Contents
腎臓系(Renal System)
学習目標(Learning Objectives):
- 腎臓(Kidney)、尿管(Ureter)、膀胱(Urinary Bladder)、尿道(Urethra)を含む尿路系(Urinary System)の構成について理解すること。
- 腎臓の血管系(Vascular)および尿路系(Urinary Parts)の構成を理解すること。
- ネフロン(Nephron)の各部分を認識し、その構造(Structure)と機能(Function)を説明できるようになること。
尿路系は腎臓(Kidneys)、尿管(Ureters)、膀胱(Urinary Bladder)、および尿道(Urethra)から構成されます。腎臓は血液からの老廃物の除去(Removal of Waste Products)と、血液や細胞間液(Intercellular Fluids)の水分および塩分のバランス調節(Regulation of Water and Salt Balance)に特化しています。
腎臓は複数の葉(Lobes)に分かれており、1つの葉は円錐形の髄質錐体(Medullary Pyramid)と、その周囲を帽子のように覆う皮質(Cortical Substance)からなります。
腎臓(Kidney, H&E染色)
高倍率でネフロン(Nephron)の異なる領域を確認します。ネフロンは腎臓の構造的かつ機能的単位(Structural and Functional Unit)です。ネフロンは以下の部分で構成されています:
- 腎小体(Renal Corpuscle)
- 血管性糸球体(Vascular Glomerulus)とその包(Bowman’s Capsule)で構成される。
- 近位尿細管(Proximal Convoluted Tubule)
- ヘンレループ(Loop of Henle)
- 太い下降脚(Thick Descending Segment)、薄いU字型脚(Thin U-Shaped Segment)、太い上行脚(Thick Ascending Segment)を含む。
- 遠位尿細管(Distal Convoluted Tubule)
腎臓の排泄部分(Excretory Portion)は、遠位尿細管(Distal Convoluted Tubule)と連続する集合細管(Collecting Tubules)から始まります。
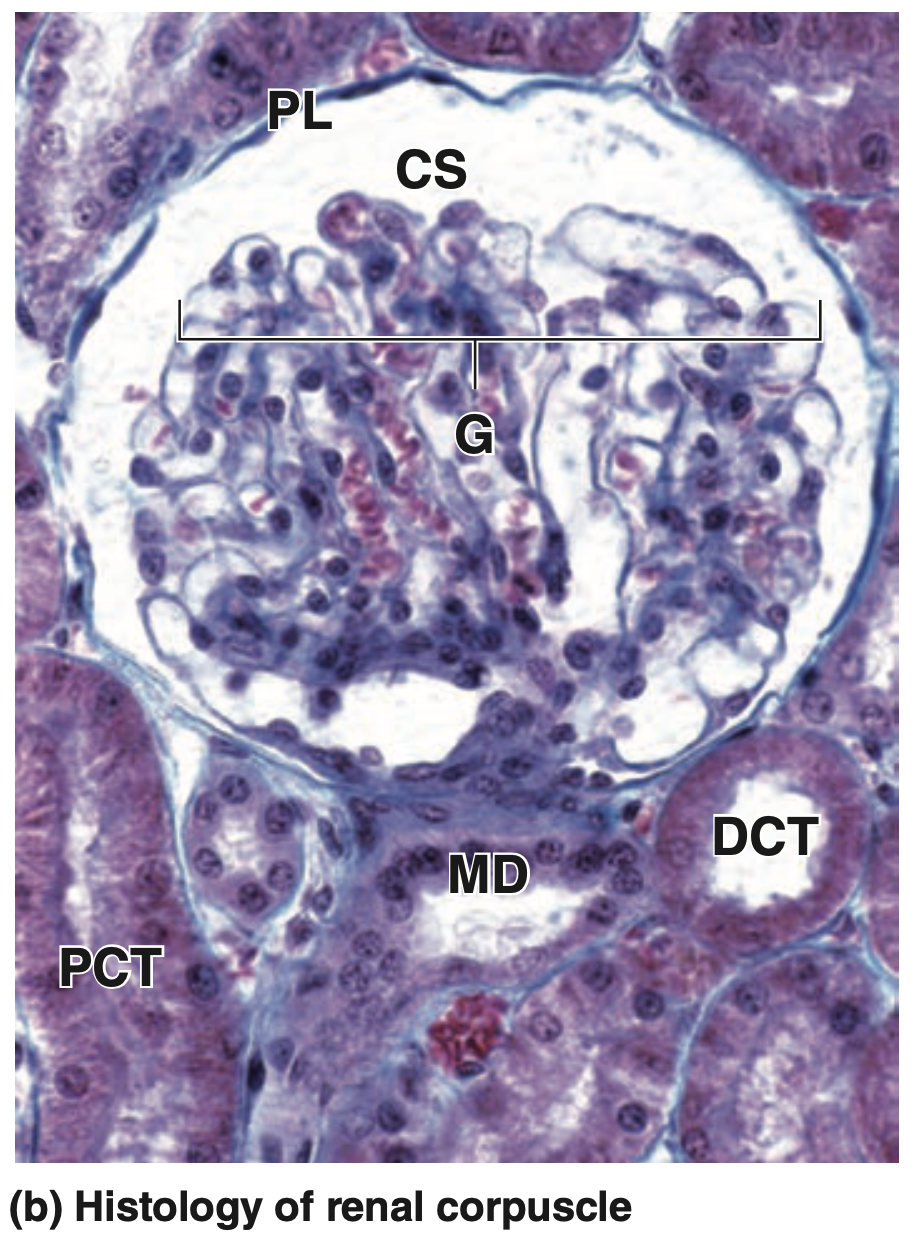 | (b) The micrograph shows the major histologic features of a renal corpuscle. The glomerulus (G) of capillaries is surrounded by the capsular space (CS) covered by the simple squamous parietal layer (PL) of Bowman capsule. Near the corpuscle is that nephron’s macula densa (MD) and sections of proximal convoluted tubules (PCT) and distal convoluted tubules (DCT). (H&E; X300) |
腎小体(Renal Corpuscle)の中では、血管性毛細血管球(Vascular Capillary Tuft)である糸球体(Glomerulus)を確認します。輸入細動脈(Afferent Arteriole)の入口と輸出細動脈(Efferent Arteriole)の出口がある血管極(Vascular Pole)を特定します。
また、ボウマン嚢(Bowman’s Capsule)の内臓葉(Visceral Layer)および壁側葉(Parietal Layer)を認識し、ボウマン嚢の壁側葉が近位尿細管(Proximal Convoluted Tubule)と連続している腎小体を探します。この接続部が尿極(Urinary Pole)であり、血管極の反対側に位置します。
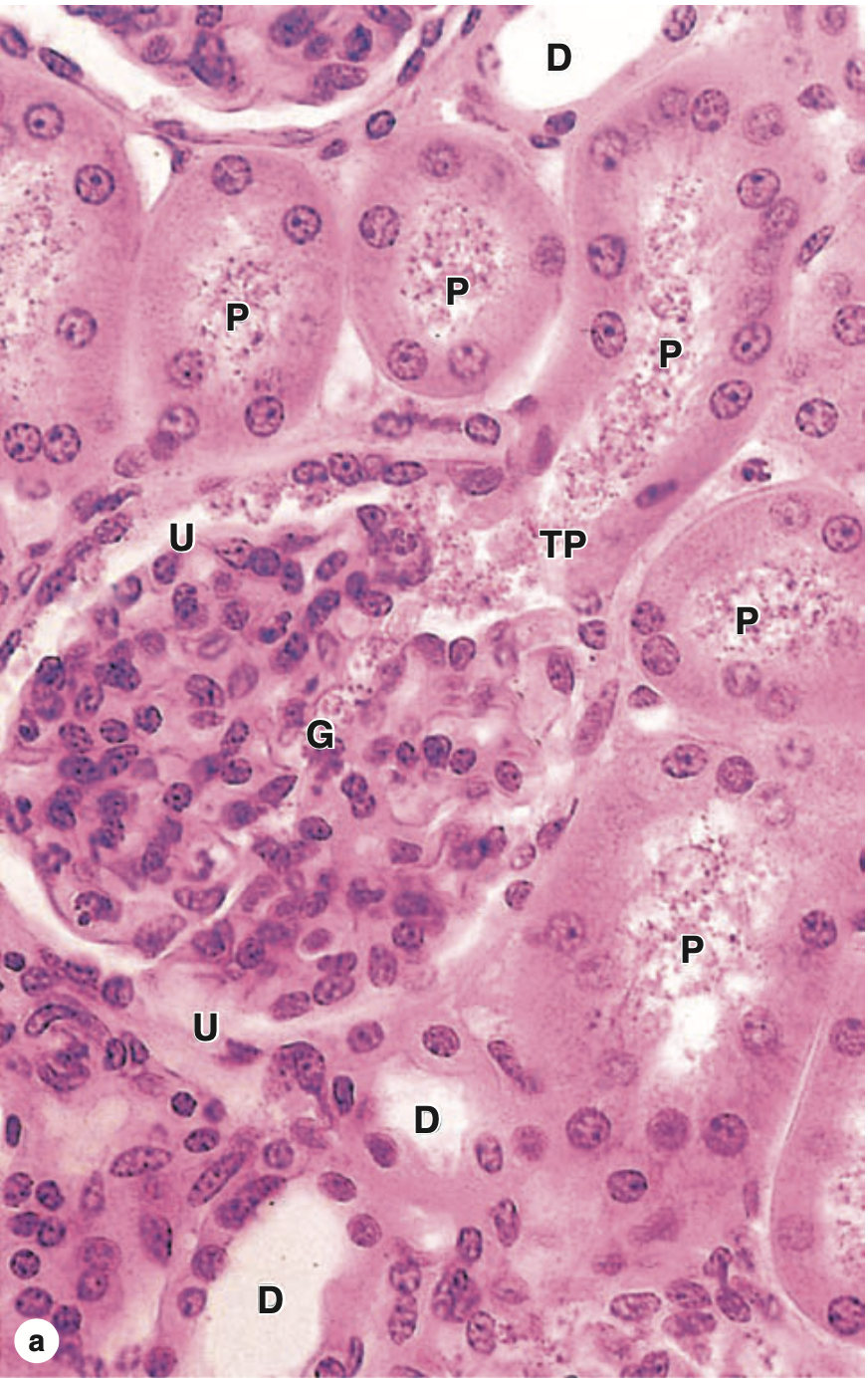 | (a) The micrograph shows the continuity at a renal corpuscle’s tubular pole (TP) between the simple cuboidal epithelium of a proximal convoluted tubule (P) and the simple squamous epithelium of the capsule’s parietal layer. The urinary space (U) between the parietal layer and the glomerulus (G) drains into the lumen of the proximal tubule. The lumens of the proximal tubules appear filled, because of the long microvilli of the brush border and aggregates of small plasma proteins bound to this structure. By contrast, the lumens of distal convoluted tubules (D) appear empty, lacking a brush border and protein. |
 | (b) Here the abundant peritubular capillaries and draining venules (arrows) surrounding the proximal (P) and distal (D) convoluted tubules are clearly seen. (Both X400; H&E) |
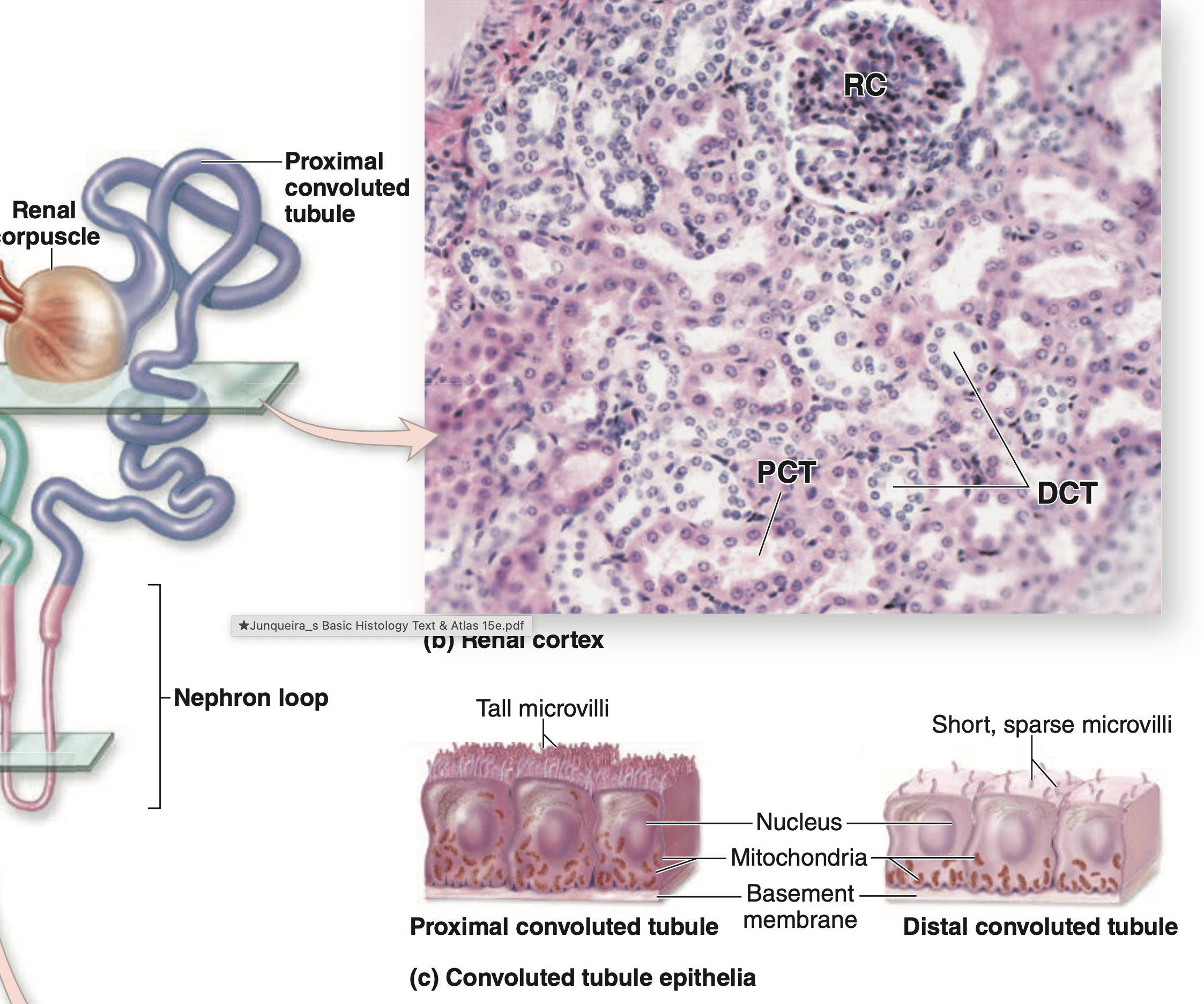 | (a) Diagram of a nephron shows levels of the sections in the photos. (b) A section of cortical tissue shows one renal corpuscle (RC), the wide, eosinophilic proximal convoluted tubules (PCT) with the smaller, less well-stained distal convoluted tubules (DCT). (X160; H&E) (c) Diagram shows the major structural differences between the cuboidal cells of proximal and distal tubules. Cells of both tubules have basal membrane invaginations associated with mitochondria. |
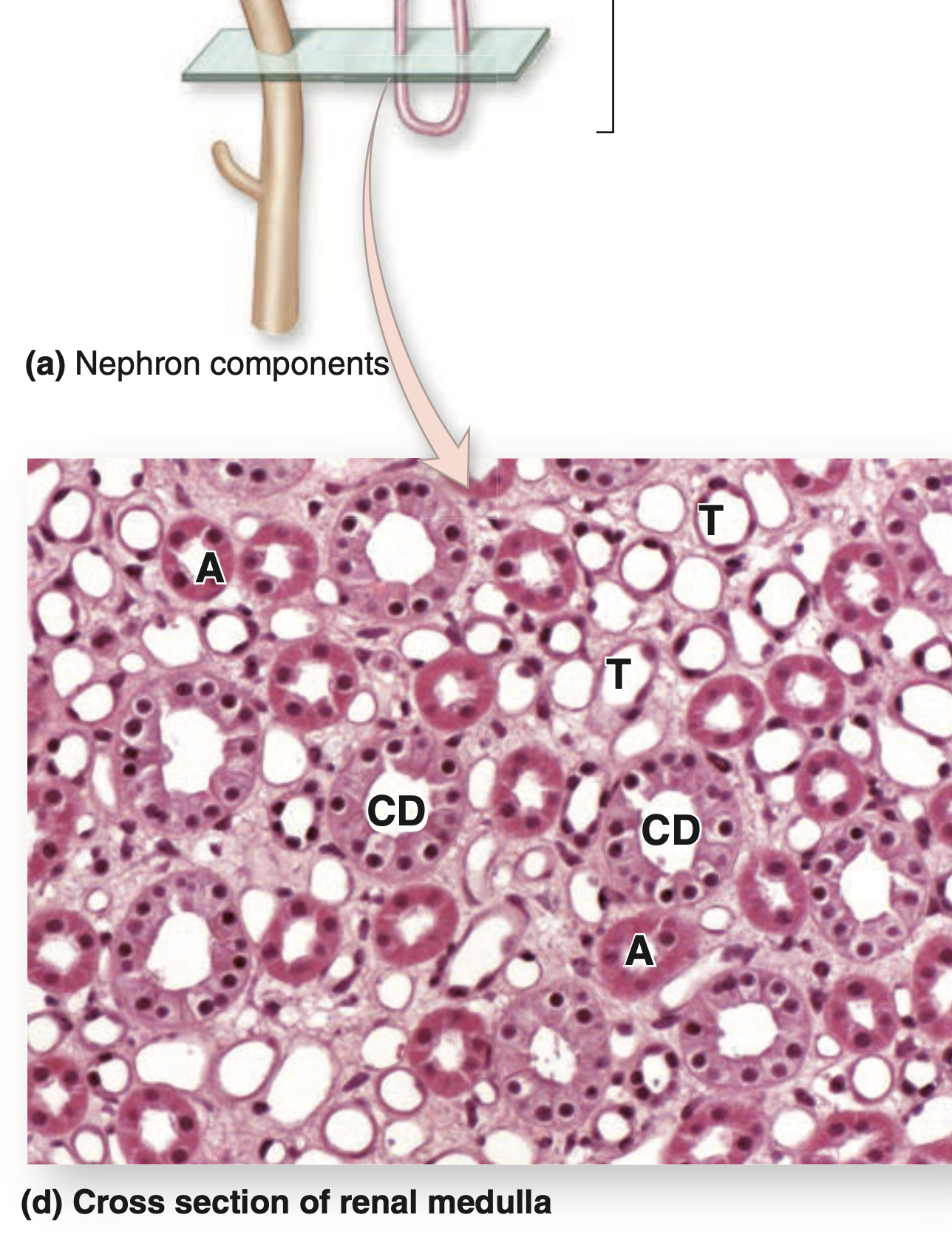 | (d) A cross section through a medullary renal pyramid shows the simple squamous epithelium of the thin descending and ascending limbs of loops of Henle (T) and its thick ascending limbs (A), as well as the pale columnar cells of collecting ducts (CD). Note also the homogeneous interstitium with capillaries smaller than the thin limbs. (X160; Mallory trichrome) |
尿管(Ureter, H&E染色)
低倍率(Low Power Magnification, LPM)
尿管は星形の管腔(Stellate-Shaped Lumen)と厚い裏打ち上皮(Lining Epithelium)を示します。筋層(Muscle Coat)は線維性外膜(Fibrous Adventitia)に囲まれ、その中に多数の血管(Vascular Channels)や神経線維(Nerve Fibers)が尿管とともに走行しています。
高倍率(Higher Magnification)
特徴的な移行上皮(Transitional Epithelium)を観察し、表面細胞(Surface Cells)のドーム状または膨らんだ外観(Dome-Shaped or Bulging Appearance)と、その強い染色親和性(Staining Affinities)に注目します。尿管壁(Wall of the Ureter)は以下の層で構成されます:
- 粘膜(Mucosa)
- 上皮(Epithelium)とその下の結合組織(Underlying Connective Tissue)。
- 筋層(Muscularis)
- 外膜(Adventitia)
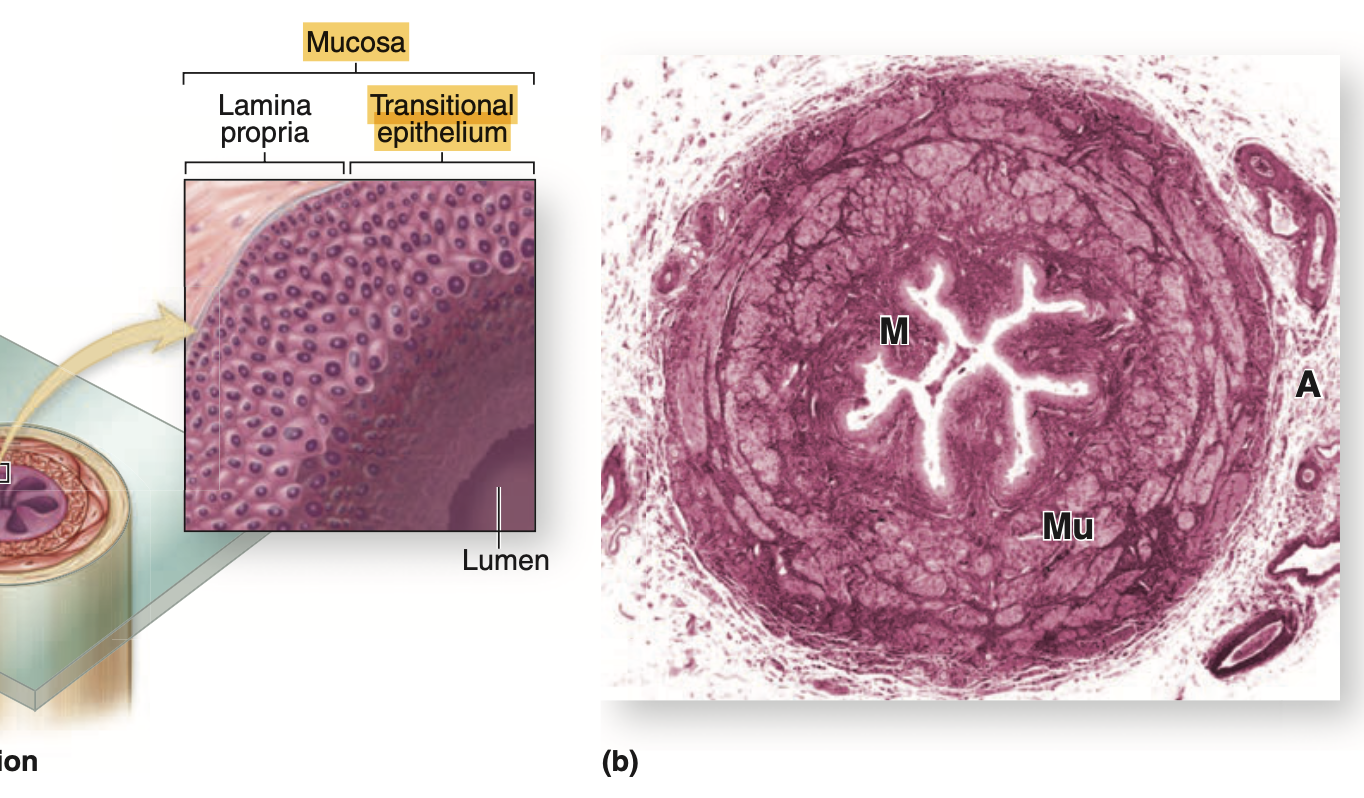 | (a) Diagram of a ureter in cross section shows a characteristic pattern of longitudinally folded mucosa, surrounded by a thick muscularis that moves urine by regular waves of peristalsis. The lamina propria is lined by a unique stratified epithelium called transitional epithelium or urothelium that is resistant to the potentially deleterious effects of contact with hypertonic urine. (b) Histologically the muscularis (Mu) is much thicker than the mucosa (M) and adventitia (A). (X18; H&E) |
膀胱(Urinary Bladder, H&E染色)
膀胱は移行上皮(Transitional Epithelium)で覆われており、一部の細胞は二核性(二核細胞, Binucleated)です。上皮は基底膜(Basal Lamina)によって基底結合組織(Underlying Connective Tissue)から分離されています。この結合組織は、固有層(Lamina Propria)と粘膜下層(Submucosa)に分けられることがあります。この領域の血管性(Vascularity)は、多数の細静脈(Venules)や細動脈(Arterioles)によって示されます。
また、厚い筋層(Thick Muscularis)は以下の3層の平滑筋(Smooth Muscle)から構成されています:
- 内縦走筋(Inner Longitudinal, IL)
- 中輪走筋(Middle Circular, MC)
- 外縦走筋(Outer Longitudinal, OL)
筋層は疎性結合組織(Loose Connective Tissue)で構成された外膜(Adventitia)に囲まれています。
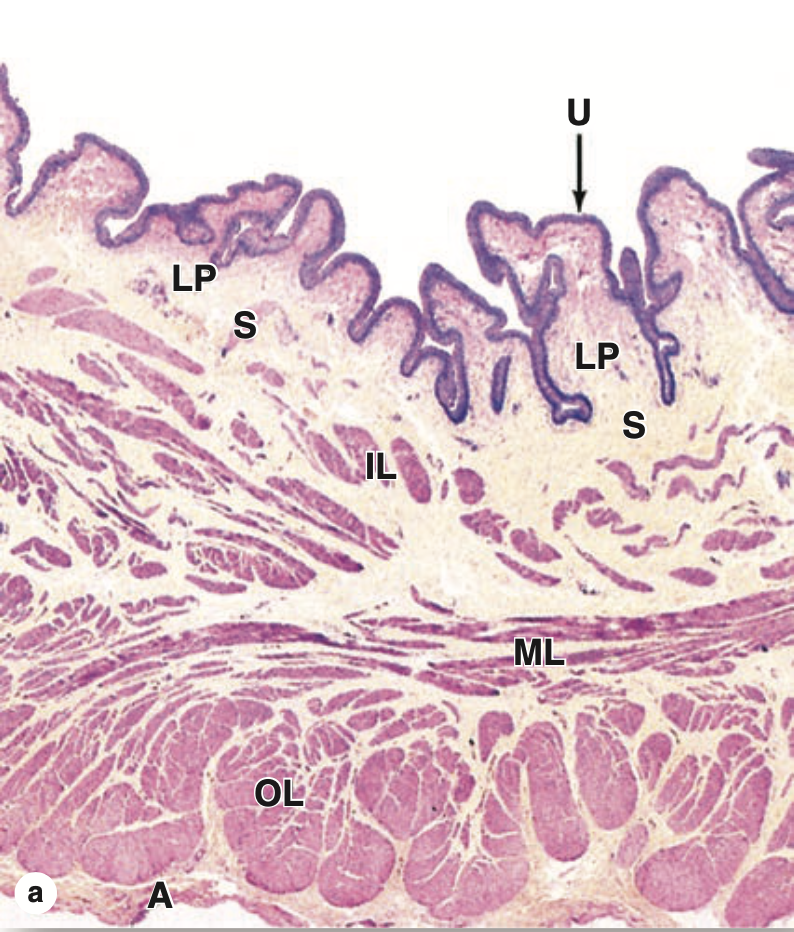 | (a) In the neck of the bladder, near the urethra, the wall shows four layers: the mucosa with urothelium (U) and lamina propria (LP); the thin submucosa (S); inner, middle, and outer layers of smooth muscle (IL, ML, and OL); and the adventitia (A). (X15; H&E) |
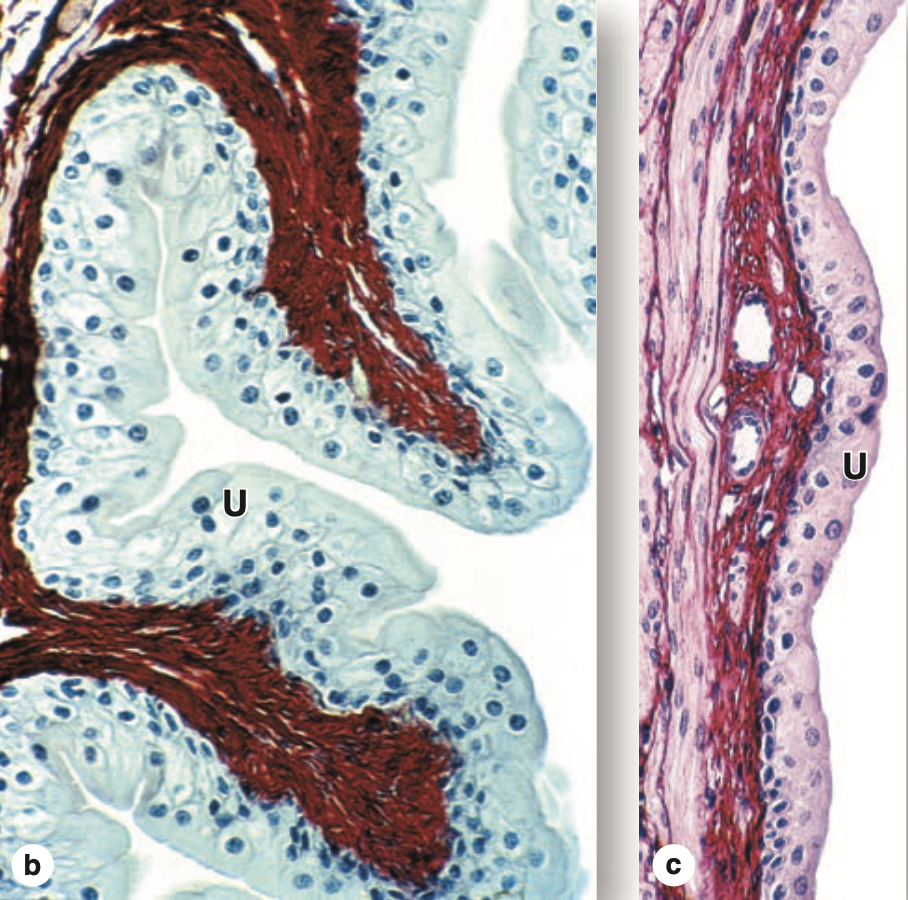 | (b) When the bladder is empty, the mucosa is highly folded and the urothelium (U) has bulbous umbrella cells. (X250; PSH) (c) When the bladder is full, the mucosa is pulled smooth, the urothelium (U) is thinner, and the umbrella cells are flatter. (X250; H&E) |
尿道(Urethra, H&E染色)
低倍率(Lowest Magnification)
陰茎尿道(Penile Urethra)の特徴的な管腔(Lumen)の形状と、海綿状の勃起組織(Sponge-Like Erectile Tissue)が血液で満たされている配置によって容易に識別できます。
上皮の観察(Epithelial Lining)
陰茎尿道の上皮(Epithelial Lining)の外観は、同じ切片の異なる領域で変化することがあります。最も一般的には、疑似重層円柱上皮(Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium)または重層円柱上皮(Stratified Columnar Epithelium)として現れます。
粘液腺(Mucous Glands)は、上皮細胞の巣状配置(Nests of Epithelial Cells)として上皮内腺(Intra-Epithelial Glands)として存在することがあります。または、典型的な尿道腺(Littre腺, Urethral Glands of Littre)として存在し、その導管(Ducts)は尿道管腔(Urethral Lumen)の局所窪みに開口します。
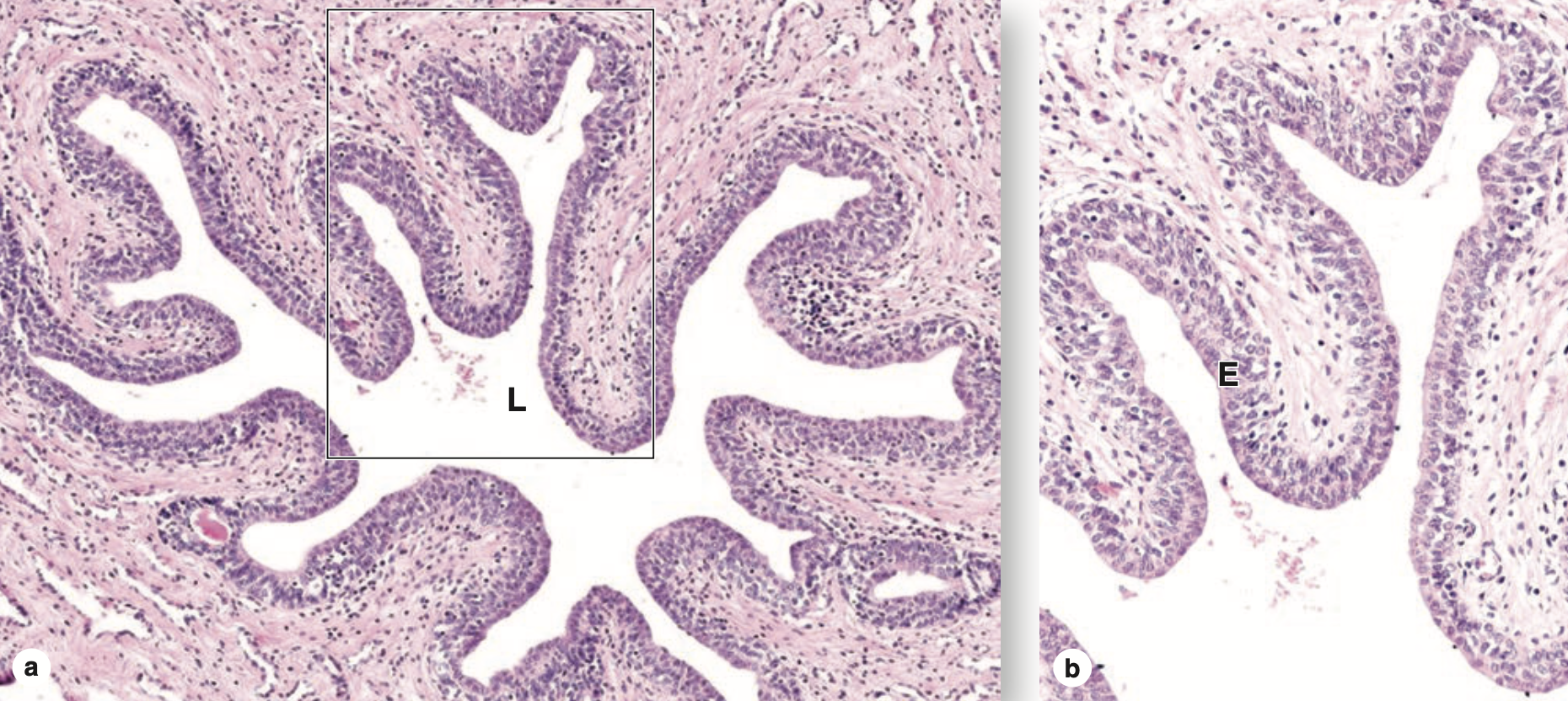 | The urethra is a fibromuscular tube that carries urine from the bladder to the exterior of the body. (a) A transverse section shows that the mucosa has large longitudinal folds around the lumen (L). (X50; H&E) (b) A higher magnification of the enclosed area shows the unusual stratified columnar nature of the urethral epithelium (E). This thick epithelial lining varies between stratified columnar in some areas and pseudostratified columnar elsewhere, but it becomes stratified squamous at the distal end of the urethra. (X250; H&E) |


コメント