Contents
- 1 PPT
- 1.1 動脈供給(Arterial Supply)
- 1.2 静脈排出(Venous Drainage)
- 1.3 リンパ排出(Lymphatic Drainage)
- 1.4 リンパ系(Lymphatics)
- 1.5 神経支配(Innervation)
- 1.6 内臓求心性反射線維の経路(Pathway of Visceral Afferent Reflex Fibers)
- 1.7 1. 血液供給(Blood Supply)
- 1.8 2. リンパ排出(Lymphatic Drainage)
- 1.9 3. 神経支配(Nerves)
- 1.10 4. 支持構造(Supports)
- 1.11 5. 付属器(Adnexa)
- 1.12 1. 生殖器系の神経支配(Genital Tract Innervation)
- 1.13 2. 卵巣(Ovary)の神経支配
- 1.14 3. 卵管(Uterine Tube)の神経支配
- 1.15 4. 子宮(Uterus)の神経支配
- 1.16 1. 動脈供給(Arterial Supply)
- 1.17 2. 静脈排出(Venous Drainage)
- 1.18 3. リンパ排出(Lymphatic Drainage)
- 1.19 4. 神経支配(Nerve Supply)
- 1.20 1. 機能(Function)
- 1.21 2. 解剖学的位置(Anatomical Location)
- 1.22 卵管の4つの部分(4 Parts of the Uterine Tube)
- 1.23 1. 概要(Overview)
- 1.24 2. 解剖学的特徴(Anatomical Features)
- 1.25 3. 子宮の2つの主要部分(2 Main Parts of the Uterus)
- 1.26 1. 子宮体(Body of the Uterus)の概要
- 1.27 2. 解剖学的特徴(Anatomical Features)
- 1.28 1. 子宮峡部(Isthmus of the Uterus)
- 1.29 2. 子宮頸部(Cervix of the Uterus)
- 1.30 1. 子宮頸部の膣上部(Supravaginal Part of the Cervix)
- 1.31 2. 子宮腔(Uterine Cavity)
- 1.32 3. 子宮角(Uterine Horns)
- 1.33 1. 子宮腔と子宮頸管(Uterine Cavity and Cervical Canal)
- 1.34 2. 子宮頸管の構造(Structure of the Cervical Canal)
- 1.35 3. 出生管(Birth Canal)
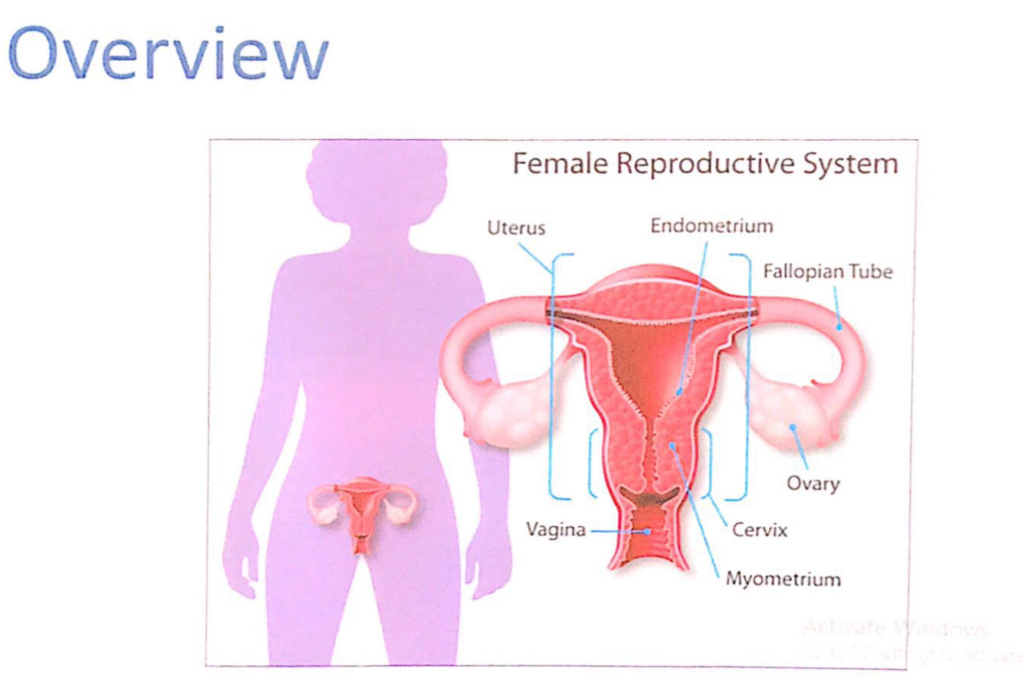
- 1.36 子宮壁の層構造(Layers of the Uterine Wall)
- 1.37 子宮(Uterus)
- 1.38 子宮頸部(Cervix)
- 1.39 動脈供給(Arterial Supply)
- 1.40 静脈排出およびリンパ排出(Venous and Lymphatic Drainage)
- 1.41 膣の神経支配
- 1.42 交感神経(Sympathetic Innervation)
- 1.43 副交感神経(Parasympathetic Innervation)
- 1.44 内臓求心性神経(Visceral Afferent Fibers)
- 1.45 主要な神経叢(Primary Plexus)
- 1.46 神経の詳細(Detailed Nerve Supply)
- 1.47 会陰(Perineum)
- 1.48 女性外陰部(Female External Genitalia)の構成
- 1.49 外陰部と陰部(Vulva and Pudendum)
- 1.50 外陰部(Vulva)の主な機能
- 1.51 恥丘(Mons Pubis)
- 1.52 恥丘(Mons Pubis)
- 1.53 大陰唇(Labia Majora)
- 1.54 大陰唇(Labia Majora)
- 1.55 1. 陰核(Clitoris)と膣前庭(Vestibule)
- 1.56 2. 外尿道口(External Urethral Orifice)
- 1.57 1. 陰核(Clitoris)と膣口(Vaginal Orifice)
- 1.58 2. 処女膜の破裂後の構造(Structure After Hymen Rupture)
- 1.59 3. 生理学的機能(Physiologic Function)
- 1.60 4. 関連構造(Associated Structures)
- 1.61 膣前庭腺(Vestibular Glands)
- 1.62 動脈供給(Arterial Supply)
- 1.63 静脈排出(Venous Drainage)
- 1.64 リンパ流(Lymphatics)
- 1.65 外陰部の神経支配(Innervation of the Vulva)
- 2 過去問
- 2.1 ★骨盤腔の特徴 (Characteristics of the Pelvic Cavity)
- 2.2 梨状筋の機能 (Function of Piriformis Muscle)
- 2.3 ★妊娠中に損傷される筋肉 (Muscles Torn During Pregnancy)
- 2.4 腹腔内圧増加への抵抗 (Resisting Increase in Intra-Abdominal Pressure)
- 2.5 ★骨盤入口損傷で脆弱な構造 (Vulnerable Structure in Pelvic Inlet Damage)
- 2.6 ★骨盤縁の構造 (Structure Damaged in Pelvic Brim Injury)
- 2.7 ★内腸骨動脈の後枝に含まれないもの (Not Part of Posterior Division of Internal Iliac Artery)
- 2.8 ★仙骨神経叢に含まれないもの (Not a Branch of Posterior Sacral Nerve)
- 2.9 ★内腸骨動脈の延長 (Continuation of Internal Iliac Artery)
- 2.10 ★大腿のリンパ排出 (Lymph Drainage of the Thigh)
- 2.11 ★陰部神経ブロックの固定ランドマーク (Landmark for Pudendal Nerve Block)
- 2.12 大坐骨切痕を通らない構造 (Does Not Pass Through Greater Sciatic Notch)
- 2.13 ★子宮支持靭帯 (Ligament Supporting the Uterus)
- 2.14 ★膀胱の緩やかな連結部位 (Part of the Urinary Bladder Loosely Connected to the Peritoneum)
- 2.15 ★受精の一般的な部位 (Common Site of Fertilization)
- 2.16 ★横頸靭帯の起点 (Origin of the Transverse Cervical Ligament)
- 2.17 ★浅会陰嚢から除外される構造 (Spared from the Superficial Perineal Pouch)
- 2.18 ★尿生殖三角に含まれない構造 (Spared from the Urogenital Triangle)
- 2.19 ★仙骨神経叢の範囲 (Sacral Plexus Range)
- 2.20 骨盤直腸空間の特徴 (True About Pelvirectal Space)
- 2.21 ★子宮頸部の支持 (Cervical Support)
- 2.22 ★会陰切開術で影響を受ける筋肉 (Muscles Spread During Episiotomy)
- 2.23 過期産児の損傷を受ける筋肉 (Muscle Damaged in Overdue Baby Delivery)
- 2.24 ★小骨盤内出血の原因動脈 (Artery Bleeding in Lesser Pelvis)
- 2.25 ★骨盤内臓器に含まれないもの (Structure NOT Included in the Pelvis)
- 2.26 ★会陰の後外側境界 (Posterolateral Boundary of the Perineum)
- 2.27 ★会陰中央腱の機能 (Function of the Perineal Body)
- 2.28 ★深会陰嚢の構造 (Structure in the Deep Perineal Pouch)
- 2.29 ★浅会陰嚢の構造 (Structure in the Superficial Perineal Pouch)
- 2.30 坐骨肛門窩内の内側構造 (Medial Structure of Ischio-Anal Fossae)
- 2.31 ★陰部管の特徴 (True About Pudendal Canal)
- 2.32 中直腸静脈の還流先 (Drainage of the Middle Rectal Vein)
- 2.33 陰嚢の区分構造 (Structure Dividing the Scrotum into Two Compartments)
- 2.34 陰茎の強固な膜状被覆 (Strong Membranous Covering of the Penis)
- 2.35 ★円靭帯の終端部 (Termination of the Round Ligament)
- 2.36 ★陰裂を囲む構造 (Structure Enclosing the Pudendal Cleft)
- 2.37 ★前陰唇神経の起源 (Origin of Anterior Labial Nerve)
- 2.38 ★陰核包皮の形成 (Formation of the Clitoral Prepuce)
- 2.39 ★外陰部の後端 (Posterior Limit of the Vulva)
- 2.40 尿道の部分の特徴 (Part of the Urethra Forming Intrabulbar and Navicular Fossae)
- 2.41 中部尿道の位置 (Location of the Intermediate Urethra)
- 2.42 ★大前庭腺の位置 (Location of the Greater Vestibular Bulb)
- 2.43 ★前庭球の位置 (Location of the Bulbs of Vestibule)
- 2.44 男性尿道の遠位部の副交感神経支配 (Parasympathetic Innervation of the Distal Male Urethra)
- 2.45 勃起組織の血流移動 (Forcing Blood in Corpora Cavernosa)
- 2.46 陰茎の輪状靭帯 (Fundiform Ligament of the Penis)
- 2.47 勃起組織の神経支配 (Innervation of the Helicine Arteries)
- 2.48 尿道球腺と陰茎海綿体への血流供給 (Arterial Supply to the Bulb and Corpus Spongiosum)
- 2.49 陰茎海綿体の融合が見られない部分 (Part of Corpora Cavernosa Not Fused)
- 2.50 ★女性外陰部への主な血液供給 (Arterial Supply to Female External Genitalia)
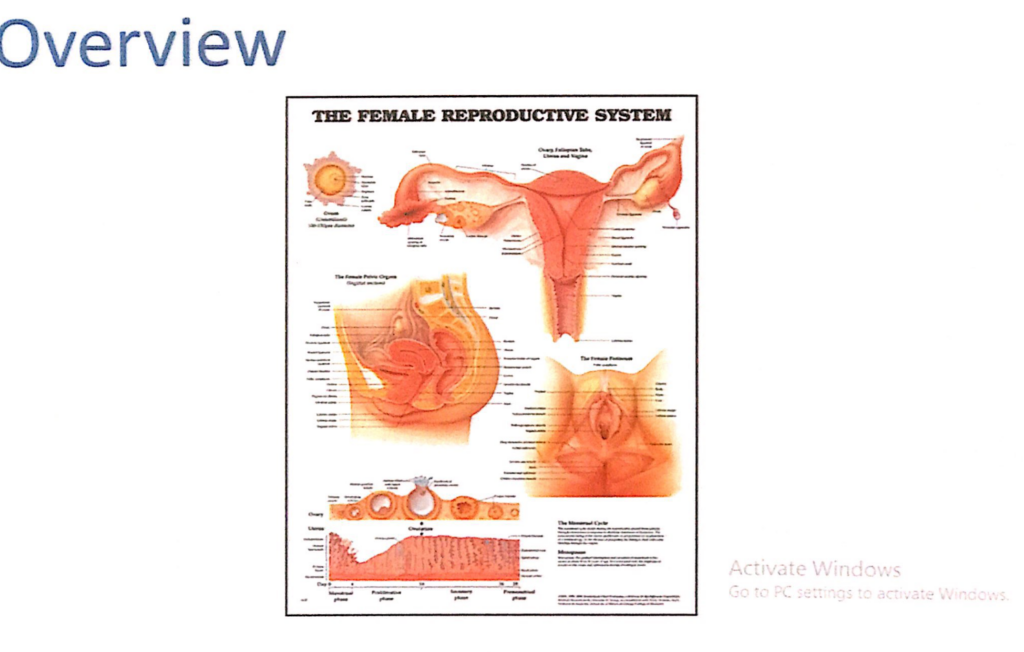
PPT

*broad ligamentは三箇所に分かれる。
二つある
ovarian arteryはsuspensary ligamentの中に入って走る
全ての血流は子宮の外側へ
膀胱は子宮の前にあり
静脈は動脈と同じ走行
左はinferior ovalal vein → IVC
右は違う
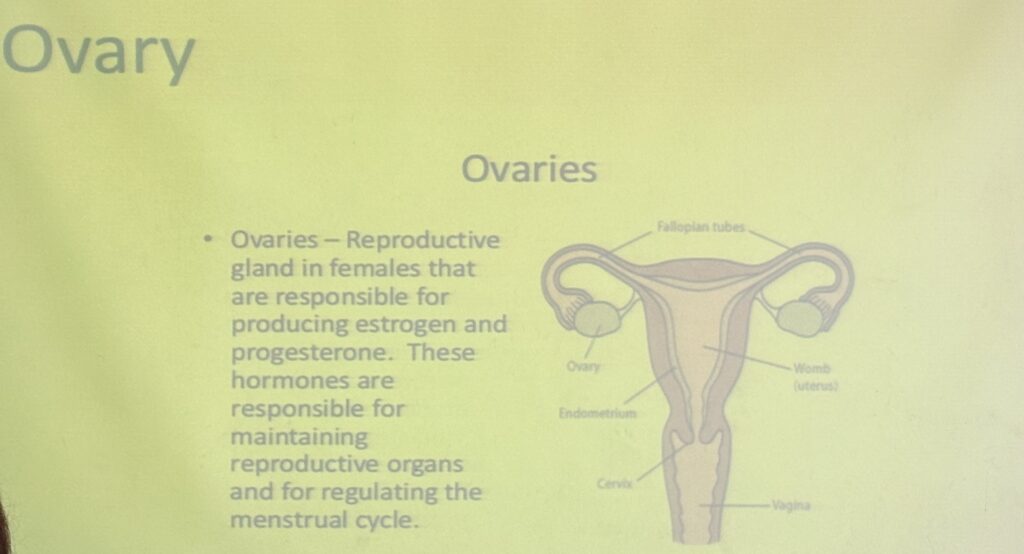

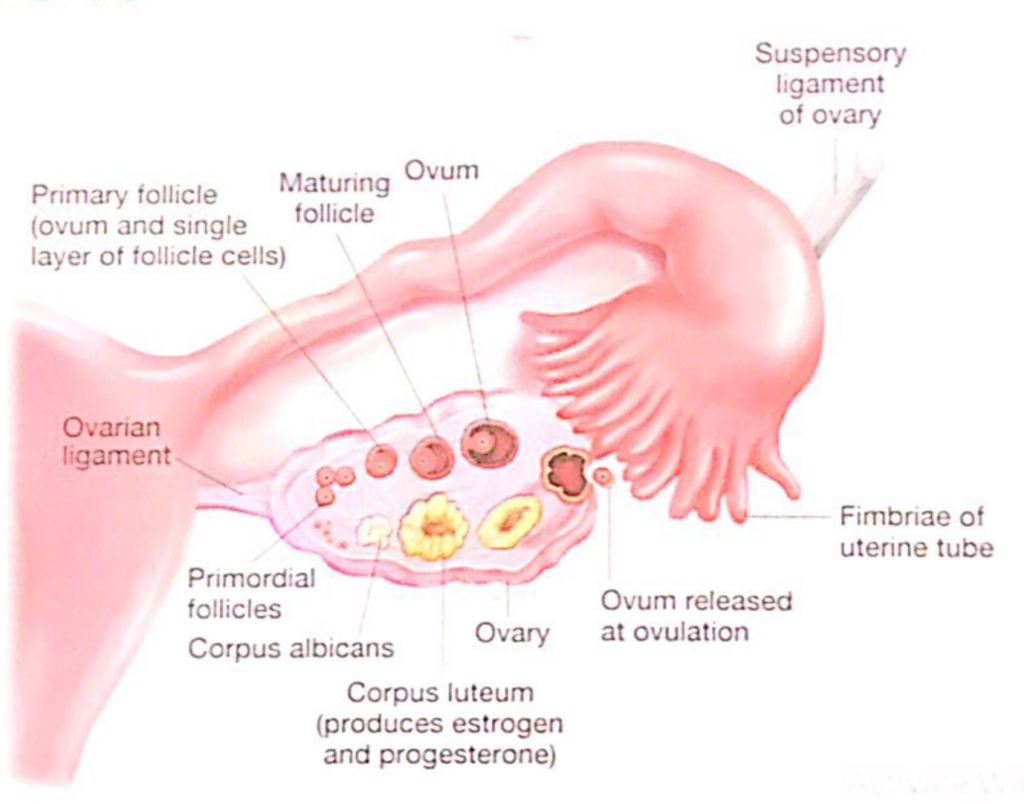
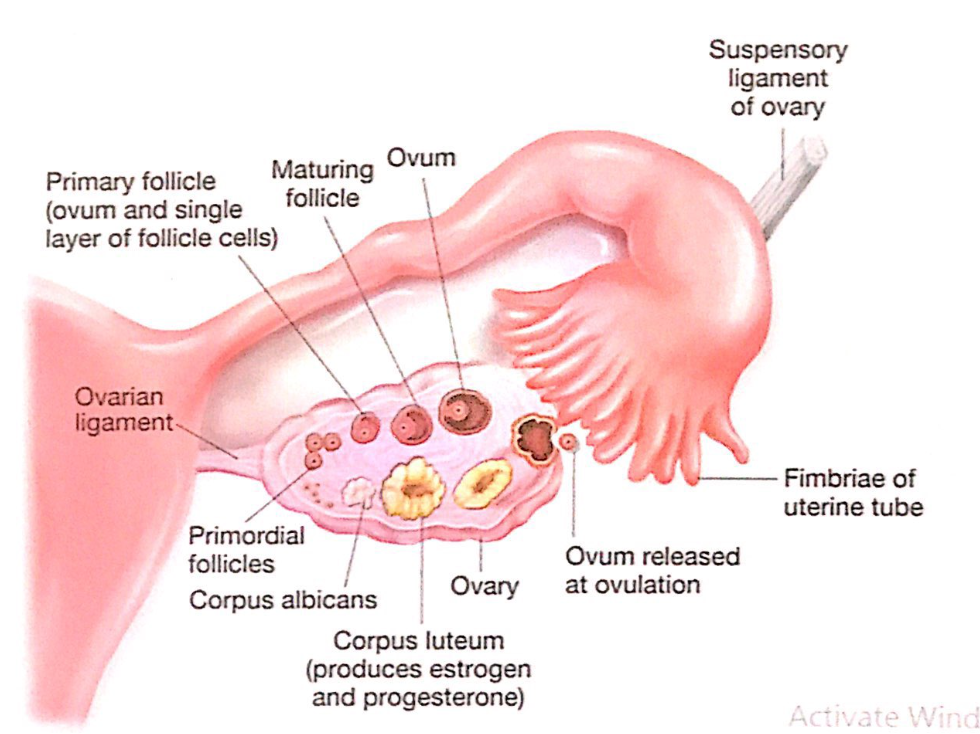
形状(Shape):
- 卵巣はアーモンド形(almond-shaped)をしており、大きさは成人女性で約3-5cm程度です。この形状はその解剖学的位置と機能に適応しています。
機能(Function):
- 卵巣は生殖ホルモン(reproductive hormones)の分泌と卵子の生成(ovum production)を担います。主なホルモンには、エストロゲン(estrogen)とプロゲステロン(progesterone)が含まれ、これらは女性の月経周期や妊娠を調整します。
位置と支持構造(Location and Supporting Structures):
- 卵巣は広靭帯(broad ligament)によって骨盤側壁(lateral pelvic walls)に接続されています。この広靭帯は腹膜ひだ(peritoneal folds)の一部であり、卵巣を支持する役割を果たします。
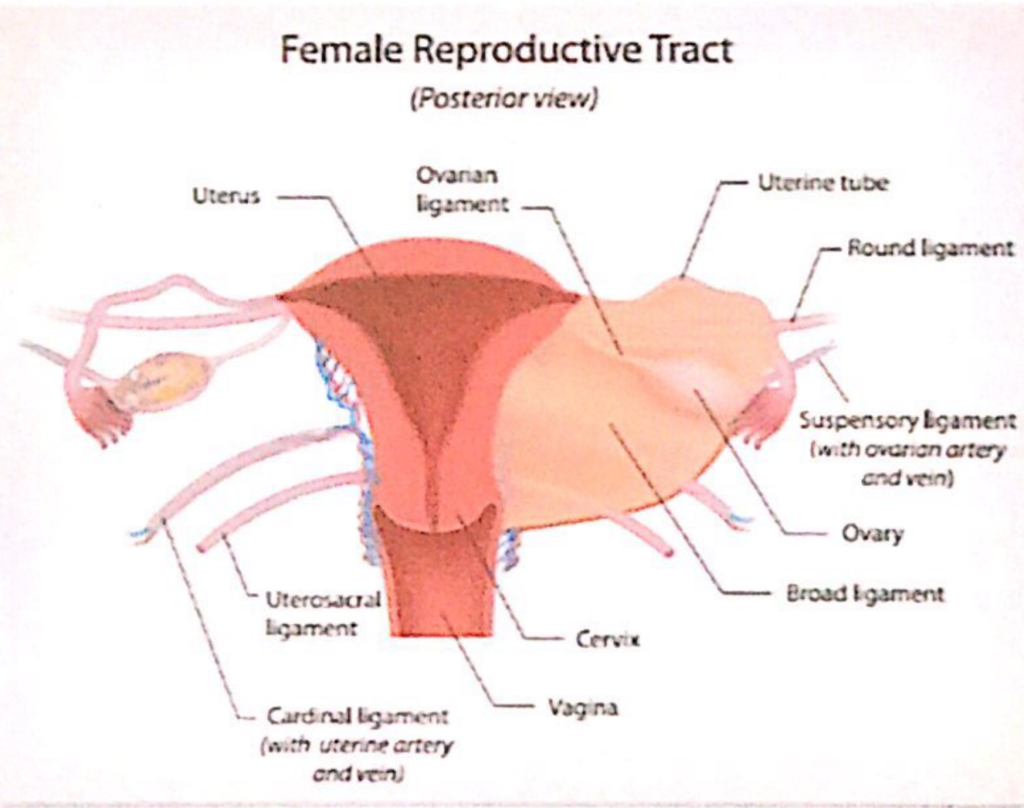
関連靭帯(Associated Ligaments):
- 中卵巣間膜(mesovarium): 広靭帯の一部で、卵巣を支える構造。
- 卵巣提索(suspensory ligament of the ovary): 卵巣の上外側部(superolateral aspect)を通って血管(vessels)、神経(nerves)、および靭帯(ligaments)を卵巣に供給します。
- 卵巣固有靭帯(ligament of the ovary): 中卵巣間膜(mesovarium)の中にあり、卵巣を子宮(uterus)に結びつけています。
血管と神経(Vessels and Nerves):
- 卵巣動脈(ovarian artery)と卵巣静脈(ovarian vein)が主要な血液供給を担います。また、神経叢(nervous plexus)を通じて感覚信号が伝わります。

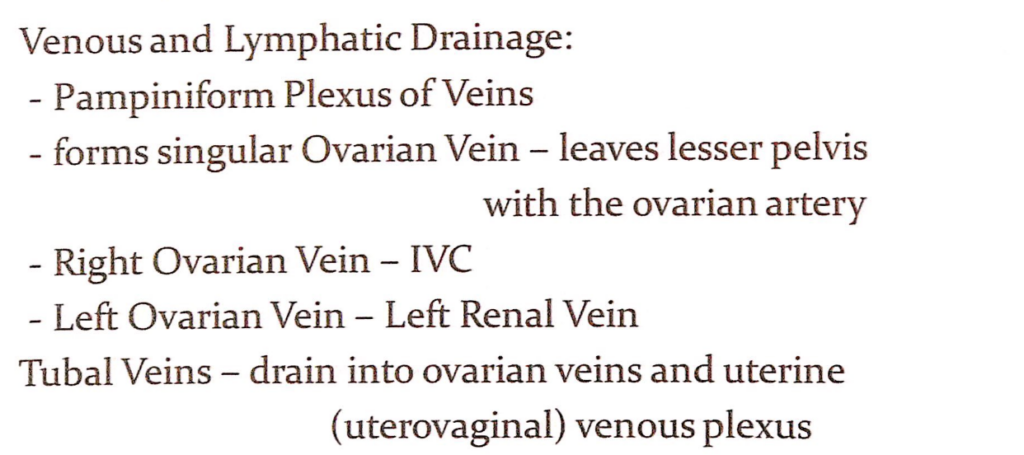
動脈供給(Arterial Supply)
- 卵巣動脈(Ovarian Arteries):
- 腹部大動脈(Abdominal Aorta)から直接分岐します。
- 卵巣動脈は外腸骨血管(external iliac vessels)を横切り、卵巣提索(suspensory ligament)の外側(lateral aspect)に入り、卵巣に血液を供給します。
- 子宮動脈の上行枝(Ascending Branches of the Uterine Arteries):
- 内腸骨動脈(Internal Iliac Arteries)から分岐します。
- 子宮動脈は卵巣と卵管(tubes)の内側(medial aspect)に向かい、接近して血液を供給します。
- 分枝(Branches):
- 卵巣動脈と子宮動脈は、卵巣枝(ovarian branches)と卵管枝(tubal branches)に分かれて終わります。
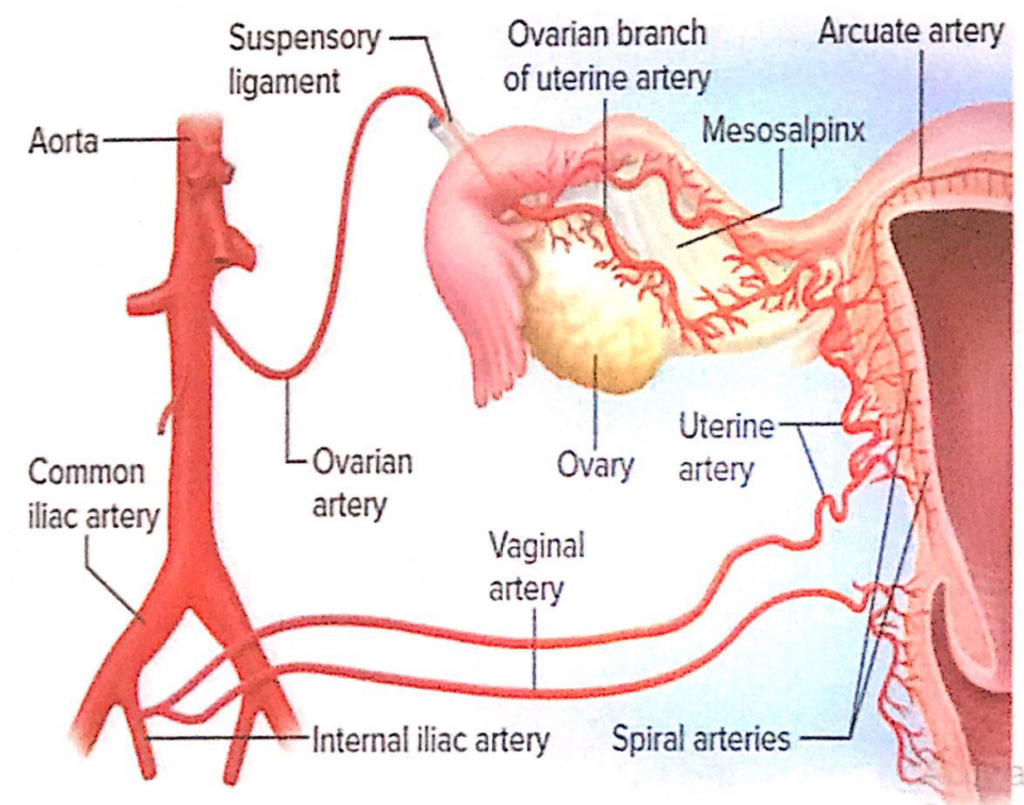
静脈排出(Venous Drainage)
- 蔓状静脈叢(Pampiniform Plexus of Veins):
- 卵巣周囲に形成される静脈叢で、体温調節に役立つとされています。
- これらの静脈叢は単一の卵巣静脈(singular Ovarian Vein)を形成し、卵巣動脈(ovarian artery)と共に小骨盤(lesser pelvis)を出ます。
- 右卵巣静脈(Right Ovarian Vein):
- 直接的に下大静脈(Inferior Vena Cava, IVC)に流入します。
- 左卵巣静脈(Left Ovarian Vein):
- 左腎静脈(Left Renal Vein)に流入します。
- 卵管静脈(Tubal Veins):
- 卵巣静脈および子宮(uterovaginal)静脈叢(venous plexus)に排出されます。
リンパ排出(Lymphatic Drainage)
- 卵巣のリンパ管は主に腹部大動脈周囲リンパ節(para-aortic lymph nodes)へ排出されます。これは卵巣が胎生期に腹膜後腔で発生したことに関連しています。

*ovarianはtumorが多い
リンパ系(Lymphatics)
- 卵巣、卵管、子宮底からのリンパ流(Lymphatic Drainage from Ovary, Uterine Tubes, and Fundus):
- 卵巣、卵管(uterine tubes)、および子宮底(fundus)のリンパ管は、卵巣血管(ovarian blood vessels)に沿って走行します。
- これらのリンパ管は右および左の腰リンパ節(Lumbar Lymph Nodes, also called Caval or Aortic Lymph Nodes)に向かって上行します。
神経支配(Innervation)
- 卵巣神経叢(Ovarian Plexus)および子宮(骨盤)神経叢(Uterine or Pelvic Plexus):
- 卵巣神経叢(ovarian plexus)は、主に交感神経(sympathetic fibers)と副交感神経(parasympathetic fibers)から成ります。
- また、一部は子宮(骨盤)神経叢(uterine or pelvic plexus)から供給されます。
- 痛みの感覚(Pain Perception):
- 卵巣は腹膜内臓器(Intraperitoneal Organ)であるため、骨盤痛覚線(pelvic pain line)の上に位置します。
- 内臓求心性痛覚線維(Visceral Afferent Pain Fibers)は、卵巣神経叢(ovarian plexus)および腰内臓神経(lumbar splanchnic nerves)の下降交感神経線維(descending sympathetic fibers)に沿って逆行性に上行します。
- これらの線維は、T11-L1脊髄感覚神経節(T11-L1 spinal sensory ganglia)で細胞体とシナプスを形成します。

内臓求心性反射線維の経路(Pathway of Visceral Afferent Reflex Fibers)
- 副交感神経と関連した経路(Retrograde Path through Parasympathetic Fibers):
- **内臓求心性反射線維(Visceral Afferent Reflex Fibers)**は、以下の経路を逆行して中枢神経系(central nervous system)に情報を伝達します。
- 子宮(骨盤)神経叢(Uterine or Pelvic Plexus)
- 下腹神経叢(Inferior Hypogastric Plexus)
- 骨盤内臓神経(Pelvic Splanchnic Nerves)
- **内臓求心性反射線維(Visceral Afferent Reflex Fibers)**は、以下の経路を逆行して中枢神経系(central nervous system)に情報を伝達します。
- 脊髄神経節への到達(Termination in Spinal Sensory Ganglia):
- これらの線維は、**S2-S4脊髄感覚神経節(S2-S4 Spinal Sensory Ganglia)**で終始します。この領域で反射的な情報が処理されます。


1. 血液供給(Blood Supply)
- 卵巣動脈(Ovarian Arteries):
- 腹部大動脈(Abdominal Aorta)から直接分岐し、卵巣に血液を供給します。
- 卵巣静脈(Ovarian Vein):
- 静脈血は以下の経路で排出されます。
- 右卵巣静脈(Right Ovarian Vein)は下大静脈(Inferior Vena Cava)に直接流入。
- 左卵巣静脈(Left Ovarian Vein)は左腎静脈(Left Renal Vein)に流入。
- 静脈血は以下の経路で排出されます。
2. リンパ排出(Lymphatic Drainage)
- 腰リンパ節(Lumbar Glands):
- 卵巣からのリンパ流は腰リンパ節(lumbar glands)へ向かいます。このリンパ排出経路は、卵巣腫瘍の転移経路の理解において重要です。
3. 神経支配(Nerves)
- 卵巣神経叢(Ovarian Plexus):
- 卵巣神経叢は交感神経(sympathetic fibers)と副交感神経(parasympathetic fibers)を含み、卵巣の機能と感覚を調整します。
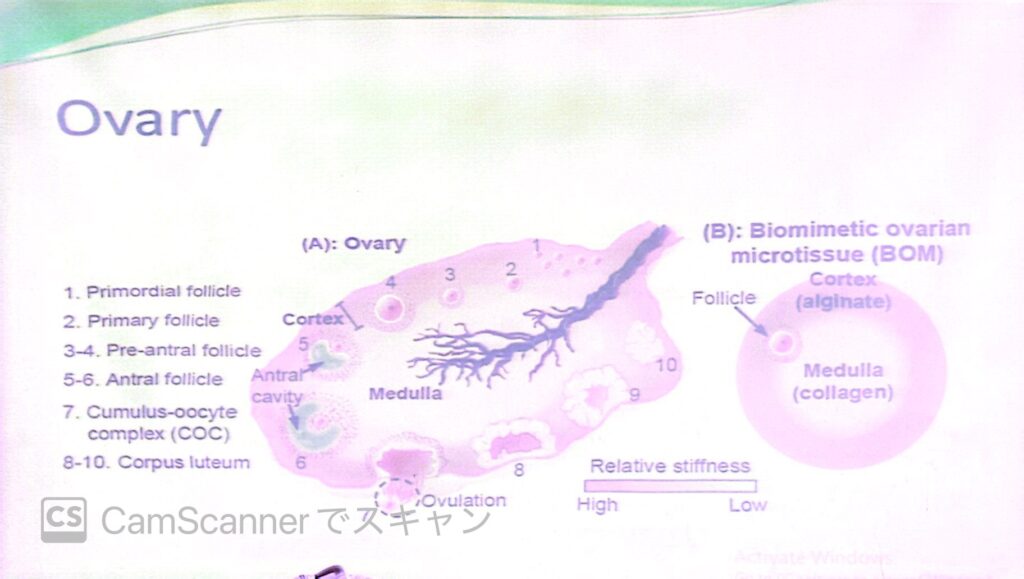
4. 支持構造(Supports)
- 位置と結合(Location and Attachments):
- 卵巣は骨盤の卵巣窩(Ovarian Fossa)に位置します。
- 広靭帯(Broad Ligament):
- 卵巣は広靭帯の一部である中卵巣間膜(Meso-ovarium)に付着しています。この間膜は卵巣を支持し、血管や神経が通過する経路を形成します。
- 広靭帯の一部(Components of Broad Ligament):
- 中卵管間膜(Meso-salpinx):
- 卵管(Fallopian Tube)と卵巣の間を広靭帯の一部として支持します。
- 中卵管間膜(Meso-salpinx):
5. 付属器(Adnexa)
- 卵管(Fallopian Tubes)、卵巣(Ovaries)、および広靭帯(Broad Ligament)はまとめて**付属器(Adnexa)**と呼ばれます。
- これらの構造は女性の生殖器系において密接に関連し、解剖学的・機能的な連続性を持っています。

1. 生殖器系の神経支配(Genital Tract Innervation)
- **交感神経(Sympathetic Nerves)と副交感神経(Parasympathetic Nerves)**の両方が、生殖器系を支配します。
2. 卵巣(Ovary)の神経支配
- 交感神経支配(Sympathetic Innervation):
- **大動脈腎神経叢(Aorticorenal Plexuses)**からの交感神経線維が卵巣に向かいます。
- これらの神経は卵巣の血管調節や痛覚伝達に関与します。
3. 卵管(Uterine Tube)の神経支配
- 交感神経支配(Sympathetic Innervation):
- **大動脈腎神経叢(Aorticorenal Plexuses)**からの交感神経線維が卵管を支配します。
- 卵管の運動(例: 収縮や緩和)を調節し、卵子の輸送を助けます。
4. 子宮(Uterus)の神経支配
- 交感神経支配(Sympathetic Innervation):
- 神経は**右および左の下腹神経(Hypogastric Nerves)**を介して子宮に到達します。
- これらの神経は、**尾側腸間膜神経叢(Caudal Mesenteric Plexus)**から始まり、**骨盤神経叢(Pelvic Plexus)**を経由して子宮に入ります。
- 子宮の筋収縮や血管収縮を調節します。

1. 動脈供給(Arterial Supply)
- 卵巣動脈(Ovarian Artery):
- 起始(Origin):
- 腹部大動脈(Aorta)のL2レベルから分岐します。
- 経路(Pathway):
- 卵巣動脈は卵巣提索(Infundibulopelvic Ligament)を通って卵巣に達します。
- 臨床的意義(Clinical Relevance):
- 動脈供給が遮断されると、卵巣捻転(Ovarian Torsion)による虚血が発生する可能性があります。
- 起始(Origin):
- 子宮動脈の卵巣枝(Ovarian Branch of the Uterine Artery):
- 供給(Supply):
- 子宮動脈(Uterine Artery)の一部が卵巣へ血液を供給します。
- 動脈吻合(Anastomosis):
- 広靭帯(Broad Ligament)の中で卵巣血管(Ovarian Vessels)と吻合します。
- 供給(Supply):
2. 静脈排出(Venous Drainage)
- 卵巣静脈(Ovarian Veins):
- 伴走(Accompanying Arteries):
- 卵巣静脈は卵巣動脈に沿って走行します。
- 蔓状静脈叢(Pampiniform Plexus of Veins)との関係:
- 卵巣静脈は蔓状静脈叢(Pampiniform Plexus of Veins)および子宮静脈(Uterine Vein)と合流します。
- 臨床的意義(Clinical Relevance):
- 静脈流の障害は卵巣静脈瘤(Ovarian Vein Varicocele)を引き起こす可能性があります。
- 伴走(Accompanying Arteries):
3. リンパ排出(Lymphatic Drainage)
- 経路(Pathway):
- 卵巣血管(Ovarian Vessels)に沿ってリンパ管が走行し、大動脈周囲リンパ節(Para-Aortic Lymph Nodes)へ流入します。
- 臨床的意義(Clinical Relevance):
- 腫瘍や感染の転移経路として、このリンパ排出経路は非常に重要です。
4. 神経支配(Nerve Supply)
- 感覚(Sensitivity):
- 卵巣は圧迫(Squeezing)に対してのみわずかに敏感であり、内診(P.V. Examination)で痛みを感じることがあります。
- 交感神経と副交感神経(Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Nerves):
- 交感神経(Sympathetic Nerves):
- T10およびT11の脊髄神経から供給されます。
- 腹大動脈神経叢(Preaortic Plexus)を介して卵巣血管に伴走します。
- 副交感神経(Parasympathetic Nerves):
- 骨盤内臓神経(Pelvic Splanchnic Nerves)が関与します。
- 交感神経(Sympathetic Nerves):
- 臨床的意義(Clinical Relevance):
- 痛みや反射の経路を理解することは、卵巣の診断や治療(例: 卵巣捻転の評価)に役立ちます。

1. 機能(Function)
- 卵子の輸送(Oocyte Transport):
- 卵管は毎月、排卵後に卵巣(Ovary)から放出される卵子(Oocyte, Ovum)を輸送します。
- 輸送経路(Pathway):
- 卵巣周囲の腹膜腔(Periovarian Peritoneal Cavity)から卵管を通じて子宮腔(Uterine Cavity)へ運ばれます。
- これは、女性の生殖可能年齢(Child-bearing Years)において生殖を可能にする重要な機能です。
2. 解剖学的位置(Anatomical Location)
- 子宮角からの出発(Lateral from Uterine Horns):
- 卵管は子宮の側部(uterine horns)から外側に伸びています。
- 広靭帯との関係(Broad Ligament Relationship):
- 卵管は広靭帯(Broad Ligament)の遊離縁(Free Edge)である**中卵管間膜(Mesosalpinx)**に包まれています。
- 全長(Length):
- 卵管の全長は約10cmです。
- 骨盤内での配置(Pelvic Orientation):
- 卵管は後外側(Posterolateral)に伸び、骨盤壁の外側(Lateral Pelvic Walls)に向かいます。
- その後、卵巣の前方および上方(Anterior and Superior to Ovaries)をアーチ状に通過します。

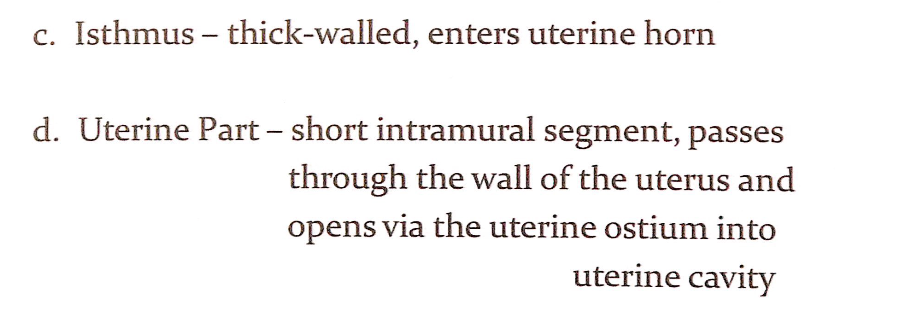
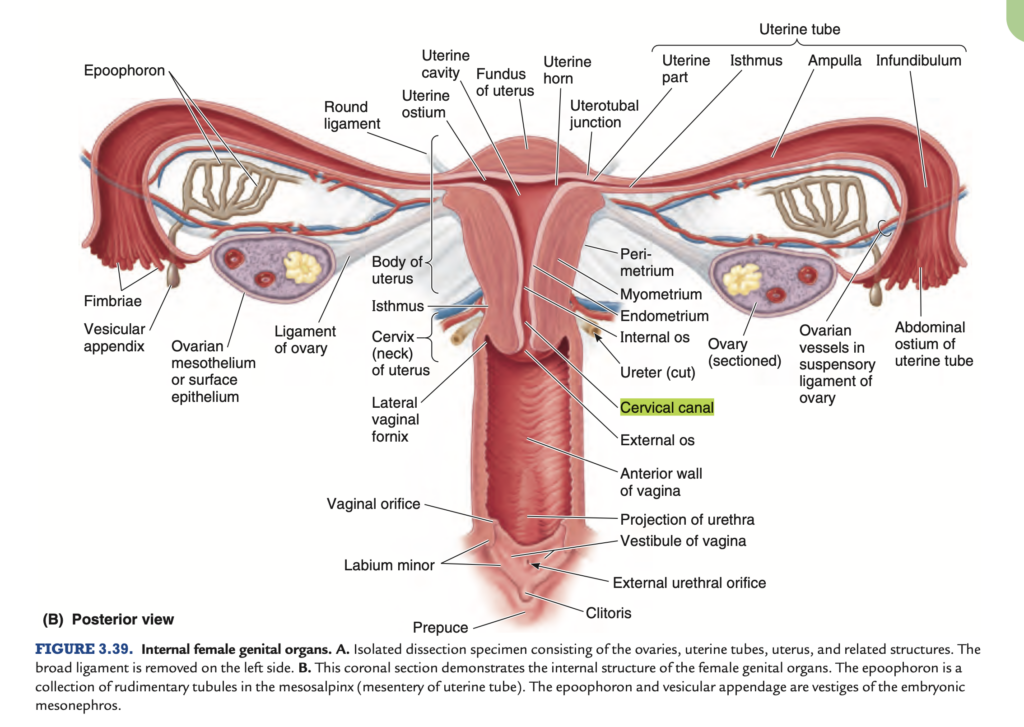
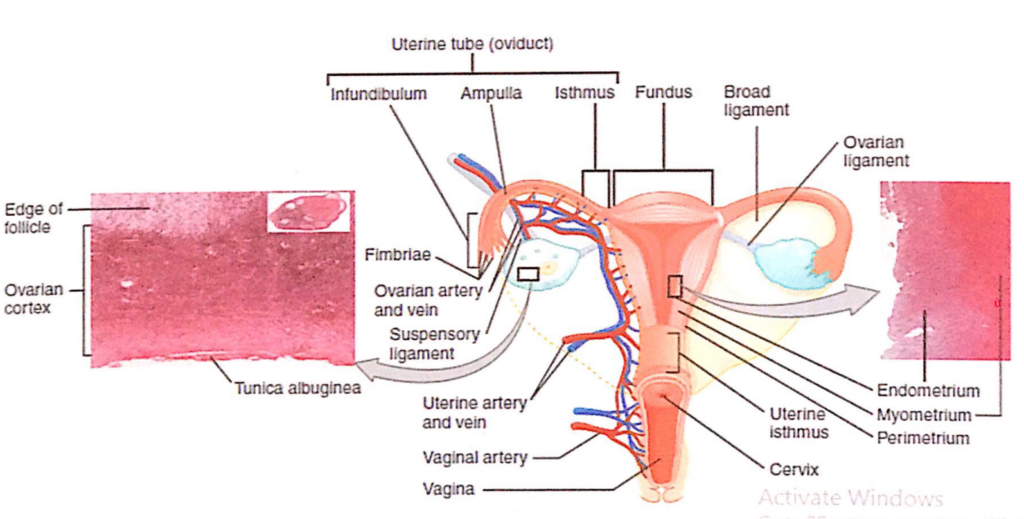
卵管の4つの部分(4 Parts of the Uterine Tube)
卵管は外側(Lateral)から内側(Medial)に向かって4つの部分に分けられ、それぞれの部分が異なる解剖学的特徴と機能を持っています。
1. 卵管采部(Infundibulum)
- 形状(Shape):
- 漏斗状(Funnel-shaped)で、卵管の外端に位置します。
- 構造(Structure):
- 腹腔開口部(Abdominal Ostium)を通じて腹腔(Abdominal Cavity)に開いています。
- 卵管采(Fimbriae):
- 指状突起(Finger-like Processes)で構成され、排卵された卵子(Oocyte)を捕捉する役割を果たします。
- 機能(Function):
- 排卵時に卵巣から放出された卵子を捕らえ、卵管内に導く重要な部分です。
2. 卵管膨大部(Ampulla)
- 形状と長さ(Shape and Length):
- 卵管の中で最も広く(Widest)かつ最も長い(Longest)部分です。
- 機能(Function):
- 受精(Fertilization):
- 卵管膨大部は、精子と卵子が出会い受精(Fertilization)が行われる主な部位です。
- 受精(Fertilization):
- 臨床的意義(Clinical Relevance):
- 異所性妊娠(Ectopic Pregnancy)はしばしば卵管膨大部で発生します。
3. 卵管峡部(Isthmus)
- 形状と構造(Shape and Structure):
- 卵管膨大部よりも細く(Narrower)、壁が厚い(Thick-walled)構造を持っています。
- 位置(Location):
- 卵管峡部は、卵管が子宮角(Uterine Horn)に入る部分です。
- 機能(Function):
- 卵子や受精卵が子宮へ移動する際の狭窄部として作用し、卵管の輸送機能を調整します。
4. 卵管子宮部(Uterine Part, Intramural Segment)
- 位置(Location):
- 卵管の最内側部分で、子宮壁(Wall of the Uterus)を貫通しています。
- 構造(Structure):
- 非常に短い(Short)部分であり、卵管腔が子宮腔(Uterine Cavity)に開く子宮開口部(Uterine Ostium)で終わります。
- 機能(Function):
- 卵管と子宮腔を接続する役割を果たします。
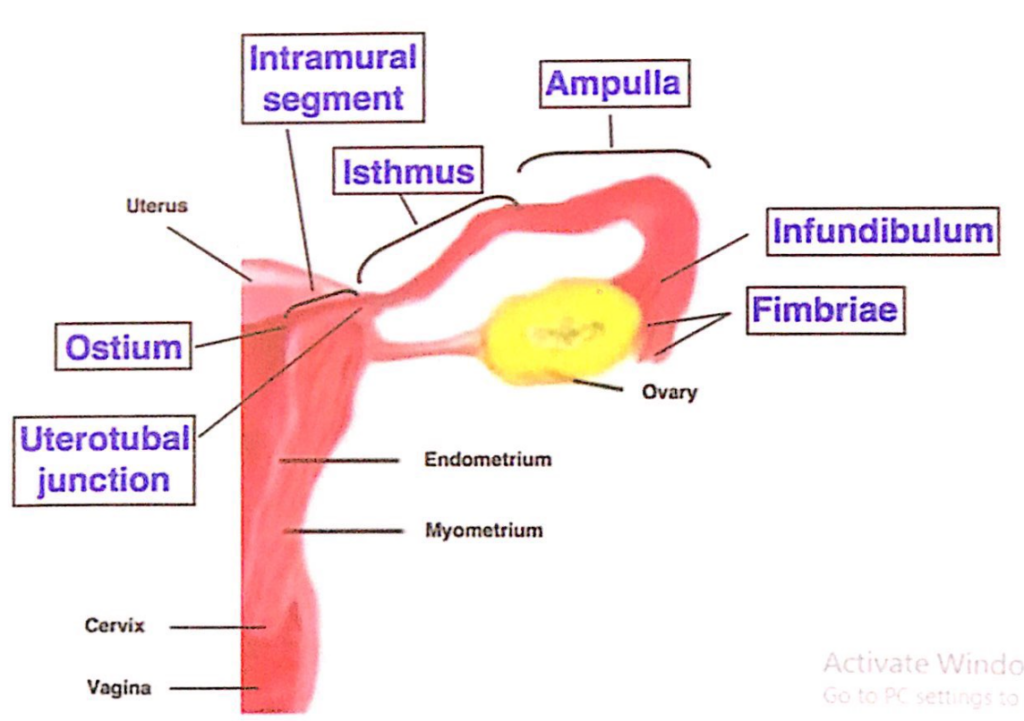
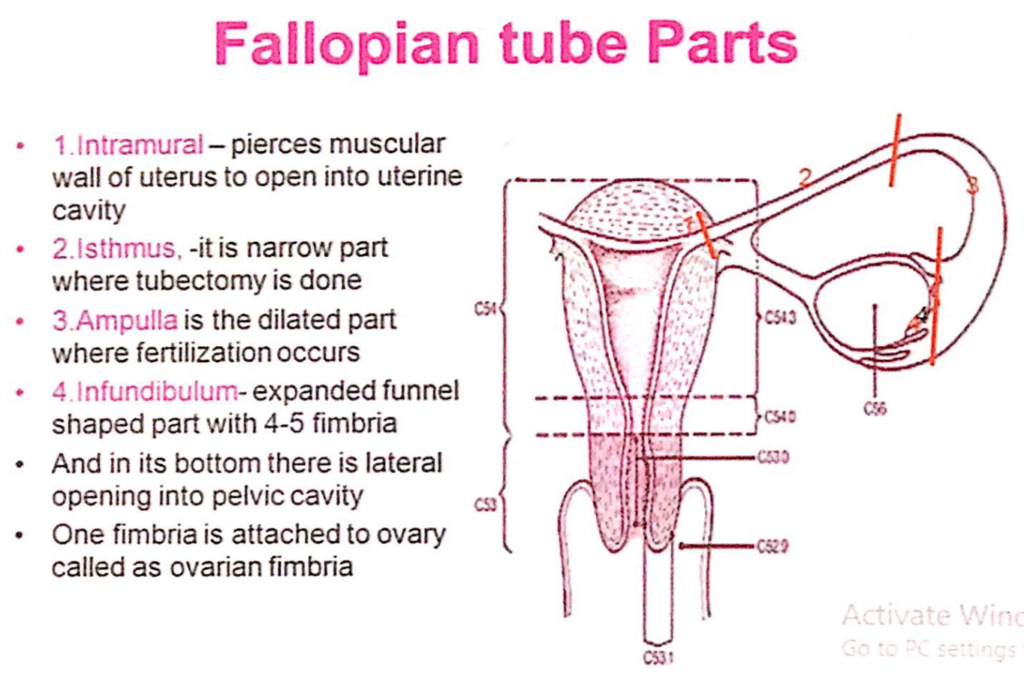
卵管(Fallopian tube)の部分
- 筋内部(Intramural)
- 子宮の筋肉壁を貫通して子宮腔(uterine cavity)に開く部分です。
- 峡部(Isthmus)
- 狭い部分で、卵管結紮術(tubectomy)が行われる場所です。
- 膨大部(Ampulla)
- 拡張した部分で、受精(fertilization)が行われる場所です。
- 漏斗部(Infundibulum)
- 拡大した漏斗状の部分で、4~5本の繊毛(fimbria)があります。
- この部分の底には、骨盤腔(pelvic cavity)への外側開口(lateral opening)があります。
- 繊毛の1本は卵巣(ovary)に付着しており、卵巣繊毛(ovarian fimbria)と呼ばれます。
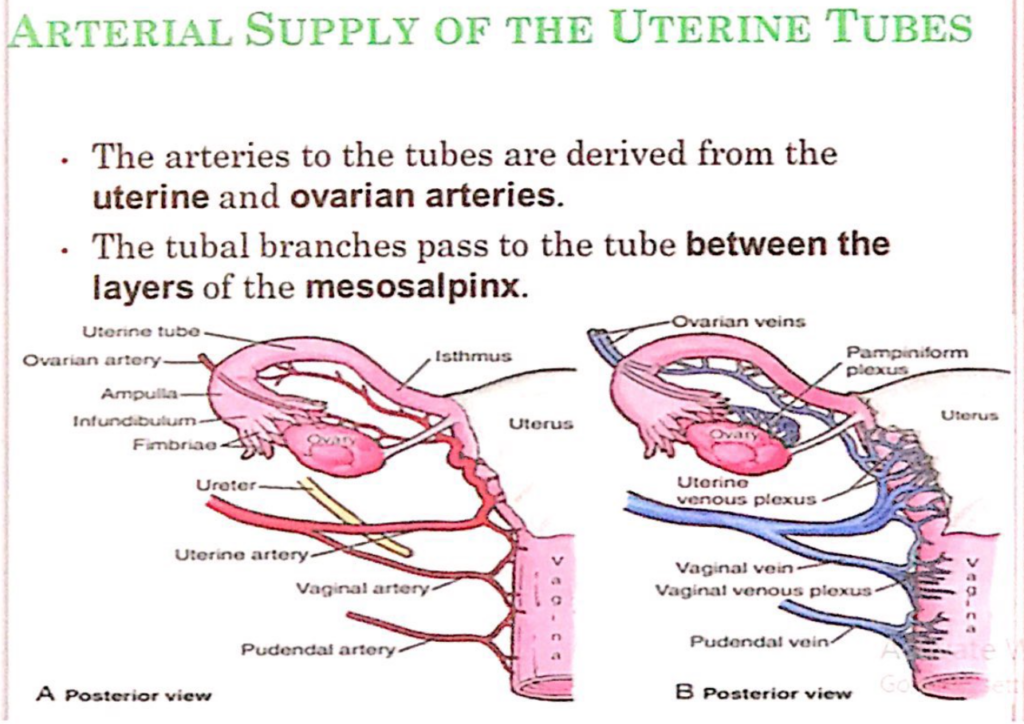
卵管(Uterine Tubes)の動脈供給(Arterial Supply)
- 卵管への動脈は、子宮動脈(uterine artery)および卵巣動脈(ovarian artery)から派生しています。
- 卵管枝(tubal branches)は、中間卵管膜(mesosalpinx)の層の間を通って卵管へ供給されます。


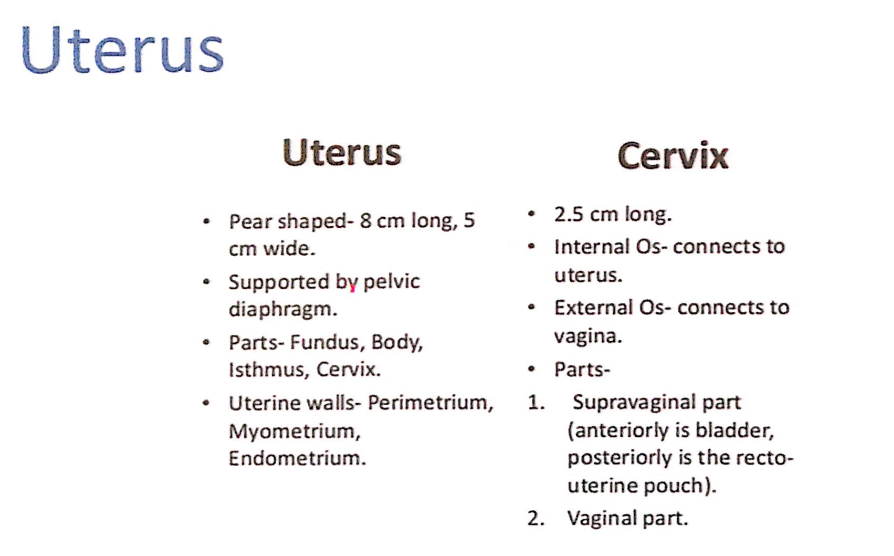
1. 概要(Overview)
- 形状と構造(Shape and Structure):
- 子宮は厚い筋層を持つ(Thick-walled)、洋ナシ形(Pear-shaped)の中空の筋肉性臓器(Hollow Muscular Organ)です。
- 位置(Location):
- 非妊娠時(Non-Gravid):
- 子宮は小骨盤(Lesser Pelvis)内に位置します。
- 体部(Body)は膀胱(Urinary Bladder)の上に乗り、頸部(Cervix)は膀胱と直腸(Rectum)の間にあります。
- 成人女性(Adult Women):
- 通常、前傾(Anteverted): 膣の軸に対して前上方に傾いています。
- 前屈(Anteflexed): 子宮体(Body)が頸部(Cervix)に対して前方に屈曲しています。この位置により子宮全体の質量が膀胱の上にあります。
- 位置の変化(Position Changes):
- 子宮の位置は膀胱や直腸の充満度(Degree of Fullness)によって変化します。
- 非妊娠時(Non-Gravid):
2. 解剖学的特徴(Anatomical Features)
- 大きさ(Size):
- 長さ: 7.5cm
- 幅: 5cm
- 厚さ: 2cm
- 重量(Weight):
- 約90グラム
3. 子宮の2つの主要部分(2 Main Parts of the Uterus)
- 子宮体(Body of the Uterus):
- 子宮の上部で、主に子宮腔(Uterine Cavity)が含まれます。
- 主な特徴(Key Features):
- 底部(Fundus):
- 卵管(Fallopian Tubes)が子宮に接続する部分の上部。
- 子宮腔(Uterine Cavity):
- 受精卵が着床し、胎児が発育するスペース。
- 前屈(Anteflexion):
- 子宮体が前方に屈曲していることで膀胱との関係が強調されます。
- 底部(Fundus):
- 子宮頸部(Cervix of the Uterus):
- 子宮の下部で、膣(Vagina)に続く部分。
- 主な特徴(Key Features):
- 外子宮口(External Os):
- 子宮腔と膣をつなぐ開口部。
- 内子宮口(Internal Os):
- 子宮腔と子宮頸管(Cervical Canal)をつなぐ開口部。
- 外子宮口(External Os):

1. 子宮体(Body of the Uterus)の概要
- 上部2/3(Superior 2/3):
- 子宮体は子宮全体の上部2/3を占めています。
- 底部(Fundus of the Uterus):
- 子宮の最も上部で丸い形状(Round)をしています。
- 子宮底は卵管開口部(Orifices of the Uterine Tubes)の上方に位置します。
2. 解剖学的特徴(Anatomical Features)
- 広靭帯との関係(Relationship with the Broad Ligament):
- 子宮体は広靭帯(Broad Ligament)の層間に位置しています。
- この配置により、子宮体は骨盤内で自由に動く(Freely Movable)ことが可能です。
- 表面(Surfaces of the Body of the Uterus):
- 膀胱面(Vesical Surface):
- 子宮の前面で、膀胱(Urinary Bladder)に接しています。
- 腸管面(Intestinal Surface):
- 子宮の後面で、小腸や直腸(Rectum)に接しています。
- 膀胱面(Vesical Surface):

1. 子宮峡部(Isthmus of the Uterus)
- 特徴(Characteristics):
- 子宮体(Body of the Uterus)と子宮頸部(Cervix of the Uterus)を分ける狭窄部(Constricted Region)。
- 長さは約1cmで、非妊娠時には細い構造です。
- 臨床的重要性(Clinical Significance):
- 妊娠中、子宮峡部は下部子宮(Lower Uterine Segment)に変化し、分娩時に重要な役割を果たします。
- 子宮峡部の損傷や感染は、子宮頸部の機能に影響を及ぼす可能性があります。
2. 子宮頸部(Cervix of the Uterus)
- 概要(Overview):
- 子宮頸部は円柱状(Cylindrical)で、子宮の下部3分の1(Inferior Third)を占めます。
- 非妊娠時の成人女性では、長さは約2.5cmです。
2.1. 頸部の部分(Parts of the Cervix)
- 膣上部(Supravaginal Part):
- 位置(Location):
- 子宮峡部(Isthmus)と膣(Vagina)の間に位置。
- 特徴(Characteristics):
- 膣の上方に位置し、直接膣に露出していません。
- 臨床的重要性(Clinical Relevance):
- 子宮動脈(Uterine Artery)がこの部分を横切り、血液供給を行います。
- 位置(Location):
- 膣部(Vaginal Part):
- 位置(Location):
- 子宮頸部の下部で、膣腔(Vaginal Cavity)に露出しています。
- 特徴(Characteristics):
- 丸みを帯びており(Rounded)、子宮口(External Os of the Uterus)を囲みます。
- この部分はさらに膣円蓋(Vaginal Fornix)と呼ばれる狭い空間に囲まれています。
- 臨床的重要性(Clinical Relevance):
- 子宮口(External Os):
- 非妊娠時には小さく、形状は経産婦と未産婦で異なります。
- 子宮頸がんの検査(Pap Smear)の際に採取される部位です。
- 子宮口(External Os):
- 位置(Location):

1. 子宮頸部の膣上部(Supravaginal Part of the Cervix)
- 前方(Anteriorly):
- 子宮頸部の膣上部は膀胱(Bladder)から**疎性結合組織(Loose Connective Tissue)**によって分離されています。
- 後方(Posteriorly):
- 直腸(Rectum)からは**直腸子宮窩(Rectouterine Pouch, ダグラス窩)**によって分離されています。
- 臨床的重要性(Clinical Significance):
- この部位の結合組織は、炎症や腫瘍が隣接する臓器(膀胱や直腸)に拡がる経路となる可能性があります。
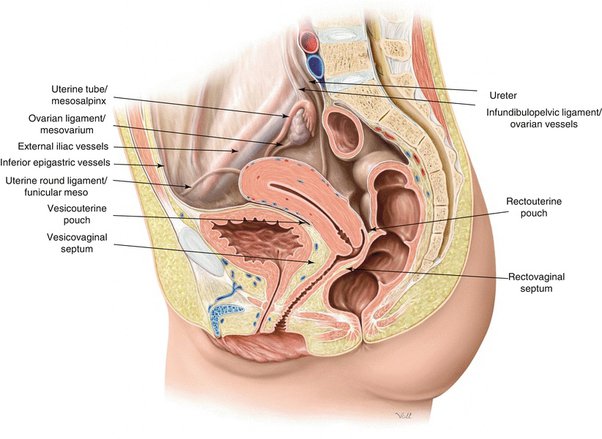
2. 子宮腔(Uterine Cavity)
- 長さ(Length):
- 子宮腔は**外子宮口(External Os)**から子宮底(Fundus)まで約6cmです。
- 特徴(Features):
- 子宮腔は扁平な三角形の形をしており、上部が広く、下部が狭くなっています。
- 子宮腔は受精卵の着床部位であり、妊娠中に胎児が発育する空間です。
- 臨床的重要性(Clinical Significance):
- 子宮腔の形状やサイズの異常は、不妊症や反復流産の原因となることがあります。
3. 子宮角(Uterine Horns)
- 位置(Location):
- 子宮腔の上外側部(Superolateral Regions)に位置します。
- 機能(Function):
- 子宮角は**卵管(Uterine Tubes)**が子宮に入る部分です。
- 臨床的重要性(Clinical Significance):
- 子宮角は異所性妊娠(Ectopic Pregnancy)の発生部位となることがあります。
- 卵管摘出術(Salpingectomy)やその他の外科的処置の際には、この部位の解剖学的関係が重要です。

1. 子宮腔と子宮頸管(Uterine Cavity and Cervical Canal)
- 子宮腔の下方への継続(Continuation of the Uterine Cavity):
- 子宮腔は下方に続き、紡錘形(Fusiform)の**子宮頸管(Cervical Canal)**となります。
- 子宮頸管は子宮体と膣をつなぐ重要な通路です。
2. 子宮頸管の構造(Structure of the Cervical Canal)
- 子宮峡部(Isthmus of the Uterus):
- 子宮体(Body of the Uterus)の狭窄部を通って子宮頸管が始まります。
- ここは**解剖学的内子宮口(Anatomical Internal Os)**として知られる構造的な境界点です。
- 膣上部と膣部の通過(Passage Through the Supravaginal and Vaginal Parts of the Cervix):
- 子宮頸管は膣上部(Supravaginal Part)と膣部(Vaginal Part)を通り、膣腔(Vaginal Lumen)に続きます。
- 外子宮口(External Os):
- 子宮頸管は膣腔と**外子宮口(External Os)**で連結します。
- 外子宮口は出産時や月経血排出時の重要な開口部です。
3. 出生管(Birth Canal)
- 構成(Constituents of the Birth Canal):
- 子宮腔(Uterine Cavity)および子宮頸管(Cervical Canal):
- 子宮腔から子宮頸管までの通路は、胎児が子宮から膣に移動するための上部出生管(Upper Birth Canal)を構成します。
- 膣腔(Lumen of the Vagina):
- 膣腔は出生管の下部を構成し、胎児が外部に出る際の最終通路です。
- 子宮腔(Uterine Cavity)および子宮頸管(Cervical Canal):
- 機能(Function):
- 月経(Menstruation):
- 子宮内膜の剥離による月経血が子宮腔から膣を通じて排出されます。
- 分娩(Childbirth):
- 出生管は胎児の出産時に拡張し、胎児が外界に出るための通路となります。
- 月経(Menstruation):

子宮壁の層構造(Layers of the Uterine Wall)
子宮壁は、外側から内側に向かって以下の3層で構成されています。
1. 外膜(Perimetrium)
- 特徴(Characteristics):
- 外膜は**漿膜(Serosa)または外側漿膜性被膜(Outer Serous Coat)**として知られています。
- 腹膜(Peritoneum)が子宮を覆い、結合組織(Connective Tissue)で構成されています。
- 機能(Function):
- 子宮を外部の構造と隔て、支持する役割を果たします。
- 臨床的重要性(Clinical Significance):
- 腹膜炎(Peritonitis)や癒着(Adhesions)は、この層に影響を与えることがあります。
2. 筋層(Myometrium)
- 特徴(Characteristics):
- 子宮の中間層で、平滑筋(Smooth Muscle)からなる**厚い筋肉層(Middle Muscular Coat)**です。
- 血管(Blood Vessels)と神経(Nerves)が豊富に分布しています。
- 機能(Function):
- 子宮収縮(Uterine Contractions)を司り、以下の場面で重要な役割を果たします。
- 分娩(Childbirth): 胎児を子宮外に押し出すための収縮。
- 月経(Menstruation): 子宮内膜の排出を促進。
- 子宮収縮(Uterine Contractions)を司り、以下の場面で重要な役割を果たします。
- 臨床的重要性(Clinical Significance):
- 子宮筋腫(Uterine Fibroids)などの病変は、この層で発生します。
- 子宮破裂(Uterine Rupture)や過度の収縮(Hypertonic Contractions)は、分娩時の合併症として生じることがあります。
3. 内膜(Endometrium)
- 特徴(Characteristics):
- 子宮の内層で、**粘膜(Inner Mucous Coat)**として知られています。
- 内膜は筋層(Myometrium)にしっかりと付着しています。
- 機能(Function):
- 月経周期(Menstrual Cycle):
- 子宮内膜はホルモンの影響を受け、周期的に厚くなります。
- 受精卵が着床しない場合、内膜が剥離(Shedding)し、月経として排出されます。
- 胚の着床(Blastocyst Implantation):
- 受精卵が内膜に着床することで妊娠が成立します。
- 月経周期(Menstrual Cycle):
- 臨床的重要性(Clinical Significance):
- 子宮内膜症(Endometriosis): 子宮内膜組織が子宮外で増殖する病態。
- 子宮内膜炎(Endometritis): 感染による内膜の炎症。
- 不妊症(Infertility): 内膜の異常は妊娠の成立を妨げる可能性があります。
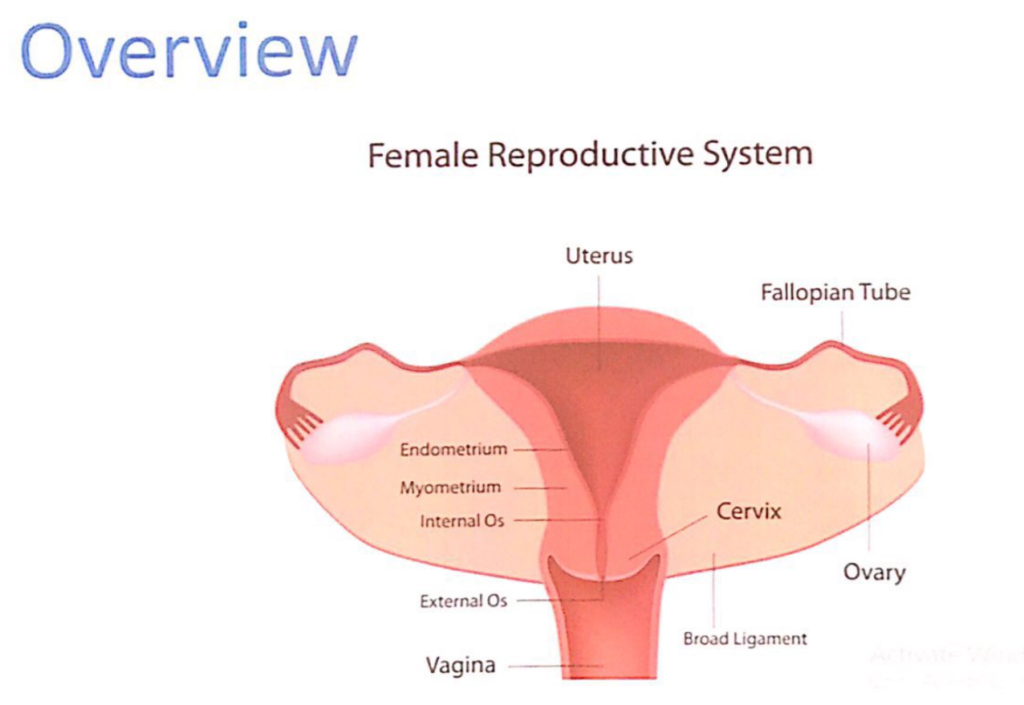
子宮(Uterus)
1. 概要(Overview)
- 形状(Shape):
- 洋ナシ形(Pear-shaped)の中空筋性器官。
- 大きさ(Size):
- 長さ: 約8cm
- 幅: 約5cm
- 支持構造(Support Structure):
- 骨盤隔膜(Pelvic Diaphragm)により支持されています。
2. 子宮の部分(Parts of the Uterus)
- 子宮底(Fundus):
- 子宮の最上部で、卵管が接続する部分の上方に位置します。
- 子宮体(Body):
- 子宮全体の上部2/3を占め、胎児が発育する主な空間を提供します。
- 子宮峡部(Isthmus):
- 子宮体と子宮頸部の間にある狭窄部です。分娩時に柔軟に拡張します。
- 子宮頸部(Cervix):
- 子宮の下部1/3を占め、膣と子宮をつなぐ部分です。
3. 子宮壁(Uterine Walls)
- 外膜(Perimetrium):
- 子宮の外側を覆う漿膜性構造。
- 筋層(Myometrium):
- 平滑筋で構成される厚い層で、月経と分娩時に収縮します。
- 内膜(Endometrium):
- 子宮の内側を覆う粘膜層で、月経周期に応じて増殖・剥離を繰り返します。
子宮頸部(Cervix)
1. 概要(Overview)
- 大きさ(Size):
- 長さは約2.5cm。
- 役割(Function):
- 内子宮口(Internal Os)を介して子宮腔と連結し、外子宮口(External Os)を介して膣腔に開きます。
- 精子の移動や月経血の排出の通路として機能します。
2. 子宮頸部の部分(Parts of the Cervix)
- 膣上部(Supravaginal Part):
- 前方(Anteriorly):
- 膀胱(Bladder)と接しています。
- 後方(Posteriorly):
- **直腸子宮窩(Recto-Uterine Pouch, ダグラス窩)**と接しています。
- 前方(Anteriorly):
- 膣部(Vaginal Part):
- 膣腔に露出しており、外子宮口(External Os)を取り囲んでいます。
- 膣円蓋(Vaginal Fornix)に囲まれています。
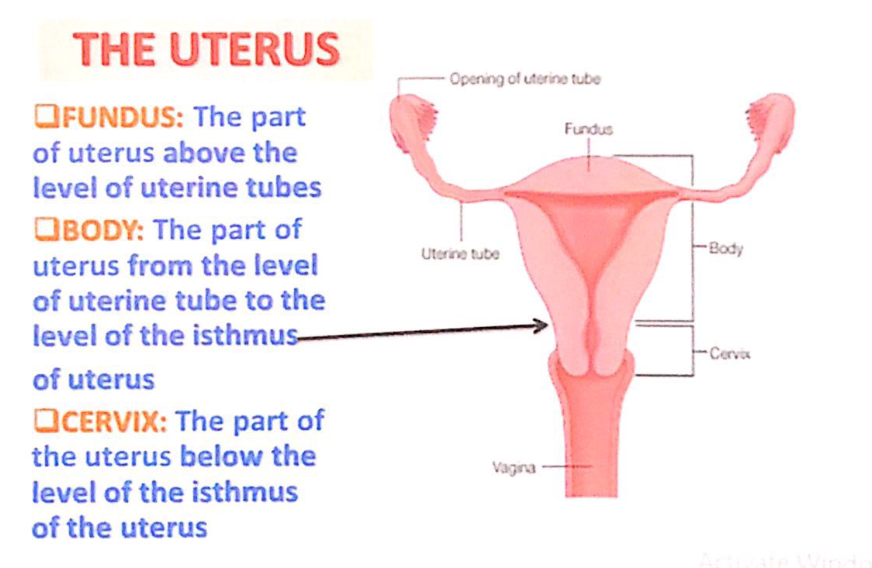
子宮(Uterus)の構造
- 子宮底(Fundus)
- 子宮の部分で、卵管(uterine tubes)の高さより上に位置します。
- 子宮体(Body)
- 卵管の高さから子宮峡部(isthmus of uterus)の高さまでの部分です。
- 子宮頸部(Cervix)
- 子宮峡部の高さより下に位置する部分です。
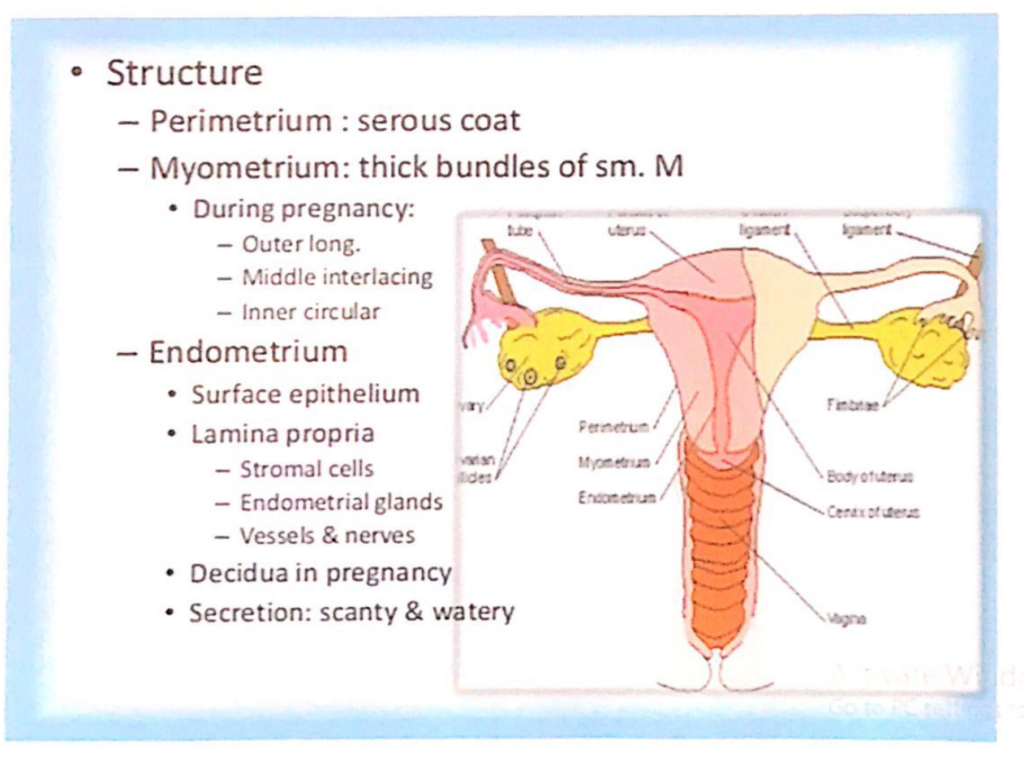
子宮(Uterus)の構造
- 漿膜(Perimetrium)
- 子宮を覆う漿膜層(serous coat)です。
- 筋層(Myometrium)
- 厚い平滑筋(sm. M)の束で構成されています。
- 妊娠中は以下の3層に分化します:
- 外層:縦走筋(Outer longitudinal layer)
- 中層:交錯筋(Middle interlacing layer)
- 内層:輪状筋(Inner circular layer)
- 内膜(Endometrium)
- 構造:
- 表面上皮(Surface epithelium)
- 固有層(Lamina propria):以下を含む
- 基質細胞(Stromal cells)
- 子宮内膜腺(Endometrial glands)
- 血管および神経(Vessels & nerves)
- 妊娠中の変化:
- 脱落膜(Decidua)を形成します。
- 分泌:少量で水様性(scanty & watery)です。
- 構造:



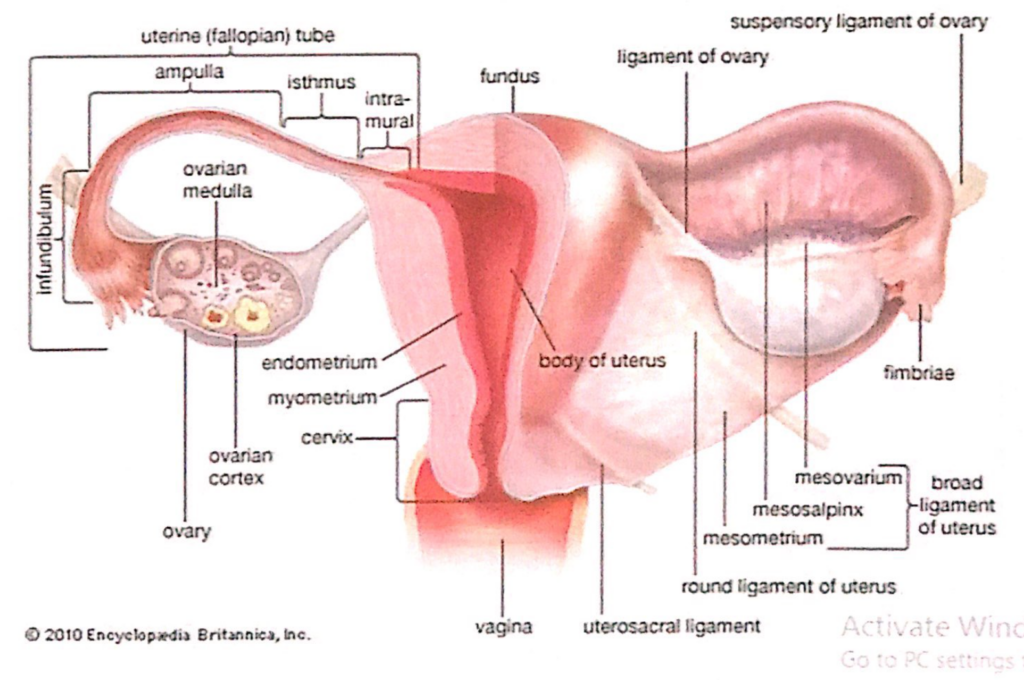
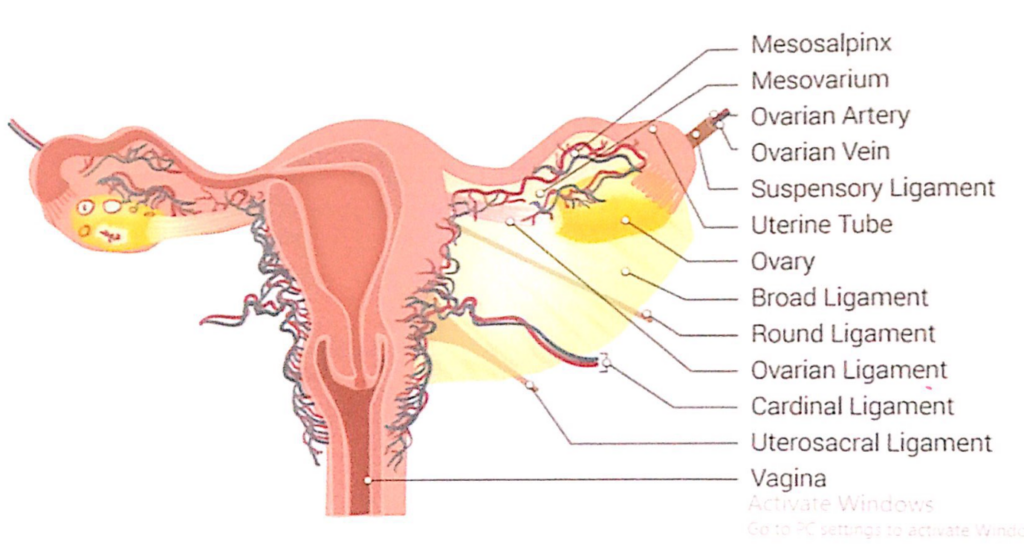
子宮(Uterus)の靭帯(Ligaments)
- 卵巣固有靭帯(Ligament of the Ovary)
- 卵管子宮接合部(uterotubal junction)の後下方に付着します。
- 子宮円索(Round Ligament of the Uterus)
- 卵管子宮接合部の前下方に付着します。
- 広靭帯(Broad Ligament of the Uterus)
- 二層構造の靭帯で、子宮の両側面、骨盤側壁、骨盤底を結びます。
- 子宮を正しい位置に保つ働きを助けます。
- 二層は卵管を囲む自由縁で連続しています。
- 上部では血管を覆い、卵巣提索(Suspensory Ligament of the Ovary)に延長します。
広靭帯の構造と位置関係
- 卵管(Uterine Tubes)
- 前上方の自由縁に位置し、小さい腸間膜(Mesosalpinx)の中にあります。
- 卵巣(Ovary)
- 後方の小さい腸間膜(Mesovarium)の中にあり、広靭帯の後面に付着しています。
- 子宮間膜(Mesometrium)
- 広靭帯の中で最も大きい部分です。
- 卵管間膜(Mesosalpinx)および卵巣間膜(Mesovarium)の下方に位置します。
- 子宮を支える腸間膜(mesentery)として機能します。
子宮の支持構造(Support of the Uterus)
- 動的支持(Dynamic Support)
- 骨盤隔膜(Pelvic diaphragm)や腹腔内圧(intra-abdominal pressure)、周囲の骨盤臓器、および骨盤内筋膜(endopelvic fascia)が子宮を支えます。
- 受動的支持(Passive Support)
- 子宮は膀胱の上で正常に前傾(anteverted)および前屈(anteflexed)した位置に保持されます。
*round ligament

*ガンの原因:HPV,
子宮頸部(Cervix)
- **子宮の中で最も可動性が低い部分(Least mobile part)**です。
- **受動的支持(Passive support)**は、骨盤内筋膜(endo-pelvic fascia)の凝縮部分(靭帯)や平滑筋(smooth muscle)によって提供されます。
靭帯(Ligaments)
- 頸横靭帯(Transverse Cervical Ligaments / Cardinal Ligaments)
- 子宮頸部(Cervix)および膣円蓋(fornix of the vagina)の外側部分から骨盤側壁(lateral walls of the pelvis)まで延びています。
- 子宮仙骨靭帯(Uterosacral Ligaments)
- 子宮頸部の側面から仙骨(sacrum)の中央まで、やや後方および上方に延びています。
- 直腸診(Digital Rectal Examination, DRE)で触知可能です。
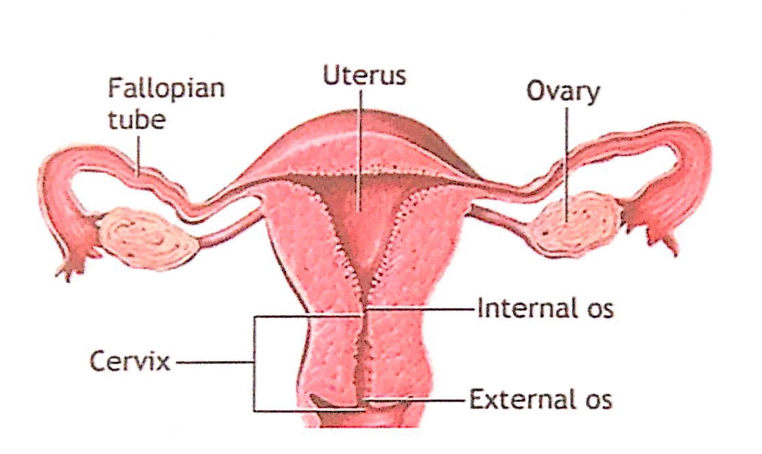

正常

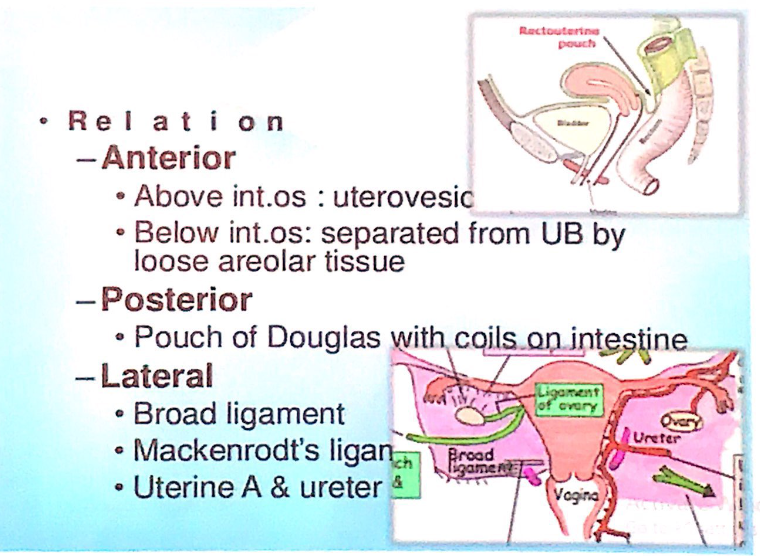
子宮(Uterus)の隣接関係(Relations)
- 腹膜(Peritoneum)
- 子宮頸部(Cervix)を除いて、子宮の前面(anterior)および上面(superior)を覆っています。
- 前方(Anterior / Anteroinferior)
- **膀胱子宮窩(Vesicouterine pouch)**および膀胱の上面(superior surface of bladder)と接しています。
- 子宮頸部の上方部分(supravaginal cervix)が関係します。
- 後方(Posterior)
- 小腸(Small intestine)および直腸の前面(anterior surface of rectum)、臓側骨盤筋膜(visceral pelvic fascia)と接しています。
- 側方(Lateral)
- 広靭帯(Broad ligament)
- 頸横靭帯(Transverse cervical ligaments / Mackenrodt’s ligament)
- 広靭帯(Broad ligament)
詳細な関係(Specific Relations)
- 前方(Anterior)
- 内子宮口(Internal os)より上:膀胱子宮窩(Uterovesical pouch)
- 内子宮口より下:疎性結合組織(Loose areolar tissue)を介して膀胱と分離
- 後方(Posterior)
- ダグラス窩(Pouch of Douglas)が小腸のループと接しています。
- 側方(Lateral)
- 卵巣固有靭帯(Ligament of the Ovary)
- 広靭帯(Broad ligament)
- 頸横靭帯(Mackenrodt’s ligament)
- 尿管(Ureter)
広靭帯の関係
- 子宮動脈(Uterine artery)および尿管(Ureter)を包含しています。
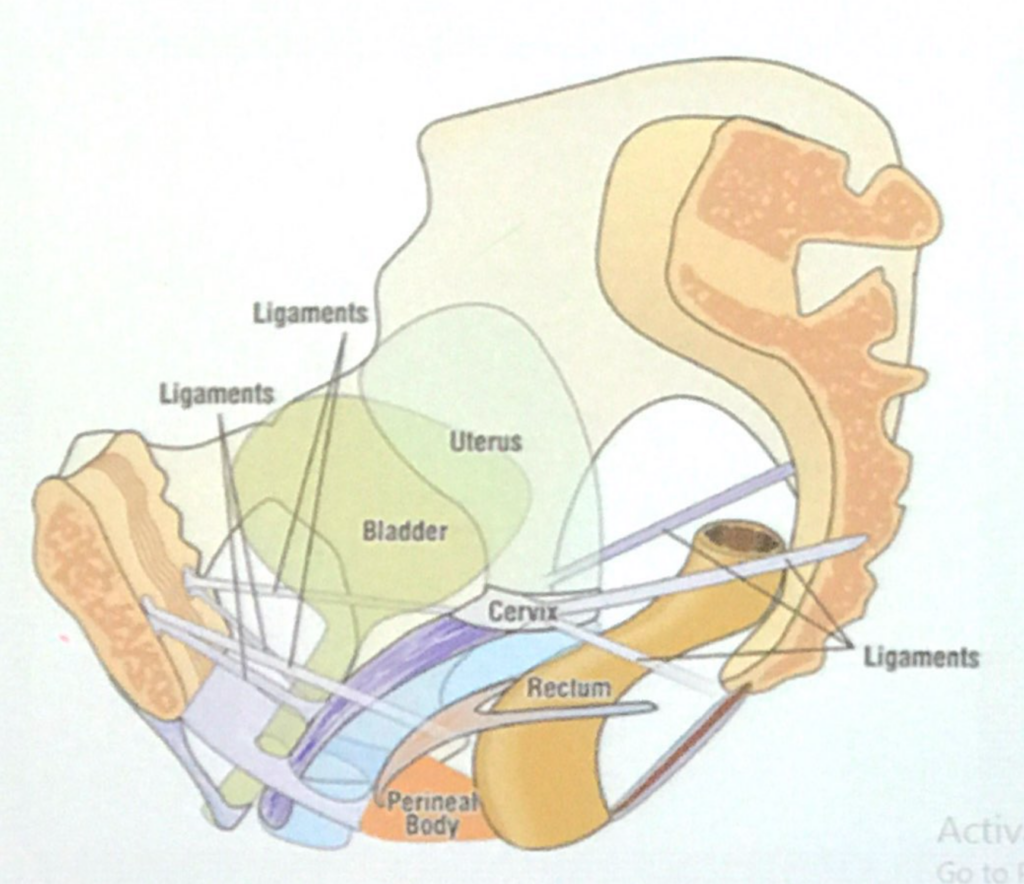

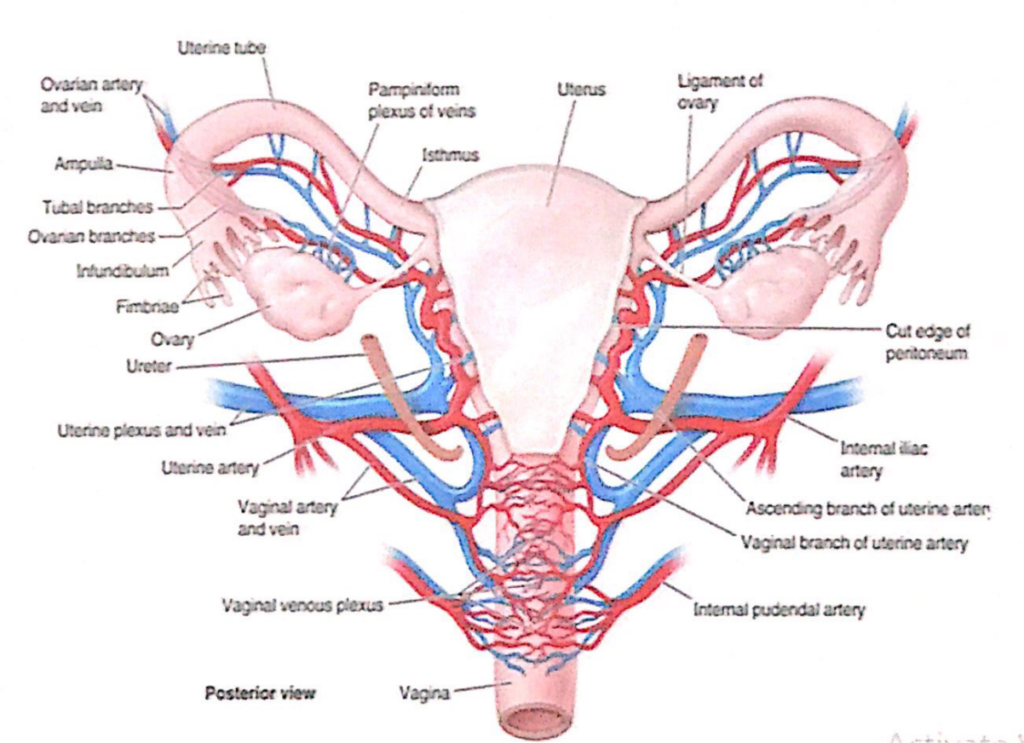
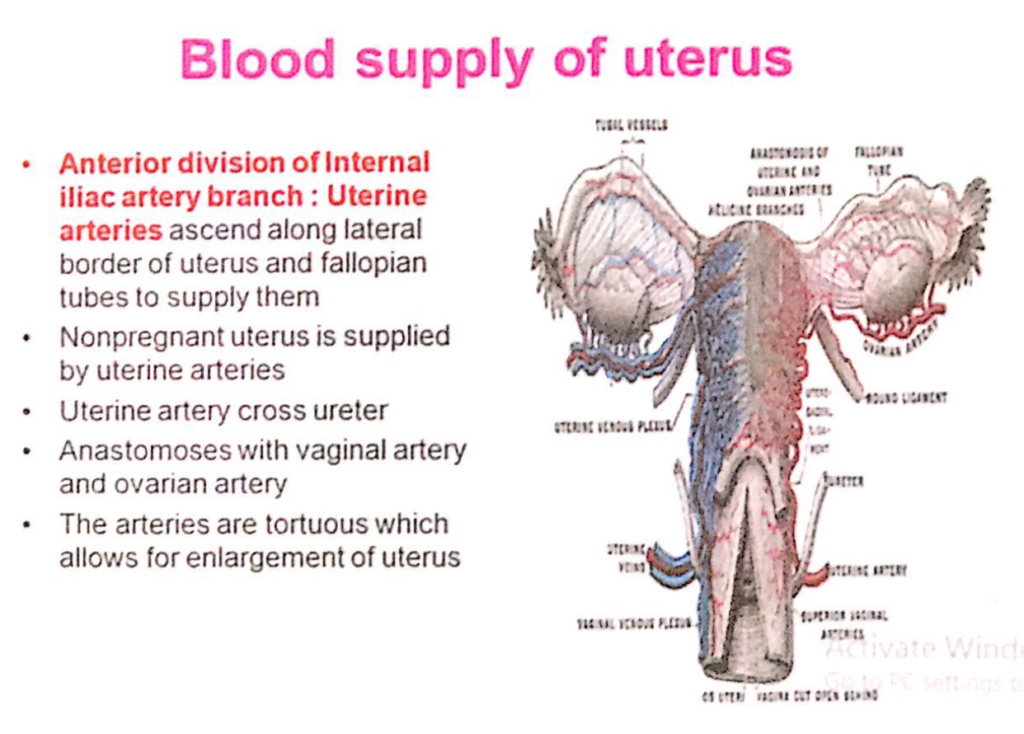
子宮(Uterus)の動脈供給、静脈・リンパ排出(Arterial Supply, Venous and Lymphatic Drainage)
動脈供給(Arterial Supply)
- 子宮動脈(Uterine Arteries)
- 卵巣動脈(Ovarian Arteries)から側副枝(Collaterals)を受けます。
- **内腸骨動脈(Internal Iliac Artery)の前枝(Anterior Division)**から分岐します。
- 子宮の外側縁および卵管(Fallopian Tubes)に沿って上行し、それらを供給します。
- **妊娠していない子宮(Nonpregnant Uterus)**は主に子宮動脈によって供給されます。
- 子宮動脈は尿管(Ureter)を交差します。
- 膣動脈(Vaginal Artery)および卵巣動脈(Ovarian Artery)と吻合(Anastomoses)します。
- 動脈は非常に屈曲しており(Tortuous)、子宮の拡大を可能にします。
静脈排出およびリンパ排出(Venous and Lymphatic Drainage)
- 子宮静脈(Uterine Veins)
- 動脈と共に広靭帯(Broad Ligaments)の中に入り、子宮静脈叢(Uterine Venous Plexus)を形成します。
- 静脈叢は子宮頸部(Cervix)の両側に位置し、内腸骨静脈(Internal Iliac Veins)に排出されます。
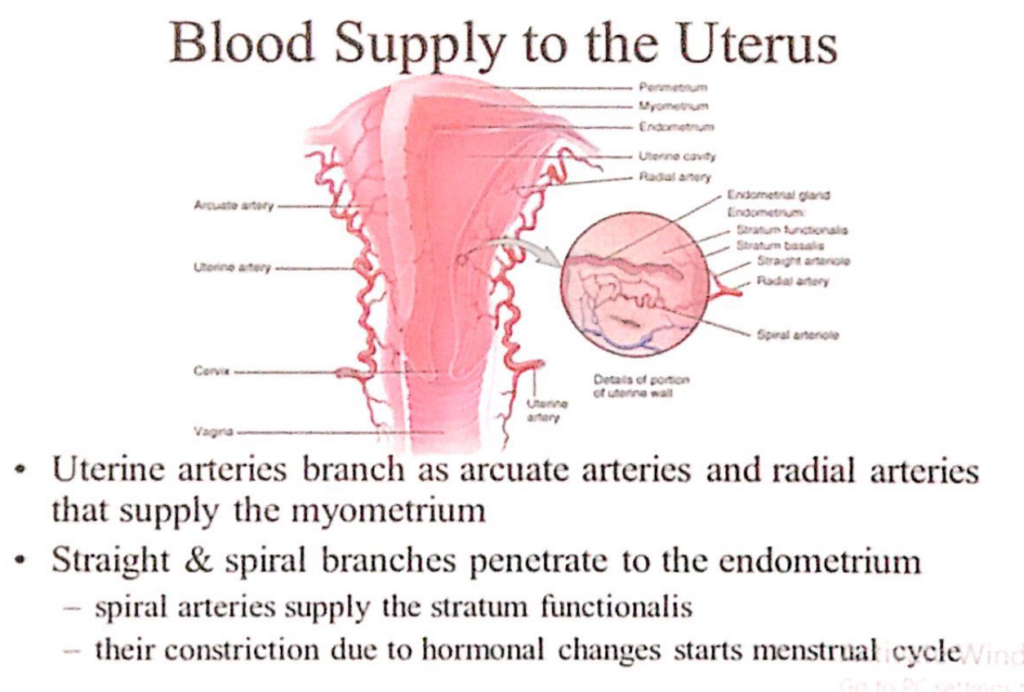
子宮(Uterus)の動脈構造と供給(Arterial Structure and Supply)
- 子宮動脈(Uterine Arteries)の分枝
- 子宮動脈は以下の枝を出して子宮筋層(Myometrium)を供給します:
- 弓状動脈(Arcuate Arteries)
- 放射状動脈(Radial Arteries)
- 子宮動脈は以下の枝を出して子宮筋層(Myometrium)を供給します:
- 子宮内膜(Endometrium)への供給
- **直動脈(Straight Arteries)およびらせん動脈(Spiral Arteries)**が内膜に浸透します。
- **らせん動脈(Spiral Arteries)**は内膜の機能層(Stratum Functionalis)を供給します。
- 月経周期の開始(Menstrual Cycle)
- らせん動脈の収縮(Constriction)はホルモン変化によって引き起こされ、月経周期が始まります。
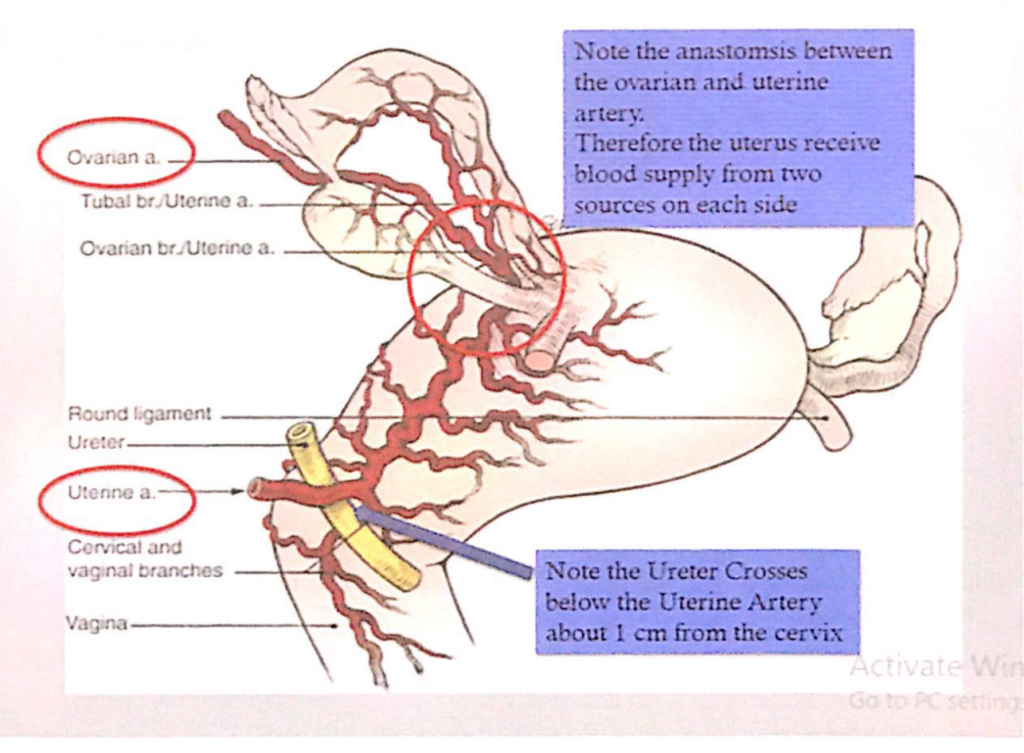
子宮(Uterus)の血管吻合と尿管との関係(Anastomosis and Relation with Ureter)
- 血管吻合(Anastomosis)
- **卵巣動脈(Ovarian Artery)と子宮動脈(Uterine Artery)**の間に重要な吻合があります。
- このため、子宮は両側で2つの血流源(卵巣動脈と子宮動脈)から血液供給を受けます。
- 尿管との関係(Relation with Ureter)
- **子宮動脈(Uterine Artery)**は尿管(Ureter)の上を交差します。
- この交差点は子宮頸部(Cervix)から約1cm離れた位置にあります


子宮(Uterus)のリンパ管系(Lymphatics)
- 子宮底(Fundus)および子宮体上部(Superior Uterine Body)
- 多くのリンパ管は卵巣動脈(Ovarian Vessels)に沿って腰部リンパ節(Lumbar Lymph Nodes)へ流れます。
- 一部のリンパ管は、子宮底から卵管(Uterine Tubes)近くを経由し、子宮円索(Round Ligament)に沿って浅鼠径リンパ節(Superficial Inguinal Lymph Nodes)に流れます。
- 子宮体の大部分(Most of the Uterine Body)および一部の子宮頸部(Cervix)
- 広靭帯(Broad Ligament)の中を通り、外腸骨リンパ節(External Iliac Lymph Nodes)に流れます。
- 子宮頸部(Uterine Cervix)
- リンパ管は子宮動脈(Uterine Vessels)に沿って走行します。
- 頸横靭帯(Transverse Cervical Ligaments)を経由し、内腸骨リンパ節(Internal Iliac Lymph Nodes)に流れます。
- 子宮膀胱靭帯(Uterovesical Ligaments / Sacrogenital Ligaments)を経由し、仙骨リンパ節(Sacral Lymph Nodes)にも流れます。
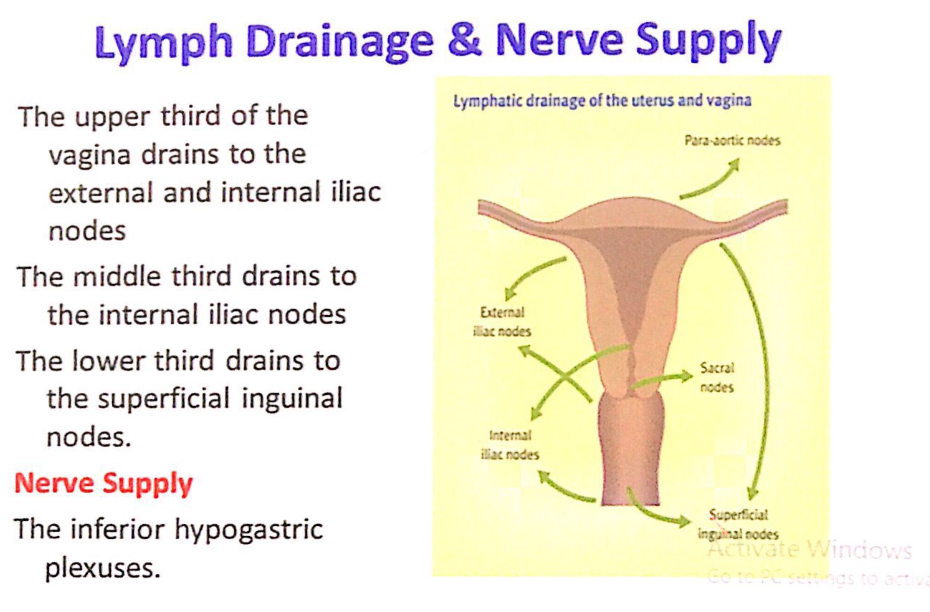
膣(Vagina)のリンパ排出および神経供給(Lymph Drainage & Nerve Supply)
リンパ排出(Lymph Drainage)
- 上3分の1(Upper Third)
- 外腸骨リンパ節(External Iliac Nodes)および内腸骨リンパ節(Internal Iliac Nodes)に排出されます。
- 中間3分の1(Middle Third)
- 内腸骨リンパ節(Internal Iliac Nodes)に排出されます。
- 下3分の1(Lower Third)
- 浅鼠径リンパ節(Superficial Inguinal Nodes)に排出されます。
神経供給(Nerve Supply)
- **下腹神経叢(Inferior Hypogastric Plexuses)**が膣の主要な神経供給源です。
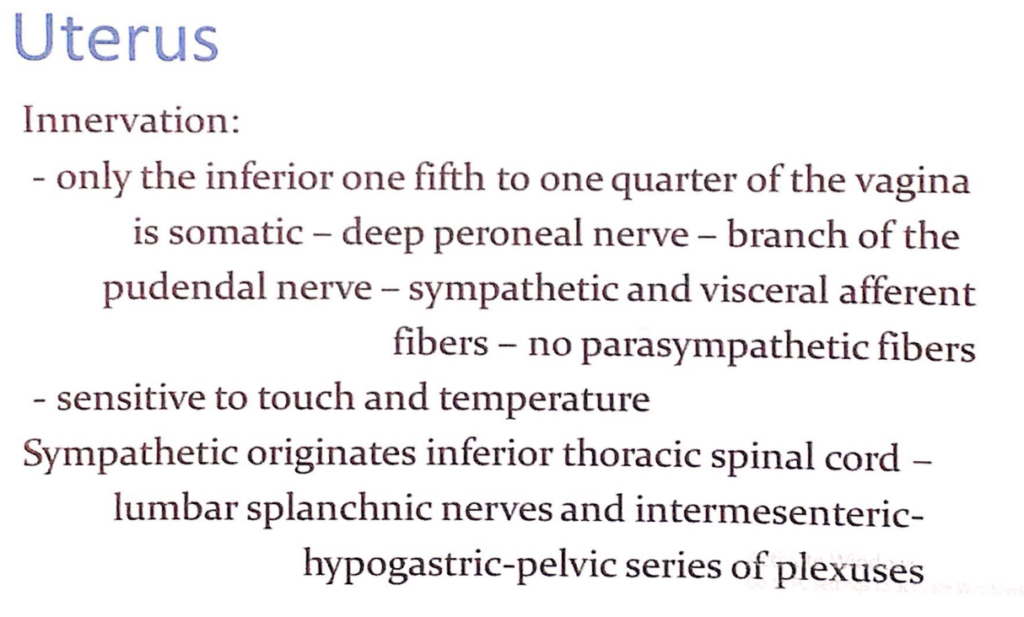

子宮(Uterus)の神経支配(Innervation)
膣の神経支配
- 膣の下部5分の1~4分の1のみが体性神経(Somatic Nerves)によって支配されています。
- 深腓骨神経(Deep Peroneal Nerve) – 陰部神経(Pudendal Nerve)の枝です。
- 交感神経(Sympathetic Fibers)および内臓求心性線維(Visceral Afferent Fibers)が含まれていますが、副交感神経(Parasympathetic Fibers)は含まれません。
- 触覚(Touch)および温度(Temperature)に敏感です。
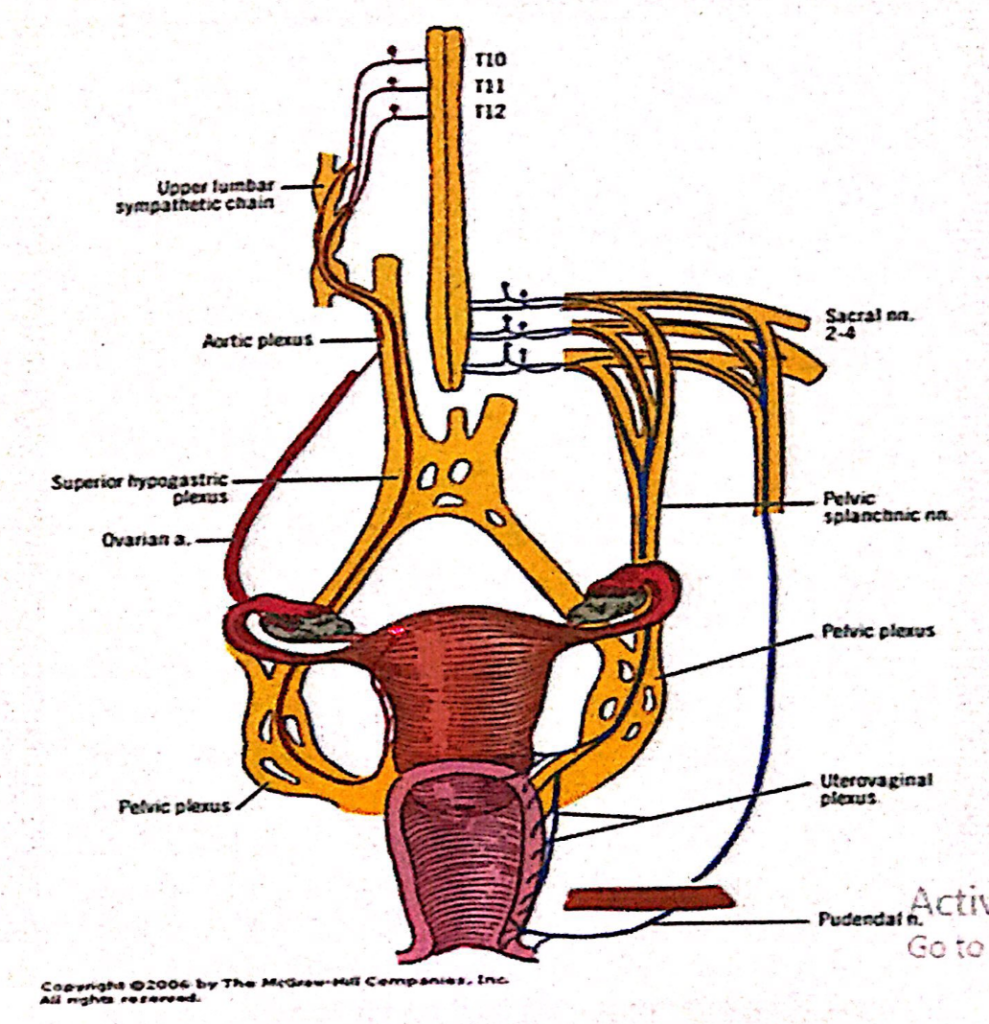
交感神経(Sympathetic Innervation)
- 起源:下部胸髄(Inferior Thoracic Spinal Cord)
- 神経経路:腰内臓神経(Lumbar Splanchnic Nerves)および腸間膜下神経叢(Intermesenteric Plexus)、下腹神経叢(Hypogastric Plexus)、骨盤神経叢(Pelvic Series of Plexuses)を通ります。
副交感神経(Parasympathetic Innervation)
- 起源:S2~S4脊髄(S2-S4 Spinal Cord Segments)
- 神経経路:骨盤内臓神経(Pelvic Splanchnic Nerves)を通り、下腹神経叢(Inferior Hypogastric Plexus)および子宮膣神経叢(Uterovaginal Plexus)に至ります。
内臓求心性神経(Visceral Afferent Fibers)
- **骨盤痛線(Pelvic Pain Line)**を境に異なる神経経路をたどります:
- 骨盤痛線より上(Superior to Pelvic Pain Line):交感神経(Sympathetic Fibers)に沿って移動します。
- 骨盤痛線より下(Inferior to Pelvic Pain Line):副交感神経(Parasympathetic Fibers)に沿って移動します。

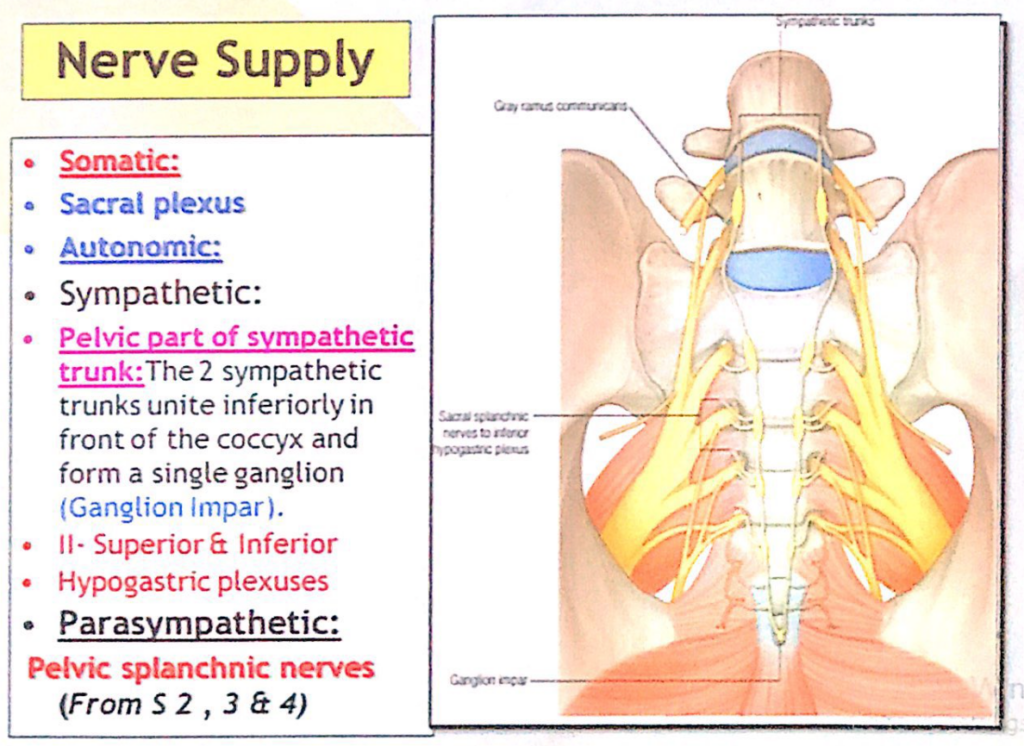
子宮および子宮頸部(Uterus / Cervix)の神経支配(Innervation)
主要な神経叢(Primary Plexus)
- 子宮膣神経叢(Uterovaginal Plexus)
- **下腹神経叢(Inferior Hypogastric Plexus / Pelvic Plexus)**の一部です。
- 子宮に向けて以下の神経を含みます:
- 交感神経(Sympathetic Fibers)
- 副交感神経(Parasympathetic Fibers)
- 内臓求心性神経(Visceral Afferent Fibers)
神経の詳細(Detailed Nerve Supply)
- 交感神経(Sympathetic Innervation)
- 起源:下部腰髄(Lower Lumbar Spinal Cord Segments)
- 経路:腰内臓神経(Lumbar Splanchnic Nerves)および中間神経叢(Intermediate Plexuses)を通ります。
- 副交感神経(Parasympathetic Innervation)
- 起源:S2~S4脊髄(Pelvic Splanchnic Nerves / S2, S3, S4)
- 経路:骨盤神経叢(Pelvic Plexus)を通ります。
- 内臓求心性神経(Visceral Afferent Fibers)
- **子宮体および子宮底(Body & Fundus of Uterus)**からの痛み:
- 神経経路:神経叢を通り腰内臓神経(Lumbar Splanchnic Nerves)に入り、T10~L1脊髄(Spinal Cord Segments)に至ります。
- 子宮頸部(Cervix)からの痛みおよびその他の感覚情報(子宮体および子宮底からの痛みを除く):
- 神経経路:副交感神経(Parasympathetic Fibers)に沿って移動します。
- **子宮体および子宮底(Body & Fundus of Uterus)**からの痛み:
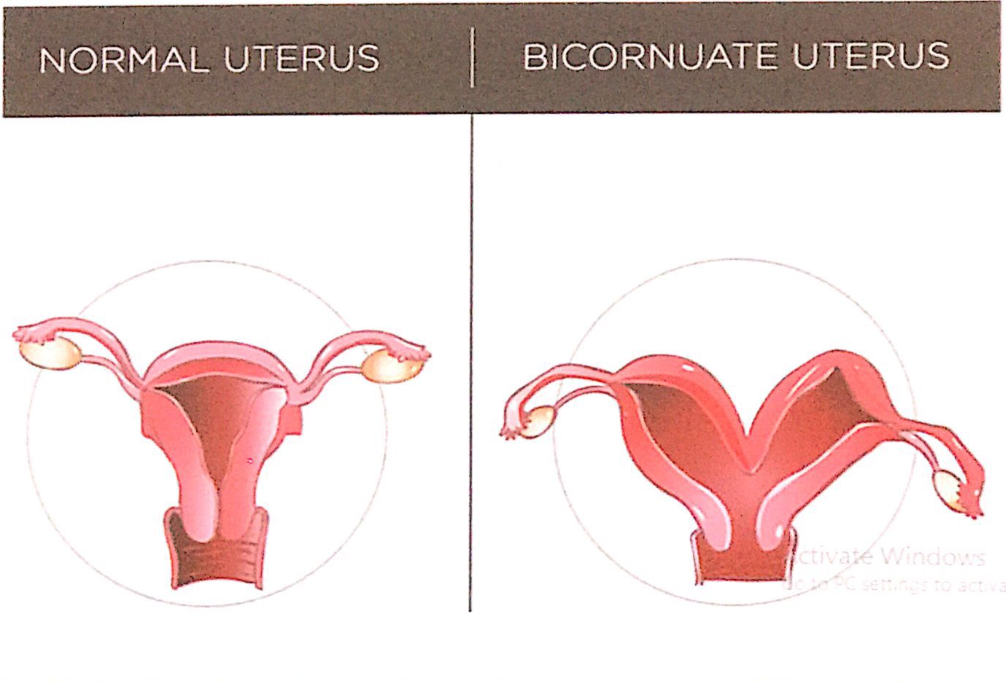
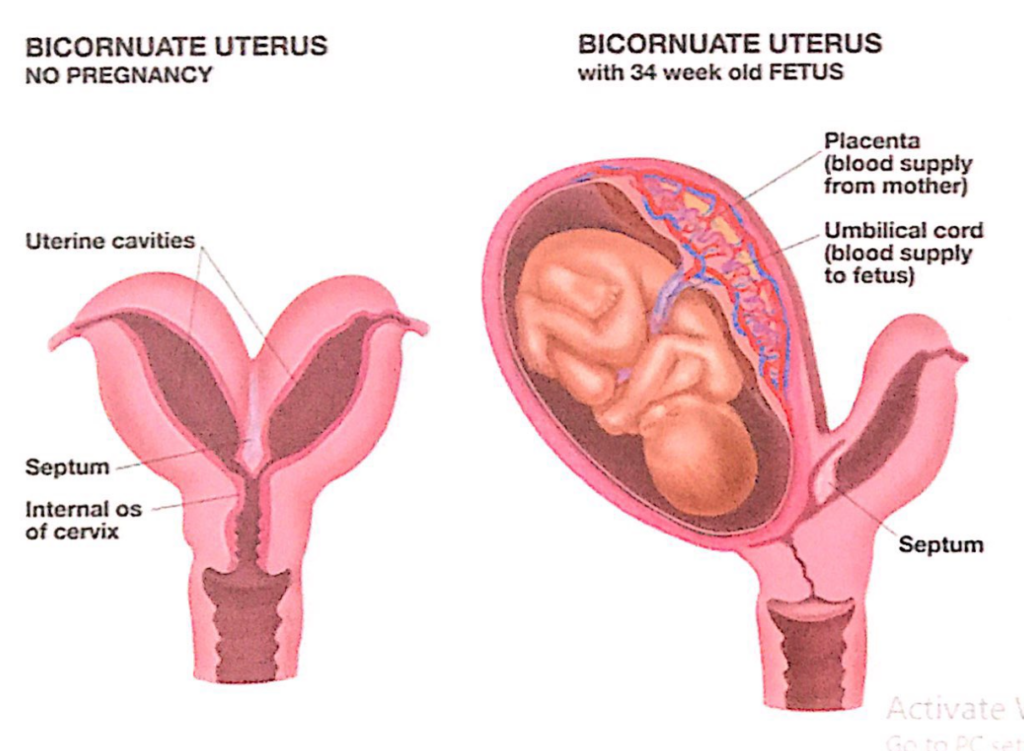
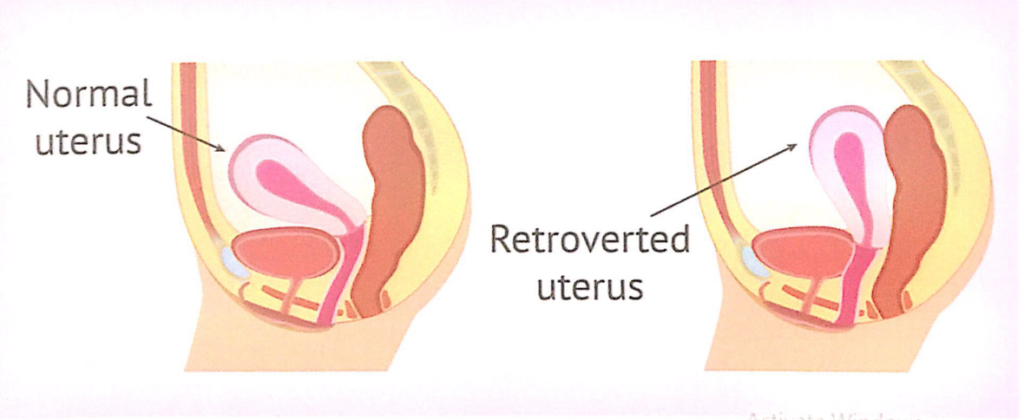

会陰(Perineum)
男性(Male)
- 外陰部(External Genitalia)
- 尿道(Urethra)
- 陰嚢(Scrotum)
- 陰茎(Penis)
- 会陰筋(Perineal Muscle)
- 肛門管(Anal Canal)
女性(Female)
- 外陰部(External Genitalia)
- 会陰筋(Perineal Muscle)
- 肛門管(Anal Canal)

女性外陰部(Female External Genitalia)の構成
- 恥丘(Mons Pubis)と大陰唇(Labia Majora, Pudendal Cleft):
- 恥骨結合(Symphysis Pubis)を覆う脂肪組織(脂肪パッド)と大陰唇が形成する裂け目(Pudendal Cleft)。
- 小陰唇(Labia Minora):
- 陰裂(Vestibule)を覆うように配置され、薄い皮膚と粘膜で構成されています。
- 陰核(Clitoris):
- 性的感覚を担う勃起組織(Erectile Tissue)で、神経が豊富に分布しています。
- 膣前庭球(Bulbs of the Vestibule):
- 陰核の左右に配置された勃起組織で、性的刺激時に膨張します。
- 大前庭腺および小前庭腺(Greater and Lesser Vestibular Glands):
- 大前庭腺(バルトリン腺, Greater Vestibular Glands):
- 性的興奮時に分泌物を生成し、潤滑を助けます。
- 小前庭腺(Lesser Vestibular Glands):
- 前庭周囲を潤す分泌物を出します。
- 大前庭腺(バルトリン腺, Greater Vestibular Glands):
外陰部と陰部(Vulva and Pudendum)
- 外陰部(Vulva, Pudendum):
- 女性外陰部の全ての構成要素を指します。
- 外陰部は排尿、性行為、出産に関与し、防御機能も担います。

外陰部(Vulva)の主な機能
- 感覚および勃起組織(Sensory and Erectile Tissue):
- 性的快感を得るための感覚器官として機能します。
- **陰核(Clitoris)と膣前庭球(Bulbs of the Vestibule)**が主要な感覚および勃起組織です。
- 尿の流れの制御(Direct Flow of Urine):
- 外陰部は排尿の流れを適切に導く役割を果たします。
- 外部からの侵入物の防御(Prevention of Entry of Foreign Material into the Urogenital Tract):
- 大陰唇と小陰唇が尿生殖管(Urogenital Tract)を保護し、異物や病原体の侵入を防ぎます。

恥丘(Mons Pubis)
- 形状と位置(Shape and Location):
- 恥骨結合(Pubic Symphysis)、恥骨結節(Pubic Tubercles)、および**恥骨上枝(Superior Pubic Rami)**に覆いかぶさる丸い脂肪性の隆起(Rounded, Fatty Eminence)です。
- 構造(Structure):
- **皮下脂肪組織(Fatty Subcutaneous Tissue)**の塊(Mass)で構成されています。
- 発達(Development):
- **思春期(Puberty)**に脂肪が増加し、隆起が目立つようになります。
- **閉経後(Post-Menopause)**には脂肪量が減少し、目立たなくなる傾向があります。
- 連続性(Continuity):
- **前腹壁(Anterior Abdominal Wall)**と連続しています。

恥丘(Mons Pubis)
1. 構造(Structure)
- 脂肪組織(Adipose Tissue)のパッド:
- 恥骨結合(Symphysis Pubis)(恥骨の関節部)上に位置する脂肪組織の塊です。
- 皮脂腺(Sebaceous Glands):
- 恥丘には多くの皮脂腺が豊富に分布しています。
2. 機能(Function)
- 外傷からの保護(Protection from Trauma):
- 脂肪組織のパッドが、恥骨の結合部を外部の衝撃から保護します。
3. 発達と毛の成長(Development and Hair Growth)
- 小児期(Childhood):
- 恥丘は毛がなく、表面は滑らか(Hairless and Smooth)です。
- 思春期(Puberty):
- 恥丘は三角形(Triangular)の粗い縮れ毛(Curly Hairs)で覆われます。この毛のパターンは、**エスカッション(Escutcheon)**と呼ばれます。
4. 性別による毛の形状の違い(Differences in Hair Growth Patterns by Sex)
- 女性(Female):
- 毛の成長パターンは三角形(Triangular)。
- 男性(Male):
- 毛の成長パターンはダイヤモンド型(Diamond-shaped)。
5. ホルモンによる影響(Hormonal Influence)
- 毛の成長(Hair Growth):
- **テストステロン(Testosterone)**が陰毛の成長を促進します。
- 毛の成長パターン(Hair Growth Pattern):
- **エストロゲン(Estrogen)**が毛の成長パターンを決定します。

大陰唇(Labia Majora)
1. 構造(Structure)
- 目立つ皮膚のひだ(Prominent Fold of Skin):
- 大陰唇は皮膚と組織で構成され、尿道口(Urethral Orifice)および膣口(Vaginal Orifice)を間接的に保護します。
- 内部構造(Internal Composition):
- 疎性皮下組織(Loose Subcutaneous Tissue):
- 指状突起(Finger-like “Digital Process”)のような構造が内部を満たしています。
- 平滑筋(Smooth Muscle):
- 皮下組織内に分布し、大陰唇の形状を支えます。
- 子宮円索(Round Ligament of the Uterus)の終端部(Termination):
- 子宮円索が大陰唇内で終わるため、子宮との構造的な連携があります。
- 疎性皮下組織(Loose Subcutaneous Tissue):
2. 位置と関連構造(Position and Related Structures)
- 陰裂(Pudendal Cleft):
- 大陰唇は中央の窪みである陰裂の両側に位置します。
- 陰裂の中には、小陰唇(Labia Minora)および膣前庭(Vestibule)が含まれます。
3. 機能(Function)
- 保護機能(Protection):
- 外部からの物理的刺激や異物の侵入から尿道口と膣口を保護します。
- 支持機能(Support):
- 平滑筋と皮下組織が大陰唇の形状を維持し、安定性を提供します。

大陰唇(Labia Majora)
1. 外観と皮膚の特徴(External Appearance and Skin Features)
- 外側(External Surface):
- 色素沈着した皮膚(Pigmented Skin)で覆われ、**皮脂腺(Sebaceous Glands)**を含みます。
- 思春期以降、**陰毛(Pubic Hair)**で覆われます。
- 内側(Internal Surface):
- 内側の表面は滑らか(Smooth)、ピンク色(Pink)で、毛がありません(Hairless)。
2. 厚さと結合(Thickness and Commissures)
- 前方(Anteriorly):
- 前方ではより厚くなり(Thicker Anteriorly)、**前交連(Anterior Commissure)**を形成します。
- 後方(Posteriorly):
- 未経産女性(Nulliparous Women)の場合、後方で合流し、**後交連(Posterior Commissure)**を形成します。
- 後交連は、**会陰体(Perineal Body)**の上に位置し、外陰部(Vulva)の後端(Posterior Limit)を構成します。
- 経腟分娩(Vaginal Birth)後には、後交連は消失することがあります。
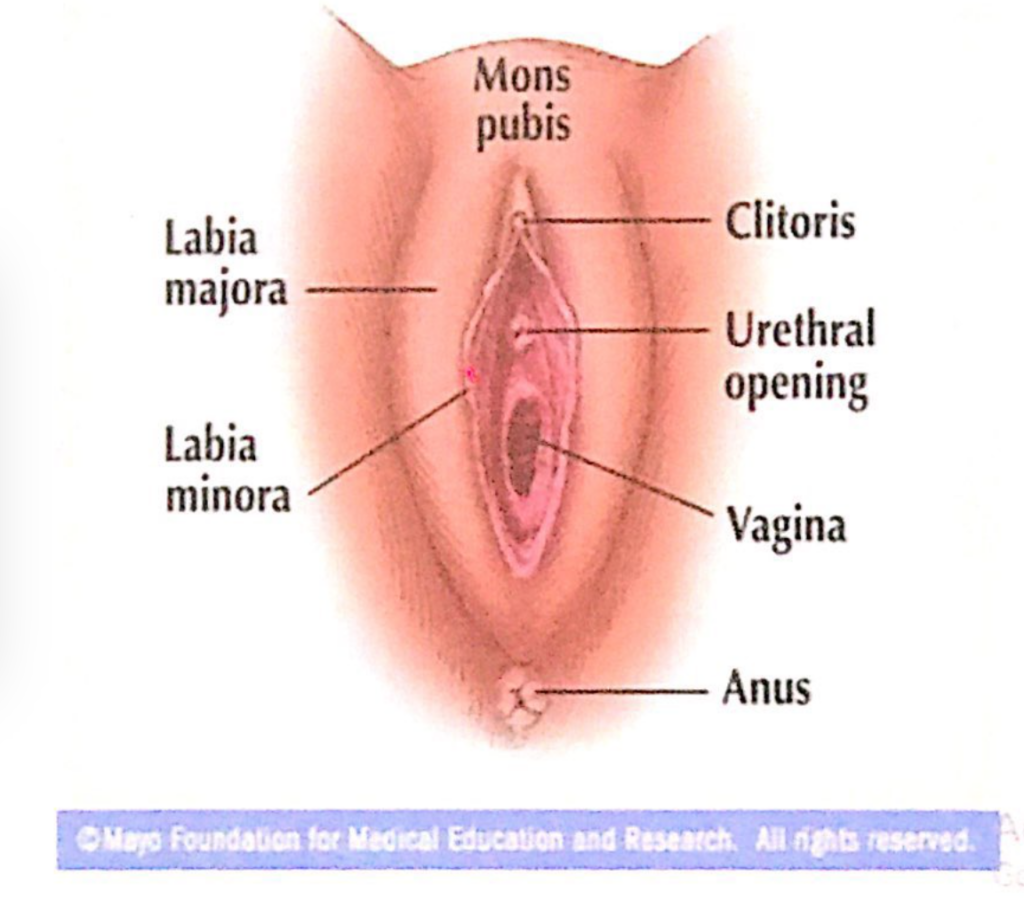

構造(Structure)
- 丸みを帯びた脂肪のない皮膚のひだ(Rounded Folds of Fat-Free, Hairless Skin):
- 毛がなく、滑らかな皮膚で構成されています。
- 陰裂内に位置(Located in the Pudendal Cleft):
- **陰裂(Pudendal Cleft)**内に位置し、**膣前庭(Vestibule)**を直接囲みます。
- 膣前庭には、**外尿道口(External Urethral Orifice)および膣口(Vaginal Orifice)**が開口しています。
- 海綿結合組織(Spongy Connective Tissue):
- 基部には**勃起組織(Erectile Tissue)**と小さな血管が含まれています。

前方での形成(Anteriorly – Formation of Laminae)
- 内側板(Medial Laminae):
- 両側の内側板が合流して、**陰核小帯(Frenulum of the Clitoris)**を形成します。
- 外側板(Lateral Laminae):
- 両側の外側板が合流し、**陰核(Clitoris)の亀頭(Glans)**の前方および下方を覆います。
- **陰核包皮(Prepuce of the Clitoris)**を形成し、陰核を保護します。

後方での結合(Posteriorly – Connection in Young Women and Virgins)
- 小陰唇小帯(Frenulum of the Labia Minora, Fourchette):
- 若年女性や未婚女性では、両側の小陰唇が後方で小さな横ひだ(Transverse Fold)を形成します。
特徴(Characteristics)
- 粘膜のピンク色(Pink Color Typical of Mucous Membrane):
- 小陰唇のピンク色は粘膜組織に由来します。
- 皮脂腺と神経終末(Sebaceous Glands and Sensory Nerve Endings):
- 多くの皮脂腺と豊富な感覚神経終末が分布し、性的感覚を担います。
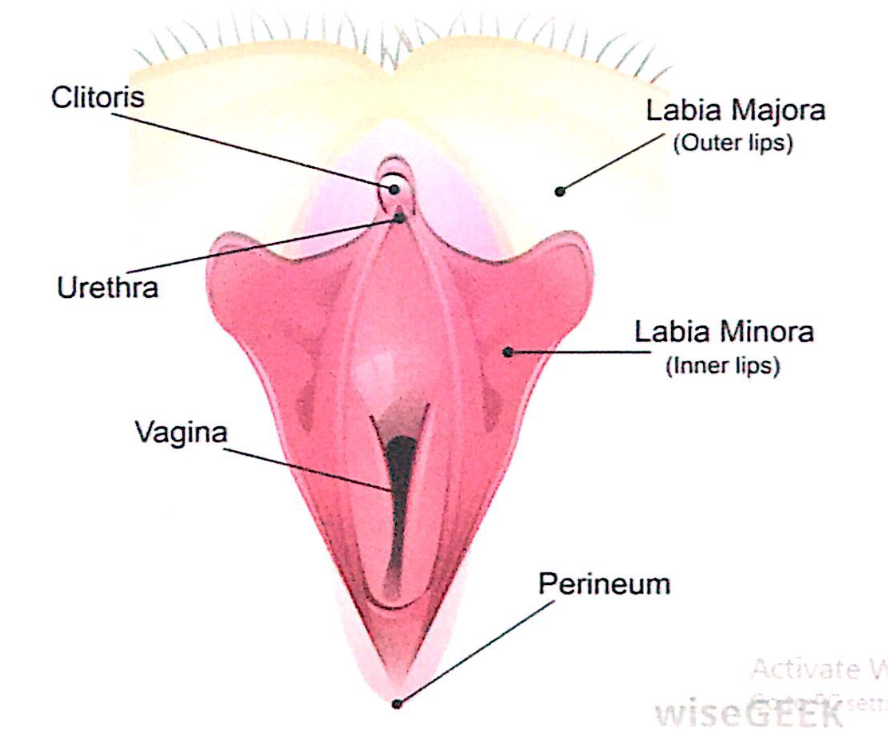
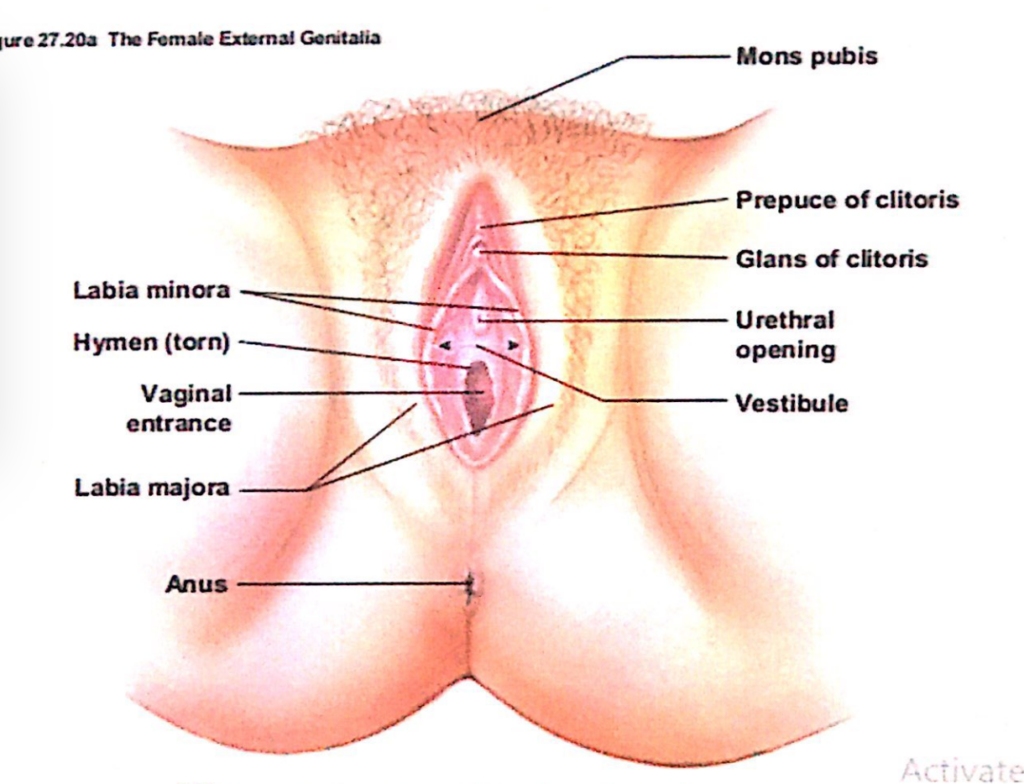

1. 陰核(Clitoris)と膣前庭(Vestibule)
膣前庭(Vestibule)
- 膣前庭(Vestibule):
- **小陰唇(Labia Minora)**に囲まれた空間。
- この空間には以下の開口部が存在します:
- 外尿道口(External Urethral Orifice)
- 膣口(Vaginal Orifice)
- **大前庭腺(Greater Vestibular Glands, バルトリン腺)および小前庭腺(Lesser Vestibular Glands)**の導管。
2. 外尿道口(External Urethral Orifice)
- 位置(Location):
- **陰核の亀頭(Glans of the Clitoris)**から約2-3cm後下方(Posteroinferior)に位置。
- **膣口(Vaginal Orifice)**の前方にあります。
- 周囲構造(Surrounding Structures):
- 外尿道口の両側には、**傍尿道腺導管(Paraurethral Glands Ducts, スキーン腺)**が開口しています。

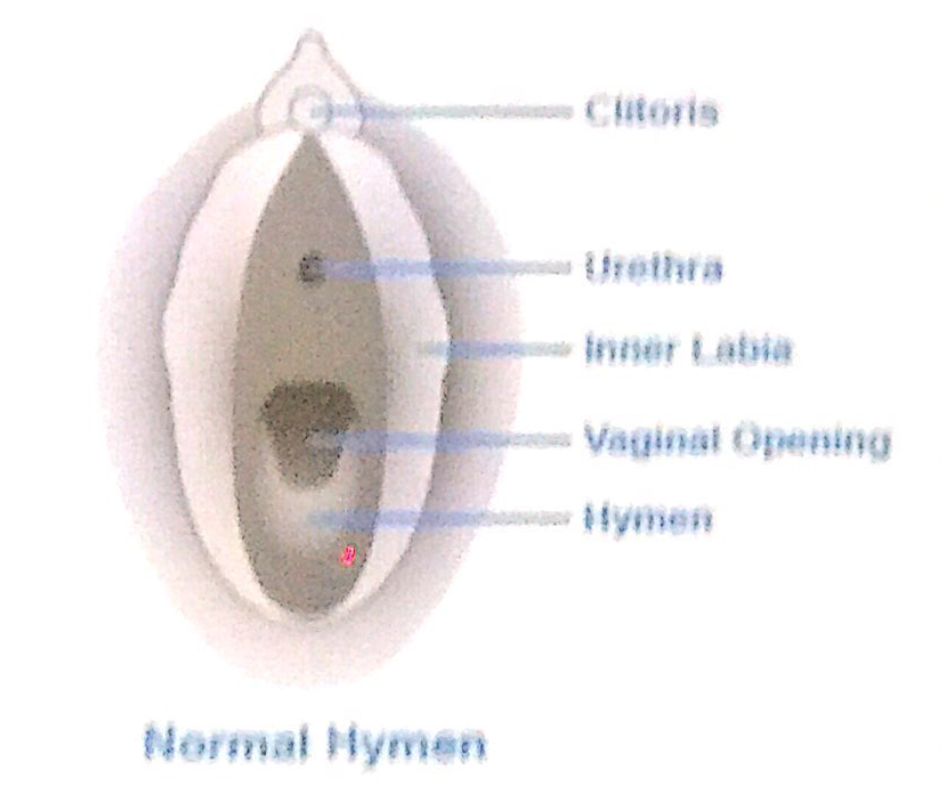
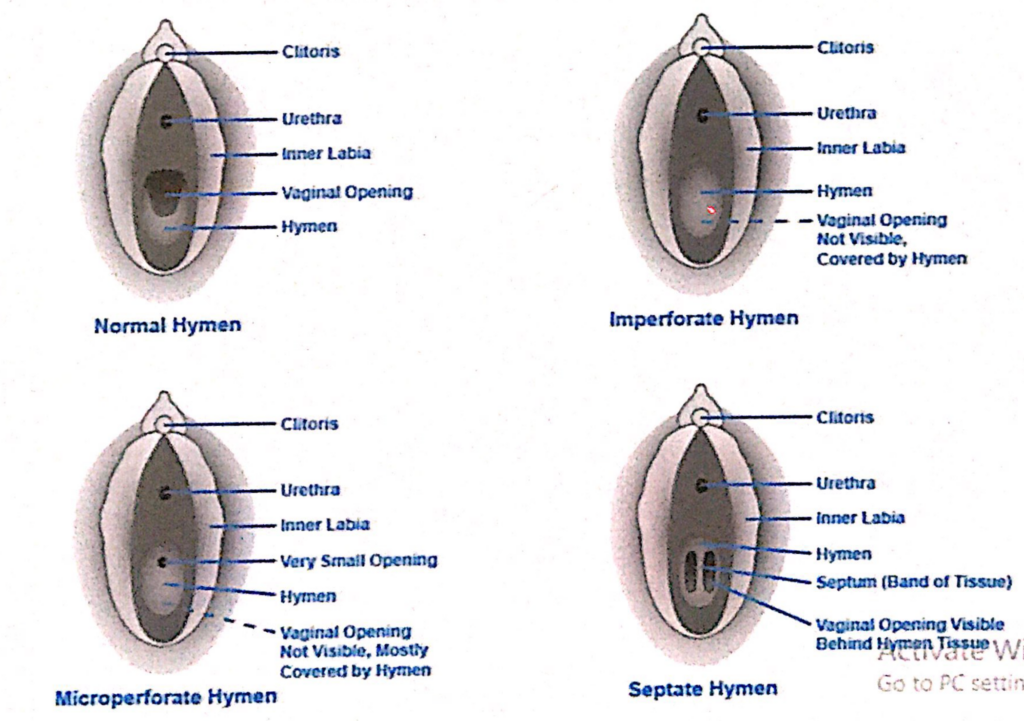
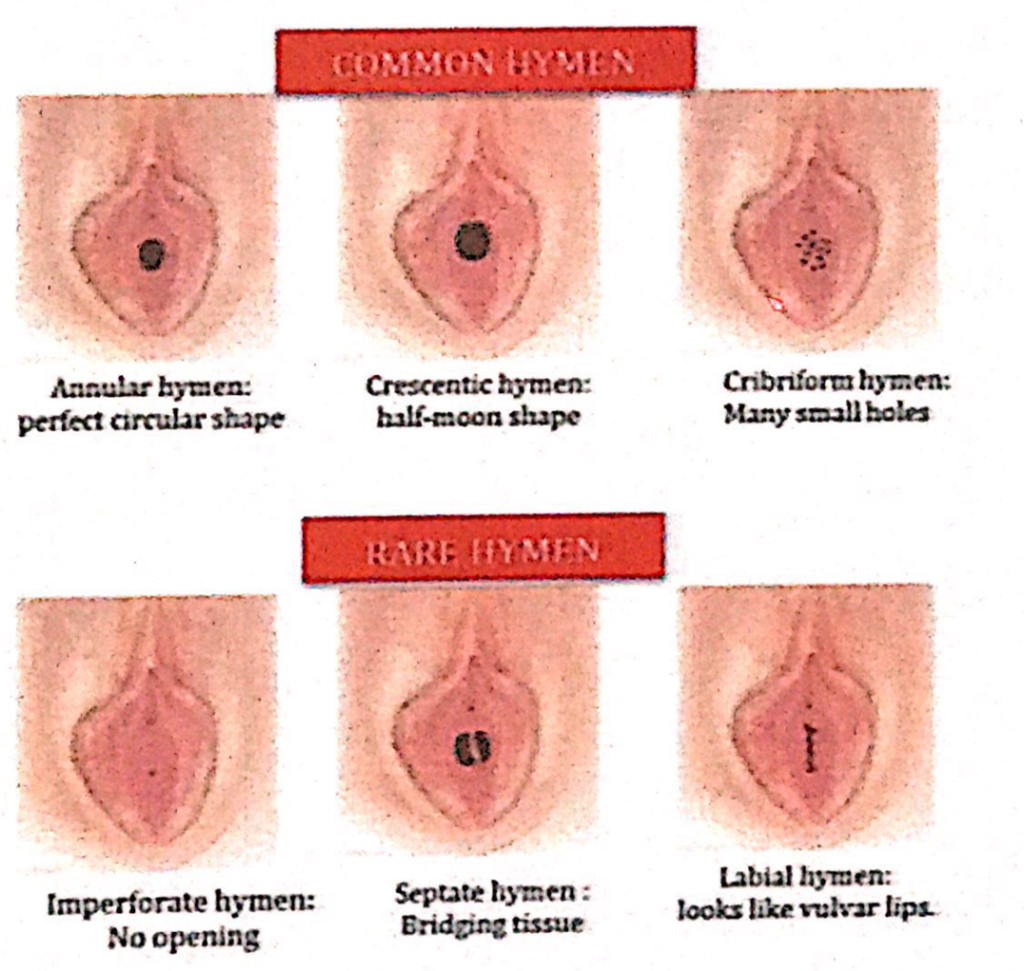
1. 陰核(Clitoris)と膣口(Vaginal Orifice)
膣口の形状と状態(Size and Appearance of the Vaginal Orifice)
- 膣口(Vaginal Orifice)の形状と外観:
- 膣口の形状と外観は、**処女膜(Hymen)**の状態によって変化します。
- **処女膜(Hymen)**は、薄い輪状の粘膜ひだ(Thin Annular Fold of Mucous Membrane)で、膣口の直内側に位置し、膣腔(Lumen)を囲みます。
2. 処女膜の破裂後の構造(Structure After Hymen Rupture)
処女膜小丘(Hymenal Caruncles)
- 特徴:
- 処女膜が破裂した後の遺残物(Remnants)です。
- 膣口と膣前庭(Vestibule)を区切る目印(Demarcation Point)として機能します。
- 臨床的重要性:
- 処女膜小丘の存在は、膣の発達や損傷歴の観察において用いられることがあります。
3. 生理学的機能(Physiologic Function)
- 処女膜には特定の生理学的機能(No Physiologic Function)はありません。
- 発生的には遺物(Developmental Vestige)と考えられます。
4. 関連構造(Associated Structures)
小陰唇小帯(Frenulum of the Labia Minora)
- 処女膜と共に発達の名残(Developmental Vestige)として分類されます。
- 小陰唇の後部を連結する小さな横ひだを形成します。
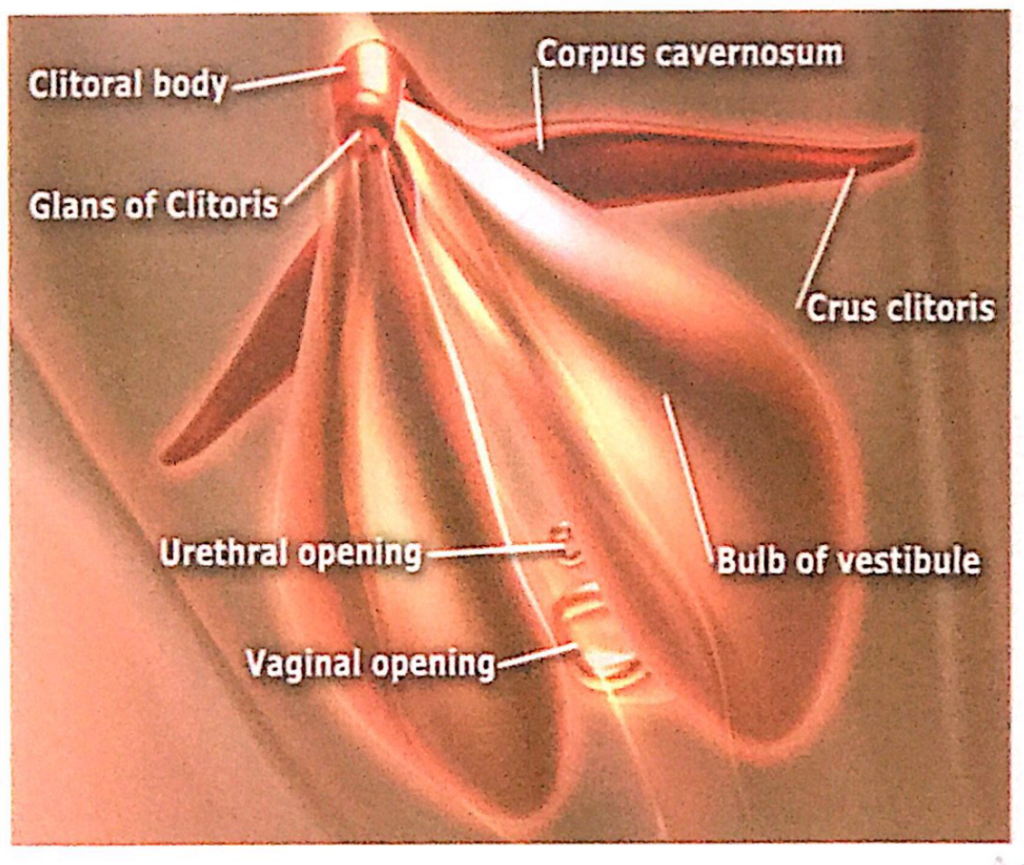

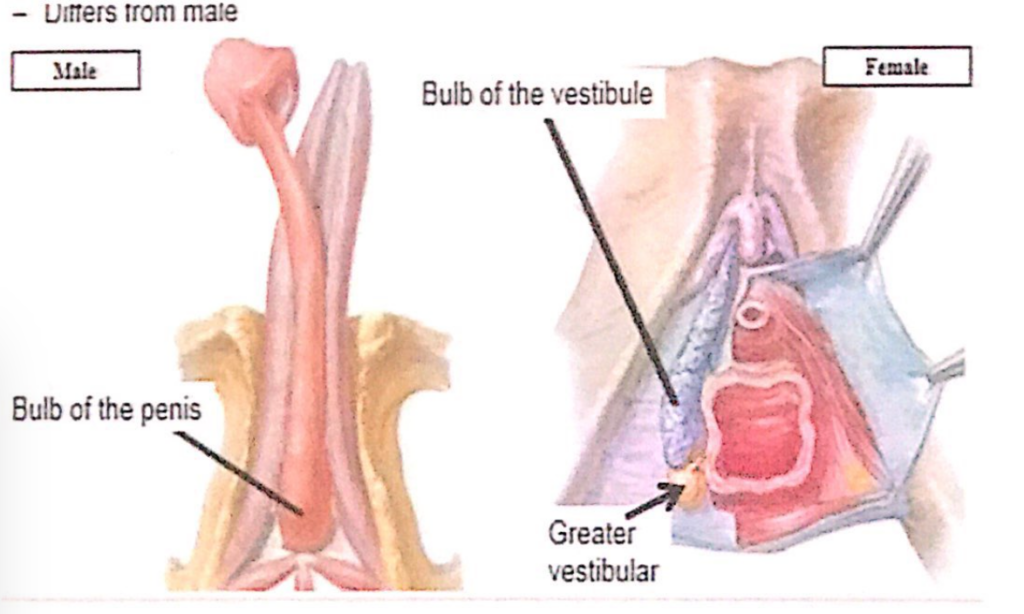
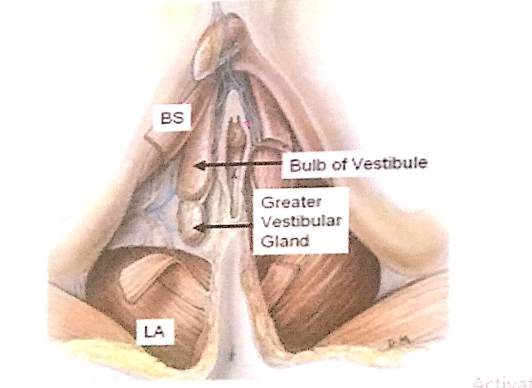
前庭球(Bulbs of the Vestibule)
- 対になった長い勃起組織(Paired masses of elongated erectile tissue)
- 長さは約3cmです。
- 位置
- 膣口(Vaginal Orifice)の両側に沿って位置し、小陰唇(Labia Minora)の上方または深部、会陰膜(Perineal Membrane)の直下にあります。
- 被覆
- 下部および外側は球海綿体筋(Bulbospongiosus Muscle)によって覆われています。
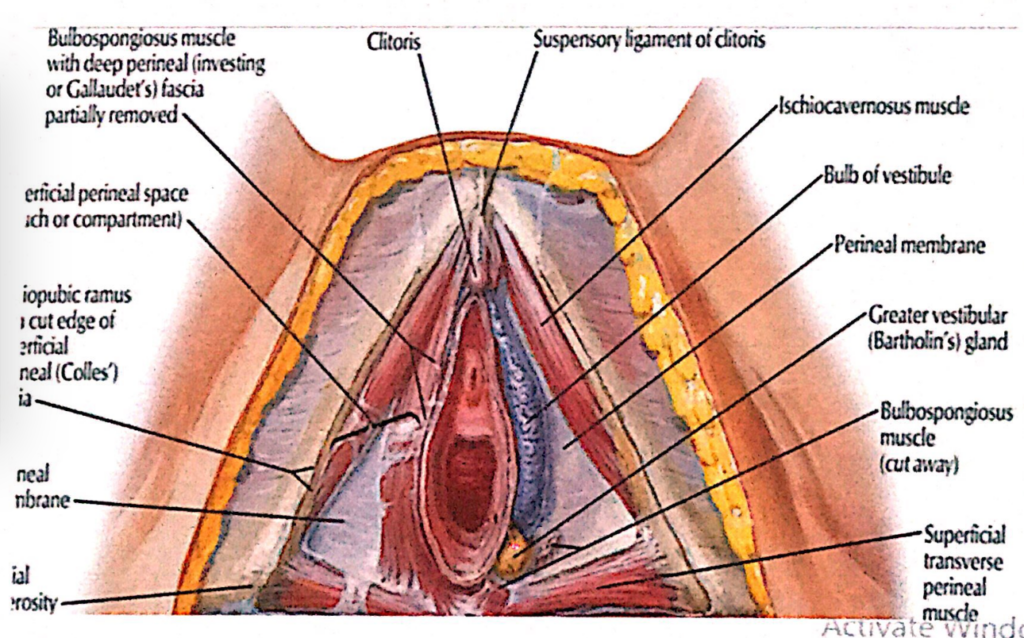

膣前庭腺(Vestibular Glands)
1. 大前庭腺(Greater Vestibular Glands, Bartholin’s Glands)
- 特徴(Characteristics):
- 直径約0.5cmの丸いまたは卵形の腺。
- **膣前庭(Vestibule)**の両側、**膣口(Vaginal Orifice)**の後外側(Posterolateral)に位置。
- **会陰膜(Perineal Membrane)**の下にあり、**浅会陰隙(Superficial Perineal Pouch)**内に存在。
- 周囲構造(Surrounding Structures):
- **膣前庭球(Bulbs of the Vestibule)**の後方に重なり、**球海綿体筋(Bulbospongiosus Muscle)**で囲まれています。
- 開口部(Openings):
- 各腺の導管は、**膣口の両側の前庭(Vestibule)**に開きます。
- 機能(Function):
- 粘液を分泌して膣前庭を潤滑し、性行為時の摩擦を軽減します。

前庭腺(Vestibular Glands)
- 大前庭腺(Greater Vestibular Glands)
- 開口部: 膣口(Vaginal Orifice)の両側で前庭(Vestibule)に開きます。
- 機能: 前庭に粘液(Mucus)を分泌します。
- 小前庭腺(Lesser Vestibular Glands)
- 位置: 前庭の両側に存在する小さな腺です。
- 機能: 粘液を分泌し、小陰唇(Labia Minora)および前庭(Vestibule)を湿らせます。

動脈供給(Arterial Supply)
動脈の特徴(Characteristics of Arteries)
- 豊富な血液供給(Abundant Blood Supply):
- 外陰部には非常に豊富な血液供給が行われています。
主要な動脈(Main Arteries)
- 外陰部動脈(External Pudendal Arteries):
- 外陰部の一部を供給します。
- 内陰部動脈(Internal Pudendal Arteries):
- 皮膚(Skin)、外陰部(External Genitalia)、および**会陰筋(Perineal Muscle)**の大部分を供給します。
- 陰唇動脈(Labial Arteries):
- **内陰部動脈(Internal Pudendal Artery)**の枝で、**陰核(Clitoris)**およびその他の外陰部構造に血液を供給します。
| 部位 (Region) | 動脈 (Arteries) | 詳細 (Details) |
|---|---|---|
| 恥丘 (Mons Pubis) | 外陰部動脈 (External Pudendal Arteries) | 恥丘および大陰唇の前部の皮膚と組織に血液を供給します。 |
| 大陰唇 (Labia Majora) | 外陰部動脈 (External Pudendal Arteries)、後陰唇動脈 (Posterior Labial Artery) | 外陰部動脈は大陰唇の前部を、後陰唇動脈は大陰唇の後部および皮膚に血液を供給します。 |
| 小陰唇 (Labia Minora) | 後陰唇動脈 (Posterior Labial Artery)、陰核深動脈 (Deep Artery of Clitoris) | 小陰唇の皮膚および周囲組織に血液を供給し、陰核への血流を補助します。 |
| 陰核 (Clitoris) | 陰核背動脈 (Dorsal Artery of Clitoris)、陰核深動脈 (Deep Artery of Clitoris) | 陰核背動脈は陰核の背側と亀頭に、陰核深動脈は陰核海綿体 (Corpora Cavernosa) に血液を供給し、勃起時に重要な役割を果たします。 |
| 膣前庭 (Vestibule of Vagina) | 膣前庭球動脈 (Artery of Bulb of Vestibule) | 膣前庭球 (Bulb of Vestibule) およびバルトリン腺 (Greater Vestibular Gland) に血液を供給します。 |
| 会陰部 (Perineum) | 内陰部動脈 (Internal Pudendal Artery)、会陰動脈 (Perineal Artery)、下直腸動脈 (Inferior Rectal Artery) | 会陰筋、膣口周囲、肛門括約筋に血液を供給します。 |
| 肛門周囲 (Peri-Anal Region) | 下直腸動脈 (Inferior Rectal Artery) | 肛門管下部、肛門括約筋、肛門周囲の皮膚に血液を供給します。 |
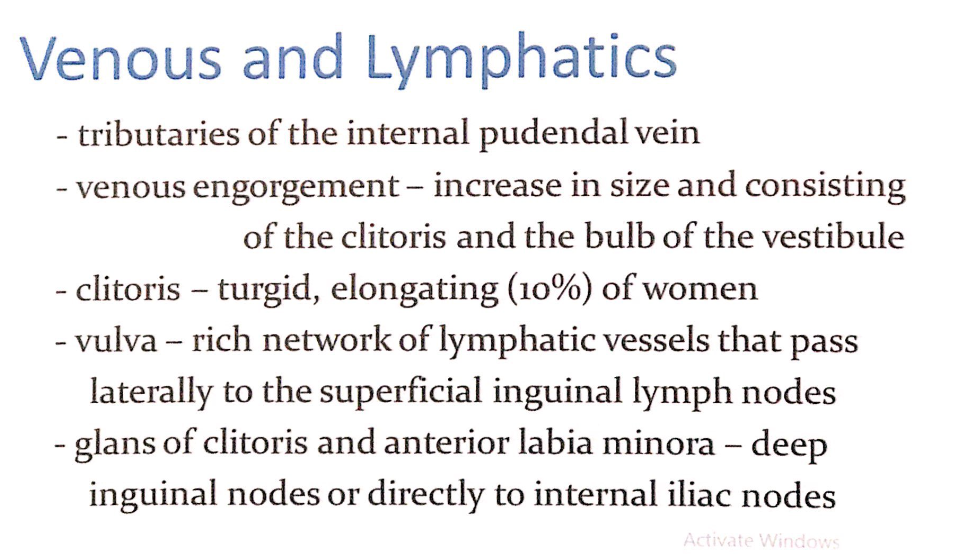
静脈排出(Venous Drainage)
静脈の特徴(Characteristics of Veins)
- 内陰部静脈(Tributaries of the Internal Pudendal Vein):
- 外陰部の静脈血は、主に内陰部静脈を通じて排出されます。
血液充満(Venous Engorgement)
- 性的興奮時に、以下の部位で静脈の充血が見られます:
- 陰核(Clitoris):
- 勃起状態になり、膨張し、10%の女性では伸長(Turgid and Elongating)します。
- 膣前庭球(Bulbs of the Vestibule):
- 膨張して大きくなります。
- 陰核(Clitoris):
リンパ流(Lymphatics)
リンパの特徴(Characteristics of Lymphatics)
- 豊富なリンパ管網(Rich Network of Lymphatic Vessels):
- 外陰部には発達したリンパ管網があり、リンパ液は側方に流れて以下に到達します:
- 浅鼠径リンパ節(Superficial Inguinal Lymph Nodes)
- 外陰部には発達したリンパ管網があり、リンパ液は側方に流れて以下に到達します:
特定部位のリンパ流(Lymphatic Drainage of Specific Regions)
- 陰核の亀頭(Glans of Clitoris)および前部小陰唇(Anterior Labia Minora):
- **深鼠径リンパ節(Deep Inguinal Nodes)または直接内腸骨リンパ節(Internal Iliac Nodes)**へ流れます。
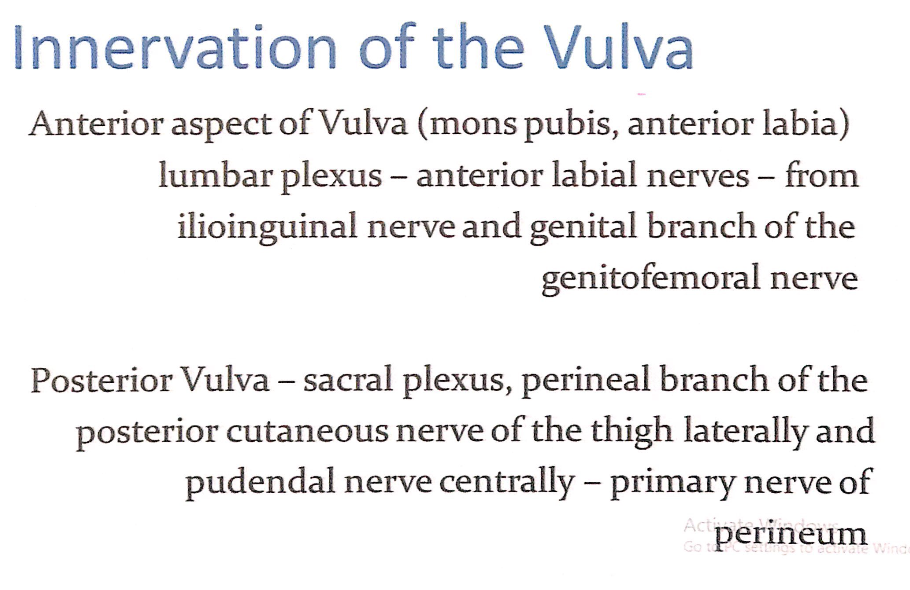
外陰部の神経支配(Innervation of the Vulva)
前部外陰部(Anterior Aspect of the Vulva)
- 支配領域(Supplied Areas):
- 恥丘(Mons Pubis)
- 前部大陰唇(Anterior Labia)
- 神経経路(Nerve Pathways):
- **腰神経叢(Lumbar Plexus)**による支配。
- 前陰唇神経(Anterior Labial Nerves):
- **腸骨鼠径神経(Ilioinguinal Nerve)**から分岐。
- **生殖大腿神経(Genitofemoral Nerve)の生殖枝(Genital Branch)**から分岐。
後部外陰部(Posterior Aspect of the Vulva)
- 支配領域(Supplied Areas):
- 後部大陰唇(Posterior Labia)
- 会陰部全体(Perineum)。
- 神経経路(Nerve Pathways):
- **仙骨神経叢(Sacral Plexus)**による支配。
- 大腿後皮神経の会陰枝(Perineal Branch of the Posterior Cutaneous Nerve of the Thigh):
- 外側(Laterally)の後部外陰部を支配。
- 陰部神経(Pudendal Nerve):
- 中央(Centrally)の会陰部および後部外陰部を支配。
- 会陰部の主要な神経(Primary Nerve of the Perineum)。
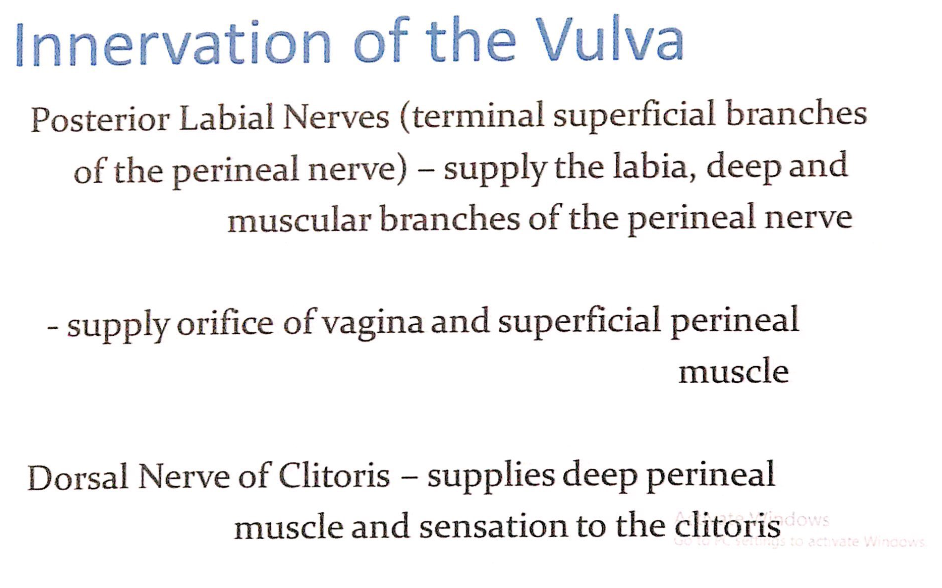
神経支配の詳細(Nerve Supply Details)
- 後陰唇神経(Posterior Labial Nerves)
- 会陰神経(Perineal Nerve)の末端の浅枝(Terminal Superficial Branches)です。
- 支配領域: 陰唇(Labia)を供給します。
- 深枝および筋枝(Deep and Muscular Branches):
- 膣口(Orifice of Vagina)および浅会陰筋(Superficial Perineal Muscle)を供給します。
- 陰核背神経(Dorsal Nerve of Clitoris)
- 支配領域: 深会陰筋(Deep Perineal Muscle)および陰核(Clitoris)の感覚を供給します。
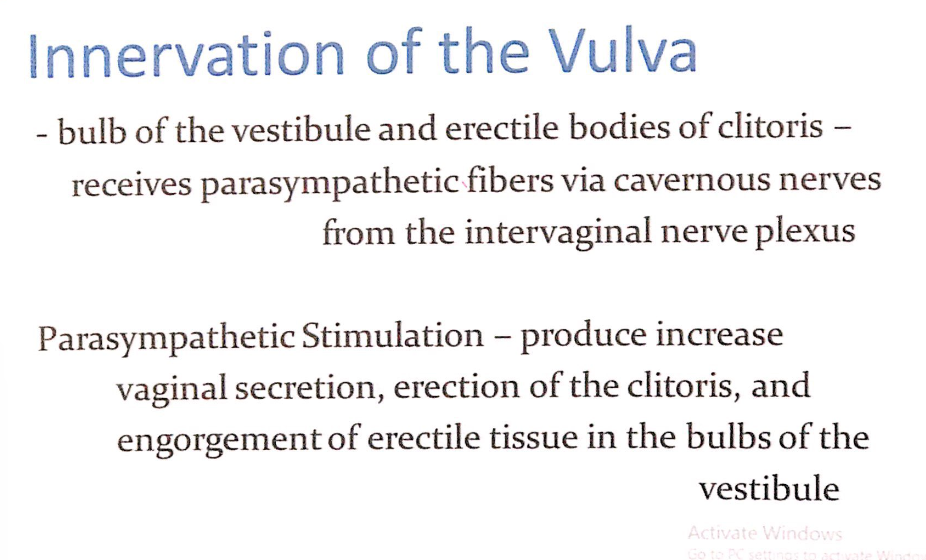
- 前庭球(Bulb of the Vestibule)および陰核の勃起組織(Erectile Bodies of Clitoris)
- **副交感神経(Parasympathetic Fibers)**を膣神経叢(Intervaginal Nerve Plexus)の陰茎洞神経(Cavernous Nerves)を介して受け取ります。
副交感神経刺激(Parasympathetic Stimulation)
- 効果:
- 膣分泌(Vaginal Secretion)の増加
- 陰核(Clitoris)の勃起
- 前庭球(Bulbs of the Vestibule)の勃起組織への充血(Engorgement)
| 部位 (Region) | 神経 (Nerves) | 詳細 (Details) |
|---|---|---|
| 恥丘 (Mons Pubis) | 前陰唇神経 (Anterior Labial Nerves) | 腸骨鼠径神経 (Ilioinguinal Nerve) の末端枝。感覚を供給。 |
| 大陰唇 (Labia Majora) | 前陰唇神経 (Anterior Labial Nerves)、生殖枝 (Genital Branch of Genitofemoral Nerve)、後陰唇神経 (Posterior Labial Nerves) | 前部は腸骨鼠径神経、生殖大腿神経が供給し、後部は会陰神経の浅枝が感覚を供給。 |
| 小陰唇 (Labia Minora) | 後陰唇神経 (Posterior Labial Nerves) | 会陰神経の浅枝 (Superficial Terminal Branch of Perineal Nerve)。感覚を供給。 |
| 会陰部 (Perineum) | 陰部神経 (Pudendal Nerve)、深会陰神経 (Deep Perineal Nerve)、大腿後皮神経の会陰枝 (Perineal Branch of Posterior Cutaneous Nerve of Thigh) | 陰部神経は会陰筋と下直腸、深会陰神経は浅会陰筋および膣前庭を供給。会陰枝は外側の会陰部を支配。 |
| 陰核 (Clitoris) | 陰核背神経 (Dorsal Nerve of Clitoris) | 陰部神経 (Pudendal Nerve) の枝で、陰核の感覚を供給。 |
| 膣前庭 (Vestibule of Vagina) | 深会陰神経 (Deep Perineal Nerve) | 会陰神経の深枝で、膣前庭および浅会陰筋の感覚と運動を供給。 |

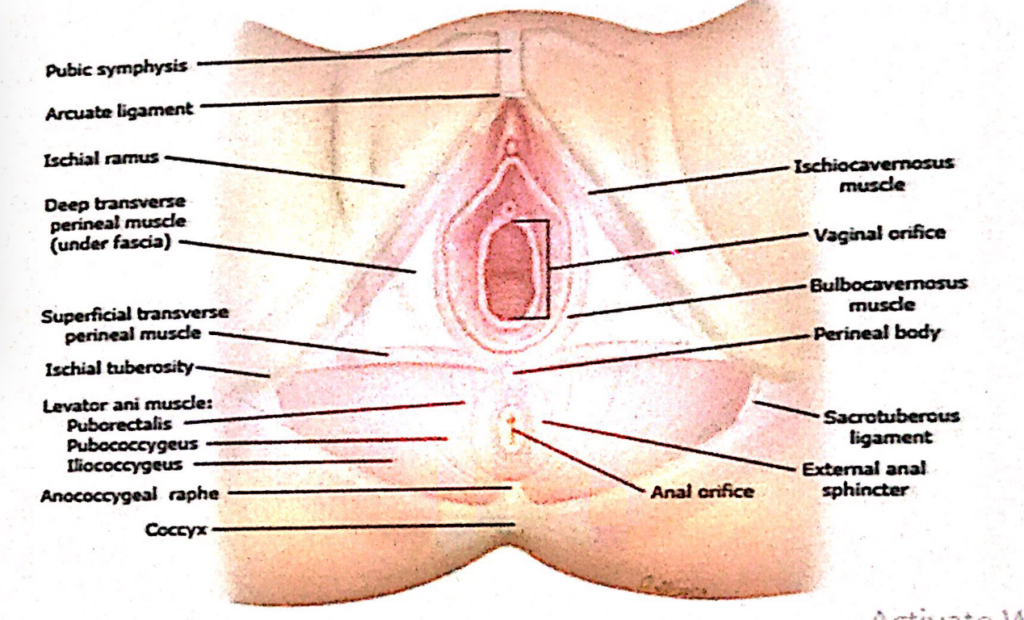
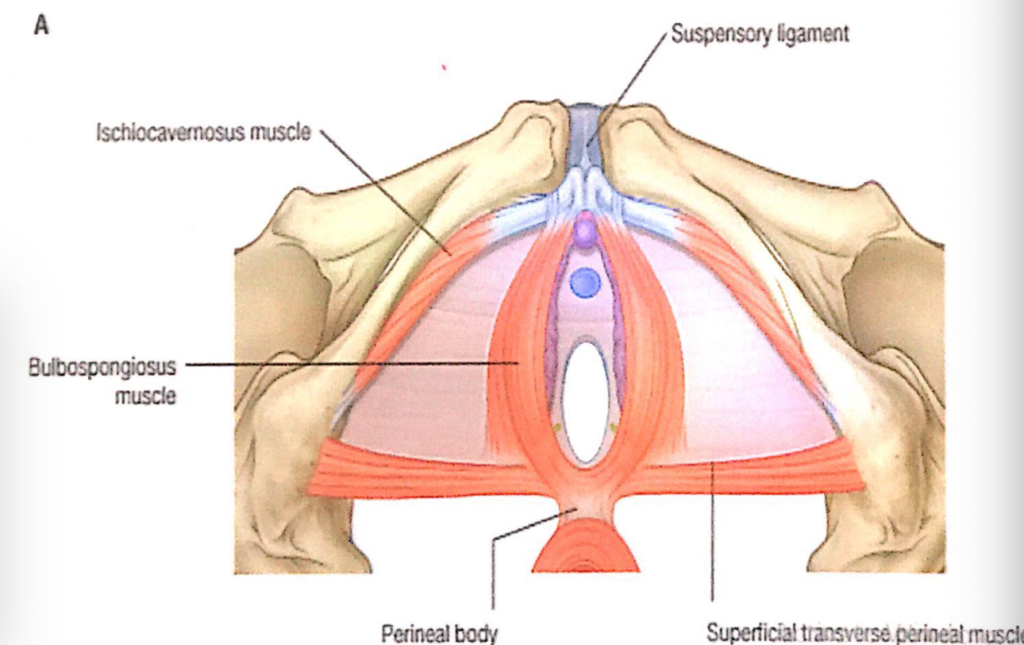
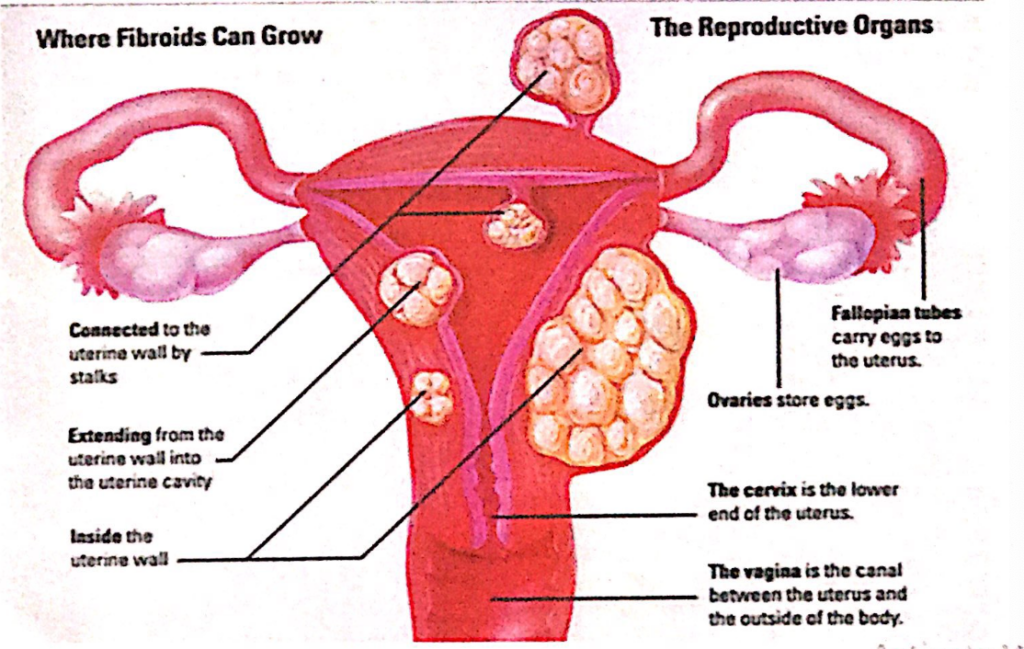
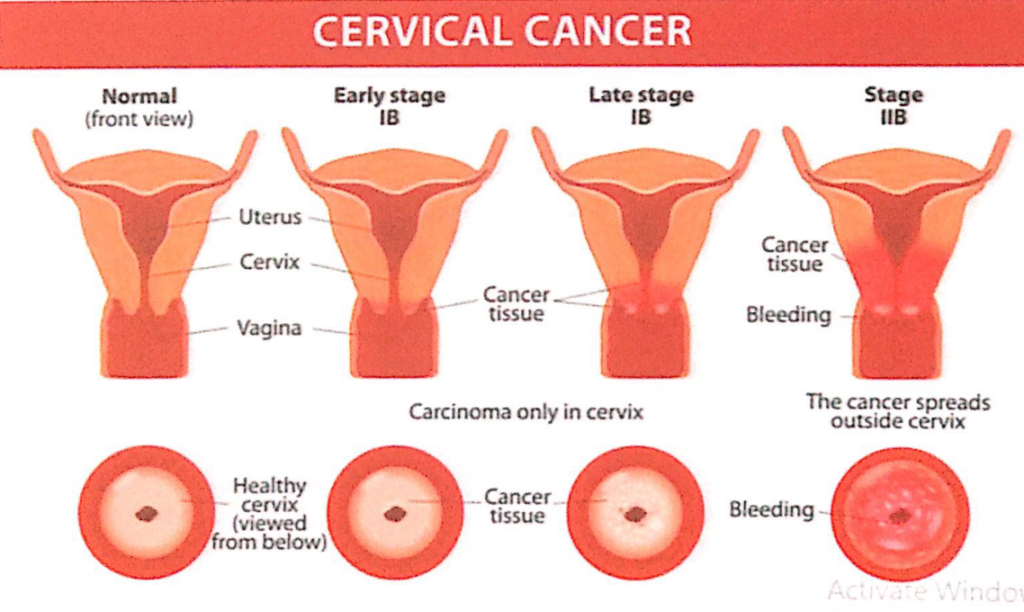
過去問
★骨盤腔の特徴 (Characteristics of the Pelvic Cavity)
Q1: True of pelvic cavity except
Answer: Angled anteriorly from abdominal cavity
Explanation:
骨盤腔 (Pelvic cavity) は腹腔に対して前方に傾いているのが正しい特徴です。他の選択肢の意味が明確でないため、この点に注意が必要です。
梨状筋の機能 (Function of Piriformis Muscle)
Q2: Muscle attached to greater trochanter, abducts and rotates thigh
Answer: Piriformis
Explanation:
梨状筋 (Piriformis) は大転子に付着し、外転と外旋に関与します。
★妊娠中に損傷される筋肉 (Muscles Torn During Pregnancy)
Q3: Torn during pregnancy
Answer: Puborectalis and pubococcygeus muscles
Explanation:
恥骨直腸筋 (Puborectalis) と恥骨尾骨筋 (Pubococcygeus) は分娩時に損傷を受けやすい骨盤底筋です。
腹腔内圧増加への抵抗 (Resisting Increase in Intra-Abdominal Pressure)
Q4: Resist increase in intra-abdominal pressure
Answer: Levator ani
Explanation:
挙肛筋 (Levator ani) は骨盤底の主要筋肉であり、腹腔内圧の上昇に対抗します。
★骨盤入口損傷で脆弱な構造 (Vulnerable Structure in Pelvic Inlet Damage)
Q5: Vulnerable in pelvic inlet damage
Answer: Sacral promontory
Explanation:
仙骨岬角 (Sacral promontory) は骨盤入口の一部で、損傷に対して脆弱です。
★骨盤縁の構造 (Structure Damaged in Pelvic Brim Injury)
Q6: Damage in pelvic brim, what structure is composed?
Answer: Lumbosacral trunk
Explanation:
腰仙幹 (Lumbosacral trunk) は骨盤縁に位置する神経構造であり、損傷を受けやすいです。
★内腸骨動脈の後枝に含まれないもの (Not Part of Posterior Division of Internal Iliac Artery)
Q7: Not part of the posterior division of internal iliac artery
Answer: Inferior gluteal artery
Explanation:
内腸骨動脈(internal iliac artery)の後枝(posterior division)は、骨盤内の後方構造や壁を主に供給する動脈のグループです。この後枝に含まれる主な枝は以下の通りです:
- 腸腰動脈(Iliolumbar artery)
骨盤壁と腰部の筋肉を供給します。 - 外側仙骨動脈(Lateral sacral arteries)
仙骨と脊髄膜を供給し、仙骨神経叢に枝を送ります。 - 上殿動脈(Superior gluteal artery)
臀部の筋肉と皮膚を供給します。これは後枝の中で最も大きな動脈です。
下殿動脈 (Inferior gluteal artery) は内腸骨動脈の前枝から分岐します。
★仙骨神経叢に含まれないもの (Not a Branch of Posterior Sacral Nerve)
Q8: Not a branch of posterior sacral nerve
Answer: Sciatic nerve
Explanation:
坐骨神経 (Sciatic nerve) は仙骨神経叢から分枝しますが、後仙骨神経の枝ではありません。
★内腸骨動脈の延長 (Continuation of Internal Iliac Artery)
Q9: Continuation of internal iliac artery
Answer: Internal pudendal artery
Explanation:
内陰部動脈 (Internal pudendal artery) は内腸骨動脈の分枝の一つです。
★大腿のリンパ排出 (Lymph Drainage of the Thigh)
Q10: Drains lymph of thigh
Answer: External iliac lymph nodes
Explanation:
外腸骨リンパ節 (External iliac lymph nodes) は大腿部のリンパを排出します。
★陰部神経ブロックの固定ランドマーク (Landmark for Pudendal Nerve Block)
Q11: Fixed structure to locate while injecting anesthesia to the pudendal nerve
Answer: Ischial spine
Explanation:
坐骨棘 (Ischial spine) は陰部神経ブロック時の重要なランドマークです。
大坐骨切痕を通らない構造 (Does Not Pass Through Greater Sciatic Notch)
Q12: Does not pass to greater sciatic notch
Answer: Obturator artery
Explanation:
閉鎖動脈 (Obturator artery) は閉鎖孔を通過しますが、大坐骨切痕は通りません。
★子宮支持靭帯 (Ligament Supporting the Uterus)
Q13: Supports the uterus
Answer: Broad ligament
Explanation:
広靭帯 (Broad ligament) は子宮を支持する主要な靭帯の一つです。
★膀胱の緩やかな連結部位 (Part of the Urinary Bladder Loosely Connected to the Peritoneum)
Q14: Part of the urinary bladder loosely connected to the peritoneum
Answer: Superior
Explanation:
膀胱の上部は腹膜と緩やかに接続されています。
★受精の一般的な部位 (Common Site of Fertilization)
Q15: Common site of fertilization
Answer: Ampulla
Explanation:
卵管膨大部 (Ampulla) は受精が最も頻繁に起こる部位です。
★横頸靭帯の起点 (Origin of the Transverse Cervical Ligament)
Q16: Where does the transverse cervical ligament of the hypogastric sheath originate?
Answer: Middle lamina
Explanation:
横頸靭帯 (Transverse cervical ligament) は下腹膜鞘 (hypogastric sheath) の中間葉 (middle lamina) から派生します。これにより骨盤壁に安定した支持を提供します。他の選択肢が間違っている理由は以下の通りです:
- Superior lamina:上部葉は主靭帯には関連しません。
- Inferior lamina:下部葉は骨盤底の他の構造を支持しますが、横頸靭帯の起点ではありません。
- Lateral lamina:外側葉も横頸靭帯には関与しません。
★浅会陰嚢から除外される構造 (Spared from the Superficial Perineal Pouch)
Q17: Spared from superficial perineal pouch
Answer: Perineal body
Explanation:
会陰中央腱 (Perineal body) は浅会陰嚢に含まれず、その代わり骨盤底筋の支持構造として独立しています。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は以下の通りです:
- Bulb of the vestibule:前庭球は浅会陰嚢に含まれます。
- Ischiocavernosus muscle:坐骨海綿体筋も浅会陰嚢内の構造です。
- Superficial transverse perineal muscle:浅横会陰筋も浅会陰嚢内に位置します。
★尿生殖三角に含まれない構造 (Spared from the Urogenital Triangle)
Q18: Urogenital triangle, spared?
Answer: Tip of coccyx
Explanation:
尾骨先端 (Tip of coccyx) は肛門三角に含まれ、尿生殖三角には含まれません。他の選択肢が関連している理由は以下の通りです:
- Ischial tuberosity:坐骨結節は尿生殖三角の外縁に位置します。
- Sacrotuberous ligament:仙結節靭帯も尿生殖三角の支持に関与します。
- Sacrospinous ligament:仙棘靭帯も骨盤底の支持構造として関与します。
★仙骨神経叢の範囲 (Sacral Plexus Range)
Q19: Sacral plexus
Answer: L4-S3
Explanation:
仙骨神経叢 (Sacral plexus) はL4-S3レベルの脊髄神経から構成されています。他の選択肢はこの範囲外であるため正しくありません。
骨盤直腸空間の特徴 (True About Pelvirectal Space)
Q20: True about pelvirectal space
Answer: Ligaments connect the rectum to the parietal fascia at the S2-S4 levels
Explanation:
骨盤直腸空間 (Pelvirectal space) では靭帯が直腸をS2-S4レベルの壁側筋膜に接続しています。これにより直腸の支持が強化されます。他の選択肢はこの空間に直接関係しません。
★子宮頸部の支持 (Cervical Support)
Q21: Supports cervix
Answer: Uterosacral ligament
Explanation:
子宮仙骨靭帯 (Uterosacral ligament) は子宮頸部を骨盤後壁に固定する支持靭帯です。他の選択肢は子宮全体の支持に関与しますが、頸部への直接的な支持力は限定的です。
★会陰切開術で影響を受ける筋肉 (Muscles Spread During Episiotomy)
Q22: Spread muscle during episiotomy?
Answer: Perineal muscle
Explanation:
会陰筋 (Perineal muscle) は会陰切開術の際に展開される主要な筋肉です。他の選択肢は会陰切開術に直接関与しません。
過期産児の損傷を受ける筋肉 (Muscle Damaged in Overdue Baby Delivery)
Q23: Overdue baby, what muscle is damaged?
Answer: Levator ani
Explanation:
挙肛筋 (Levator ani) は過期産児の出産中に損傷を受けやすい骨盤底筋です。他の筋肉は損傷のリスクが比較的低いです。
★小骨盤内出血の原因動脈 (Artery Bleeding in Lesser Pelvis)
Q24: Bleeding of an artery that stays in lesser pelvis?
Answer: Umbilical artery
Explanation:
臍動脈 (Umbilical artery) は小骨盤内に位置し、出血の原因として一般的です。他の動脈は小骨盤を越えて血液を供給することが多いため、関与しません。
★骨盤内臓器に含まれないもの (Structure NOT Included in the Pelvis)
Q25: Pelvis includes abdominopelvic viscera, except
Answer: Transverse colon
Explanation:
横行結腸 (Transverse colon) は腹腔に位置し、骨盤内臓器には含まれません。他の選択肢は骨盤内臓器に含まれます。
★会陰の後外側境界 (Posterolateral Boundary of the Perineum)
Q1: What forms the posterolateral boundary of the perineum?
Answer: Sacrotuberous ligaments
Explanation:
仙結節靭帯 (Sacrotuberous ligaments) は、会陰の後外側境界を形成します。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は以下の通りです:
- 他の選択肢は関連がなく、会陰の境界形成に直接関与しません。
★会陰中央腱の機能 (Function of the Perineal Body)
Q2: What is the site of convergence and interlacing of fibers of several muscles?
Answer: Perineal body
Explanation:
会陰中央腱 (Perineal body) は、複数の筋肉が集まって交差する重要な支持構造です。
★深会陰嚢の構造 (Structure in the Deep Perineal Pouch)
Q3: Which structure is found in the deep perineal pouch?
Answer: Bulbo-urethral glands
Explanation:
尿道球腺 (Bulbo-urethral glands) は深会陰嚢に含まれ、潤滑液を分泌します。
★浅会陰嚢の構造 (Structure in the Superficial Perineal Pouch)
Q4: Which structure is found in the superficial perineal pouch?
Answer: Vestibular bulb
Explanation:
前庭球 (Vestibular bulb) は浅会陰嚢に含まれ、膣の両側に位置します。
坐骨肛門窩内の内側構造 (Medial Structure of Ischio-Anal Fossae)
Q5: Which structure is found medial to the ischio-anal fossae?
Answer: External anal sphincter
Explanation:
外肛門括約筋 (External anal sphincter) は坐骨肛門窩の内側に位置します。
★陰部管の特徴 (True About Pudendal Canal)
Q6: Which is true about the pudendal canal?
Answer: Lines the lateral wall of ischio-anal fossa
Explanation:
陰部管 (Pudendal canal) は坐骨肛門窩の外側壁に沿って位置します。
中直腸静脈の還流先 (Drainage of the Middle Rectal Vein)
Q7: Into which vein does the middle rectal vein drain?
Answer: Internal iliac veins
Explanation:
中直腸静脈 (Middle rectal vein) は内腸骨静脈に還流します。
陰嚢の区分構造 (Structure Dividing the Scrotum into Two Compartments)
Q8: What structure divides the scrotum into two compartments?
Answer: Dartos fascia
Explanation:
ダートス筋膜 (Dartos fascia) は陰嚢を左右に分ける構造です。
陰茎の強固な膜状被覆 (Strong Membranous Covering of the Penis)
Q9: What forms a strong membranous covering for the penis?
Answer: Buck’s fascia
Explanation:
陰茎深筋膜 (Buck’s fascia) は陰茎の強固な被覆を形成します。
★円靭帯の終端部 (Termination of the Round Ligament)
Q10: Where does the round ligament terminate?
Answer: Labia majora
Explanation:
円靭帯 (Round ligament) は大陰唇 (Labia majora) に終わります。
★陰裂を囲む構造 (Structure Enclosing the Pudendal Cleft)
Q11: Which structure encloses the pudendal cleft?
Answer: Labia majora
Explanation:
大陰唇 (Labia majora) は陰裂 (Pudendal cleft) を囲みます。
★前陰唇神経の起源 (Origin of Anterior Labial Nerve)
Q12: What is the origin of the anterior labial nerve?
Answer: Genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve
Explanation:
前陰唇神経 (Anterior labial nerve) は生殖大腿神経の生殖枝 (Genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve) に由来します。
★陰核包皮の形成 (Formation of the Clitoral Prepuce)
Q13: Which laminae form the prepuce(homologus) of the clitoris?
Answer: Lateral
Explanation:
陰核包皮 (Clitoral prepuce) は小陰唇の外側葉によって形成されます。
★外陰部の後端 (Posterior Limit of the Vulva)
Q14: What is the posterior limit of the vulva?
Answer: Posterior commissure
Explanation:
後交通 (Posterior commissure) は外陰部の後端を形成します。
Q15: Which part of the urethra forms the intrabulbar and navicular fossae?
Answer: Spongy urethra
Explanation:
尿道海綿体部 (Spongy urethra) は球部窩 (intrabulbar fossa) および舟状窩 (navicular fossa) を形成します。他の選択肢はこれらの窩には関与しません。
中部尿道の位置 (Location of the Intermediate Urethra)
Q16: Where does the intermediate urethra begin?
Answer: Begins at the apex of prostate and transverses the deep perineal pouch
Explanation:
中部尿道 (Intermediate urethra) は前立腺の頂点から始まり、深会陰嚢を通過します。
★大前庭腺の位置 (Location of the Greater Vestibular Bulb)
Q17: Where is the greater vestibular bulb located?
Answer: Posterolateral to the vaginal orifice, inferior to the perineal membrane
Explanation:
大前庭腺 (Greater vestibular bulb) は膣口の後外側、会陰膜の下方に位置します。
★前庭球の位置 (Location of the Bulbs of Vestibule)
Q18: Where are the bulbs of the vestibule located?
Answer: Lie along the sides of the vaginal orifice, inferior to the perineal membrane
Explanation:
前庭球 (Bulbs of vestibule) は膣口の両側、会陰膜の下方に位置します。
男性尿道の遠位部の副交感神経支配 (Parasympathetic Innervation of the Distal Male Urethra)
Q19: Which nerves provide parasympathetic innervation to the distal male urethra?
Answer: Pelvic splanchnic nerves
Explanation:
骨盤内臓神経 (Pelvic splanchnic nerves) は男性尿道の遠位部を副交感神経支配します。
勃起組織の血流移動 (Forcing Blood in Corpora Cavernosa)
Q20: Which muscles force blood from the cavernous spaces of the crura into the distal parts of the corpora cavernosa?
Answer: Ischiocavernosus muscles
Explanation:
坐骨海綿体筋 (Ischiocavernosus muscles) は脚部 (crura) から陰茎海綿体の遠位部に血液を送ります。
陰茎の輪状靭帯 (Fundiform Ligament of the Penis)
Q21: What is the irregular mass of collagen and elastic fibers descending from the linea alba?
Answer: Fundiform ligament of the penis
Explanation:
陰茎輪状靭帯 (Fundiform ligament of the penis) は白線 (linea alba) から下方に伸びる結合組織の塊です。
勃起組織の神経支配 (Innervation of the Helicine Arteries)
Q22: Which nerves innervate the helicine arteries of the erectile tissue?
Answer: Cavernous nerves
Explanation:
海綿体神経 (Cavernous nerves) は勃起組織の螺旋動脈 (helicine arteries) を神経支配します。
尿道球腺と陰茎海綿体への血流供給 (Arterial Supply to the Bulb and Corpus Spongiosum)
Q23: Which arteries supply the posterior part of the corpus spongiosum and the bulbo-urethral gland?
Answer: Arteries of the bulb of the penis
Explanation:
陰茎球動脈 (Arteries of the bulb of the penis) は尿道球腺および陰茎海綿体の後部に血液を供給します。
陰茎海綿体の融合が見られない部分 (Part of Corpora Cavernosa Not Fused)
Q24: Corpora cavernosa are fused with each other in the median plane except at which part?
Answer: Posterior
Explanation:
陰茎海綿体は後方で融合せず、脚部 (crura) として分離しています。
★女性外陰部への主な血液供給 (Arterial Supply to Female External Genitalia)
Q25: Which artery supplies most of the female skin, external genitalia, and perineal muscles?
Answer: Internal pudendal arteries
Explanation:
内陰部動脈 (Internal pudendal arteries) は女性の外陰部および会陰筋の主要な血液供給源です。


コメント