複数の細胞分裂 (cell division) を経て、最終的に胚盤胞 (blastocyst) になります。
Question 1: Early Nutrition of the Embryo (胚の初期栄養)
Q: The early nutrition of the embryo is provided by _______ cells, which develop into _______ cells after implantation, and these cells store large amounts of _______ for the growing embryo.
Answer: stromal / decidual / glycogen
Explanation:
胚の初期栄養 (early nutrition of the embryo) は、間質細胞 (stromal cells) から脱落膜細胞 (decidual cells) への変化によって提供されます。これらの細胞は、グリコーゲン (glycogen)、タンパク質、脂質を蓄え、発育中の胚 (embryo) に栄養を供給します。
Question 2: Trophoblastic Nutrition (栄養膜栄養)
Q: Trophoblastic nutrition occurs as the _______ cells invade the _______, digesting and absorbing stored _______ from the endometrial cells.
Answer: trophoblast / decidua / nutrients
Explanation:
栄養膜栄養 (trophoblastic nutrition) は、栄養膜細胞 (trophoblast cells) が脱落膜 (decidua) に侵入し、子宮内膜 (endometrium) の細胞に蓄えられた栄養 (nutrients) を消化・吸収することによって行われます。
Question 3: Placental Development (胎盤の発達)
Q: The placenta forms when _______ villi develop, containing fetal _______ surrounded by maternal _______, creating a site for nutrient and gas exchange.
Answer: trophoblastic / capillaries / blood sinuses
Explanation:
胎盤 (placenta) は、栄養膜絨毛 (trophoblastic villi) が発達し、胎児の毛細血管 (fetal capillaries) が母体の血液洞 (maternal blood sinuses) に囲まれることで形成されます。この構造は、栄養 (nutrients) およびガス交換 (gas exchange) に重要な役割を果たします。
Question 4: Placental Oxygen Exchange (胎盤の酸素交換)
Q: Oxygen diffuses from the maternal _______ to the fetal _______, driven by a pressure gradient of about _______ mmHg.
Answer: blood / blood / 20
Explanation:
胎盤 (placenta) における酸素交換 (oxygen exchange) は、母体の血液 (maternal blood) から胎児の血液 (fetal blood) へ、約20 mmHg の酸素分圧勾配により拡散が行われます。
Question 5: Factors Enhancing Oxygen Delivery (酸素供給を高める要因)
Q: Oxygen delivery to the fetus is enhanced by the higher concentration of _______ in fetal blood, the presence of _______ hemoglobin, and the _______ effect, which increases oxygen release from maternal hemoglobin.
Answer: hemoglobin / fetal / Bohr
Explanation:
胎児への酸素供給 (oxygen delivery) は、胎児の血中ヘモグロビン濃度 (fetal hemoglobin concentration) の高さ、胎児ヘモグロビン (fetal hemoglobin) の存在、およびボーア効果 (Bohr effect) によって強化されます。ボーア効果は、母体の酸素放出を促進します。
Question 6: Placental Diffusion (胎盤の拡散機構)
Q: The placenta allows diffusion of nutrients and gases through the _______ membrane, which becomes thinner as pregnancy progresses, and the total _______ area of the placenta increases.
Answer: placental / surface
Explanation:
胎盤の拡散 (placental diffusion) は、胎盤膜 (placental membrane) を通じて行われます。この膜は、妊娠の進行に伴い薄く (thinner) なり、表面積 (surface area) が増加するため、栄養素やガスの拡散が促進されます。
Question 7: Fetal Carbon Dioxide Removal (胎児の二酸化炭素の排出)
Q: Carbon dioxide produced by the fetus diffuses into the maternal _______, driven by a pressure gradient of about _______ mmHg, and diffuses 20 times faster than _______.
Answer: blood / 2 to 3 / oxygen
Explanation:
胎児の二酸化炭素排出 (fetal carbon dioxide removal) は、胎児の血液 (fetal blood) から母体の血液 (maternal blood) への2~3 mmHg の圧力勾配によって拡散します。二酸化炭素 (carbon dioxide) は酸素 (oxygen) よりも20倍速く拡散します。
Question 8: Nutrient Transport Across Placenta (胎盤を通過する栄養素の輸送)
Q: Nutrients such as _______ are transported through the placenta via facilitated diffusion, while _______ acids diffuse more slowly, and ions such as _______ move with relative ease.
Answer: glucose / fatty / sodium
Explanation:
胎盤 (placenta) では、グルコース (glucose) が促進拡散 (facilitated diffusion) によって輸送されます。脂肪酸 (fatty acids) はより遅く拡散し、ナトリウム (sodium) や他のイオンは比較的簡単に拡散します。
Question 9: Excretion of Fetal Waste (胎児の老廃物の排泄)
Q: Waste products such as _______ and _______ diffuse from fetal blood into maternal blood, but _______ has a higher concentration in fetal blood due to its lower diffusion rate.
Answer: urea / uric acid / creatinine
Explanation:
胎児の老廃物の排泄 (excretion of fetal waste) では、尿素 (urea) と尿酸 (uric acid) は胎児の血液 (fetal blood) から母体の血液 (maternal blood) へ拡散しますが、クレアチニン (creatinine) の拡散速度は遅いため、胎児の血中濃度は高くなります。
Question 10: Double Bohr Effect (二重のボーア効果)
Q: The double Bohr effect increases oxygen uptake in _______ blood and enhances oxygen release from _______ blood due to the exchange of _______ across the placental membrane.
Answer: fetal / maternal / carbon dioxide
Explanation:
二重のボーア効果 (double Bohr effect) は、胎児の血液 (fetal blood) における酸素の取り込み (oxygen uptake) を高め、母体の血液 (maternal blood) からの酸素の放出 (oxygen release) を促進します。これらの変化は、二酸化炭素 (carbon dioxide) が胎児から母体の血液に拡散する際に発生します。
Question 1: Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (ヒト絨毛性ゴナドトロピン, hCG)
Q: Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is secreted by _______ cells, prevents the involution of the _______ and stimulates the male fetal testes to produce _______.
Answer: syncytial trophoblast / corpus luteum / testosterone
Explanation:
ヒト絨毛性ゴナドトロピン (hCG) は、合胞体栄養膜細胞 (syncytial trophoblast cells) によって分泌されます。このホルモンは黄体 (corpus luteum) の退縮を防ぎ、男性胎児の精巣 (male fetal testes) を刺激してテストステロン (testosterone) を分泌させます。
Question 2: Secretion of Estrogen by the Placenta (胎盤によるエストロゲンの分泌)
Q: Estrogens secreted by the placenta are synthesized from _______ produced by the fetal adrenal glands, converted to estrogens by _______ cells, and promote enlargement of the mother’s _______.
Answer: androgens / trophoblast / uterus
Explanation:
胎盤 (placenta) によるエストロゲン (estrogen) の分泌は、胎児の副腎 (fetal adrenal glands) で生成されたアンドロゲン (androgens) から行われます。これらのアンドロゲンは、栄養膜細胞 (trophoblast cells) でエストロゲンに変換され、母体の子宮 (mother’s uterus) を拡大させます。
Question 3: Role of Progesterone in Pregnancy (妊娠中のプロゲステロンの役割)
Q: Progesterone promotes the formation of _______ cells in the endometrium, reduces uterine _______ to prevent spontaneous abortion, and helps prepare the mother’s _______ for lactation.
Answer: decidual / contractions / breasts
Explanation:
プロゲステロン (progesterone) は、子宮内膜 (endometrium) に脱落膜細胞 (decidual cells) を形成させ、子宮収縮 (uterine contractions) を抑制して流産 (spontaneous abortion) を防ぎます。また、母体の乳房 (breasts) を授乳 (lactation) に備えて準備します。
Question 4: Human Chorionic Somatomammotropin (ヒト絨毛性ソマトマンモトロピン, hCS)
Q: Human chorionic somatomammotropin (hCS) promotes the development of _______ tissue, decreases the mother’s sensitivity to _______, and increases the release of _______ from fat stores for maternal energy.
Answer: breast / insulin / free fatty acids
Explanation:
ヒト絨毛性ソマトマンモトロピン (hCS) は、乳腺組織 (breast tissue) の発達を促進し、インスリン感受性 (insulin sensitivity) を低下させ、脂肪酸 (free fatty acids) の放出を促します。これにより、母体は代替エネルギー源を得て、胎児の成長のためにグルコース (glucose) が利用できるようになります。
Question 5: Hormonal Maintenance of Pregnancy (妊娠のホルモン維持)
Q: During the first few weeks of pregnancy, the _______ secretes estrogen and progesterone, but after 13 to 17 weeks, the _______ takes over, ensuring the development of the _______.
Answer: corpus luteum / placenta / endometrium
Explanation:
妊娠初期 (early pregnancy) には、黄体 (corpus luteum) がエストロゲン (estrogen) とプロゲステロン (progesterone) を分泌しますが、13週から17週以降は、胎盤 (placenta) がこの役割を担い、子宮内膜 (endometrium) の発達を維持します。
Question 6: Role of hCG in Male Fetal Development (男性胎児の発達におけるhCGの役割)
Q: Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) stimulates the _______ of the male fetus, leading to the production of _______ and the descent of the _______ into the scrotum.
Answer: testes / testosterone / testes
Explanation:
ヒト絨毛性ゴナドトロピン (hCG) は、男性胎児の精巣 (testes of the male fetus) を刺激してテストステロン (testosterone) の産生を促進します。これにより、精巣 (testes) は陰嚢 (scrotum) へ降下します。
Question 7: Source of Placental Hormones (胎盤ホルモンの供給源)
Q: Placental estrogens are produced by the conversion of _______ from the maternal and fetal adrenal glands, with the production occurring in the _______ cells of the placenta, leading to increased growth of the mother’s _______.
Answer: androgens / syncytial trophoblast / breast ducts
Explanation:
胎盤のエストロゲン (placental estrogens) は、母体および胎児の副腎 (maternal and fetal adrenal glands) から供給されるアンドロゲン (androgens) から変換されます。この変換は、合胞体栄養膜細胞 (syncytial trophoblast cells) で行われ、母体の乳管 (breast ducts) の成長を促進します。
Question 8: Pregnancy Hormones and Glucose Regulation (妊娠ホルモンとグルコース調節)
Q: Human chorionic somatomammotropin (hCS) reduces maternal _______ sensitivity, increases the release of _______ from fat stores, and increases the availability of _______ for the fetus.
Answer: insulin / free fatty acids / glucose
Explanation:
ヒト絨毛性ソマトマンモトロピン (hCS) は、母体のインスリン感受性 (maternal insulin sensitivity) を低下させ、脂肪の貯蔵 (fat stores) からの遊離脂肪酸 (free fatty acids) の放出を増加させます。これにより、胎児 (fetus) に利用できるグルコース (glucose) の量が増加します。
Question 9: Function of Decidual Cells (脱落膜細胞の役割)
Q: Decidual cells develop in the endometrium in response to _______ secretion, provide early nutrition for the _______, and form the _______ that supports embryonic development.
Answer: progesterone / embryo / decidua
Explanation:
脱落膜細胞 (decidual cells) は、プロゲステロン (progesterone) の分泌に応答して子宮内膜 (endometrium) に発達し、胚 (embryo) に初期の栄養を供給します。これらの細胞は脱落膜 (decidua) を形成し、胚発生 (embryonic development) をサポートします。
Question 10: Role of hCG in Corpus Luteum Maintenance (hCGの黄体維持の役割)
Q: Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) maintains the _______ during the first weeks of pregnancy, prevents _______ from occurring, and promotes the secretion of _______ and estrogen.
Answer: corpus luteum / menstruation / progesterone
Explanation:
ヒト絨毛性ゴナドトロピン (hCG) は、妊娠の最初の数週間に黄体 (corpus luteum) を維持し、月経 (menstruation) が起こるのを防ぎます。また、プロゲステロン (progesterone) とエストロゲン (estrogen) の分泌を促進し、妊娠 (pregnancy) を維持します。
Question 1: Hormonal Changes During Pregnancy (妊娠中のホルモン変化)
Q: During pregnancy, the anterior pituitary gland increases the secretion of _______, the adrenal glands increase the production of _______, and the parathyroid glands increase the secretion of _______ to support fetal development.
Answer: prolactin / glucocorticoids / parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Explanation:
妊娠中のホルモン変化では、下垂体前葉 (anterior pituitary gland) がプロラクチン (prolactin) の分泌を増加させ、副腎 (adrenal glands) がグルココルチコイド (glucocorticoids) の分泌を促進します。また、副甲状腺 (parathyroid glands) は、胎児の骨形成を支えるために副甲状腺ホルモン (parathyroid hormone, PTH) の分泌を増加させます。
Question 2: Relaxin and Its Role (リラキシンの役割)
Q: Relaxin is secreted by the _______ and placenta, helps to soften the _______, and may act as a _______ to increase blood flow.
Answer: corpus luteum / cervix / vasodilator
Explanation:
リラキシン (relaxin) は、黄体 (corpus luteum) や胎盤 (placenta) から分泌され、子宮頸部 (cervix) を柔らかくする役割を担います。また、血管拡張因子 (vasodilator) としても働き、血流 (blood flow) の増加を促進する可能性があります。
Question 3: Maternal Weight Gain During Pregnancy (妊娠中の母体の体重増加)
Q: During pregnancy, the average weight gain is between _______ pounds, with _______ pounds attributed to fetal weight, and an additional _______ pounds resulting from fluid retention, uterine growth, and breast development.
Answer: 25-35 / 8 / 12-22
Explanation:
妊娠中の体重増加 (weight gain during pregnancy) は平均25~35ポンド (25-35 pounds) であり、そのうち8ポンド (8 pounds) は胎児の体重 (fetal weight) に関連しています。さらに、12~22ポンド (12-22 pounds) は、体液貯留 (fluid retention)、子宮の拡大 (uterine growth)、および乳房の発達 (breast development) によるものです。
Question 4: Changes in the Maternal Circulatory System (母体の循環系の変化)
Q: During pregnancy, maternal blood volume increases by _______ percent, cardiac output increases by _______, and approximately _______ ml of blood flows through the placenta each minute.
Answer: 30% / 30-40% / 625
Explanation:
妊娠中の循環系の変化では、母体の血液量 (maternal blood volume) は30%増加 (30% increase) し、心拍出量 (cardiac output) は30-40%増加 (30-40% increase) します。さらに、胎盤 (placenta) には1分あたり625 ml の血液が流れます。
Question 5: Role of Estrogen in Pregnancy (妊娠中のエストロゲンの役割)
Q: During pregnancy, estrogen promotes the enlargement of the _______, enhances the growth of the _______ in the breasts, and increases the flexibility of the _______ to facilitate childbirth.
Answer: uterus / ductal system / pelvic ligaments
Explanation:
妊娠中のエストロゲン (estrogen) は、子宮 (uterus) の拡大を促進し、乳房の管系 (ductal system in the breasts) の成長を促します。さらに、骨盤靭帯 (pelvic ligaments) の柔軟性を高め、出産 (childbirth) を容易にする役割を果たします。
Question 6: Thyroid Gland Changes During Pregnancy (妊娠中の甲状腺の変化)
Q: The maternal thyroid gland increases in size by _______, increases thyroxine production, and is stimulated by _______ secreted by the placenta, along with human _______ thyrotropin.
Answer: 50% / human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) / chorionic
Explanation:
妊娠中の甲状腺 (thyroid gland during pregnancy) は、50%のサイズ増加 (50% increase in size) を示し、サイロキシン (thyroxine) の生産が増加します。さらに、胎盤 (placenta) から分泌されるヒト絨毛性ゴナドトロピン (hCG) およびヒト絨毛性甲状腺刺激ホルモン (human chorionic thyrotropin) によって刺激を受けます。
Question 7: Placental Hormones and Water Retention (胎盤ホルモンと水分保持)
Q: Placental secretion of _______ and _______ increases sodium and water retention in the maternal kidneys, leading to an increase of about _______ pounds of extra fluid in the mother’s body.
Answer: aldosterone / estrogen / 5
Explanation:
胎盤ホルモン (placental hormones) であるアルドステロン (aldosterone) とエストロゲン (estrogen) は、腎臓 (kidneys) におけるナトリウム (sodium) および水 (water) の再吸収を増加させます。これにより、母体 (maternal body) には約5ポンド (about 5 pounds) の追加の体液が蓄積されます。
Question 8: Role of Parathyroid Hormone (副甲状腺ホルモンの役割)
Q: Parathyroid hormone (PTH) increases calcium absorption from the _______, supports calcium needs of the _______, and its secretion increases significantly during _______ to meet the demands of milk production.
Answer: bones / fetus / lactation
Explanation:
副甲状腺ホルモン (parathyroid hormone, PTH) は、骨 (bones) からのカルシウム吸収 (calcium absorption) を増加させ、胎児 (fetus) のカルシウム需要 (calcium needs) を支えます。さらに、授乳期 (lactation) には、乳汁生産 (milk production) に必要なカルシウムの需要を満たすためにPTHの分泌 (PTH secretion) が著しく増加します。
Question 9: Endocrine Changes in Pregnancy (妊娠中の内分泌変化)
Q: The anterior pituitary increases its production of _______ and _______, while secretion of _______ and LH is almost completely suppressed due to high estrogen and progesterone levels.
Answer: prolactin / ACTH / FSH
Explanation:
妊娠中の内分泌変化 (endocrine changes in pregnancy) では、下垂体前葉 (anterior pituitary) はプロラクチン (prolactin) と副腎皮質刺激ホルモン (ACTH) の分泌を増加させますが、エストロゲン (estrogen) とプロゲステロン (progesterone) の高い濃度により、FSH (卵胞刺激ホルモン) とLH (黄体形成ホルモン) の分泌はほぼ完全に抑制されます。
*排卵後の黄体期や妊娠中に見られ、卵胞の新たな成長や排卵を防ぐ役割を果たしています。
Question 1: Onset of Labor (分娩の開始)
Q: The transition from Braxton Hicks contractions to active labor is triggered by _______ feedback, which involves _______ of the cervix and increased secretion of _______ by the posterior pituitary.
Answer: positive / stretching / oxytocin
Explanation:
分娩の開始 (Onset of labor) は、陽性フィードバック (positive feedback) によって引き起こされます。子宮頸部の伸展 (stretching of the cervix) による反射が、後葉下垂体 (posterior pituitary) からのオキシトシン (oxytocin) の分泌を促進し、これが子宮の収縮 (uterine contractions) をさらに強化して、分娩が進行します。
Question 2: Hormonal Factors in Parturition (分娩に関与するホルモン要因)
Q: Toward the end of pregnancy, the increase in the _______ to progesterone ratio, the rising levels of _______, and the release of _______ from the fetal membranes all contribute to increased uterine contractility.
Answer: estrogen / oxytocin / prostaglandins
Explanation:
分娩に関与するホルモン要因 (Hormonal factors in parturition) では、エストロゲンとプロゲステロンの比率 (estrogen-to-progesterone ratio) の上昇が子宮収縮 (uterine contractility) の増加をもたらします。さらに、オキシトシン (oxytocin) の分泌が増加し、胎児の膜 (fetal membranes) からのプロスタグランジン (prostaglandins) の放出も、子宮の収縮 (uterine contractions) を強化する重要な要因です。
Question 3: Mechanical Factors in Labor (分娩における機械的要因)
Q: The mechanical factors that increase uterine contractions include _______ of the uterine muscles, intermittent stretch caused by fetal _______, and _______ of the cervix during labor.
Answer: stretching / movements / irritation
Explanation:
分娩における機械的要因 (Mechanical factors in labor) には、子宮筋の伸展 (stretching of uterine muscles)、胎児の動き (fetal movements) による断続的な伸展 (intermittent stretch)、および子宮頸部の刺激 (irritation of the cervix) が含まれます。これらの機械的な要因は、子宮の収縮 (uterine contractions) を強化し、分娩が進行します。
Question 4: Role of Oxytocin in Labor (分娩におけるオキシトシンの役割)
Q: The secretion of oxytocin increases as labor progresses, causing the uterine muscle to increase the number of _______ receptors, and this hormone is released by the _______ in response to _______ of the cervix.
Answer: oxytocin / posterior pituitary / stretching
Explanation:
分娩におけるオキシトシンの役割 (Role of oxytocin in labor) では、オキシトシン (oxytocin) は、後葉下垂体 (posterior pituitary) から分泌され、子宮筋 (uterine muscle) におけるオキシトシン受容体 (oxytocin receptors) の数を増加させます。さらに、子宮頸部の伸展 (stretching of the cervix) による反射が、オキシトシンの分泌 (oxytocin release) を引き起こし、分娩の進行を助けます。
Question 5: Positive Feedback in Labor (分娩における陽性フィードバック)
Q: Positive feedback during labor is initiated by _______ of the cervix, which triggers reflex contraction of the _______, causing further stretching and leading to more secretion of _______ by the posterior pituitary.
Answer: stretching / uterus / oxytocin
Explanation:
分娩における陽性フィードバック (Positive feedback in labor) では、子宮頸部の伸展 (stretching of the cervix) が最初の刺激となります。これにより、子宮 (uterus) の反射的な収縮 (reflex contraction) が引き起こされ、さらなる子宮頸部の伸展 (stretching of the cervix) が生じます。このサイクルは後葉下垂体 (posterior pituitary) からのオキシトシンの分泌 (oxytocin secretion) をさらに促進し、子宮の収縮 (uterine contractions) が強化されていきます。
Question 6: Role of Fetal Hormones in Labor (分娩における胎児ホルモンの役割)
Q: Fetal hormones that contribute to uterine contractions include _______, which is secreted by the fetal pituitary gland, _______, which is secreted by the fetal adrenal glands, and _______, which is released from the fetal membranes.
Answer: oxytocin / cortisol / prostaglandins
Explanation:
分娩における胎児ホルモンの役割 (Role of fetal hormones in labor) では、胎児の下垂体 (fetal pituitary gland) からオキシトシン (oxytocin) が分泌され、胎児の副腎 (fetal adrenal glands) からコルチゾール (cortisol) が分泌されます。さらに、胎児の膜 (fetal membranes) からはプロスタグランジン (prostaglandins) が放出され、これらのホルモンは子宮収縮 (uterine contractions) を促進します。
Question 7: Abdominal Muscle Contractions in Labor (分娩における腹筋の収縮)
Q: During labor, intense pain signals from the uterus and birth canal trigger reflexive contraction of the _______ muscles, which increases intra-abdominal pressure, facilitating the _______ of the baby through the birth canal. This process is controlled by neurogenic reflexes from the _______.
Answer: abdominal / expulsion / spinal cord
Explanation:
分娩における腹筋の収縮 (Abdominal muscle contractions in labor) では、子宮 (uterus) や産道 (birth canal) からの痛みの信号 (pain signals) が、脊髄 (spinal cord) を通じた神経反射 (neurogenic reflexes) を引き起こし、腹筋 (abdominal muscles) の収縮を促します。これにより、腹腔内圧 (intra-abdominal pressure) が増加し、赤ちゃんの排出 (expulsion of the baby) を助けます。
Question 8: Braxton Hicks Contractions (ブラクストンヒックス収縮)
Q: Braxton Hicks contractions are characterized by _______ intensity, _______ rhythmicity, and they generally become more pronounced in the _______ trimester of pregnancy.
Answer: weak / slow / third
Explanation:
ブラクストンヒックス収縮 (Braxton Hicks contractions) は、弱い (weak) 強さ、緩やかなリズム (slow rhythmicity) を特徴とし、妊娠第3期 (third trimester) に入ると、より明確 (pronounced) になります。これらの収縮は分娩の準備的な不規則な子宮収縮 (irregular uterine contractions) であり、本格的な分娩の前兆 (precursor to labor) としても知られています。
Question 1: Mechanics of Parturition (分娩の力学)
Q: Uterine contractions during labor begin at the _______ and spread downward. The intensity of the contraction is stronger at the _______ of the uterus and weaker at the _______ near the cervix.
Answer: fundus / body / lower segment
Explanation:
分娩の力学 (Mechanics of Parturition) では、子宮の収縮 (uterine contractions) は子宮底 (fundus) から始まり、子宮の体部 (body of the uterus) を通って子宮下部 (lower segment) に向かって下向きに広がる (spread downward) という特徴があります。収縮の強度は子宮底 (fundus) と子宮体部 (body) で最も強く、子宮下部 (lower segment) に行くにつれて弱まります。
Question 2: Stages of Labor (分娩の段階)
Q: The first stage of labor involves _______ of the cervix, which lasts until the opening is as large as the _______ of the fetus. The second stage of labor begins with the rupture of the _______ and the descent of the fetal head into the birth canal.
Answer: dilation / head / fetal membranes
Explanation:
分娩の段階 (Stages of Labor) では、第一段階 (first stage) は子宮頸部の拡張 (dilation of the cervix) が進行し、胎児の頭 (head of the fetus) が通過できるサイズまで開きます。第二段階 (second stage) では、胎児膜 (fetal membranes) が破裂 (rupture) し、胎児の頭 (fetal head) が産道 (birth canal) に降りてきます。
Question 3: Separation of Placenta (胎盤の分離)
Q: After the birth of the baby, the uterus continues to _______ in size, causing the placenta to detach due to a _______ effect. Blood loss is limited by the constriction of blood vessels surrounded by _______ muscle fibers.
Answer: contract / shearing / smooth
Explanation:
胎盤の分離 (Separation of the Placenta) は、赤ちゃんの出産後 (after birth of the baby) に子宮の収縮 (uterine contractions) が続き、せん断効果 (shearing effect) によって胎盤が分離 (placenta detaches) します。血管の周囲 (around blood vessels) に配置された平滑筋繊維 (smooth muscle fibers) の収縮 (constriction) により、出血量は制限されます (limited)。
Question 4: Involution of the Uterus (子宮の復古)
Q: After parturition, the uterus undergoes _______ over 4 to 5 weeks, reducing its size. The endometrial site of the placenta undergoes autolysis, causing a vaginal discharge called _______ that initially appears bloody and later becomes _______.
Answer: involution / lochia / serous
Explanation:
子宮の復古 (Involution of the Uterus) では、分娩後 (after parturition)、子宮 (uterus) は4〜5週間にわたって復古 (involution) し、サイズが減少します。胎盤の着床部 (placental site) は自己溶解 (autolysis) を起こし、膣分泌物 (vaginal discharge) として悪露 (lochia) が排出されます。悪露 (lochia) は最初は血性 (bloody) ですが、その後は漿液性 (serous) に変化します。
Question 5: Labor Pains (陣痛の痛み)
Q: Labor pain during the first stage is caused by _______ of the uterine muscle, while pain in the second stage is due to _______ of the cervix and the stretching or tearing of the _______ in the birth canal.
Answer: hypoxia / stretching / structures
Explanation:
陣痛の痛み (Labor Pains) の第一段階 (first stage) では、子宮筋 (uterine muscle) の低酸素 (hypoxia) により痛みが生じます。第二段階 (second stage) では、子宮頸部の伸展 (stretching of the cervix) や、産道 (birth canal) における構造物の伸展または破裂 (stretching or tearing of structures) によって痛み (pain) が発生します。
Question 6: Role of Prolactin in Lactation (授乳におけるプロラクチンの役割)
Q: During pregnancy, the levels of _______ rise steadily, but milk production is inhibited by high levels of _______ and _______ from the placenta.
Answer: prolactin / estrogen / progesterone
Explanation:
授乳におけるプロラクチンの役割 (Role of Prolactin in Lactation) では、妊娠中 (during pregnancy)、プロラクチン (prolactin) の血中濃度 (blood concentration) が上昇 (rises steadily) しますが、エストロゲン (estrogen) とプロゲステロン (progesterone) の抑制効果 (inhibitory effects) によって、乳の分泌 (milk production) は抑えられます。
Question 7: Reflex Mechanism of Milk Ejection (乳射出の反射機構)
Q: Milk ejection is stimulated by _______ signals from the nipples to the _______ of the brain, leading to the release of _______ from the posterior pituitary.
Answer: nervous / hypothalamus / oxytocin
Explanation:
乳射出の反射機構 (Reflex Mechanism of Milk Ejection) では、乳頭 (nipples) からの神経信号 (nervous signals) が脳の視床下部 (hypothalamus) に送られ、後葉下垂体 (posterior pituitary) からオキシトシン (oxytocin) が分泌 (released) されます。これにより、乳腺胞 (alveoli of mammary glands) からの乳の射出 (milk ejection) が促進されます。
Question 8: Role of Hormones in Breast Development (乳房発育におけるホルモンの役割)
Q: The development of breast ducts is primarily stimulated by _______ from the placenta, while _______ is essential for the development of alveoli. Additional support comes from hormones such as _______ and glucocorticoids.
Answer: estrogen / progesterone / growth hormone
Explanation:
乳房発育におけるホルモンの役割 (Role of Hormones in Breast Development) では、エストロゲン (estrogen) によって乳管 (breast ducts) の発育が促進されます。アルベオリ (alveoli) の発育にはプロゲステロン (progesterone) が必須であり、さらに成長ホルモン (growth hormone) やグルココルチコイド (glucocorticoids) も乳房の発育 (breast development) に関与します。
Question 1: Prolactin Inhibitory Mechanism (プロラクチンの抑制機構)
Q: The hypothalamus inhibits prolactin secretion through the release of _______. Damage to the _______ or blockage of the _______ increases prolactin secretion while reducing the secretion of other anterior pituitary hormones.
Answer: dopamine / hypothalamus / hypothalamic-hypophysial portal system
Explanation:
プロラクチンの抑制機構 (Prolactin Inhibitory Mechanism) では、視床下部 (hypothalamus) はドーパミン (dopamine) を分泌し、これがプロラクチンの分泌を抑制 (inhibits prolactin secretion) します。視床下部 (hypothalamus) の損傷 (damage) または視床下部-下垂体門脈系 (hypothalamic-hypophysial portal system) の閉塞により、他の下垂体前葉ホルモンの分泌が減少 (reduced) し、プロラクチン (prolactin) の分泌が増加 (increased) します。
Question 2: Suppression of Ovarian Cycles (卵巣サイクルの抑制)
Q: Suckling during nursing inhibits _______ secretion from the hypothalamus, which decreases the secretion of _______ and _______ from the anterior pituitary.
Answer: gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) / luteinizing hormone (LH) / follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
Explanation:
卵巣サイクルの抑制 (Suppression of Ovarian Cycles) では、授乳中の吸啜 (suckling during nursing) により、視床下部 (hypothalamus) からのゴナドトロピン放出ホルモン (gonadotropin-releasing hormone; GnRH) の分泌が抑制 (inhibition) されます。これにより、下垂体前葉 (anterior pituitary) からの黄体形成ホルモン (luteinizing hormone; LH) および卵胞刺激ホルモン (follicle-stimulating hormone; FSH) の分泌が減少 (decreases) し、排卵 (ovulation) が抑制されます。
Question 3: Ejection of Milk (乳射出の仕組み)
Q: The ejection of milk is triggered by _______ signals from the nipples to the _______ of the brain, leading to the release of _______ from the posterior pituitary.
Answer: sensory / hypothalamus / oxytocin
Explanation:
乳射出の仕組み (Ejection of Milk) では、乳頭 (nipples) からの感覚信号 (sensory signals) が視床下部 (hypothalamus) に送られ、後葉下垂体 (posterior pituitary) からオキシトシン (oxytocin) の分泌 (release) が引き起こされます。これにより、乳腺胞 (alveoli) を取り囲む筋上皮細胞 (myoepithelial cells) が収縮 (contraction) し、乳管 (ductal system) へ乳が押し出される (milk is ejected) という仕組みです。
Question 4: Role of Prolactin in Lactation (授乳におけるプロラクチンの役割)
Q: Prolactin is secreted by the _______ and increases after childbirth due to the sudden loss of _______ and _______ produced by the placenta.
Answer: anterior pituitary / estrogen / progesterone
Explanation:
授乳におけるプロラクチンの役割 (Role of Prolactin in Lactation) では、下垂体前葉 (anterior pituitary) からプロラクチン (prolactin) が分泌されます。分娩後 (after childbirth)、胎盤 (placenta) から分泌されていたエストロゲン (estrogen) とプロゲステロン (progesterone) が急激に減少 (loss) し、これによりプロラクチンの作用が強化 (enhanced) されます。
Question 5: Metabolic Drain on the Mother (母体の代謝的負担)
Q: During lactation, the mother loses large amounts of _______ and _______ in milk production, which can lead to a deficiency of _______ in the mother.
Answer: fat / lactose / calcium
Explanation:
母体の代謝的負担 (Metabolic Drain on the Mother) では、授乳中 (during lactation)、脂肪 (fat) や乳糖 (lactose) が母乳 (milk) に取り込まれます。これにより、母体のカルシウム (calcium) 欠乏が引き起こされる可能性 (deficiency may occur) があります。カルシウム不足 (calcium deficiency) を補うために、副甲状腺 (parathyroid gland) が拡大し、骨 (bone) からの脱灰 (decalcification) が生じることがあります。
Question 6: Composition of Human Milk (ヒトの母乳の組成)
Q: Human milk contains more _______ but less _______ and _______ compared to cow’s milk.
Answer: lactose / protein / minerals (ash)
Explanation:
ヒトの母乳の組成 (Composition of Human Milk) では、ヒトの母乳 (human milk) にはラクトース (lactose) が多く (more) 含まれていますが、タンパク質 (protein) と灰分 (minerals/ash) は牛乳 (cow’s milk) に比べて少ない (less) です。
Question 7: Role of Antibodies in Milk (母乳における抗体の役割)
Q: Breast milk contains antibodies and _______ cells that protect the baby from infections, including those caused by _______ bacteria, which are known to cause severe _______ in newborns.
Answer: white blood / Escherichia coli (E. coli) / diarrhea
Explanation:
母乳における抗体の役割 (Role of Antibodies in Milk) では、母乳 (breast milk) には抗体 (antibodies) や白血球 (white blood cells) が含まれており、新生児 (newborns) に感染を引き起こす大腸菌 (Escherichia coli; E. coli) などの細菌感染 (bacterial infections) から保護 (protection) します。特に、大腸菌 (E. coli) による重篤な下痢 (severe diarrhea) を防ぐ効果があります。


コメント