Contents
- 1 教科書サマリー
- 2 過去問(50問)
- 2.1 Question:腹部尿管のリンパ管
- 2.2 Question:中副腎動脈
- 2.3 Question:腎臓の位置
- 2.4 Question:大腰筋
- 2.5 Question:上副腎動脈
- 2.6 Question:腎臓は5つのセグメント
- 2.7 Question:左腎の後面
- 2.8 Question:腎臓と横隔膜
- 2.9 Question:右副腎静脈
- 2.10 Question:尿管と総腸骨動脈
- 2.11 Question:尿管の狭窄部位
- 2.12 Question:左腎静脈の排出先
- 2.13 Question:副腎皮質
- 2.14 Question:尿路結石
- 2.15 Question:腎門部
- 2.16 Question:尿管の平均長
- 2.17 Question:右腎と十二指腸
- 2.18 Question:腎乳頭
- 2.19 Question:腎臓の内外側縁
- 2.20 Question:腎臓のリンパ管
- 2.21 Question:右腎の位置
- 2.22 Question:尿管の血管吻合
- 2.23 Question:腎炎症
- 2.24 Question:腎臓の下極
- 2.25 Question:腎筋膜
- 2.26 Question:nephros/nephroi
- 2.27 Question:ゲロータ筋膜(Gerota’s fascia)
- 2.28 Question:近位尿細菅への血液共有
- 2.29 Question:腎臓の大きさ
- 2.30 Question:前上区域動脈
- 2.31 Question:ベルティニ腎柱(renal columns of Bertini)
- 2.32 Question:腎洞(renal sinus)
- 2.33 Question:腎臓の葉(lobe)
- 2.34 Question:腎盂
- 2.35 Question:腎動脈の位置
- 2.36 Question:腎臓上極間の空間
- 2.37 Question:腎下垂症(nephroptosis)
- 2.38 Question:腎門と幽門横断面
- 2.39 Question:副腎と後腹壁
- 2.40 Question:尿管と総腸骨動脈
- 2.41 Question:腎乳頭と遠位集合管
- 2.42 Question:尿管腹部部分と腎動脈
- 2.43 Question:腎臓内臓求心性神経線維
- 2.44 Question:弓状動脈
- 3 自作問題教科書
- 3.1 Question:後腹膜器官
- 3.2 Question:腎臓の位置
- 3.3 Question:腎筋膜
- 3.4 Question:腎門部
- 3.5 Question:左腎の位置
- 3.6 Question:尿管狭窄部
- 3.7 Question:右副腎
- 3.8 Question:副腎皮質ホルモン
- 3.9 Question:腎筋膜
- 3.10 Question:呼吸時の腎臓位置
- 3.11 Question:上部分節動脈
- 3.12 Question:左腎静脈
- 3.13 Question:腎神経叢
- 3.14 Question:尿路結石
- 3.15 Question:右副腎静脈
- 3.16 Question:腎動脈の位置
- 3.17 Question:副腎と下横隔動脈
- 3.18 Question:尿管と動脈
- 3.19 Question:副腎髄質と神経
- 3.20 Question:尿管結石
- 3.21 Question:左副腎静脈
- 3.22 Question:尿管の腹部部分
- 3.23 Question:腎臓からのリンパ
- 3.24 Question:副腎髄質と神経
- 3.25 Question:腎臓鏡
- 3.26 Question:尿管の弁
- 3.27 Question:尿管と精管
- 3.28 Question:下膀胱動脈
- 3.29 Question:内尿道括約筋
- 3.30 Question:尿管と子宮動脈
- 3.31 Question:膀胱と直腸
- 3.32 Question:小児の膀胱位置
- 3.33 Question:パラコルピウム
- 3.34 Question:膀胱頂部
- 3.35 Question:女性外尿道口
- 3.36 Question:尿管と子宮動脈
- 3.37 Question:尿管とリンパ節
- 3.38 Question:デトルソル筋
- 3.39 Question:射精管
- 3.40 Question:前立腺静脈叢と膀胱静脈叢
教科書サマリー
腎臓(Kidneys)
- 位置: 原発性後腹膜臓器(primary retroperitoneal organs)で、T12〜L3椎骨レベルに位置し、第12肋骨の深部にあります。
- 脂肪組織: 腎周囲脂肪(perinephric fat)に包まれており、腎筋膜(renal fascia)によって傍腎脂肪(paranephric fat)と分離されています。
- 移動: 横隔膜の動きに伴い上下に移動します。
- 副腎(Suprarenal glands): 腎臓の上内側(superomedial)に位置しますが、腎臓に直接付着していません。
- 構造: 腎臓は中空で腎洞(renal sinus)を持ち、その中に腎杯(renal calices)、腎盂(renal pelvis)、区域動脈(segmental arteries)、および腎静脈(renal veins)が含まれています。
- 尿の流れ: 腎錐体(renal pyramids)の乳頭部(papillae)が尿を小腎杯(minor calices)に排出し、それが合流して大腎杯(major calices)、さらに腎盂(renal pelvis)になります。
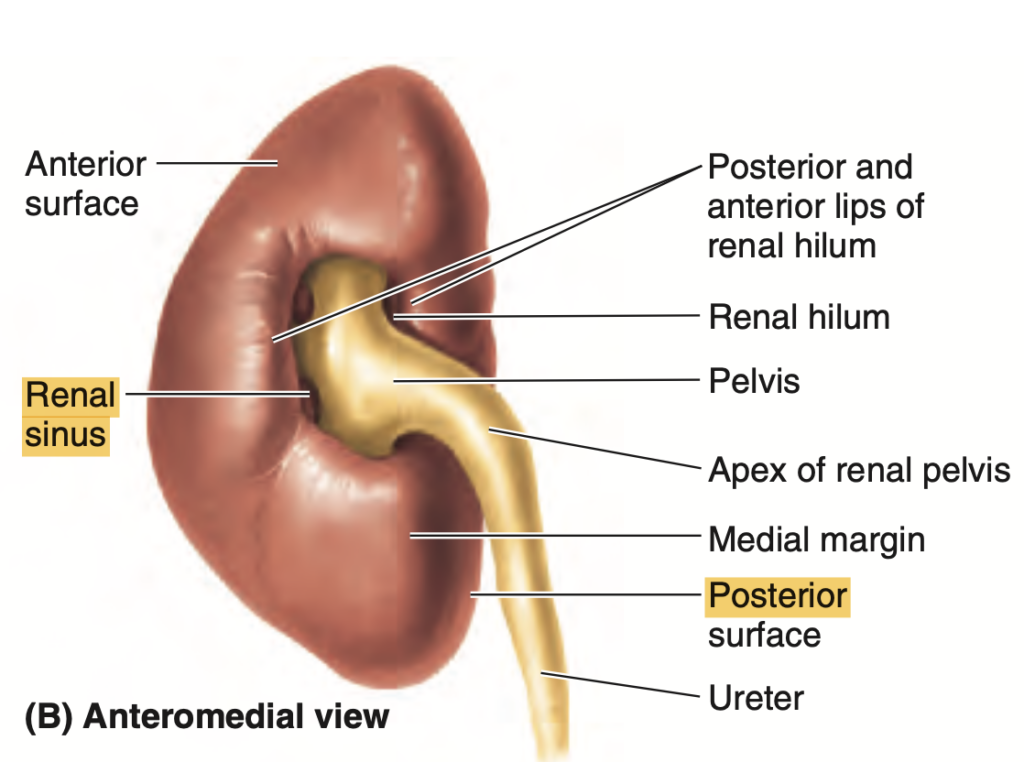
- 腎門(Hilum): 血管構造や腎盂が腎門を通じて出入りします。
尿管(Ureters)
- 走行: 腎盂から骨盤縁(pelvic brim)に至るまで、大腰筋(psoas muscles)の前面を下降します。
- 結石が詰まりやすい部位:
- 腎盂尿管移行部(ureteropelvic junction)
- 骨盤縁(pelvic brim)
- 膀胱壁(bladder wall)
- 血液供給: 腎動脈(renal artery)、精巣/卵巣動脈(testicular/ovarian artery)、総腸骨動脈(common iliac artery)、腹大動脈(abdominal aorta)から供給されます。
- 位置推定: 腰椎棘突起の外側5 cmに垂直線を引くことで大まかに位置を推定可能です。
副腎(Suprarenal Glands)
- 位置: 腎臓の上内側(superomedial)に位置し、腎筋膜(renal fascia)を介して横隔膜脚(diaphragmatic crura)に付着しています。
- 構成:
- 副腎皮質(suprarenal cortex): 中胚葉(mesoderm)由来で、コルチコステロイド(corticosteroids)とアンドロゲン(androgens)を分泌します。
- 副腎髄質(suprarenal medulla): 神経堤細胞(neural crest cells)由来で、カテコールアミン(catecholamines)を分泌します。
- 形状: 右副腎は三角形(pyramidal)で腎臓の頂端に近く、左副腎は三日月形(crescent-shaped)で腎臓の上部内側に位置します。
神経血管(Neurovasculature)
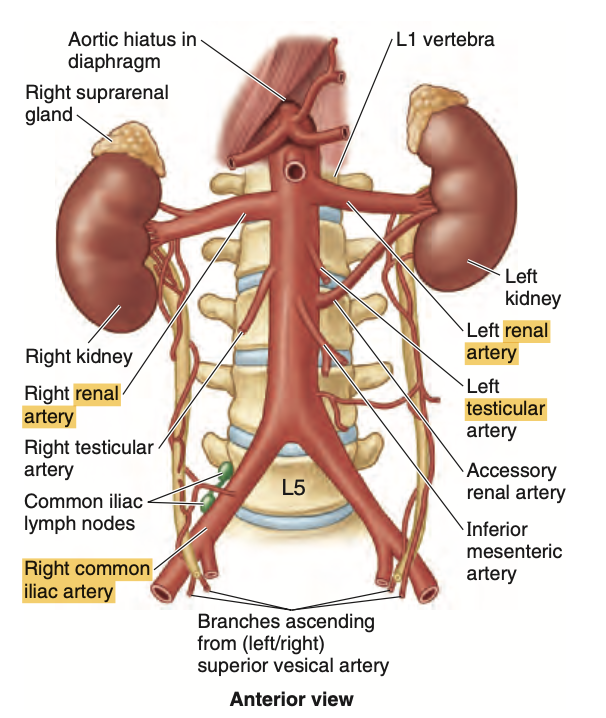
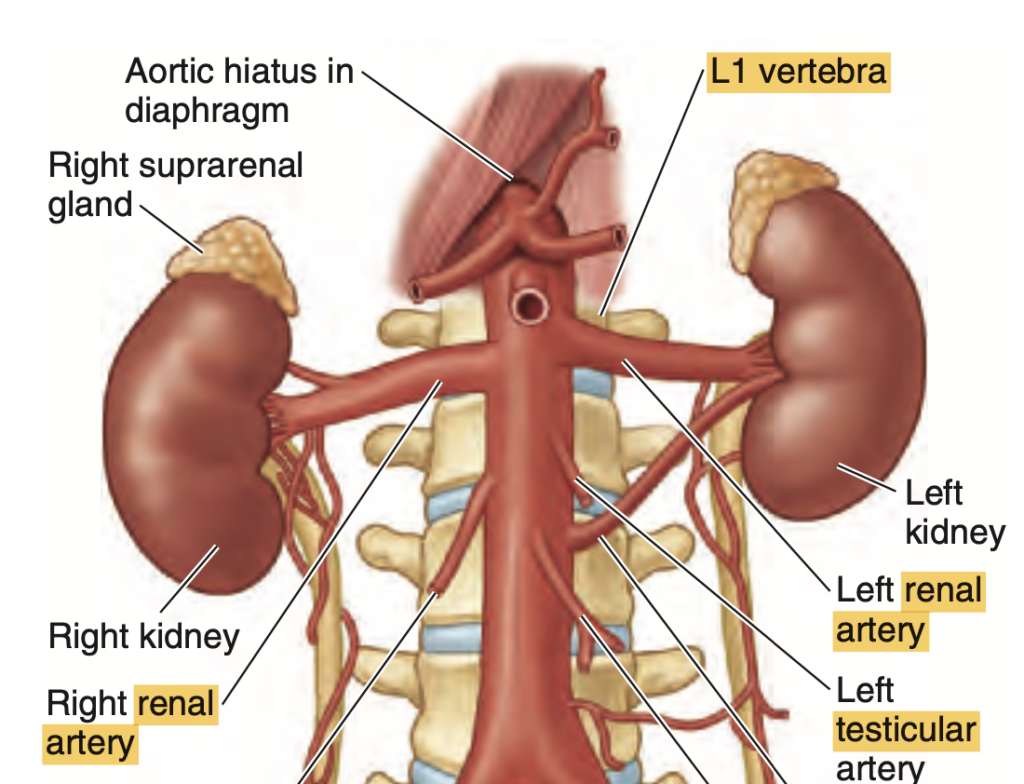
- 腎動脈(Renal Arteries): 腹大動脈(abdominal aorta)からL1〜L2レベルで分岐し、右腎動脈は左よりも長い。腎門近くで前枝と後枝に分かれ、さらに4つの区域動脈に分岐します。
- 腎静脈(Renal Veins): 下大静脈(IVC)に流入し、左腎静脈は右よりも長く、左副腎静脈(left suprarenal vein)、左性腺静脈(left gonadal vein)、左上行腰静脈(left ascending lumbar vein)を受け入れます。
- 副腎動脈(Suprarenal Arteries):
- 上副腎動脈(superior suprarenal arteries): 下横隔動脈(inferior phrenic arteries)から分岐
- 中副腎動脈(middle suprarenal arteries): 腹大動脈から分岐
- 下副腎動脈(inferior suprarenal arteries): 腎動脈から分岐
- 副腎静脈(Suprarenal Veins): 右は下大静脈に、左は左腎静脈に流入します。
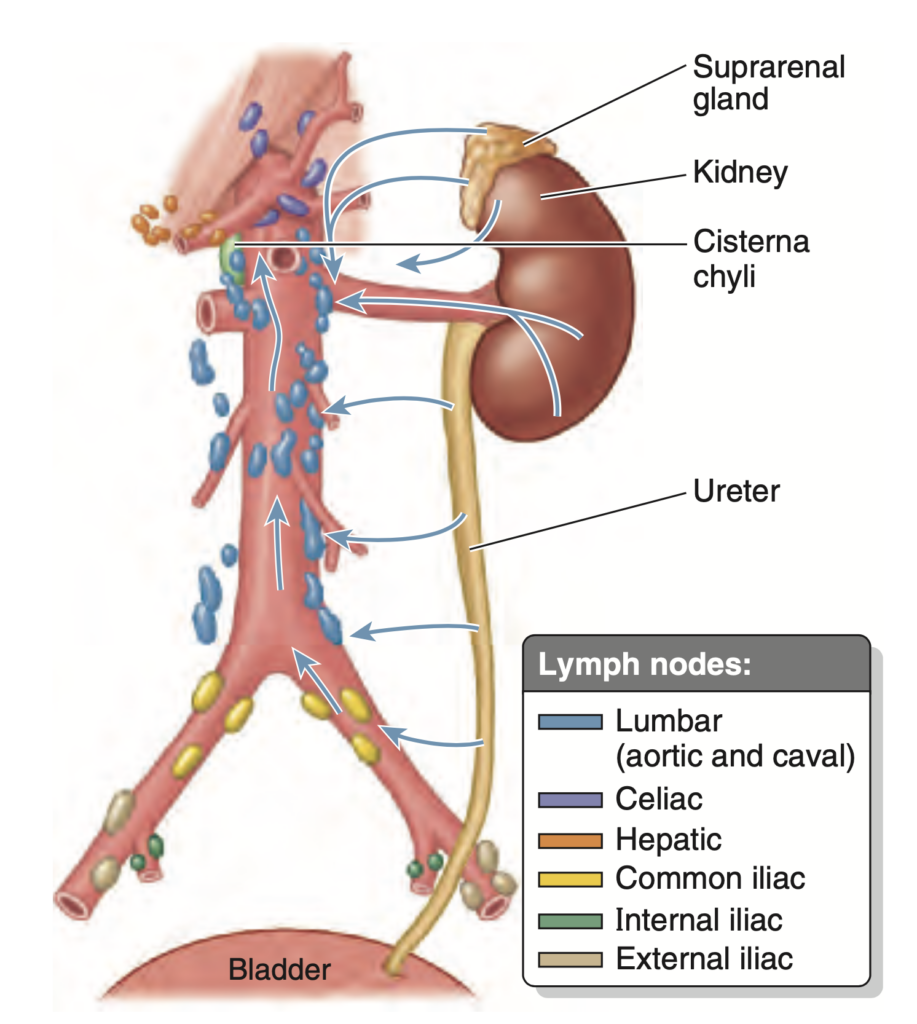
リンパ系(Lymphatics)
- 排出経路: 副腎(suprarenal glands)、腎臓(kidneys)、および尿管上部(upper ureters)は、静脈排出路に沿って腰部リンパ節(lumbar lymph nodes, caval or aortic)にリンパを排出します。
神経支配(Innervation)
腎臓と尿管
- 痛覚線維(Visceral afferent fibers):
- 尿管からの痛覚信号はT11〜L2脊髄節(spinal segments)に伝達され、腰部(loin)や鼠径部(groin)の皮膚分節に関連する放散痛を引き起こします。
副腎
- 交感神経(Sympathetic fibers):
- T10〜L1の交感神経節前線維(presynaptic sympathetic fibers)は、副腎髄質(suprarenal medulla)のクロマフィン細胞(chromaffin cells)で終止し、シナプスを介さず直接刺激を伝えます。
尿管(Ureters)
- 機能: 腎盂(renal pelvis)から膀胱(urinary bladder)まで尿を運搬します。
- 走行: 腹膜下(subperitoneally)で骨盤内に下降します。
- 男性: 精管(ductus deferens)の下を通過
- 女性: 子宮動脈(uterine artery)の下を通過
- 手術上の重要性: 手術中、尿管がこれらの構造物に隣接しているため注意が必要です。
- 膀胱壁への進入: 尿管は膀胱壁に斜めに進入し、逆流を防ぐ一方向の弁を形成します。
- 血液供給:
- 男性: 下膀胱動脈(inferior vesical artery)
- 女性: 膣動脈(vaginal artery)
- 静脈排出は膀胱静脈叢(vesical venous plexus)と内腸骨静脈(internal iliac veins)を介します。
- 結石の停滞部位: 骨盤縁(pelvic brim)および膀胱入口(bladder entry)は結石が詰まりやすく、鼠径部の激痛を引き起こします。
膀胱(Urinary Bladder)
- 構造:
- 体部(Body): 拡張性が高く、腹膜外脂肪(extraperitoneal fat)に囲まれ、腹膜(peritoneum)で覆われています。充満時に拡張が可能。
- 頸部(Neck): 骨盤靭帯(pelvic ligaments)によって固定され、充満中も安定性を維持します。この領域には三角部(trigone)が含まれます。
- 血液供給:
- 体部: 上膀胱動脈(superior vesical arteries)と静脈が供給
- 頸部: 下膀胱動脈(inferior vesical arteries)
- 神経支配:
- 交感神経(Sympathetic fibers):
- 下胸部および上腰部の脊髄節(inferior thoracic and superior lumbar segments)から供給され、膀胱頸部の緊張を維持します(男性では精液逆流を防止)。
- 副交感神経(Parasympathetic fibers):
- S2〜S4の脊髄節から供給され、膀胱頸部を弛緩させ、排尿筋(detrusor muscle)を刺激します。
- 痛覚線維:
- 膀胱頂部の痛みは交感神経経路を通じて伝達され、その他の部位は副交感神経線維を介します。
- 交感神経(Sympathetic fibers):
尿道(Urethra)
男性
- 構造: 4つの部分に分けられます。
- 壁内部(Intramural part): 膀胱の充満または排尿によって長さが変化します。
- 前立腺部(Prostatic urethra): 前立腺に囲まれ、前立腺管(prostatic ducts)が開口します。
- 生殖と排尿: 前立腺部で生殖管と尿路が合流します。
女性
- 構造: 尿道は膣(vagina)に並行して走行し、生殖器とは共有していません。そのため、内部尿道括約筋(internal urethral sphincter)が存在しません。
直腸(Rectum)
- 機能: 一時的に糞便を貯蔵し、直腸S状部接合部(rectosigmoid junction)で始まります。
- 終端: 骨盤横隔膜(pelvic diaphragm)を通過して肛門管(anal canal)となる肛門直腸屈曲部(anorectal flexure)で終了します。
- 構造:
- 屈曲: 内側の横方向直腸ヒダ(transverse rectal folds)によって仙骨屈曲部(sacral flexures)と側方屈曲部(lateral flexures)があります。
- 直腸膨大部(Rectal ampulla): 骨盤底の上で拡張します。
- 血液供給: 上直腸動脈および中直腸動脈(superior and middle rectal vessels)の吻合により供給され、門脈体循環吻合(portocaval venous anastomosis)が存在します。
- 神経支配:
- 交感神経(Sympathetic fibers): 下腹部/骨盤神経叢(hypogastric/pelvic plexuses)を介して血管および内肛門括約筋(internal anal sphincter)に供給されます。
- 副交感神経(Parasympathetic fibers): 中仙骨部(middle sacral segments)および脊髄神経節(spinal ganglia)を介して繋がります。
過去問(50問)
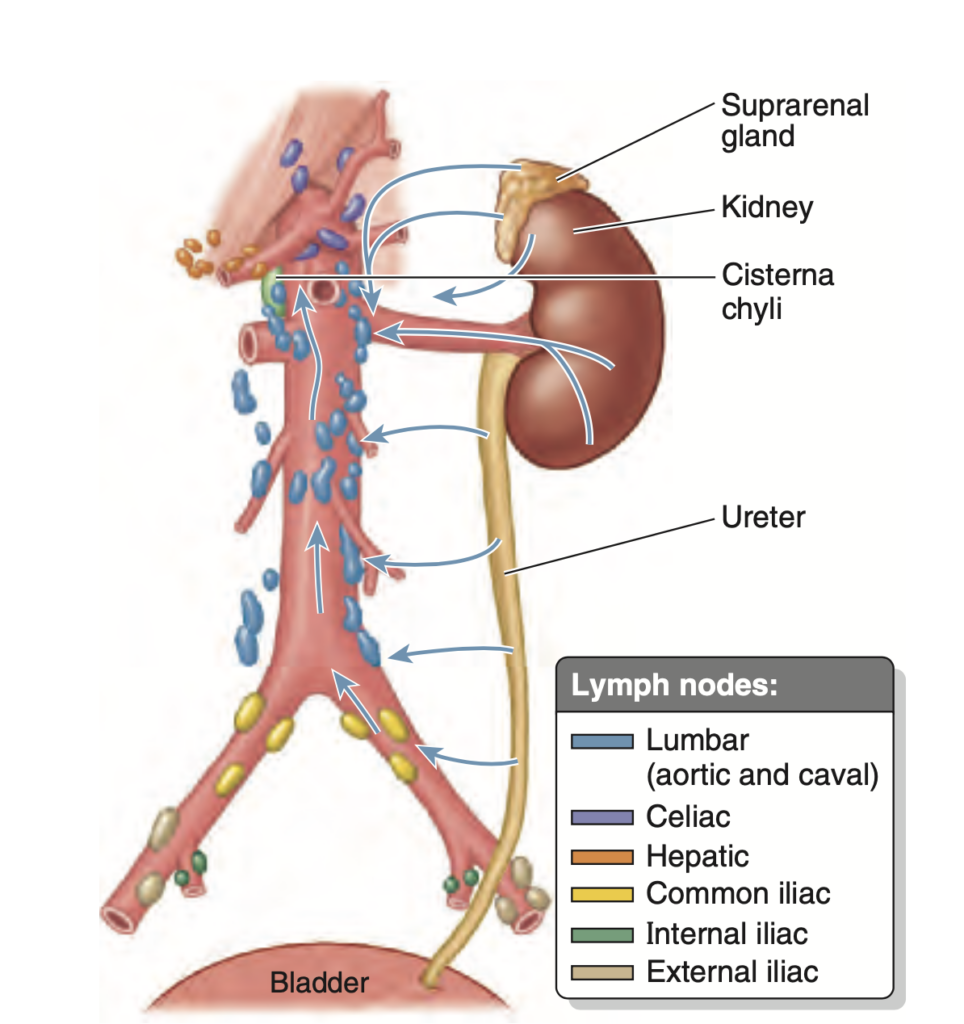
Question:腹部尿管のリンパ管
問題文:Lymphatic vessels draining the abdominal part of the ureter join renal collecting vessels and pass directly first to what group of lymph nodes?
a) Lumbar
b) External Iliac
c) Vena Cava
d) Aortic
Answer: a) Lumbar
解説: 腹部の尿管からリンパ液を排出するリンパ管は、まず腰部(lumbar)のリンパ節に向かいます。これは尿管が腎臓に近接しており、腎臓と同様に腰部リンパ節にリンパを排出するためです。
- b) External Iliac は、骨盤腔のリンパ流と関連が深いため、尿管の腹部とは直接的な関係がありません。
- c) Vena Cava はリンパ節ではなく、主要な静脈であり、リンパ排出の対象とは異なります。
- d) Aortic は一部の臓器からのリンパを受けるものの、尿管の腹部のリンパはまず腰部リンパ節に向かうことが多いです。
尿管の「上部」「中部」「下部」の位置
- 上部(Superior part):
- 腎臓から始まり、腹部を通過する部分が該当します。したがって、abdominal partは尿管の「上部」にあたります。
- 腎臓に近いため、リンパは腎臓からのリンパ管と合流したり、直接腰リンパ節(lumbar nodes)に排出されます。
- 中部(Middle part):
- 尿管が骨盤に向かって下がり始める部分で、骨盤の縁(pelvic brim)に近い位置です。
- この部分のリンパは、通常**総腸骨リンパ節(common iliac lymph nodes)**に排出されます。
- 下部(Inferior part):
- 尿管が骨盤に入り、膀胱へ向かう最終区間です。
- この部分のリンパは**総腸骨、外腸骨、または内腸骨リンパ節(common, external, or internal iliac lymph nodes)**に排出されます。
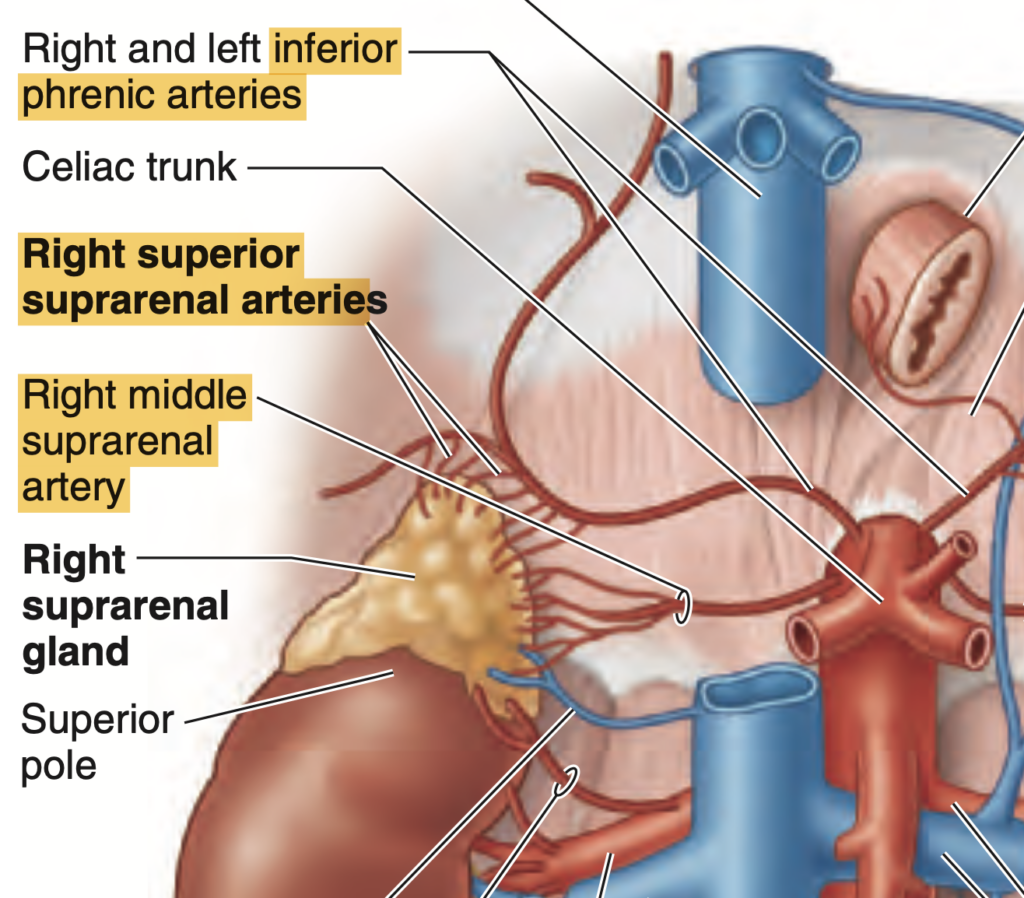
Question:中副腎動脈
問題文:The middle suprarenal artery arises from?
a) Abdominal aorta
b) SMA
c) Inferior phrenic artery
d) IMA
Answer: a) Abdominal aorta
解説: 中副腎動脈(middle suprarenal artery)は、腹部大動脈(abdominal aorta)から直接分岐します。副腎は腹部大動脈と近接しているため、直接供給されることが一般的です。
- b) SMA(上腸間膜動脈)は腸に血液を供給する動脈で、副腎とは関連がありません。
- c) Inferior phrenic artery は上副腎動脈(superior suprarenal arteries)を供給する可能性があるが、中副腎動脈は直接的には供給していません。
- d) IMA(下腸間膜動脈)は下部の消化器官に供給するため、副腎には関連しません。

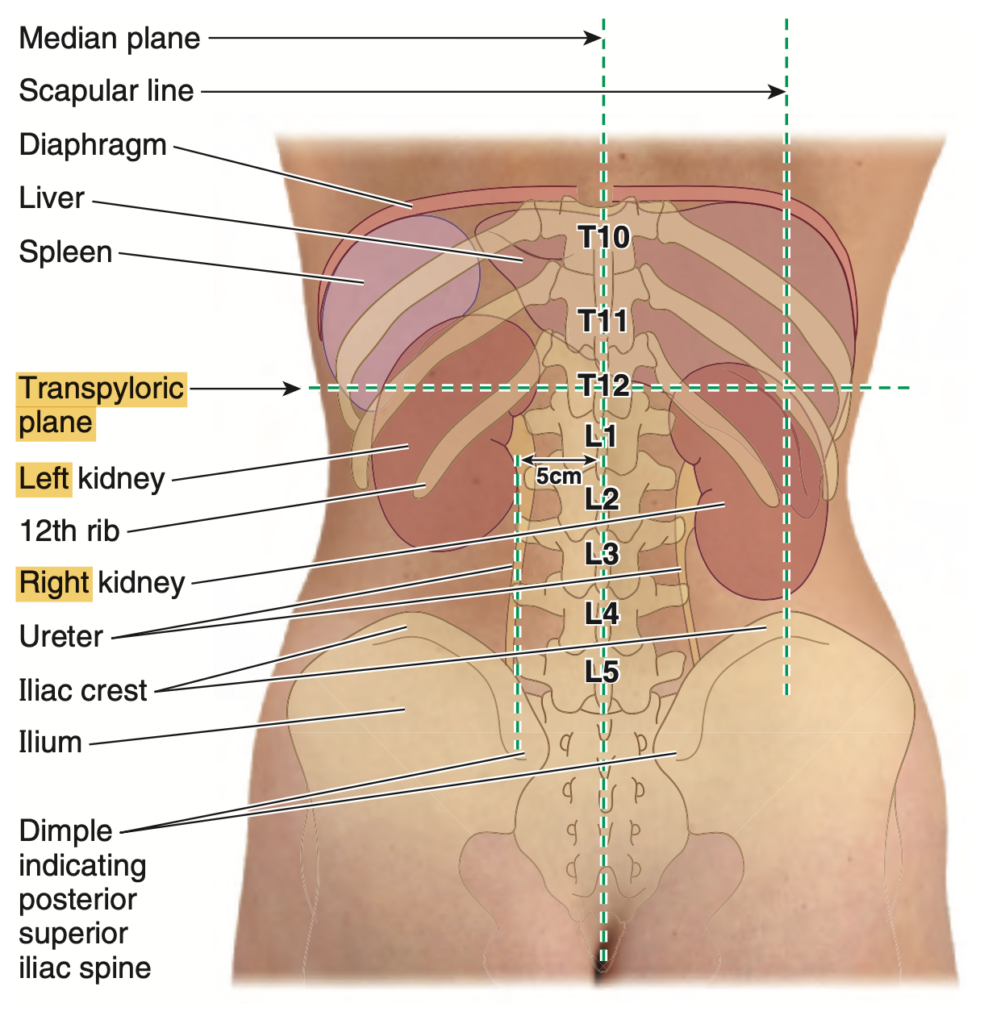
Question:腎臓の位置
問題文:The kidneys in relation to the level of vertebrae are located at:
a) L1-L5
b) T10-L1
c) T9-T12
d) T12-L3
Answer: d) T12-L3
解説: 腎臓の位置は一般的にT12からL3の間に位置しています。右腎は左腎より少し低い位置にあるため、この範囲に収まります。
- a) L1-L5 は通常腎臓の位置を越え、低すぎる範囲となります。
- b) T10-L1 は上すぎる範囲で、腎臓の位置とは一致しません。
- c) T9-T12 も上部すぎて腎臓の範囲とは一致しません。
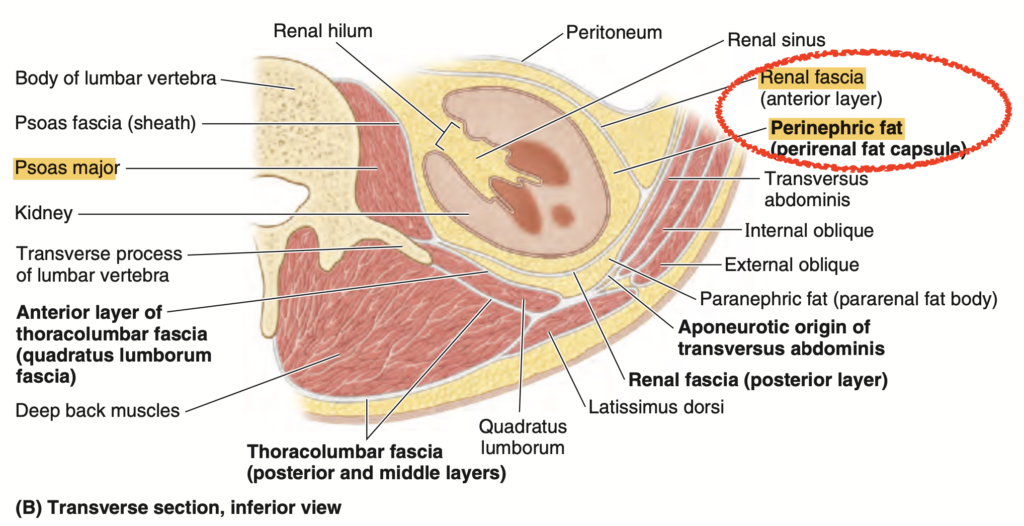
Question:大腰筋
問題文:Which of the following structures occupy the biggest area in relation to the posterior surface of the kidney?
a) 12th Rib Projection
b) Psoas Major Muscle
c) Quadratus Lumborum Muscle
d) Transversus Abdominis Muscle
Answer: b) Psoas Major Muscle
解説: 大腰筋(Psoas Major Muscle)は、腎臓の後面に対して最も広範囲を占めています。腎臓は後腹壁に接しているため、大腰筋が広範囲を覆います。
- a) 12th Rib Projection は腎臓の上部に限られるため、面積は限られます。
- c) Quadratus Lumborum Muscle も腎臓の一部に接していますが、大腰筋よりも面積が小さいです。
- d) Transversus Abdominis Muscle は腎臓の後面にはあまり影響を与えません。
Question:上副腎動脈
問題文:The superior suprarenal arteries arise from?
a) Renal arteries
b) Inferior phrenic artery
c) None of the above
d) Abdominal aorta
Answer: b) Inferior phrenic artery
解説: 上副腎動脈(superior suprarenal arteries)は、下横隔動脈(inferior phrenic artery)から分岐します。この動脈は横隔膜に近い位置にあり、副腎の上部に供給されます。
- a) Renal arteries は腎臓に直接供給する動脈で、副腎の上部に直接供給することはありません。
- c) None of the above は誤りです。
- d) Abdominal aorta は中副腎動脈を供給するものの、上副腎動脈の供給源ではありません。
Question:腎臓は5つのセグメント
問題文:How many segments are there on the kidney when viewed laterally based on Moore’s Clinical Oriented Anatomy textbook?
a) Five
b) Six
c) Four
d) Seven
Answer: a) Five
解説: Moore’s Clinical Oriented Anatomy 教科書によると、腎臓は5つのセグメントに分かれています。それぞれのセグメントは血流が独立しており、腎臓の特定の機能に寄与しています。
- b) Six は、実際の腎セグメント数よりも多すぎます。
- c) Four は少なすぎ、腎臓の分節に正確に対応していません。
- d) Seven は過剰な数で、腎臓の構造に一致しません。
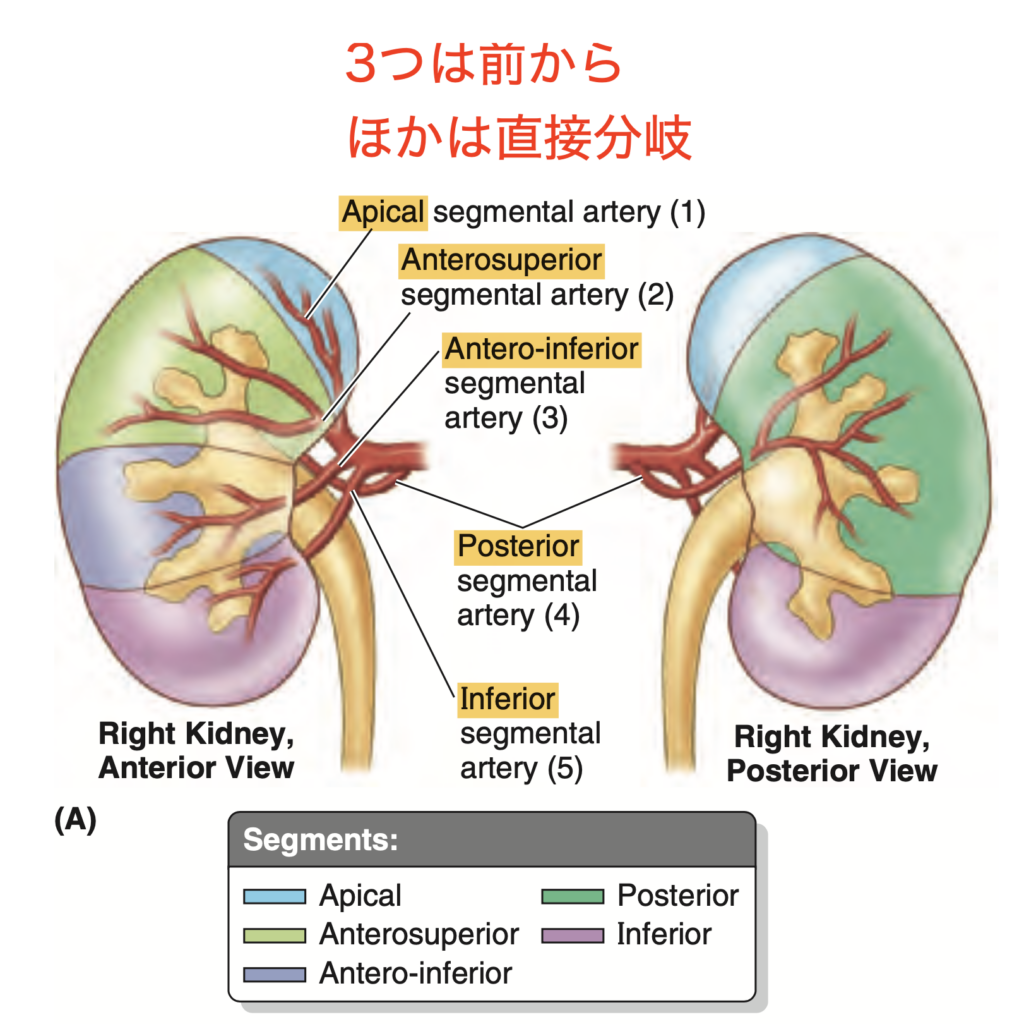
Question:左腎の後面
問題文:Which of the following structures is related to the posterior surface of the left kidney?
a) Ilioinguinal nerve
b) Quadratus lumborum muscle
c) Projection of 11th rib
d) Costodiaphragmatic recess of the pleura
Answer: b) Quadratus lumborum muscle
解説: 左腎の後面は、腰方形筋(Quadratus lumborum muscle)と接しています。これは腎臓の位置と直接関係し、後方の保護となっています。
- a) Ilioinguinal nerve は通常、腎臓の表面よりも外側を走行します。
- c) Projection of 11th rib は腎臓の上部に近接するものの、広範囲には及びません。
- d) Costodiaphragmatic recess of the pleura は胸腔に位置し、腎臓の後面には直接関与しません。

Question:腎臓と横隔膜
問題文:Which of the following structures separate the kidney from the pleural cavity and the 11th or 12th ribs?
a) Psoas Major Muscle
b) Diaphragm
c) Stomach
d) Rectus Sheath
Answer: b) Diaphragm
解説: 横隔膜(diaphragm)は、腎臓と胸膜腔および11番目または12番目の肋骨との間に位置しており、これらの構造を隔てる役割を果たしています。横隔膜は、胸腔と腹腔を分ける筋肉性の膜です。
- a) Psoas Major Muscle は腎臓の後面に接していますが、横隔膜と胸膜腔を隔てる構造ではありません。
- c) Stomach は胃の位置にあり、腎臓と直接的には関係がありません。
- d) Rectus Sheath は腹壁の構造であり、腎臓と胸膜腔の隔たりには関与しません。
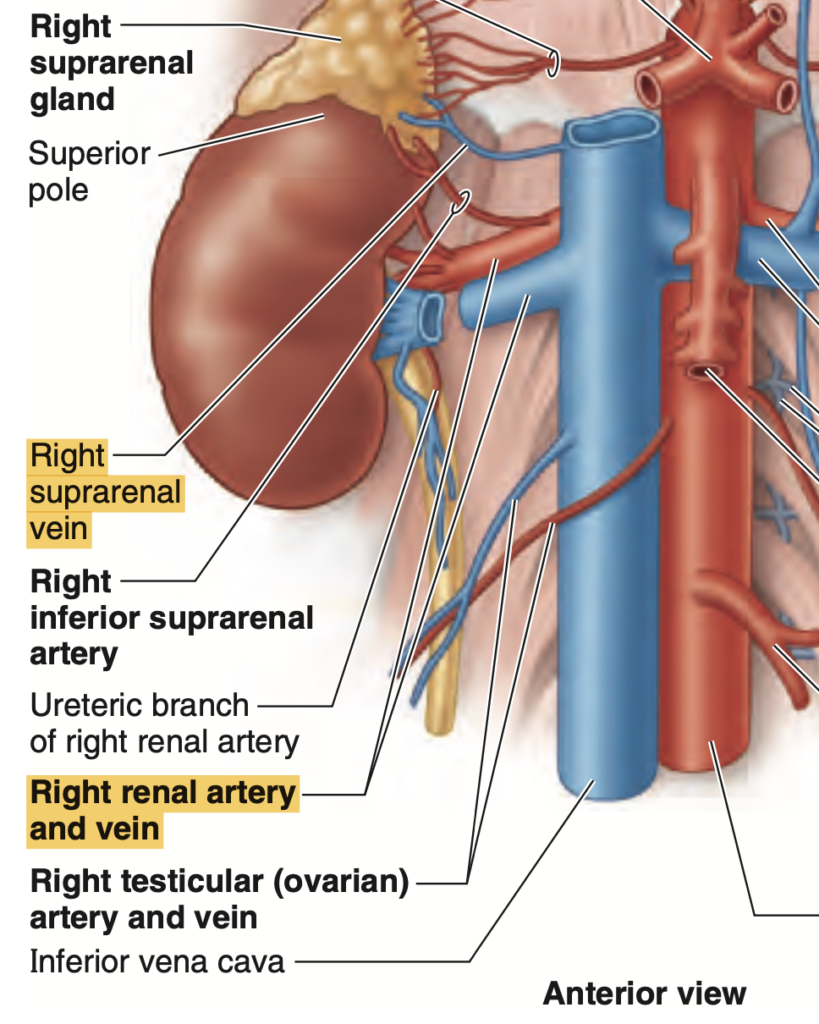
Question:右副腎静脈
問題文:The right suprarenal vein empties into the _____.?
a) Left renal vein
b) Right renal vein
c) Inferior vena cava
d) Inferior phrenic vein
Answer: c) Inferior vena cava
解説: 右副腎静脈(right suprarenal vein)は、直接的に下大静脈(inferior vena cava)に流入します。右側の副腎静脈は短く、直接的に下大静脈に接続しています。
- a) Left renal vein は左副腎静脈の流出先であり、右側ではありません。
- b) Right renal vein は右腎に関連する静脈で、副腎静脈の排出先とは異なります。
- d) Inferior phrenic vein は横隔膜の静脈で、副腎静脈とは直接的な接続はありません。
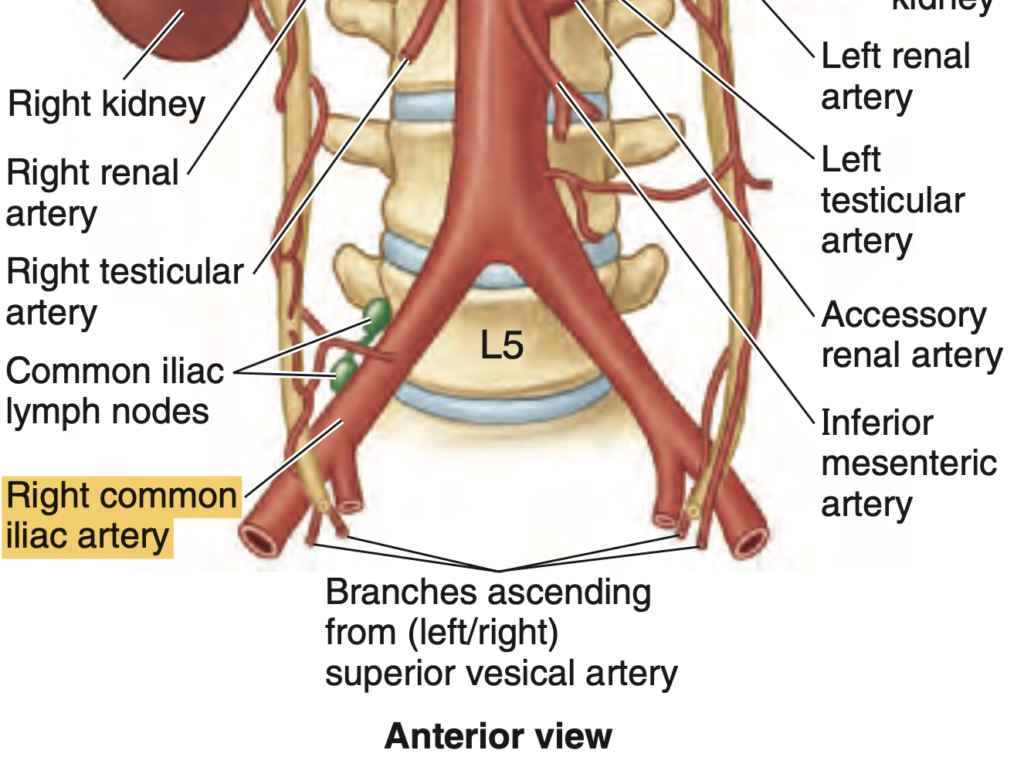
Question:尿管と総腸骨動脈
問題文:In the course of the ureter, it passes through the pelvic brim at the bifurcation of what particular structure?
a) Abdominal Aorta
b) Common Iliac Artery
c) External Iliac Artery
d) Internal Iliac Artery
Answer: b) Common Iliac Artery
解説: 尿管(ureter)は、骨盤縁を通過する際、総腸骨動脈(common iliac artery)の分岐部に沿って走行します。この位置は臨床的に重要であり、尿路結石が詰まりやすい部位の一つです。
- a) Abdominal Aorta は腸骨動脈の前段階の構造で、尿管の骨盤入口通過には直接関係しません。
- c) External Iliac Artery と d) Internal Iliac Artery は、それぞれ総腸骨動脈から分岐する動脈ですが、尿管は総腸骨動脈の分岐部で骨盤縁を越えます。
Question:尿管の狭窄部位
問題文:Which of the following statements is correct regarding the normal constrictions of the ureter?
a) Found at the junction of the ureter and major calyx
b) Non-potential sites of stone obstruction
c) Cross the brim of the pelvic outlet
d) Ends at the trigone of the urinary bladder
Answer: c) Cross the brim of the pelvic outlet
解説: 尿管は通常の狭窄部位として、腎盂(renal pelvis)と尿管の接合部、総腸骨動脈の交差部(骨盤入口)、および膀胱に入る部分があります。骨盤入口を越える位置は臨床的に重要で、尿路結石の詰まりやすい箇所として知られています。
- a) Found at the junction of the ureter and major calyx は誤りで、狭窄部は腎盂との接合部です。
- b) Non-potential sites of stone obstruction は誤りで、尿管には結石が詰まりやすい狭窄部位が存在します。
- d) Ends at the trigone of the urinary bladder は尿管の終端部ですが、狭窄部位ではありません。
1 at the junction of the ureters and renal pelves,
2 where the ureters cross the brim of the pelvic inlet, and
3 during their passage through the wall of the urinary bladder
Question:左腎静脈の排出先
問題文:Where does the left renal vein drain directly?
a) Inferior Vena Cava
b) Left Suprarenal Vein
c) Portal Vein
d) Splenic Vein
Answer: a) Inferior Vena Cava
解説: 左腎静脈(left renal vein)は下大静脈(inferior vena cava)に直接排出されます。左腎静脈は長く、下大静脈を横切って流入するため、この構造は臨床的にも重要です。
- b) Left Suprarenal Vein は左副腎静脈であり、腎静脈の排出先ではありません。
- c) Portal Vein は消化器系からの静脈血を集めるもので、腎静脈とは関係がありません。
- d) Splenic Vein も腎静脈とは直接の関係がありません。
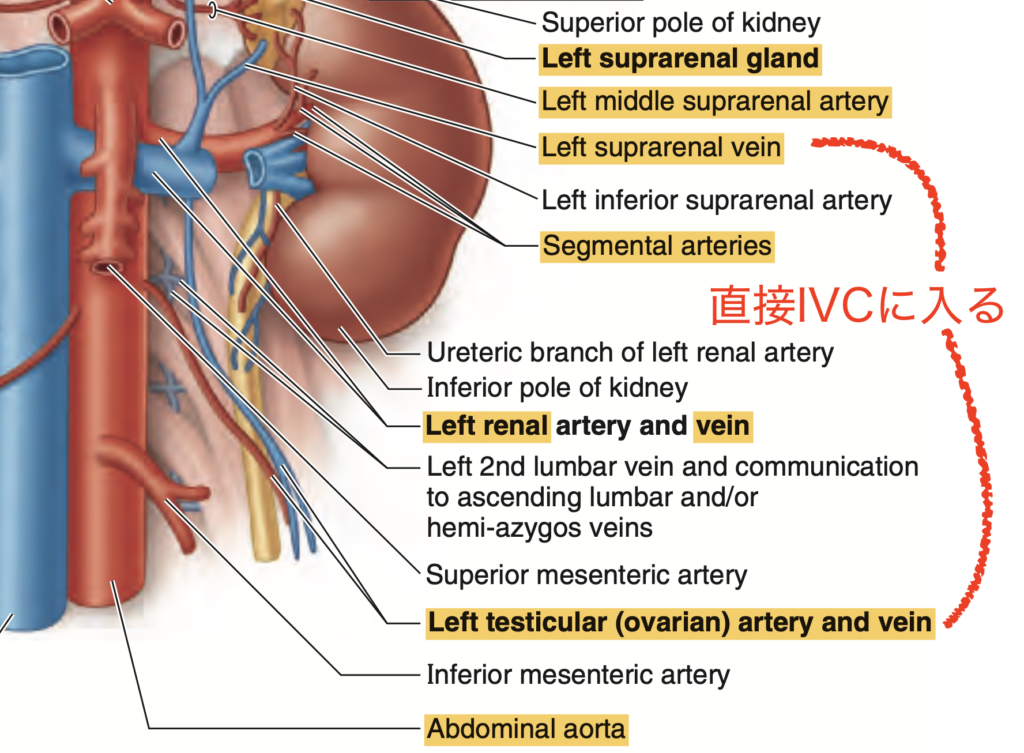
Question:副腎皮質
問題文:Which of the following is true about the suprarenal cortex?
a) These hormones affect organs like heart, kidney, and muscles
b) Secretes steroids and androgens
c) All of the above
d) Derived from mesoderm
Answer: c) All of the above
解説: 副腎皮質(suprarenal cortex)はステロイドホルモンやアンドロゲンを分泌し、これらのホルモンは心臓、腎臓、筋肉などの臓器に影響を与えます。また、副腎皮質は中胚葉(mesoderm)由来であるため、選択肢のすべてが正しいです。
- a) や b) は部分的に正しいですが、全体を表す c) が最適です。
- d) は発生学的な情報を示していますが、副腎皮質の全体的な機能を網羅する c) が最も適切です。
Question:尿路結石
問題文:Location in which there is a LOW likelihood of canaliculi obstruction:
a) Ureter-renal pelvis junction
b) Urinary bladder walls
c) Urethra
d) Brim of the pelvic inlet
Answer: c
1 at the junction of the ureters and renal pelves,
2 where the ureters cross the brim of the pelvic inlet, and
3 during their passage through the wall of the urinary bladder
Urethra:尿道
Ureter:尿管
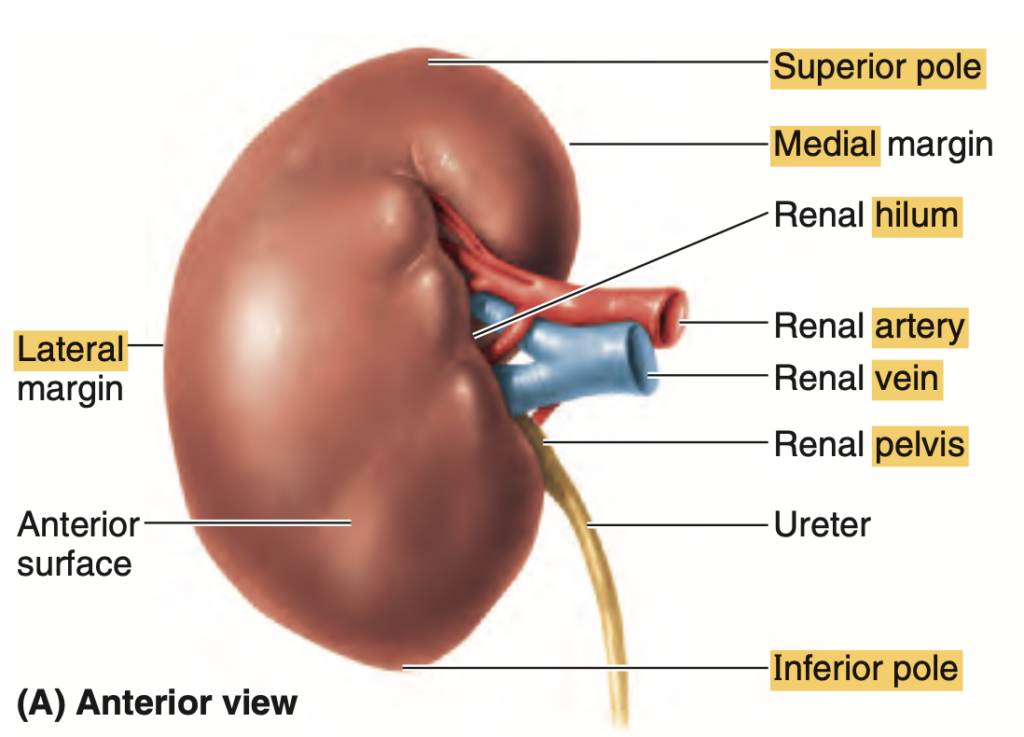
Question:腎門部
問題文:Which of the following is the proper order of structures from most anterior to most posterior?
a) Renal Hilum > Renal Artery > Renal Pelvis
b) Renal Artery > Renal Vein > Renal Pelvis
c) Renal Vein > Renal Artery > Renal Pelvis
d) Renal Artery > Renal Hilum > Renal Pelvis
Answer: c) Renal Vein > Renal Artery > Renal Pelvis
解説: 腎門部では、腎静脈(renal vein)が最も前方に位置し、次に腎動脈(renal artery)、最後に腎盂(renal pelvis)が最も後方に位置します。これにより、血液の出入りと尿の流れが効率的に行われるような配置が確保されています。
- a) と b) は順序が異なります。
- d) は腎門部の解剖学的順序として誤りです。

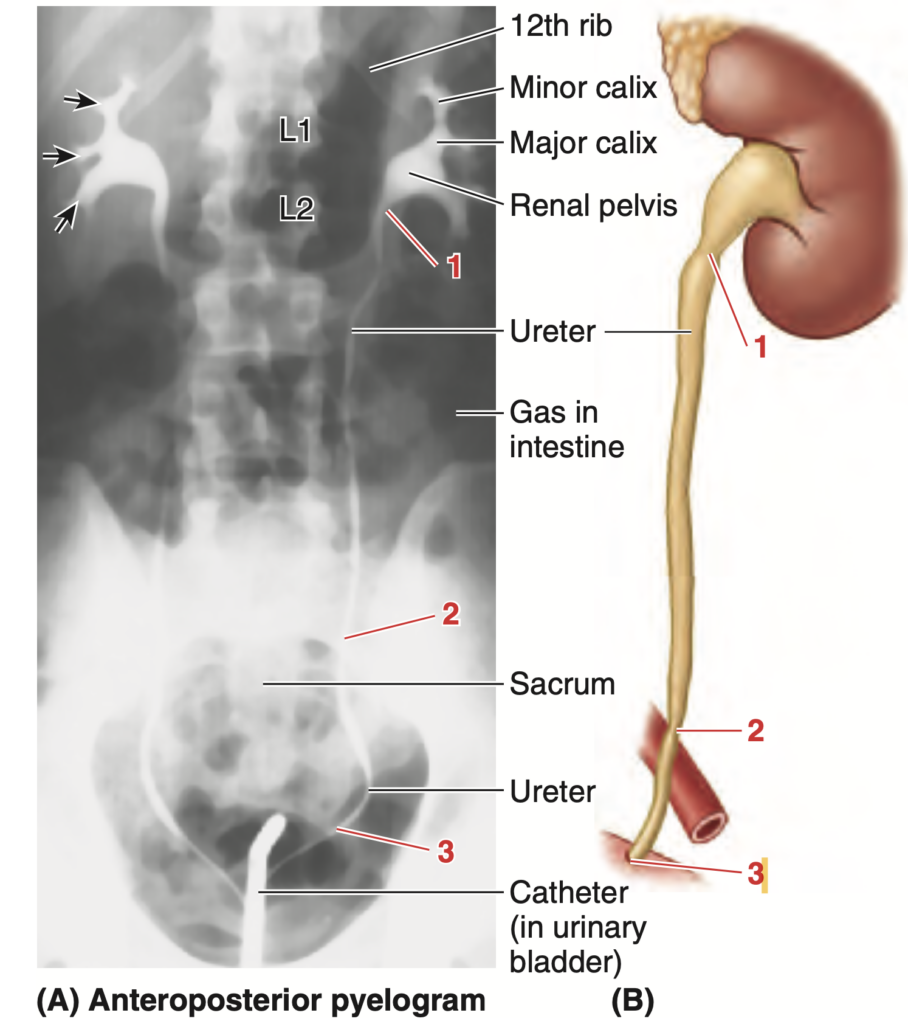
Question:尿管の平均長
問題文:The ureter measures?
a) 20-25cm
b) 30cm-40cm
c) 25-30cm
d) 10-15cm
Answer: c) 25-30cm
解説: 尿管の平均長さは約25〜30cmです。これにより、腎臓から膀胱まで尿が効率的に運ばれます。
- a) は実際の尿管の範囲より短すぎます。
- b) は長すぎる範囲です。
- d) はかなり短く、正常な尿管の範囲外です。
Question:右腎と十二指腸
問題文:Which of the following is NOT related to the left kidney?
a) Duodenum
b) Spleen
c) Jejunum
d) Stomach
Answer: a) Duodenum
解説: 十二指腸(duodenum)は右腎と関連があり、左腎とは関係がありません。左腎は脾臓(spleen)、小腸(jejunum)、胃(stomach)と接しています。
- b)、c)、d) は左腎に関連する構造です。

Question:腎乳頭
問題文:What do you call the apex of the renal pyramid that indents the minor calyx?
a) Renal Column
b) Renal Papilla
c) Renal Sinus
d) Renal Medulla
Answer: b) Renal Papilla
解説: 腎乳頭(renal papilla)は、腎錐体の頂点で、小腎盃(minor calyx)に突き出す部分です。ここで尿が収集され、腎盂に向かいます。
- a) Renal Column は腎錐体間の構造であり、乳頭ではありません。
- c) Renal Sinus は腎門の内側の空間で、乳頭とは関係ありません。
- d) Renal Medulla は腎髄質のことですが、腎乳頭とは異なります。

Question:腎臓の内外側縁
問題文:What are the two margins called in the kidney?
a) Anterior and Posterior
b) Internal and External
c) Superior and Inferior
d) Medial and Lateral
Answer: d) Medial and Lateral
解説: 腎臓には内側縁(medial margin)と外側縁(lateral margin)があります。内側縁には腎門があり、血管や尿管が出入りします。
- a)、b)、c) は腎臓の縁を正確に表していません。
Question:腎臓のリンパ管
問題文:Renal lymphatic vessels initially drain to what group of lymph nodes?
a) Caval
b) Aortic
c) Iliac
d) Lumbar
Answer: d) Lumbar
解説: 腎臓のリンパ管は、最初に腰部リンパ節(lumbar lymph nodes)に排出されます。これにより、腎臓周囲のリンパが効果的に循環されます。
- a) Caval や b) Aortic は腎臓に隣接するが、主なリンパ排出先ではありません。
- c) Iliac は骨盤内のリンパ流と関係しており、腎臓には直接関係がありません。
Question:右腎の位置
問題文:The right kidney is more easily palpable because it is positioned 1-2 cm lower than the left kidney. Where is this palpable location?
a) Between the 11th/12th rib and the iliac crest
b) At the midclavicular line of the 11th intercostal space
c) The left kidney is the one normally palpable, not the right
d) Directly inferolateral to the xiphoid process
Answer: a) Between the 11th/12th rib and the iliac crest
解説: 右腎は左腎よりも1〜2cm低い位置にあるため、11番目と12番目の肋骨および腸骨稜(iliac crest)の間で触知しやすいです。この位置は、右腎が触診で確認されやすい解剖学的特徴です。
- b) は位置が異なり、腎臓を触知する最適な部位ではありません。
- c) は誤りで、右腎が通常触知されやすいです。
- d) は解剖学的に腎臓が触診される部位ではありません。
Question:尿管の血管吻合
問題文:What is the main reason why ischemia is still found in the ureter despite the presence of a rich vascular anastomosis?
a) Longitudinal direction of its collaterals
b) Arise from the common iliac arteries
c) Presence of ascending and descending branches
d) Small and delicate network of branches
Answer: d) Small and delicate network of branches
解説: 尿管には豊富な血管吻合があるものの、枝が小さく繊細であるため、血流が制限されやすく虚血が発生しやすいです。
- a) や c) は構造的な特徴であるが、主因ではありません。
- b) は虚血の原因として不十分です。
Question:腎炎症
問題文:Inflammation of the kidneys and its surrounding areas can cause pain and difficulty in the flexion and movement of the hip due in part to this muscle being affected.
a) Pectineus
b) Psoas major
c) Iliacus
d) Piriformis
Answer: b) Psoas major
解説: 腎臓の炎症は、隣接する大腰筋(Psoas major)に影響を与えることで、股関節の屈曲や動作に困難を引き起こすことがあります。大腰筋は腎臓と近接しており、痛みが関連することがあります。
- a) Pectineus は腎臓とは遠く、影響は少ないです。
- c) Iliacus と d) Piriformis は大腰筋ほど腎臓に近くありません。
Question:腎臓の下極
問題文:At the inferior pole of the kidney, the posterior surface is related to what specific posterior abdominal wall muscle?
a) Iliopsoas
b) Psoas Major
c) Iliacus
d) Quadratus Lumborum
Answer: d) Quadratus Lumborum
解説: 腎臓の下極において、後面は腰方形筋(Quadratus Lumborum)に接しています。この筋肉は腎臓の位置を安定させる役割を担っています。
- a) Iliopsoas や c) Iliacus は腎臓のより内側で関係しません。
- b) Psoas Major は腎臓の一部に接しているが、下極での主要な筋肉ではありません。
Question:腎筋膜
問題文:The renal fascia:
a) Encloses the kidneys alone completely
b) Encloses both the kidneys and the suprarenal glands except the inferior portions of the kidney
c) Encloses the kidneys except the superior aspect due to the placement of the suprarenal glands
d) Encloses the kidneys alone except inferiorly
Answer: b) Encloses both the kidneys and the suprarenal glands except the inferior portions of the kidney
解説: 腎筋膜(renal fascia)は、腎臓と副腎の両方を包みますが、腎臓の下部(inferior portions)は完全には覆われていません。これは腎臓の位置と隣接する組織との関係に基づいています。
- a) は誤りで、腎筋膜は副腎も含みます。
- c) は不正確で、上部を含みます。
- d) は不完全な表現です。
下部が完全に覆われていない理由
- 腎筋膜は腎臓の上部から側方および前方へと広がり、副腎とともに包み込むように形成されていますが、下部では筋膜が収束せず、一部開放的な構造になっています。
- これは、腎臓が尿管を通じて下方に続き、尿管の動きや伸縮性が必要なため、下部を固定せずに柔軟性を持たせる設計となっているためです。
- 腎臓は呼吸運動や体位の変化によって位置が多少変動するため、下部が完全に覆われていないことで、腎臓が自由に動ける余地が生まれ、身体の動きに柔軟に対応できます。
Question:nephros/nephroi
問題文:The term nephros/nephroi is a Greek root word for nephron which means?
a) Convolving tubules
b) Filter
c) Glomerulus
d) Kidney
Answer: d) Kidney
解説: 「nephros/nephroi」はギリシャ語で「腎臓(kidney)」を意味します。この語根は、腎臓関連の用語(例:nephron)に使用されます。
- a)、b)、c) は腎臓の構造に関連する部分ですが、nephrosの直接の意味ではありません。
Question:ゲロータ筋膜(Gerota’s fascia)
問題文:What do you call the fascial fibrous tissue that surrounds the kidney?
a) Camper’s
b) Transversalis
c) Gerota’s
d) Scarpa’s
Answer: c) Gerota’s
解説: 腎臓を包む線維性組織はゲロータ筋膜(Gerota’s fascia)と呼ばれ、腎臓と周囲の脂肪を包む役割を果たします。ゲロータ筋膜(Gerota’s fascia)は腎筋膜(renal fascia)とも呼ばれ、腎臓と副腎を取り囲む結合組織の膜のことを指します。
- a) Camper’s と d) Scarpa’s は皮膚の浅層筋膜で、腎臓には関連しません。
- b) Transversalis は腹膜の筋膜で、腎臓を直接覆ってはいません。
Question:近位尿細菅への血液共有
問題文:Where does the main arterial blood supply of the proximal ureter in males come from?
a) Direct branch from abdominal aorta
b) Renal Artery
c) Direct branch from common iliac artery
d) Testicular Artery
Answer: b) Renal Artery
解説: 尿管の近位部(proximal ureter)は、腎動脈(renal artery)から主に血液供給を受けます。この部位は腎臓に近接しているため、腎動脈からの供給が最も適しています。
- a) は一般的ではありません。
- c) や d) は尿管の遠位部に関連する場合がありますが、近位部には適していません。
Question:腎臓の大きさ
問題文:Which of the following statement is true about the kidney?
a) All of the above
b) It is reddish brown
c) It measures 5cm in width, 10cm in length and 2.5cm in thickness
d) It is closely associated to the diaphragm superiorly
Answer: a) All of the above
解説: 腎臓は赤褐色であり、通常のサイズは幅5cm、長さ10cm、厚さ2.5cmです。また、上部は横隔膜と接しているため、全ての選択肢が正しいと言えます。
- b)、c)、d) の各選択肢はそれぞれ正しいですが、すべてを網羅する a) が最も適切です。
During life, the kidneys are reddish brown and measure approximately 10 cm in length, 5 cm in width, and 2.5 cm in thickness. Superiorly, the posterior aspects of the kidneys are associated with the diaphragm, which separates them from the pleural cavities and the 12th pair of ribs (Fig. 2.76). More inferiorly, the posterior surfaces of the kidney are related to the psoas major muscles medially and the quadratus lumbo- rum muscle
Question:前上区域動脈
問題文:Which among the arterial branches arise directly from the anterior branch of the renal artery?
a) Superior Segmental
b) Anterior Superior Segmental
c) Inferior Segmental
d) Anterior Inferior Segmental
Answer: b) Anterior Superior Segmental
解説: 腎動脈の前枝から分岐する動脈には、前上区域動脈(Anterior Superior Segmental)が含まれます。これにより、腎臓の前部上区域が適切に血液供給されます。
- a)、c)、および d) は正しい分枝ではありません。
Question:ベルティニ腎柱(renal columns of Bertini)
問題文:The renal columns of Bertini are occupied by which of the following?
a) Arcuate artery
b) Loop of Henle
c) Interlobar vessels
d) Convoluting tubules
Answer: c) Interlobar vessels
解説: ベルティニ腎柱(renal columns of Bertini)は、腎錐体の間に位置し、主に葉間動脈(Interlobar vessels)を含んでいます。これらの血管は腎臓の血液供給において重要な役割を果たしています。
- a) は腎臓の表層に位置する動脈であり、腎柱内にはありません。
- b) および d) は腎臓内の他の部分に位置しています。
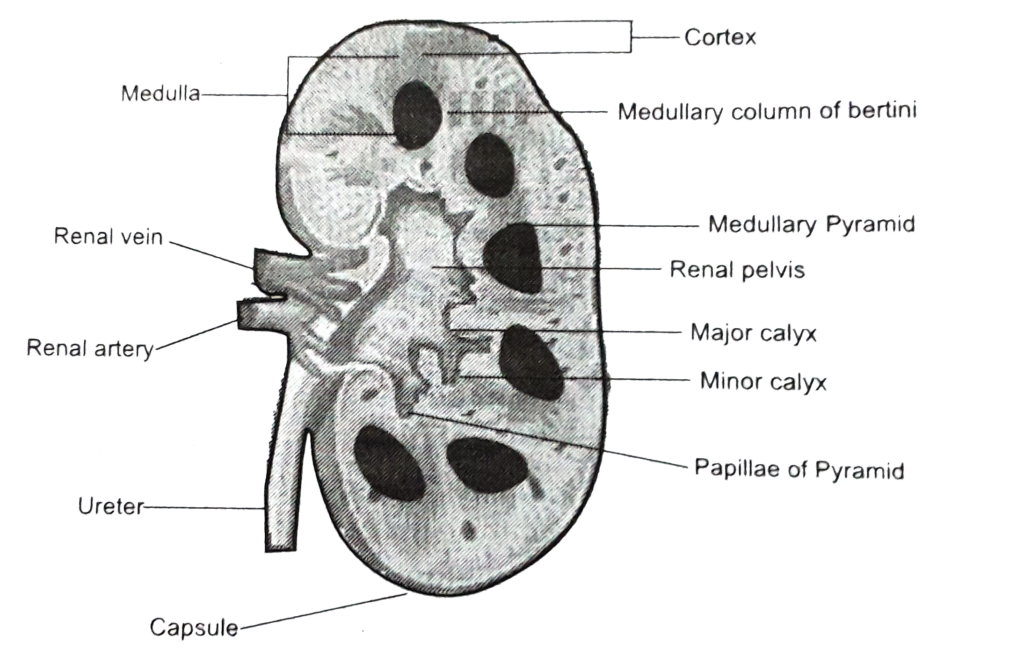
Question:腎洞(renal sinus)
問題文:What do you call a space within the kidney where the pelvis, calices, vessels, and nerves occupy it?
a) Renal Sinus
b) Renal Hilum
c) Renal Pyramid
d) Renal Papilla
Answer: a) Renal Sinus
解説: 腎洞(renal sinus)は腎臓内部の空間であり、腎盂、腎杯、血管、神経が配置されています。これにより、腎臓内の重要な構造がまとまっています。
- b) Renal Hilum は腎門であり、腎臓への入口を指します。
- c) および d) は腎臓内部の別の構造です。
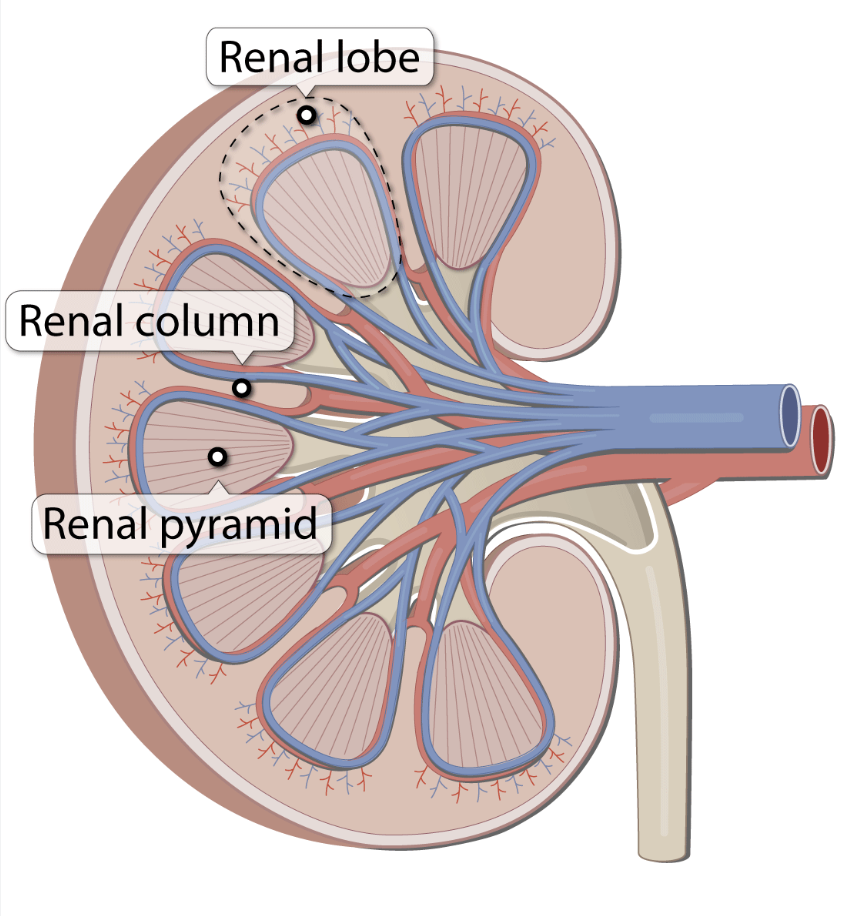
Question:腎臓の葉(lobe)
問題文:The cortex and what other structure or part forms the lobes of the kidney?
a) Renal Medulla
b) Renal Pyramid
c) Renal Column
d) Renal Papilla
Answer: b) Renal Pyramid
解説: 腎臓の葉(lobe)は、皮質(cortex)と腎錐体(renal pyramid)で構成されています。腎錐体は腎臓の髄質部分に位置し、尿生成の機能を持っています。
- a) Renal Medulla は髄質全体を指し、腎葉の構成要素とは異なります。
- c) および d) は腎葉の構成には含まれません。
Question:腎盂
問題文:It is a funnel shape expansion at the superior end of the ureter?
a) Renal hilum
b) Minor calices
c) Renal pelvis
d) Major calices
Answer: c) Renal pelvis
解説: 腎盂(renal pelvis)は、尿管の上端にある漏斗状の拡張部分であり、腎杯からの尿を収集し尿管へ送ります。
- a) Renal hilum は腎門であり、腎臓の入口部分を指します。
- b) および d) は腎杯に関する構造で、尿管との接続部分にはなりません。
Question:腎動脈の位置
問題文:The renal arteries lie between the level of intervertebral disc vertebrae?
a) T12-L3
b) L2-L3
c) L1-L2
d) L3-L4
Answer: c) L1-L2
解説: 腎動脈は通常、L1とL2の椎間板のレベルで発生します。この位置は腎臓に血液を供給するのに適しています。
- a)、b)、および d) は腎動脈の一般的な発生レベルではありません。
Question:腎臓上極間の空間
問題文:The space between the two kidneys at its superior pole, from left to right, contain the structures:
a) IVC, right crus of the diaphragm, celiac trunk, celiac ganglion, superior mesenteric artery, left crus of the diaphragm
b) IVC, right crus of the diaphragm, celiac ganglion, celiac trunk, left crus of the diaphragm, superior mesenteric artery
c) Superior mesenteric artery, left crus of the diaphragm, right crus of the diaphragm, celiac trunk, celiac ganglion, IVC
d) Left crus of the diaphragm, superior mesenteric artery, celiac trunk,
celiac ganglion, right crus of the diaphragm, IVC
Answer: a) IVC, right crus of the diaphragm, celiac trunk, celiac ganglion, superior mesenteric artery, left crus of the diaphragm, d
解説: 腎臓の上極間の空間には、IVC、右横隔脚(right crus of the diaphragm)、腹腔動脈(celiac trunk)、腹腔神経節(celiac ganglion)、上腸間膜動脈(superior mesenteric artery)、左横隔脚(left crus of the diaphragm)が左から右に並んでいます。これは腎臓の上極の位置関係に基づいています。
Question:腎下垂症(nephroptosis)
問題文:In the condition nephroptosis, there is an abnormally high amount of movement in the kidney(s) due to improper attachment to the renal fascia. Which of the following best describes the condition?
a) Kidneys descend more and so do the suprarenal glands
b) Kidneys descend more but the suprarenal glands remain in normal position
c) Ureters are of longer length due to the repositioned kidney
d) Pain caused by traction of the kidney and nearby vessels are relieved while standing up
Answer: b) Kidneys descend more but the suprarenal glands remain in normal position
解説: 腎下垂症(nephroptosis)では、腎臓が腎筋膜との結合が弱くなるため、異常な移動が起こりますが、副腎は通常の位置に留まります。腎臓のみが下方へ移動し、痛みを伴うことがあります。
- a) は副腎も下がるとしており、誤りです。
- c) は尿管の長さの変化について述べていますが、主な特徴ではありません。
- d) は、立位で痛みが軽減されることを示していますが、一般的には動きに伴う痛みが発生します。
Nephroptosis
Because the layers of renal fascia do not fuse firmly inferiorly to offer resistance, abnormally mobile kidneys may descend more than the normal 3 cm when the body is erect. When kidneys descend, the suprarenal glands remain in place because they lie in a separate fascial compartment and are firmly attached to the diaphragm. Nephroptosis (dropped kidney) is distinguished from an ectopic kidney (congenital misplaced kidney) by a ureter of normal length that has loose coiling or kinks because the distance to the bladder has been reduced. The kinks do not seem to be of significance. Symptoms of inter- mittent pain in the renal region, relieved by lying down, appear to result from traction on the renal vessels. The lack of inferior support for the kidneys in the lumbar region is one of the reasons transplanted kidneys are placed in the iliac fossa of the greater pelvis. Other reasons for this place- ment are the availability of major blood vessels and conve- nient access to the nearby bladder.
Question:腎門と幽門横断面
問題文:In the anterior surface anatomy of the kidney, the transpyloric plane from the median plane corresponds to what part of the right kidney?
a) Renal Hilum
b) Inferior Pole
c) Superior Pole
d) Renal Pelvis
Answer: a) Renal Hilum
解説: 右腎の腎門(renal hilum)は、腹部の表面解剖学で、正中面からの横断面である幽門横断面(transpyloric plane)と一致します。この腎門は腎臓への主要な血管と尿管が出入りする部位です。
- b) および c) は腎門の位置として不正確です。
- d) は腎盂の位置であり、腎門の位置と一致しません。

Question:副腎と後腹壁
問題文:The suprarenal gland is attached to the?
a) To the lesser curvature of stomach
b) Posterior abdominal wall
c) To psoas major muscle
d) Crura of diaphragm
Answer: d
解説: The suprarenal gland (adrenal gland) is primarily attached to the diaphragmatic crura via the surrounding renal fascia (Gerota’s fascia), which helps anchor it in place. Although the suprarenal glands are located superomedially to the kidneys, they are not directly attached to the kidneys themselves. Instead, they are held in position by the connective tissue (renal fascia) that also surrounds the kidneys, securing the glands close to the diaphragm.
Question:尿管と総腸骨動脈
問題文:The ureter runs inferiorly from the renal pelvis and passes the pelvic brim at the level of which of the following arteries?
a) Internal Iliac Artery
b) External Iliac Artery
c) Distal Part of Abdominal Aorta
d) Common Iliac Artery
Answer: d) Common Iliac Artery
解説: 尿管は腎盂から下行し、骨盤縁で総腸骨動脈(common iliac artery)のレベルを通過します。この部位は、臨床的に尿路結石が詰まりやすい部位としても重要です。
- a) および b) は尿管の交差部位として不正確です。
- c) は誤った位置です。
Question:腎乳頭と遠位集合管
問題文:The renal papilla is capped by the minor calyx; it is therefore occupied by what structure?
a) Convolving tubules
b) Proximal collecting tubules
c) Loop of Henle
d) Distal collecting ducts
Answer: d) Distal collecting ducts
解説: 腎乳頭(renal papilla)は、小腎杯(minor calyx)で覆われており、遠位集合管(distal collecting ducts)がここに開口します。集合管は尿を腎杯へと導く役割を果たします。
- a)、b)、および c) は腎乳頭とは直接的に関係しません。
Question:尿管腹部部分と腎動脈
問題文:The abdominal portion of the ureter is supplied by what artery?
a) Gonadal
b) External Iliac
c) Renal
d) Internal Iliac
Answer: c) Renal
解説: 尿管の腹部部分は腎動脈(renal artery)から血液供給を受けます。この供給は、尿管が腎臓に隣接する部位に位置しているため重要です。
- a)、b)、および d) は尿管の他の部分に関連することが多いですが、腹部部分の主な供給源ではありません。
Question:腎臓内臓求心性神経線維
問題文:The visceral afferent nerve fibers follow the sympathetic fibers to what spinal cord segment?
a) T10 – L1 Cords
b) T11 – L2 Cords
c) T12 – L3 Cords
d) L1 – L4 Cords
Answer: b) T11 – L2 Cords
解説: 腎臓の内臓求心性神経線維は、交感神経線維に沿ってT11からL2の脊髄セグメントに達します。この領域は腎臓の痛覚伝導に関与しています。
- a)、c)、および d) は腎臓の痛覚伝導において適切な範囲ではありません。
Question:弓状動脈
問題文:Which of the following structures delineates the renal cortex from the renal medulla?
a) Arcuate artery
b) Vasa recta
c) Afferent arteriole
d) Efferent arteriole
Answer: a) Arcuate artery, b
解説: 弓状動脈(arcuate artery)は腎皮質と腎髄質を区切る境界となる構造であり、これにより腎臓の内層と外層が分けられます。
- b)、c)、および d) は腎臓内の他の血管構造であり、皮質と髄質の境界には直接関与しません。

自作問題教科書
Question:後腹膜器官
問題文: Which of the following structures is NOT considered a retroperitoneal structure?
- a. Kidneys
- b. Ureters
- c. Suprarenal glands
- d. Urinary bladder
Answer: d. Urinary bladder
解説: 腎臓 (Kidneys)、尿管 (Ureters)、副腎 (Suprarenal glands) は全て腹膜の後方、つまり後腹膜に位置しているため、retroperitoneal(後腹膜器官)と呼ばれます。一方、膀胱 (Urinary bladder) は骨盤内に位置しており、後腹膜構造には含まれません。そのため、選択肢dが正解です。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、腎臓、尿管、副腎が全て後腹膜に位置するという点にあります。
Question:腎臓の位置
問題文: Where are the superior poles of the kidneys located in relation to the vertebral column?
- a. T8–T10
- b. T12–L3
- c. L1–L4
- d. L3–L5
Answer: b. T12–L3
解説: 腎臓は背骨のT12からL3にかけて位置しています。特に左腎の上端はT12、右腎の上端は肝臓の影響でやや下がり、T12付近に位置します。したがって、正解は選択肢bです。他の選択肢が間違いである理由は、腎臓の解剖学的位置が異なる部位にあることにあります。
Question:腎筋膜
問題文: Which structure is directly responsible for holding the kidneys in a relatively fixed position?
- a. Renal capsule
- b. Renal fascia
- c. Perinephric fat
- d. Paranephric fat
Answer: b. Renal fascia
解説: 腎臓は主に腎筋膜 (Renal fascia) によって支えられ、その位置がほぼ固定されています。また、腎周囲の脂肪(腎周囲脂肪および腎前脂肪)も腎臓を保護しますが、直接的な固定は筋膜によって行われます。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、腎包膜や脂肪が支える役割を果たしますが、固定に関しては腎筋膜が主たる役割を果たしているためです。
Question:腎門部
問題文: The renal hilum contains which of the following structures in the correct anterior-to-posterior order?
- a. Renal pelvis, renal vein, renal artery
- b. Renal vein, renal artery, renal pelvis
- c. Renal artery, renal vein, renal pelvis
- d. Renal vein, renal pelvis, renal artery
Answer: b. Renal vein, renal artery, renal pelvis
解説: 腎門部 (Renal hilum) には腎静脈 (Renal vein)、腎動脈 (Renal artery)、腎盂 (Renal pelvis) が前から後ろに並んでいます。この順序は腎門部の構造上重要であり、血流や尿の流れに影響を及ぼします。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、順序が異なり、腎門部の解剖学的な位置関係と一致しないためです。
Question:左腎の位置
問題文: Which of the following describes the correct anatomical relationship between the left kidney and surrounding organs?
- a. Anterior to the liver
- b. Posterior to the spleen
- c. Lateral to the descending colon
- d. Medial to the stomach
Answer: b. Posterior to the spleen
解説: 左腎 (Left kidney) は脾臓 (Spleen) の後方に位置し、また胃、膵臓、空腸、下行結腸にも隣接しています。したがって、選択肢bが正解です。他の選択肢が間違いである理由は、左腎が肝臓の前には位置せず、また下行結腸の外側や胃の内側にはないためです。
Question:尿管狭窄部
問題文: The ureters are typically constricted in three areas. Which of the following is NOT one of these constricted areas?
- a. Junction of the ureters and renal pelves
- b. Where the ureters cross the brim of the pelvic inlet
- c. Entry point into the renal hilum
- d. Passage through the wall of the urinary bladder
Answer: c. Entry point into the renal hilum
解説: 尿管 (Ureter) は通常、3つの狭窄部位があります。これらは腎盂 (Renal pelvis) との接合部、骨盤の入口 (Pelvic inlet) を横切る部分、および膀胱壁を通過する部分です。これらの狭窄部位は尿管結石が引っかかりやすい場所として知られています。選択肢cは誤りであり、腎門部 (Renal hilum) は尿管の狭窄部位には該当しません。
Question:右副腎
問題文: What is the main difference between the right and left suprarenal (adrenal) glands in terms of their shape and position?
- a. The right gland is crescent-shaped and contacts the stomach.
- b. The left gland is more apical and contacts the liver.
- c. The right gland is pyramidal and is positioned over the superior pole of the right kidney.
- d. The left gland is pyramidal and positioned over the superior pole of the left kidney.
Answer: c. The right gland is pyramidal and is positioned over the superior pole of the right kidney.
解説: 右の副腎 (Right suprarenal gland) はピラミッド状で、右腎の上極に位置しています。また、肝臓 (Liver) にも接しています。一方、左の副腎 (Left suprarenal gland) は三日月形で、脾臓 (Spleen) や胃 (Stomach) といった他の臓器と関係があります。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、左右の副腎の形状と位置が異なるためです。
Question:副腎皮質ホルモン
問題文: What is the primary function of the suprarenal cortex?
- a. Secretes catecholamines such as epinephrine
- b. Retains sodium and water in response to stress
- c. Transports urine from the kidney to the bladder
- d. Filters blood to remove metabolic waste
Answer: b. Retains sodium and water in response to stress
解説: 副腎皮質 (Suprarenal cortex) はコルチコステロイド (Corticosteroids) やアンドロゲン (Androgens) を分泌し、ストレス反応に応じて腎臓にナトリウムや水分を保持させる働きがあります。これにより血圧や血液量が増加します。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、アドレナリン分泌は副腎髄質 (Suprarenal medulla) の役割であり、尿の輸送や血液のろ過は腎臓の機能です。
Question:腎筋膜
問題文: Which of the following structures provides the primary fixation for the kidneys?
- a. Perinephric fat
- b. Paranephric fat
- c. Renal fascia
- d. Diaphragmatic fascia
Answer: c. Renal fascia
解説: 腎筋膜 (Renal fascia) は腎臓を固定する主な構造であり、腎臓を後腹膜の位置に保持しています。腎周囲の脂肪(腎周囲脂肪および腎前脂肪)は腎臓を保護する役割がありますが、直接的な固定は腎筋膜によって行われています。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、脂肪組織が腎臓の位置を支える役割はあるものの、筋膜ほどの固定力はないためです。
Question:呼吸時の腎臓位置
問題文: How much movement is typical for the kidneys during respiration?
- a. 0.5 cm
- b. 1 cm
- c. 2-3 cm
- d. 5 cm
Answer: c. 2-3 cm
解説: 呼吸時には腎臓が垂直方向に2〜3 cm移動します。この移動量は腰椎の一椎体の高さと同程度であり、横隔膜の上下運動によって生じます。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、0.5 cmや1 cmでは腎臓の典型的な動きとしては小さすぎ、5 cmは通常の動きよりも大きすぎます。
Question:上部分節動脈
問題文: Which artery supplies the superior (apical) segment of the kidney?
- a. Anterosuperior segmental artery
- b. Inferior segmental artery
- c. Posterior segmental artery
- d. Superior segmental artery
Answer: d. Superior segmental artery
解説: 腎臓の上部(上極)は上部(apical)分節動脈 (Superior segmental artery) によって供給されています。この動脈は腎動脈の前枝から分岐し、腎臓の特定の部分に酸素供給を行います。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、anterosuperior segmental artery や inferior segmental artery は異なる腎臓の部分を供給し、posterior segmental artery は腎臓の後部を供給するからです。
Question:左腎静脈
問題文: The left renal vein receives blood from which of the following veins before draining into the IVC?
- a. Right gonadal vein
- b. Right suprarenal vein
- c. Left suprarenal vein
- d. Left iliac vein
Answer: c. Left suprarenal vein
解説: 左腎静脈 (Left renal vein) はIVCに流入する前に左副腎静脈 (Left suprarenal vein)、左精巣(または卵巣)静脈、そして上行腰静脈との接続を受けます。これに対し、右側は直接IVCに流れ込みます。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、右側の静脈はIVCに直接流入し、また左腸骨静脈とは関係がないためです。
Question:腎神経叢
問題文: Which structure primarily innervates the kidneys?
- a. Celiac plexus
- b. Renal nerve plexus
- c. Inferior mesenteric plexus
- d. Phrenic nerve
Answer: b. Renal nerve plexus
解説: 腎臓は腎神経叢 (Renal nerve plexus) によって主に支配されており、この神経叢は交感神経と副交感神経の線維を含んでいます。特に下腹部内臓神経 (Least splanchnic nerve) が重要な役割を果たします。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、腹腔神経叢 (Celiac plexus) は副腎に関連し、下腸間膜神経叢や横隔神経は直接的に腎臓を支配しません。
Question:尿路結石
問題文: What is the usual location of referred pain due to ureteric calculi (kidney stones)?
- a. Upper abdominal region
- b. Anterior thigh
- c. Ipsilateral lower quadrant and groin
- d. Lower back
Answer: c. Ipsilateral lower quadrant and groin
解説: 尿路結石 (Ureteric calculi) による痛みは通常、側腹部から鼠径部に放散されます。これはT11-L2の脊髄神経によって支配される領域であり、尿管の炎症が原因で痛みが特定の皮膚領域に現れることがあります。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、尿路結石の痛みが特に鼠径部に放散され、その他の領域には一般的に影響を与えないためです。
Question:右副腎静脈
問題文: The short right suprarenal vein drains directly into which vessel?
- a. Left renal vein
- b. Inferior vena cava (IVC)
- c. Superior mesenteric vein
- d. Right renal artery
Answer: b. Inferior vena cava (IVC)
解説: 右副腎静脈 (Right suprarenal vein) は短く、直接IVC (Inferior vena cava) に流入します。一方、左副腎静脈は左腎静脈を経由してIVCに流れ込みます。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、左腎静脈や右腎動脈、上腸間膜静脈とは直接的な関連がないためです。
Question:腎動脈の位置
問題文: At what vertebral level do the renal arteries typically arise?
- a. T12–L1
- b. L1–L2
- c. L2–L3
- d. L3–L4
Answer: b. L1–L2
解説: 腎動脈 (Renal arteries) は通常、L1とL2の椎間円板の高さから分岐します。右腎動脈はIVCの後方を通るため、その走行が異なるのが特徴です。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、腎動脈がL1–L2レベル以外から分岐することは一般的ではないためです。
Question:副腎と下横隔動脈
問題文: Which of the following arteries does NOT contribute to the blood supply of the suprarenal (adrenal) glands?
- a. Inferior phrenic artery
- b. Superior mesenteric artery
- c. Abdominal aorta
- d. Renal artery
Answer: b. Superior mesenteric artery
解説: 副腎 (Suprarenal glands) は下横隔動脈 (Inferior phrenic artery)、腹大動脈 (Abdominal aorta)、および腎動脈 (Renal artery) からの動脈分枝によって供給されます。上腸間膜動脈 (Superior mesenteric artery) は副腎に直接的な血流供給をしていません。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、これらの動脈が副腎の血液供給に関与しているからです。
Question:尿管と動脈
問題文: Which statement is correct regarding the blood supply of the ureters?
- a. The ureters are supplied only by the renal arteries.
- b. The ureters receive arterial branches from the renal, gonadal, abdominal aorta, and common iliac arteries.
- c. The ureters are supplied only by the common iliac arteries.
- d. The ureters have no blood supply along their length.
Answer: b. The ureters receive arterial branches from the renal, gonadal, abdominal aorta, and common iliac arteries.
解説: 尿管 (Ureters) には腎動脈 (Renal arteries)、精巣(または卵巣)動脈 (Gonadal arteries)、腹大動脈 (Abdominal aorta)、および総腸骨動脈 (Common iliac arteries) からの血流が供給されています。これにより尿管全体に血流が行き渡り、必要な酸素が供給されます。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、尿管の血流供給が複数の動脈から成り立っているためです。
Question:副腎髄質と神経
問題文: Which nerve plexus primarily provides sympathetic innervation to the suprarenal medulla?
- a. Renal plexus
- b. Superior hypogastric plexus
- c. Celiac plexus
- d. Inferior mesenteric plexus
Answer: c. Celiac plexus
解説: 副腎髄質 (Suprarenal medulla) は腹腔神経叢 (Celiac plexus) および腹腔内臓神経 (Splanchnic nerves) からの交感神経支配を受けます。副腎髄質のクロマフィン細胞は交感神経節を介さずに支配され、直接的に神経刺激を受けてホルモンを分泌します。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、これらの神経叢が副腎髄質の主な神経支配には関与しないからです。
Question:尿管結石
問題文: Which of the following methods is commonly used to treat ureteric calculi (kidney stones)?
- a. Appendectomy
- b. Lithotripsy
- c. Hemodialysis
- d. Angioplasty
Answer: b. Lithotripsy
解説: 尿管結石 (Ureteric calculi) の治療にはリトトリプシー (Lithotripsy) が一般的に使用されます。この方法は、体外からの衝撃波で結石を砕き、尿と一緒に自然に排出されるようにします。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、虫垂切除 (Appendectomy)、血液透析 (Hemodialysis)、および血管形成術 (Angioplasty) は尿管結石の治療には使用されないからです。
Question:左副腎静脈
問題文: Which vein does the left suprarenal vein typically drain into?
- a. Inferior vena cava (IVC)
- b. Left renal vein
- c. Left gonadal vein
- d. Ascending lumbar vein
Answer: b. Left renal vein
解説: 左副腎静脈 (Left suprarenal vein) は通常、左腎静脈 (Left renal vein) に流入し、その後IVCに向かいます。右副腎静脈はIVCに直接流入するため、左右で還流経路が異なります。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、左副腎静脈が直接IVCに流入することはないためです。
Question:尿管の腹部部分
問題文: Into which veins does the abdominal part of the ureters typically drain?
- a. Hepatic veins
- b. Inferior mesenteric vein
- c. Renal and gonadal veins
- d. Superior vena cava (SVC)
Answer: c. Renal and gonadal veins
解説: 尿管の腹部部分は、腎静脈 (Renal veins) および精巣/卵巣静脈 (Gonadal veins) に静脈還流を行います。これにより尿管からの血液が最終的にIVCに戻ります。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、肝静脈やSVCは尿管の静脈還流には関与しないからです。
Question:腎臓からのリンパ
問題文: The lymphatic vessels of the kidneys drain into which lymph nodes?
- a. Cervical lymph nodes
- b. Thoracic lymph nodes
- c. Lumbar (caval and aortic) lymph nodes
- d. Inguinal lymph nodes
Answer: c. Lumbar (caval and aortic) lymph nodes
解説: 腎臓からのリンパは、腰部(大静脈および大動脈)リンパ節 (Lumbar, caval, and aortic lymph nodes) に流入します。これにより、腹部リンパ系の重要な経路となっています。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、頸部や胸部、鼠径リンパ節は腎臓のリンパ還流には関与しないからです。
Question:副腎髄質と神経
問題文: What is unique about the sympathetic innervation of the suprarenal medulla?
- a. It involves only parasympathetic fibers.
- b. It bypasses the paravertebral and prevertebral ganglia without synapse.
- c. It originates from the celiac ganglion.
- d. It requires synapse in the renal plexus.
Answer: b. It bypasses the paravertebral and prevertebral ganglia without synapse.
解説: 副腎髄質 (Suprarenal medulla) への交感神経支配は、交感神経節を介さず、直接クロマフィン細胞に作用するという特徴があります。これにより、素早いホルモン応答が可能となります。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、副腎髄質が特異的な経路で交感神経支配を受けているからです。
Question:腎臓鏡
問題文: Which of the following procedures is commonly used to visualize and remove ureteric calculi?
- a. Appendectomy
- b. Nephroscopy
- c. Hemodialysis
- d. Angioplasty
Answer: b. Nephroscopy
解説: 腎臓鏡 (Nephroscope) は、尿管結石 (Ureteric calculi) を観察および除去するために使用される器具です。小さな切開から挿入し、結石の確認と除去が可能です。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、腎臓鏡以外の手術は尿管結石の治療には適用されないからです。
Question:尿管の弁
問題文: Which structure forms a one-way flap valve to prevent urine from refluxing into the ureters during bladder contraction?
- a. Internal urethral sphincter
- b. External urethral sphincter
- c. Oblique passage of the ureters through the bladder wall
- d. Detrusor muscle
Answer: c. Oblique passage of the ureters through the bladder wall
解説: 尿管 (Ureters) が膀胱壁 (Bladder wall) を斜めに貫通することで、一方向の弁 (Flap valve) が形成されます。これにより、膀胱内圧が上昇しても尿が逆流するのを防ぎます。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、内尿道括約筋 (Internal urethral sphincter) や外尿道括約筋 (External urethral sphincter) は尿の流出制御に関与しており、膀胱収縮による尿の逆流防止には直接関与しません。
Question:尿管と精管
問題文: In males, which structure crosses superior to the ureter as it approaches the bladder?
- a. Ductus deferens
- b. Uterine artery
- c. Internal iliac artery
- d. Rectum
Answer: a. Ductus deferens
解説: 男性において、尿管 (Ureter) は膀胱に接近する際、精管 (Ductus deferens) が上方を横切ります。精管は尿管の後外側に位置し、膀胱の後上方角で膀胱に接続します。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、子宮動脈 (Uterine artery) は女性の解剖学的構造であり、内腸骨動脈 (Internal iliac artery) や直腸 (Rectum) は尿管の直上を横切りません。
Question:下膀胱動脈
問題文: The main arterial supply to the urinary bladder in males, specifically the fundus and neck, is provided by which artery?
- a. Superior vesical artery
- b. Inferior vesical artery
- c. Middle rectal artery
- d. Internal pudendal artery
Answer: b. Inferior vesical artery
解説: 男性の膀胱 (Urinary bladder) において、底部 (Fundus) と頸部 (Neck) には主に下膀胱動脈 (Inferior vesical artery) が血流を供給します。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、上膀胱動脈 (Superior vesical artery) は膀胱の前上部に血液を供給し、中直腸動脈 (Middle rectal artery) や内陰部動脈 (Internal pudendal artery) は直接的には膀胱の底部と頸部の血流供給には関与しません。
Question:内尿道括約筋
問題文: What is the function of the internal urethral sphincter in males during ejaculation?
- a. To relax and allow urine to flow
- b. To prevent reflux of semen into the bladder
- c. To assist in bladder filling
- d. To maintain constant pressure in the urethra
Answer: b. To prevent reflux of semen into the bladder
解説: 男性において、内尿道括約筋 (Internal urethral sphincter) は射精時に収縮し、精液が膀胱に逆流 (Ejaculatory reflux) するのを防ぎます。これは膀胱内への逆流を防止する重要な役割です。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、この筋肉の役割が射精時に特化したものであり、通常の排尿には関与しません。
Question:尿管と子宮動脈
問題文: In females, the ureter passes inferiorly to which artery as it approaches the bladder?
- a. Superior vesical artery
- b. Uterine artery
- c. Inferior vesical artery
- d. Middle rectal artery
Answer: b. Uterine artery
解説: 女性において、尿管 (Ureter) は膀胱に向かう際、子宮動脈 (Uterine artery) の下を通過します。この解剖学的関係は手術中に損傷のリスクがあるため注意が必要です。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、上膀胱動脈 (Superior vesical artery)、下膀胱動脈 (Inferior vesical artery)、中直腸動脈 (Middle rectal artery) は尿管と子宮動脈の位置関係に関与しないためです。
Question:膀胱と直腸
問題文: Which of the following structures is considered a true pelvic viscus?
- a. Sigmoid colon
- b. Small intestine
- c. Urinary bladder
- d. Liver
Answer: c. Urinary bladder
解説: 膀胱 (Urinary bladder) と直腸 (Rectum) は「真の骨盤内臓器」(True pelvic viscera) と呼ばれ、骨盤内に位置し、腹部で始まる消化器系および泌尿器系の延長です。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、S状結腸 (Sigmoid colon) や小腸 (Small intestine) は一部が骨盤に入り込むものの、腹部臓器として分類され、肝臓 (Liver) も同様に腹部に位置します。
Question:小児の膀胱位置
問題文: In infants and young children, the urinary bladder is typically located:
- a. Entirely within the lesser pelvis
- b. Partially in the lesser pelvis
- c. In the abdomen, even when empty
- d. Anterior to the rectum
Answer: c. In the abdomen, even when empty
解説: 幼児や小児では、膀胱 (Urinary bladder) は空の状態でも腹腔内に位置します。通常、6歳頃には大骨盤に収まり、思春期以降に小骨盤内に位置するようになります。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、成人になるまで膀胱が完全に小骨盤内に位置することはないためです。
Question:パラコルピウム
問題文: Which structure provides indirect support to the urinary bladder in females by attaching the vagina to the pelvic fascia?
- a. Puboprostatic ligament
- b. Pubovesical ligament
- c. Paracolpium
- d. Uterosacral ligament
Answer: c. Paracolpium
解説: 女性において、膣 (Vagina) を骨盤筋膜 (Pelvic fascia) に間接的に固定することで膀胱 (Urinary bladder) を支える構造は、膣側支持組織である「パラコルピウム」(Paracolpium) です。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、恥骨膀胱靱帯 (Pubovesical ligament) は直接的に膀胱を支え、他の選択肢も膣の間接的な支持には関与しないためです。
Question:膀胱頂部
問題文: Which part of the urinary bladder points toward the pubic symphysis when the bladder is empty?
- a. Fundus
- b. Apex
- c. Neck
- d. Trigone
Answer: b. Apex
解説: 空の膀胱 (Urinary bladder) において、膀胱の頂部 (Apex) は恥骨結合 (Pubic symphysis) の上縁に向かって配置されています。膀胱の底部 (Fundus) は逆に後方にあり、膀胱の主な部分である体部 (Body) の間に位置します。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、これらの部分が膀胱の異なる方向に位置するためです。
Question:女性外尿道口
問題文: In females, the external urethral orifice is located:
- a. At the tip of the glans clitoris
- b. Anterior to the vaginal orifice in the vestibule
- c. Between the labia majora
- d. At the midpoint of the labia minora
Answer: b. Anterior to the vaginal orifice in the vestibule
解説: 女性の外尿道口 (External urethral orifice) は膣口 (Vaginal orifice) の前方、外陰部の前庭 (Vestibule) に位置します。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、外尿道口が陰核の先端や小陰唇の中間には位置しないためです。
Question:尿管と子宮動脈
問題文: Which arteries most commonly supply the terminal parts of the ureter in females?
- a. Inferior vesical arteries
- b. Vaginal arteries
- c. Ovarian arteries
- d. Uterine arteries
Answer: d. Uterine arteries
解説: 女性において、尿管の骨盤部の終端に最も頻繁に血液供給を行うのは、子宮動脈 (Uterine arteries) の分枝です。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、下膀胱動脈 (Inferior vesical arteries) は通常男性での供給源であり、卵巣動脈 (Ovarian arteries) や膣動脈 (Vaginal arteries) も尿管に対して直接的な供給源にはなりません。
Question:尿管とリンパ節
問題文: The lymphatic drainage from the pelvic part of the ureters primarily drains into which lymph nodes?
- a. Inguinal lymph nodes
- b. Common and internal iliac lymph nodes
- c. Superior mesenteric lymph nodes
- d. Para-aortic lymph nodes
Answer: b. Common and internal iliac lymph nodes
解説: 尿管の骨盤部のリンパは、主に共通腸骨リンパ節 (Common iliac lymph nodes) と内腸骨リンパ節 (Internal iliac lymph nodes) に流入します。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、これらのリンパ節が尿管の骨盤部に関与するリンパ節であるためです。
Question:デトルソル筋
問題文: What is the role of the detrusor muscle in the bladder wall?
- a. To open the external urethral sphincter
- b. To contract the bladder during urination
- c. To provide structural support to the bladder
- d. To prevent the backflow of urine from the ureters
Answer: b. To contract the bladder during urination
解説: 膀胱壁のデトルソル筋 (Detrusor muscle) は、排尿時に収縮して膀胱内の尿を押し出す役割を担います。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、デトルソル筋が主に排尿に関与しており、構造的サポートや尿管からの逆流防止は異なる筋肉や機構が担当するためです。
Question:射精管
問題文: In males, which structure opens into the prostatic urethra, merging the urinary and reproductive tracts?
- a. Seminal colliculus
- b. Ejaculatory ducts
- c. Prostatic utricle
- d. Urethral crest
Answer: b. Ejaculatory ducts
解説: 男性において、射精管 (Ejaculatory ducts) が前立腺部尿道 (Prostatic urethra) に開口し、ここで尿路系と生殖器系が合流します。他の選択肢が誤りである理由は、尿道稜 (Urethral crest) や前立腺小室 (Prostatic utricle) は合流に関与せず、主に構造的な特徴であるためです。
Question:前立腺静脈叢と膀胱静脈叢
問題文: Which venous plexus does the vesical venous plexus communicate with in males?
- a. Rectal venous plexus
- b. Prostatic venous plexus
- c. Dorsal vein of the penis
- d. Sacral venous plexus
Answer: b. Prostatic venous plexus
解説: 男性では、膀胱静脈叢 (Vesical venous plexus) は前立腺静脈叢 (Prostatic venous plexus) と連絡しています。膀胱の底部および尿管下端からの血液がこの静脈叢を経由して流れます。他の選択肢が誤りである理由として、直腸静脈叢や陰茎背静脈は異なる部位に関連しています。


コメント