Contents
- 1 アセス1
- 1.1 Question 1 of 40
- 1.2 Question 2 of 40
- 1.3 Question 3 of 40
- 1.4 Question 4 of 40
- 1.5 Question 5 of 40
- 1.6 Question 6 of 40
- 1.7 Question 7 of 40
- 1.8 Question 8 of 40
- 1.9 Question 9 of 40
- 1.10 Question 10 of 40
- 1.11 Question 11 of 40
- 1.12 Question 12 of 40
- 1.13 Question 13 of 40
- 1.14 Question 14 of 40
- 1.15 Question 15 of 40
- 1.16 Question 16 of 40
- 1.17 Question 17 of 40
- 1.18 Question 18 of 40
- 1.19 Question 19 of 40
- 1.20 Question 20 of 40
- 1.21 Question 21 of 40
- 1.22 Question 22 of 40
- 1.23 Question 23 of 40
- 1.24 Question 24 of 40
- 1.25 Question 25 of 40
- 1.26 Question 26 of 40
- 1.27 Question 27 of 40
- 1.28 Question 28 of 40
- 1.29 Question 29 of 40
- 1.30 Question 30 of 40
- 1.31 Question 31 of 40
- 1.32 Question 32 of 40
- 1.33 Question 33 of 40
- 1.34 Question 34 of 40
- 1.35 Question 35 of 40
- 1.36 Question 36 of 40
- 1.37 Question 37 of 40
- 1.38 Question 38 of 40
- 1.39 Question 39 of 40
- 1.40 Question 40 of 40
- 1.41 ADDITIONAL
- 2 アセス2(22nd Oct 2024)
- 2.1 Question 1 of 20
- 2.2 Question 2 of 20
- 2.3 Question 3 of 20
- 2.4 Question 4 of 20
- 2.5 Question 5 of 20
- 2.6 Question 6 of 20
- 2.7 Question 7 of 20
- 2.8 Question 8 of 20
- 2.9 Question 9 of 20
- 2.10 Question 10 of 20
- 2.11 Question 11 of 20
- 2.12 Question 12 of 20
- 2.13 Question 13 of 20
- 2.14 Question 14 of 20
- 2.15 Question 15 of 20
- 2.16 Question 16 of 20
- 2.17 Question 17 of 20
- 2.18 Question 18 of 20
- 2.19 Question 19 of 20
- 2.20 Question 20 of 20
- 3 ブロック
- 3.1 Question 136 of 185
- 3.2 Question 137 of 185
- 3.3 Question 138 of 185
- 3.4 Question 139 of 185
- 3.5 Question 140 of 185
- 3.6 Question 141 of 185
- 3.7 Question 142 of 185
- 3.8 Question 143 of 185
- 3.9 Question 144 of 185
- 3.10 Question 145 of 185
- 3.11 Question 146 of 185
- 3.12 Question 147 of 185
- 3.13 Question 148 of 185
- 3.14 Question 149 of 185
- 3.15 Question 150 of 185
- 3.16 Question 151 of 185
- 3.17 Question 152 of 185
- 3.18 Question 153 of 185
- 3.19 Question 154 of 185
- 3.20 Question 155 of 185
- 3.21 Question 156 of 185
- 3.22 Question 157 of 185
- 3.23 Question 158 of 185
- 3.24 Question 159 of 185
- 3.25 Question 160 of 185
- 3.26 Question 161 of 185
- 3.27 Question 162 of 185
- 3.28 Question 163 of 185
- 3.29 Question 164 of 185
- 3.30 Question 165 of 185
- 3.31 Question 166 of 185
- 3.32 Question 167 of 185
- 3.33 Question 168 of 185
- 3.34 Question 169 of 185
- 3.35 Question 170 of 185
- 3.36 Question 171 of 185
- 3.37 Question 172 of 185
- 3.38 Question 173 of 185
- 3.39 Question 174 of 185
- 3.40 Question 175 of 185
- 3.41 Question 176 of 185
- 3.42 Question 177 of 185
- 3.43 Question 178 of 185
- 3.44 Question 179 of 185
- 3.45 Question 180 of 185
- 3.46 Question 181 of 185
- 3.47 Question 182 of 185
- 3.48 Question 183 of 185
- 3.49 Question 184 of 185
- 3.50 Question 185 of 185
- 4 自作問題(50問、22nd Oct 2024)
アセス1
Question 1 of 40
Digestive enzymes secreted by the small intestine do NOT include:
a. Peptidases
b. Bile
c. Lipase
d. Sucrases
Answer: b. Bile
解説: 小腸はペプチダーゼ、リパーゼ、スクラーゼなどの消化酵素を分泌しますが、**胆汁(bile)**は肝臓で生成され、胆嚢から分泌されます。胆汁は消化酵素ではなく、脂肪の乳化を助ける液体です。
- a. Peptidases: 小腸で分泌され、タンパク質をペプチドに分解します。
- c. Lipase: 脂肪を分解する酵素で、小腸でも分泌されます。
- d. Sucrases: スクロース(砂糖)をグルコースとフルクトースに分解する酵素で、小腸で分泌されます。

Question 2 of 40
The esophageal secretions include:
a. Bile only
b. Trypsin and chymotrypsin
c. Mucus only
d. Pepsinogen and intrinsic factor
Answer: c. Mucus only
解説: 食道は主に**粘液(mucus)**のみを分泌し、食物が食道を滑らかに通過するのを助けます。他の選択肢は食道で分泌されません。
- a. Bile only: 胆汁は肝臓で生成され、胆嚢から分泌され、食道では分泌されません。
- b. Trypsin and chymotrypsin: これらの酵素は膵臓から分泌され、タンパク質の消化を助けます。
- d. Pepsinogen and intrinsic factor: ペプシノーゲンと内因子は胃で分泌されます。
Question 3 of 40
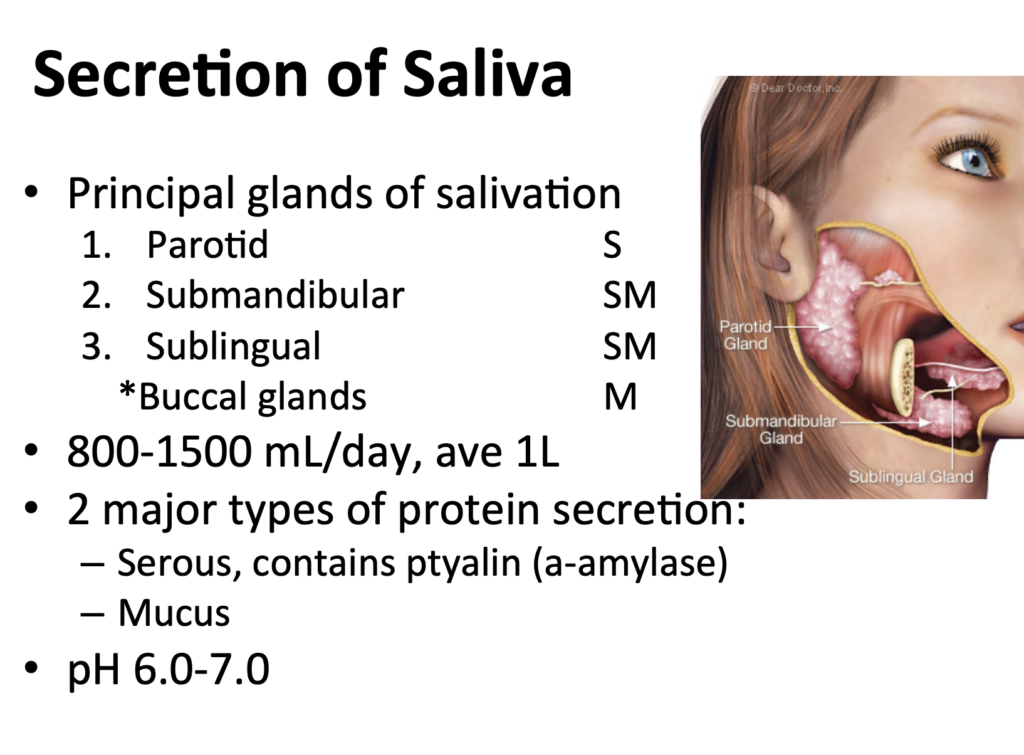
Which of the following is characteristic of saliva?
a. A lower HCO3- concentration than plasma
b. The presence of proteases
c. Isotonic relative to plasma
d. Modification by the salivary ductal cells involves secretion of K+ and HCO3-
Answer: d. Modification by the salivary ductal cells involves secretion of K+ and HCO3-
解説: 唾液腺の導管細胞は、唾液の成分を修正し、カリウム(K+)と炭酸水素イオン(HCO3-)を分泌します。これにより、唾液の成分が血漿と異なるものになります。
- a. A lower HCO3- concentration than plasma: 唾液は血漿よりも高いHCO3-濃度を持っています。
- b. The presence of proteases: 唾液にはプロテアーゼは含まれていません。プロテアーゼは主に胃や膵臓から分泌されます。
- c. Isotonic relative to plasma: 唾液は等張ではなく、通常は低張(hypotonic)です。
Question 4 of 40
Secretion of gastric juice:
a. Is essential for protein digestion
b. Is essential for vitamin B12 absorption
c. Decreases when food stimulates mucosal cells in the pyloric region
d. In response to food is increased after vagotomy
Answer: b. Is essential for vitamin B12 absorption
解説: 胃液に含まれる内因子(intrinsic factor)は、ビタミンB12の吸収に不可欠です。胃液自体はタンパク質の消化やその他の役割も果たしますが、ビタミンB12の吸収に特に重要です。
- a. Is essential for protein digestion: 胃液はタンパク質の消化に重要ですが、唯一の役割ではありません。
- c. Decreases when food stimulates mucosal cells in the pyloric region: 幽門部の粘膜細胞が刺激されると、胃酸の分泌は増加します。
- d. In response to food is increased after vagotomy: 迷走神経切断術後、胃酸分泌は減少する傾向にあります。

Question 5 of 40
Which GI secretion is inhibited when the pH of the stomach contents is 1.0?
a. Bile
b. Saliva
c. Gastric Secretion
d. Pancreatic Secretion
Answer: c. Gastric Secretion
解説: 胃のpHが1.0まで低下すると、胃酸の分泌は抑制されます。胃内が非常に酸性になると、さらに酸を分泌する必要がなくなります。
- a. Bile: 胆汁は小腸で脂肪を乳化するために分泌され、胃のpHには直接関与しません。
- b. Saliva: 唾液分泌は胃のpHに影響されません。
- d. Pancreatic Secretion: 膵液の分泌は胃のpHには直接影響されません。
Question 6 of 40
When oxyntic cells are stimulated, they secrete:
a. Mucus and pepsinogen
b. HCO3- and intrinsic factor
c. HCl and pepsinogen
d. HCl and intrinsic factor
Answer: d. HCl and intrinsic factor
解説: 壁細胞(oxyntic cells)は塩酸(HCl)と内因子(intrinsic factor)を分泌し、タンパク質の消化とビタミンB12の吸収に関与します。
- a. Mucus and pepsinogen: ペプシノーゲンは主細胞が分泌し、粘液は粘液細胞が分泌します。
- b. HCO3- and intrinsic factor: HCO3-は壁細胞ではなく膵臓や小腸で分泌されます。
- c. HCl and pepsinogen: HClは壁細胞から分泌されますが、ペプシノーゲンは主細胞から分泌されます。
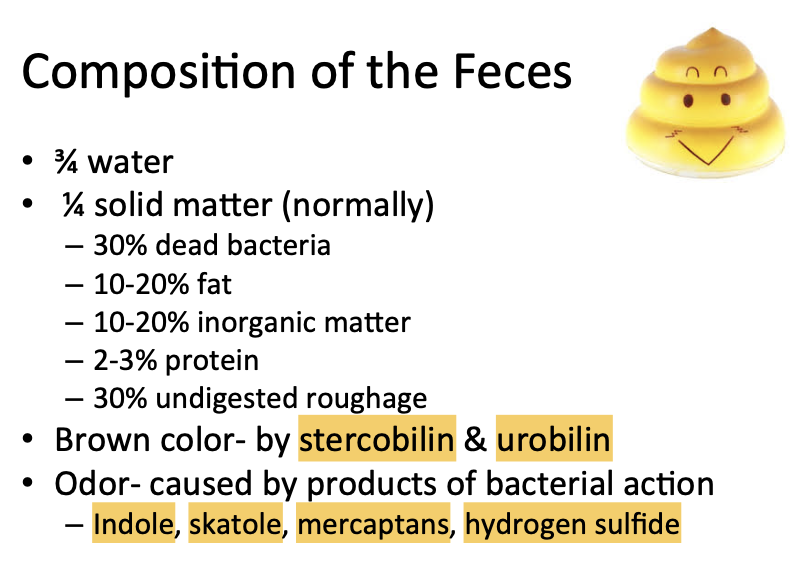
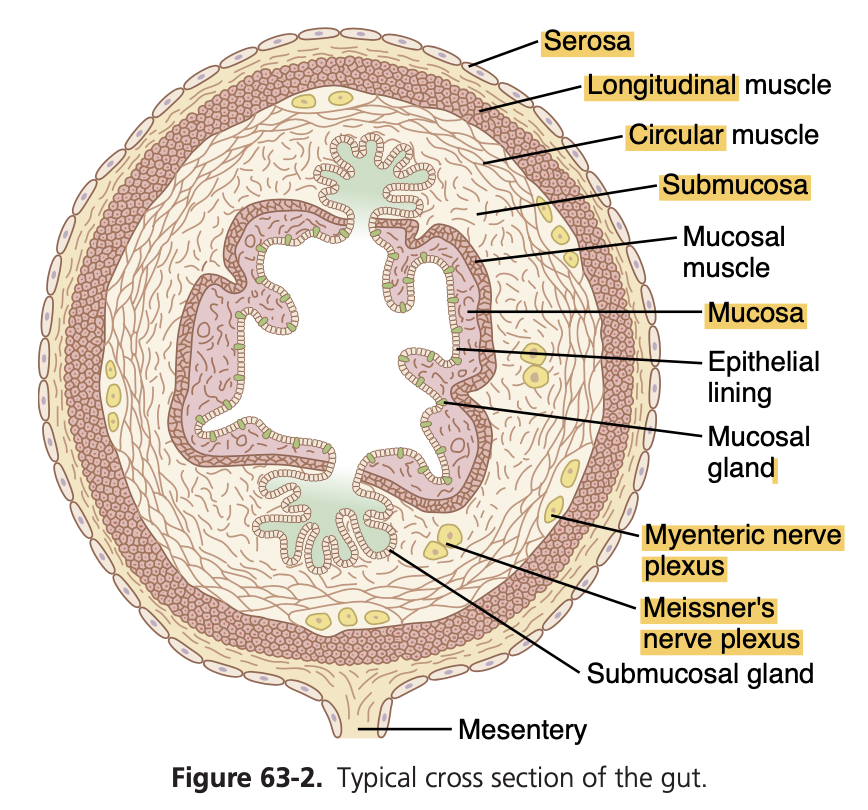
Secretions From the Gastric (Oxyntic) Glands
A typical stomach oxyntic gland is shown in Figure 65-4. It is composed of three main types of cells:
(1) mucous neck cells, which secrete mainly mucus;
(2) peptic (or chief) cells, which secrete large quantities of pepsinogen; and
(3) parietal (or oxyntic) cells, which secrete hydrochloric acid and intrinsic factor.
Oxyntic glands also contain some additional cells types, including the enterochromaffin-like (ECL) cells that secrete histamine.
Question 7 of 40
The most important enzyme for digestion of triglycerides:
a. Salivary amylase
b. Lingual lipase
c. Pancreatic lipase
d. Enteric lipase
Answer: c. Pancreatic lipase
解説: 膵リパーゼ(pancreatic lipase)はトリグリセリドを分解する主要な酵素で、脂肪の消化に不可欠です。
- a. Salivary amylase: 唾液アミラーゼは炭水化物の消化に関与します。
- b. Lingual lipase: リンガルリパーゼは少量の脂肪分解に関与しますが、主な役割はありません。
- d. Enteric lipase: 腸リパーゼは脂肪分解に関与しますが、膵リパーゼほど重要ではありません。
Question 8 of 40
Which of the following choices is NOT a characteristic of mucus?
a. It is composed mainly of water, electrolytes, and a mixture of several glycoproteins, which are composed of large polysaccharides bound with much smaller quantities of protein.
b. It is the same in composition in all parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
c. It has adherent qualities that make it adhere tightly to the food or other particles and to spread as a thin film over the surfaces.
d. It has the ability to allow easy slippage of food along the gastrointestinal tract.
Answer: b. It is the same in composition in all parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
解説: 粘液の組成は消化管の異なる部分で異なり、異なる役割を果たします。例えば、胃の粘液と腸の粘液は異なる組成を持ちます。
- a. Composed of water, electrolytes, glycoproteins: これは粘液の一般的な特徴です。
- c. Adherent qualities: 粘液は食品や消化管の表面に密着します。
- d. Easy slippage: 食物の滑りを助けます。
Question 9 of 40
Which of the following type of gland does NOT match with its location?
a. Tubular glands: stomach
b. Pits: small intestine
c. Complex glands: large intestine
d. Goblet cells: esophagus
Answer: c
Explanation:
- Tubular glands (stomach): Tubular glands are present in the stomach, where they secrete various digestive enzymes and acids to aid in digestion.
- Pits (small intestine): In the small intestine, especially in the duodenum, crypts (often referred to as intestinal glands or pits) are present, which secrete digestive enzymes and mucus to help in nutrient absorption and digestion.
- Complex glands (large intestine): Complex glands are generally not a characteristic of the large intestine. The large intestine primarily contains simple tubular glands, especially goblet cells, which secrete mucus to facilitate the movement of waste material.
- Goblet cells (esophagus): Goblet cells are typically found in the intestines rather than the esophagus. They produce mucus, which is important for lubrication. The esophagus, while containing mucus-secreting cells, does not have goblet cells as part of its normal histology.


Question 10 of 40
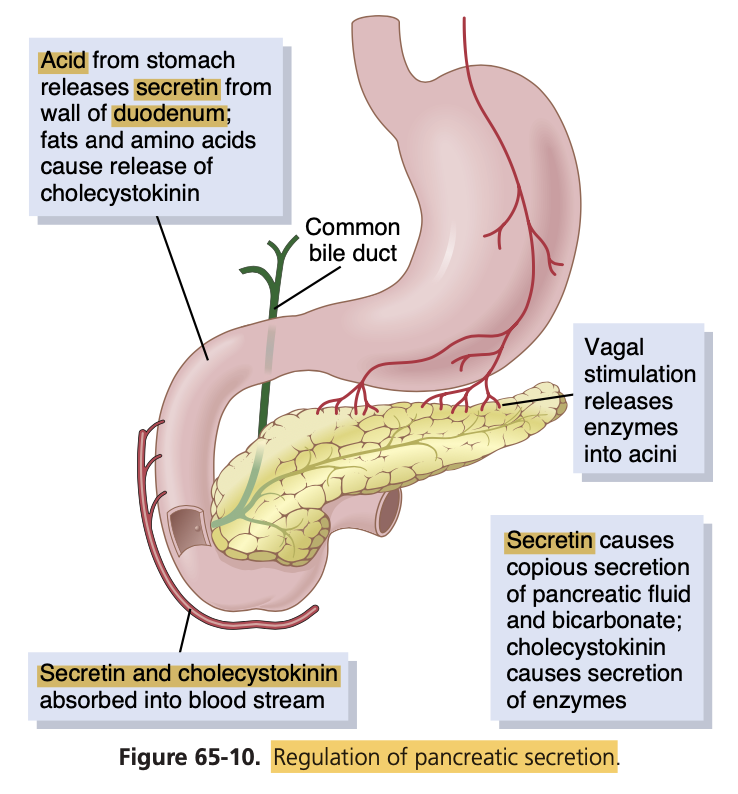
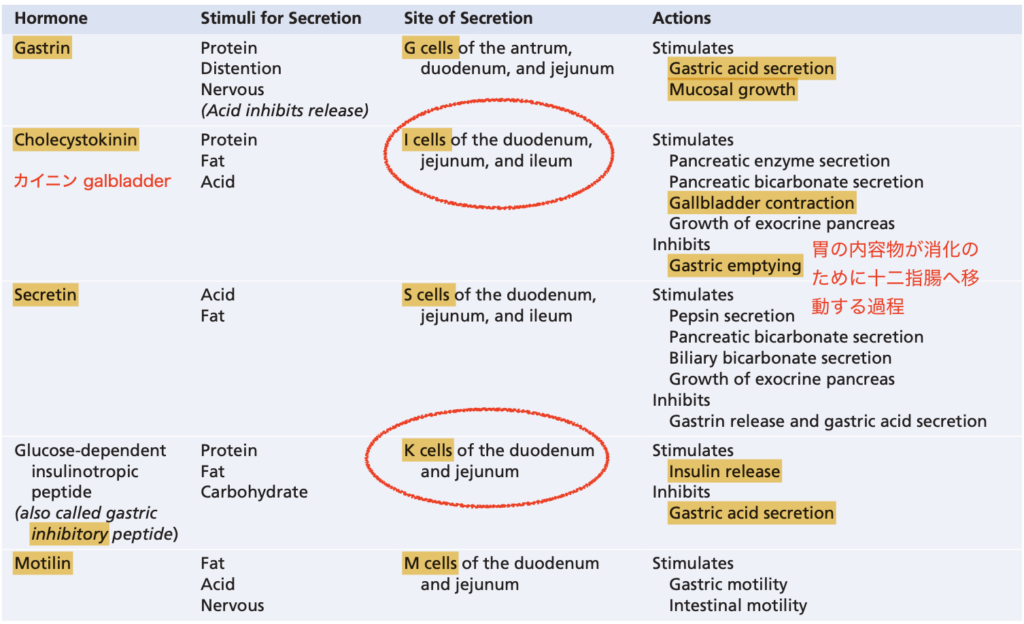
Hormone that is secreted in the duodenum when highly acidic food enters the small intestine and in turn causes the pancreas to secrete large quantities of fluid with a high concentration of bicarbonate ions:
a. Secretin
b. Gastrin
c. Histamine
d. Cholecystokinin
Answer: a. Secretin
解説: **セクレチン(Secretin)**は十二指腸に酸性の内容物が入ったときに分泌され、膵臓に大量の炭酸水素イオンを含む液体を分泌させ、酸を中和します。
- b. Gastrin: ガストリンは胃酸の分泌を促進します。
- c. Histamine: ヒスタミンは胃酸の分泌を促進しますが、酸性の内容物が腸に入った後の反応には関与しません。
- d. Cholecystokinin: コレシストキニンは胆嚢の収縮を促し、膵臓から酵素を分泌させますが、炭酸水素イオンの分泌には関与しません。
Question 11 of 40
All of the following processes require pancreatic secretion EXCEPT:
a. Protein digestion
b. Electrolyte absorption
c. Fat absorption
d. Carbohydrate digestion
Answer: b. Electrolyte absorption
解説: 膵液はタンパク質、脂肪、炭水化物の消化に必要ですが、電解質の吸収には直接関与しません。電解質の吸収は腸壁の細胞によって行われます。
- a. Protein digestion: 膵臓から分泌されるトリプシンやキモトリプシンがタンパク質を消化します。
- c. Fat absorption: 膵リパーゼは脂肪を分解して吸収可能な形にします。
- d. Carbohydrate digestion: 膵アミラーゼが炭水化物を消化します。

Question 12 of 40
A carbohydrate found in the human diet with no known digestive enzymes capable of hydrolyzing it:
a. Cellulose
b. Sucrose
c. Lactose
d. Starches
Answer: a. Cellulose
解説: **セルロース(Cellulose)**は人間の消化酵素では分解できない炭水化物です。これは植物の細胞壁に含まれ、食物繊維として機能します。
- b. Sucrose: スクラーゼが分解します。
- c. Lactose: ラクターゼが分解します。
- d. Starches: アミラーゼが分解します。

Question 13 of 40
Small, spherical and cylindrical globules composed of 20-40 molecules of bile salts which perform a “ferrying function” in fat absorption:
a. Micelles
b. Monoglycerides
c. Microbilirubin
d. Pinocytic vesicles
Answer: a. Micelles
解説: ミセル(Micelles)は胆汁酸から成り、脂肪を吸収するために「輸送」機能を果たします。ミセルは脂肪酸やモノグリセリドを腸壁まで運びます。
- b. Monoglycerides: モノグリセリドは脂肪の消化産物です。
- c. Microbilirubin: 存在しない構造です。
- d. Pinocytic vesicles: 飲作用による小胞です。
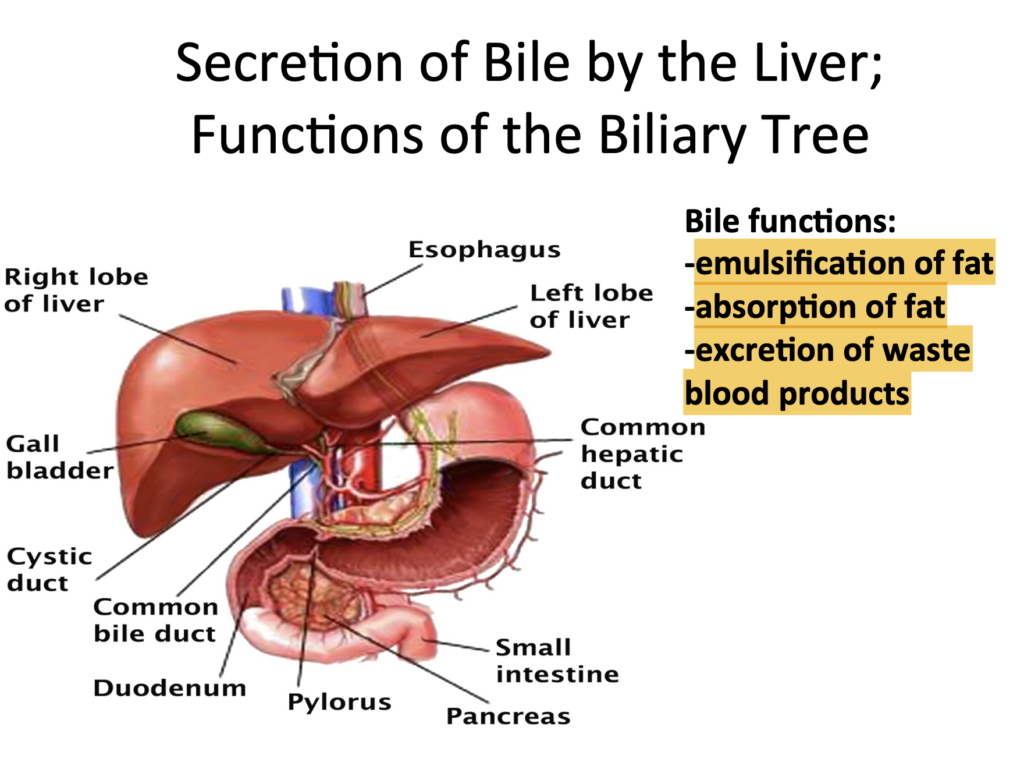
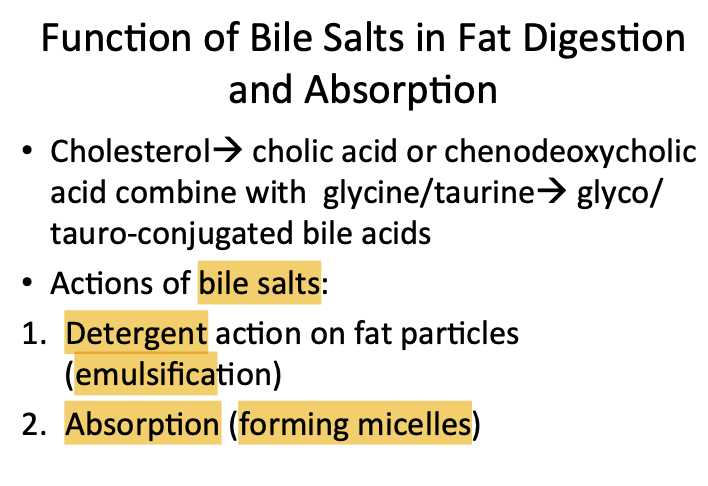

Question 14 of 40
Pepsinogen:
a. Its active form pepsin functions optimally in pH of 5
b. When first secreted has no digestive activity
c. Is inactivated when in contact with HCl
d. Regulation of secretion is through gastrin & histamine
Answer: b. When first secreted has no digestive activity
解説: ペプシノーゲン(Pepsinogen)は不活性な前駆体であり、塩酸(HCl)によって活性型のペプシンに変わり、タンパク質の消化に関与します。ペプシンは低pHで最もよく機能します。
- a. pH of 5: ペプシンはpH1.5〜3.5で最適に機能します。
- c. Inactivated when in contact with HCl: ペプシノーゲンはHClに触れると活性化します。
- d. Regulation of secretion: ペプシノーゲンの分泌は主にアセチルコリンとガストリンによって調節されます。

Question 15 of 40
TRUE statement about large intestinal secretions when compared to the small intestinal secretions:
a. The large intestinal secretions help in absorption of the digestates
b. The large intestine secretes less mucus than the small intestine
c. The large intestine secretes more enzymes for carbohydrate, protein and fat digestion
Answer: a. The large intestinal secretions help in absorption of the digestates
解説: 大腸の分泌物(主に粘液)は消化物の吸収を助けますが、大腸では消化酵素の分泌はほとんど行われません。消化酵素は主に小腸で分泌されます。
- b. Secretes less mucus: 大腸は小腸よりも多くの粘液を分泌します。
- c. Secretes more enzymes: 大腸は消化酵素をほとんど分泌しません。

Question 16 of 40
The most abundant substance secreted in the bile:
a. Cholesterol
b. Lecithin
c. Bile salts
d. Bilirubin
Answer: c. Bile salts
解説: 胆汁の中で最も豊富な成分は胆汁酸(bile salts)であり、脂肪の乳化と消化を助けます。
- a. Cholesterol: 胆汁に含まれていますが、主要成分ではありません。
- b. Lecithin: レシチンは胆汁の一成分ですが、量は少ないです。
- d. Bilirubin: 胆汁に含まれるが、主に老廃物として排泄されます。
Question 17 of 40
The main driving force for hydrochloric acid secretion by the parietal cells:
a. Na pump
b. H-K ATPase pump
c. Na-K ATPase pump
d. Na-Ca pump
Answer: b. H-K ATPase pump
解説: 壁細胞(parietal cells)はH-K ATPaseポンプを使用してH+を胃内に分泌し、胃酸を生成します。このプロセスは胃酸分泌の主要な駆動力です。
- a. Na pump: ナトリウムポンプは異なる役割を果たします。
- c. Na-K ATPase pump: これは他の細胞で使用されますが、胃酸分泌には関与しません。
- d. Na-Ca pump: これはカルシウムの輸送に関与しますが、胃酸分泌には関与しません。
Question 18 of 40
An active digestive enzyme secreted by the chief cells of the stomach which digests collagen, a major constituent of the intercellular connective tissue of meats:
a. Chymotrypsin
b. Pepsin
c. Elastase
d. Trypsin
Answer: b. Pepsin
解説: ペプシンは主細胞(chief cells)から分泌され、コラーゲンを消化して肉の結合組織を分解し、他の酵素がさらにタンパク質を消化できるようにします。
- a. Chymotrypsin: これは膵臓から分泌される酵素です。
- c. Elastase: 膵臓から分泌される酵素です。
- d. Trypsin: これも膵臓から分泌される酵素です。
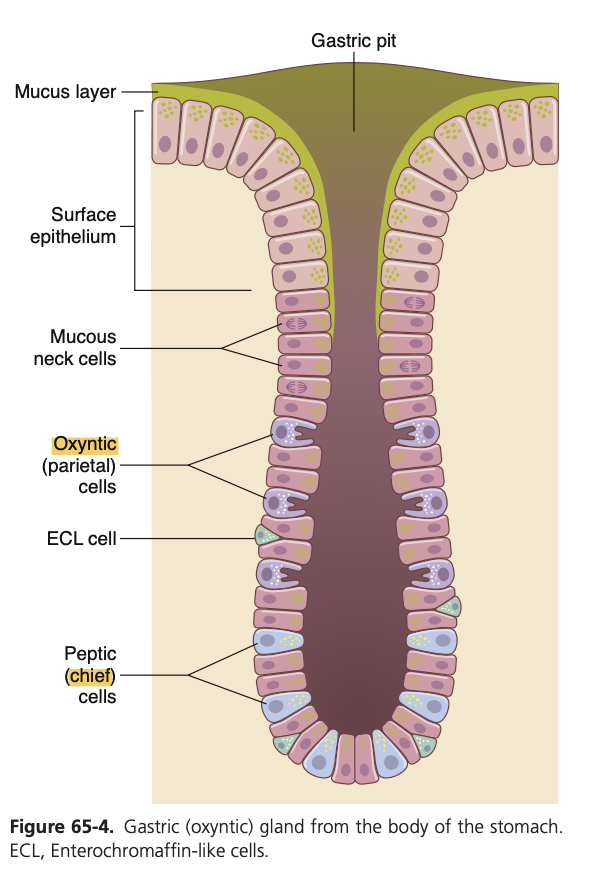
Question 19 of 40
Which of the following components of bile is critical for fat digestion?
a. Bilirubin
b. Lecithin
c. Cholesterol
d. Calcium salts
Answer: b. Lecithin
解説: レシチンは脂肪の乳化を助け、脂肪の消化に重要な役割を果たします。胆汁の中には胆汁酸も含まれ、これも脂肪消化に必要です。
- a. Bilirubin: これは老廃物であり、脂肪消化には関与しません。
- c. Cholesterol: 胆汁に含まれますが、脂肪消化には関与しません。
- d. Calcium salts: これも脂肪消化には関与しません。
Question 20 of 40
These provide the greatest surface area for the absorption in the small intestine:
a. Villi
b. Taenia coli
c. Valvulae conniventes
d. Microvilli
Answer: d. Microvilli
解説: 小腸の吸収面積を最大化する構造は微絨毛(microvilli)です。これは腸上皮細胞の表面に存在し、栄養素の吸収を助けます。
- a. Villi: 絨毛は吸収面積を増やしますが、微絨毛の方が面積が大きいです。
- b. Taenia coli: これは大腸の筋層です。
- c. Valvulae conniventes: これは小腸のヒダですが、微絨毛ほど面積を提供しません。
Question 21 of 40
Regarding gastric secretion, the pyloric glands:
a. Are located on the body and fundus of the stomach, in the proximal 80%
b. Secrete mucus & gastrin
c. Secrete intrinsic factor & HCl
d. Are acid-forming glands
Answer: b. Secrete mucus & gastrin
解説: 幽門腺(pyloric glands)は、幽門部に位置し、**粘液とガストリン(mucus & gastrin)**を分泌します。ガストリンは胃酸の分泌を刺激するホルモンです。
- a. Located on the body and fundus: 幽門腺は胃の体部や底部ではなく、幽門部に位置しています。
- c. Secrete intrinsic factor & HCl: 内因子とHClは壁細胞(oxyntic cells)から分泌されます。
- d. Are acid-forming glands: 幽門腺は酸を生成しませんが、ガストリンを分泌して酸分泌を刺激します。


Question 22 of 40
Most abundant fat in the human diet:
a. Triglycerides
b. Cholesterol esters
c. Phospholipids
d. Cholesterol
Answer: a. Triglycerides
解説: トリグリセリド(Triglycerides)は人間の食事において最も豊富な脂肪の形態です。これは脂肪酸とグリセロールの結合で構成されています。
- b. Cholesterol esters: コレステロールエステルは脂肪の一形態ですが、食事で摂取される量は少ないです。
- c. Phospholipids: リン脂質は細胞膜の構成成分ですが、食事中の量は限られています。
- d. Cholesterol: コレステロールは食事に含まれますが、トリグリセリドほど多くはありません。
Question 23 of 40
Gastrin:
a. Is a hormone secreted by G cells located in the pyloric glands in the proximal end of the stomach
b. Lies in the deep recesses of the oxyntic glands and therefore releases histamine
c. Is a large polypeptide secreted in two forms, G-34 & G-17, of which the larger is more abundant
d. Released by gastrin cells that are stimulated when meats reach the antrum
Answer: d
Gastrin and G cells: Gastrin is a hormone produced and secreted by G cells, primarily found in the pyloric glands located at the distal end of the stomach (specifically in the antrum region). Gastrin plays a key role in stimulating gastric acid (HCl) secretion from parietal cells in the stomach lining.
Histamine and Oxyntic Glands (b): Histamine is secreted by enterochromaffin-like cells (ECL cells), not G cells, and is found within the oxyntic glands (gastric glands in the fundus and body of the stomach). Histamine stimulates acid secretion but is not directly related to the primary function of gastrin.
Polypeptide Forms of Gastrin (c): Gastrin does exist in different molecular forms, including G-34 and G-17, with G-17 being the more active and abundant form in the human stomach, not the larger G-34.
Gastrin Stimulation (d): While gastrin secretion is indeed stimulated by the presence of proteins in the stomach, it occurs when protein digestion products (like amino acids and peptides) reach the antrum, rather than whole pieces of meat.
Question 24 of 40
This contributes the greatest amount in the total volume of intestinal juices:
a. Saliva
b. Gastric juices
c. Small intestine secretions
d. Large intestine secretions
Answer: c
Small intestine secretions contribute the greatest amount to the total volume of intestinal juices. The small intestine produces large quantities of digestive juices, including enzymes from the pancreas and bile from the liver, as well as fluids from intestinal cells, which aid in the breakdown and absorption of nutrients.
Saliva (a) primarily aids in the initial digestion of food in the mouth but does not contribute significantly to the total volume of intestinal juices.
Gastric juices (b), while essential for digestion in the stomach, do not match the volume of secretions produced in the small intestine.
Large intestine secretions (d) are minimal compared to the small intestine. The large intestine primarily secretes mucus, which aids in the movement of waste material but contributes very little to the overall volume of digestive juices.
Question 25 of 40
Which of the following is NOT true about the importance of bile?
a. Bile aids in the absorption of digested fat
b. Bile serves as a means of excretion of bilirubin
c. Bile helps to emulsify large fat particles into smaller particles
d. Bile is needed for carbohydrate absorption
Answer: d. Bile is needed for carbohydrate absorption
解説: 胆汁は脂肪の乳化や吸収に重要ですが、炭水化物の吸収には関与しません。炭水化物の吸収は腸の酵素によって行われます。
- a. Bile aids in the absorption of digested fat: 正しいです。
- b. Bile serves as a means of excretion of bilirubin: 正しいです。
- c. Bile helps to emulsify large fat particles: 正しいです。
Question 26 of 40
The absorption of glucose by the small intestine is via:
a. Sodium cotransport
b. Diffusion
c. Solvent drag
d. Active transport
Answer: a
Sodium cotransport (a): The absorption of glucose in the small intestine primarily occurs via sodium-glucose cotransport (also known as secondary active transport). This process involves a cotransporter protein (SGLT1) that moves glucose into the intestinal cells alongside sodium ions, using the electrochemical gradient of sodium created by the sodium-potassium pump.
Diffusion (b): Diffusion is a passive process and does not sufficiently explain glucose absorption, which requires energy to move against the concentration gradient in the small intestine.
Solvent drag (c): Solvent drag refers to the movement of dissolved substances with water as it is absorbed, but this is not the primary mechanism for glucose absorption.
Active transport (d): While glucose absorption does involve an active component, it is specifically through sodium cotransport (secondary active transport) rather than direct primary active transport.


Question 27 of 40
Phase of pancreatic secretion where secretion becomes copious secondary to secretin:
a. Oral phase
b. Cephalic phase
c. Gastric phase
d. Intestinal phase
Answer: d. Intestinal phase
解説: セクレチンは**腸相(intestinal phase)**で分泌され、膵臓の水分と炭酸水素イオンの分泌を増加させます。これは酸性の食物が十二指腸に到達した際に起こります。
- a. Oral phase: 口腔相は主に唾液分泌に関連します。
- b. Cephalic phase: 頭部相は主に胃酸分泌に関与します。
- c. Gastric phase: 胃相は胃の分泌に関連します。
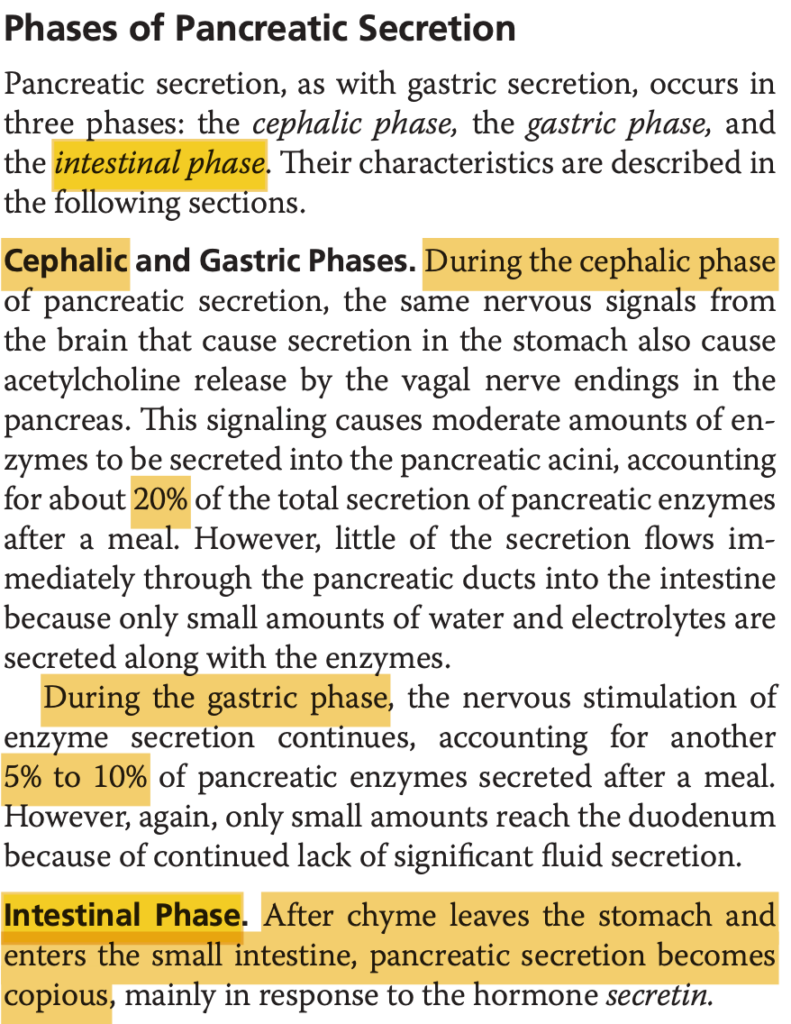
Question 28 of 40
Which is transported in intestinal epithelial cells by a Na+-dependent cotransport process:
a. Oligopolypeptides
b. Fatty acids
c. Fructose
d. Alanine
Answer: d. Alanine
解説: アラニン(Alanine)などのアミノ酸は、ナトリウム依存性の共輸送によって腸の上皮細胞に取り込まれます。
- a. Oligopolypeptides: アミノ酸に分解された後、ナトリウム共輸送によって吸収されます。
- b. Fatty acids: 脂肪酸は拡散によって吸収されます。
- c. Fructose: フルクトースはGLUT5によって輸送され、ナトリウムに依存しません。
Question 29 of 40
Which of the following characterizes protein digestion?
a. For pepsin to cause digestion of proteins, the pH of the stomach must be above 5.0
b. Trypsin initiates the process of protein digestion in meats
c. More than 99% of the final protein digestive products absorbed are individual amino acids
d. All proteins are digested all the way to their constituent amino acids by the pancreatic juices
Answer: c. More than 99% of the final protein digestive products absorbed are individual amino acids
解説: タンパク質の消化では、最終的に99%以上がアミノ酸として吸収されます。ただし、一部の短鎖ペプチドも吸収されます。ペプシンやトリプシンが最初の消化段階を担い、最終的にアミノ酸まで分解されるのは主に膵臓や小腸の酵素によるものです。
- a. For pepsin to cause digestion of proteins, the pH of the stomach must be above 5.0: ペプシンはpH1.5-3.5の酸性環境で最適に機能します。pH5.0以上ではペプシンの活性はほとんどありません。
- b. Trypsin initiates the process of protein digestion in meats: タンパク質の消化は胃のペプシンによって始まり、トリプシンは膵臓でのさらなる消化を助けます。
- d. All proteins are digested all the way to their constituent amino acids by the pancreatic juices: すべてのタンパク質がアミノ酸まで完全に分解されるわけではなく、一部はペプチドとして吸収されます。
Question 30 of 40
The most important pancreatic enzyme needed for protein digestion is:
a. Chymotrypsin
b. Carboxypeptidase
c. Trypsin
d. Aminopeptidase
Answer: c. Trypsin
解説: トリプシン(Trypsin)は膵臓から分泌され、他のタンパク質分解酵素(キモトリプシンやカルボキシペプチダーゼ)を活性化し、タンパク質の消化を開始する重要な酵素です。
- a. Chymotrypsin: これも重要ですが、トリプシンによって活性化されます。
- b. Carboxypeptidase: タンパク質の最終段階で働きますが、最も重要ではありません。
- d. Aminopeptidase: 小腸で働きますが、膵臓ではなく、腸内で活性化されます。
Question 31 of 40
Which of the following does NOT characterize the absorption of glucose by intestinal mucosal cells?
a. It is impaired by blockade of active sodium transport in the cells.
b. Involves the same carriers that are used for the absorption of fructose
c. It relies on a carrier mechanism in the cell membrane.
d. It takes place mainly in the duodenum and jejunum
Answer: b. Involves the same carriers that are used for the absorption of fructose
解説: グルコースはナトリウム依存性共輸送体を介して吸収されますが、フルクトースはGLUT5を介して吸収され、異なるメカニズムです。
- a. Impaired by blockade of active sodium transport: グルコース吸収はナトリウム依存性のため、ナトリウム輸送の阻害によって吸収が妨げられます。
- c. Relies on a carrier mechanism: グルコース吸収にはキャリア機構が必要です。
- d. Takes place mainly in the duodenum and jejunum: グルコースの主な吸収は十二指腸と空腸で行われます。
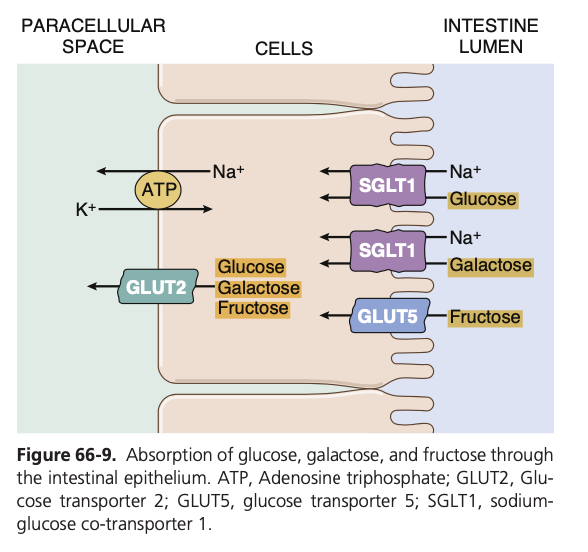
Question 32 of 40
Carbohydrate digestion:
a. Begins when food comes in contact with saliva
b. Begins when food comes in contact with gastric juice
c. Ends when starch has been converted to maltose
d. Splits sucrose into a molecule of galactose and a molecule of glucose
Answer: a. Begins when food comes in contact with saliva
解説: 炭水化物の消化は唾液アミラーゼによって口腔内で始まります。
- b. Gastric juice: 胃液は炭水化物の消化に直接関与しません。
- c. Ends when starch has been converted to maltose: デンプンの消化はマルトースに変換される途中段階で終わりません。
- d. Splits sucrose into galactose and glucose: スクロースはフルクトースとグルコースに分解されます。
Question 33 of 40
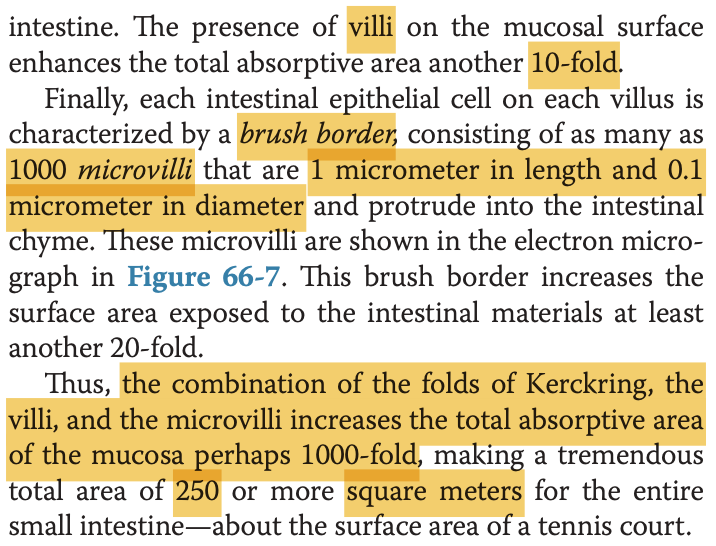
Regarding absorption in the gastrointestinal tract, which of the following is not true:
a. Total surface area of the small intestine is about 250 or more square meters
b. Villi on the mucosal surface of the small intestine enhances the total absorptive area another 10-fold
c. Folds of Kerckring in the small intestine increase the surface area of the absorptive mucosa about 3x
d. The stomach is a good absorptive area because of the typical villus type of absorptive membrane
Answer: d. The stomach is a good absorptive area because of the typical villus type of absorptive membrane
解説: 胃には絨毛がなく、主な吸収場所は小腸です。胃は吸収には適していません。
- a. Surface area of small intestine: 小腸の表面積は非常に広いです。
- b. Villi enhance absorptive area: 絨毛は吸収面積を10倍にします。
- c. Folds of Kerckring: ケルクリングのヒダが吸収面積を増加させます。

Question 34 of 40
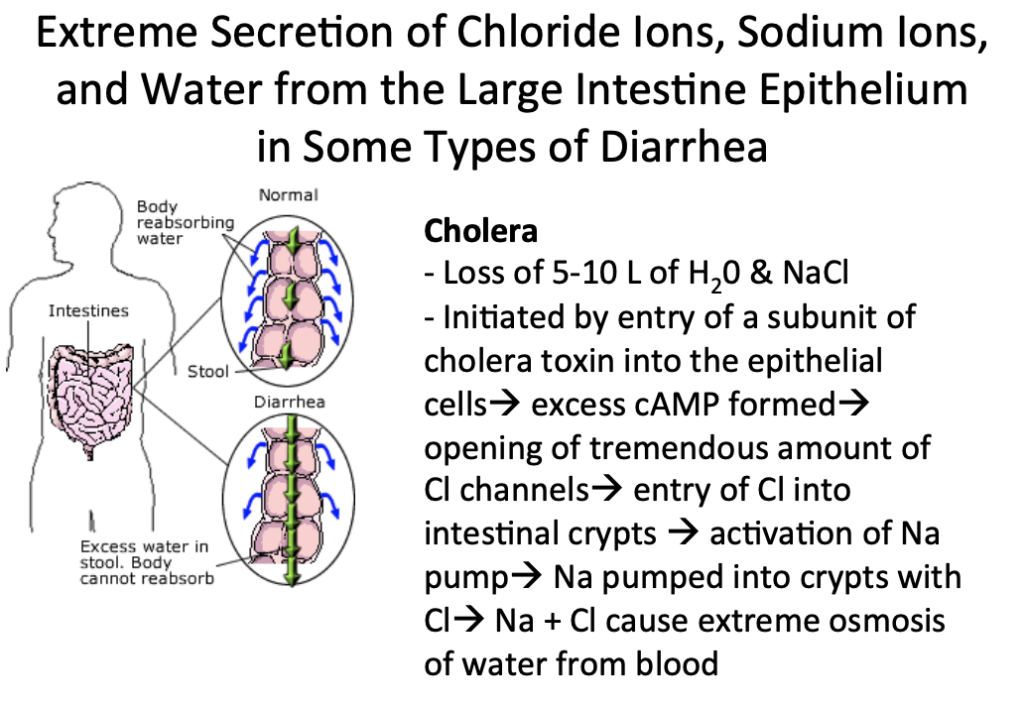
Vibrio cholerae causes diarrhea because it:
a. Inhibits cAMP production in intestinal epithelial cells
b. Increases Cl- secretory channels in crypt cells
c. Increases HCO3- secretory channels in intestinal epithelial cells
d. Prevents the absorption of glucose, causing water to be retained in the intestinal lumen isosmotically
Answer: b. Increases Cl- secretory channels in crypt cells
解説: コレラ毒素は腸陰窩細胞の塩化物分泌チャネルを活性化し、下痢を引き起こします。
- a. Inhibits cAMP production: コレラ毒素はcAMP生成を増加させます。
- c. Increases HCO3- secretory channels: 主にCl-分泌が関与します。
- d. Prevents glucose absorption: コレラは直接的にグルコース吸収を妨げませんが、下痢は結果として水分の再吸収を阻害します。

Question 35 of 40
The following statements are true about bile salts, EXCEPT:
a. They aid in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins
b. They are important in the emulsification of fats
c. Enterohepatic circulation of bile salts occurs through diffusion and active transport
d. They are not reabsorbed into the blood from the small intestine
Answer: d. They are not reabsorbed into the blood from the small intestine
解説: 胆汁酸は腸肝循環を通じて小腸で再吸収されます。
- a. Aid in absorption of fat-soluble vitamins: 胆汁酸は脂溶性ビタミンの吸収を助けます。
- b. Important in emulsification of fats: 胆汁酸は脂肪の乳化に重要です。
- c. Enterohepatic circulation occurs through diffusion and active transport: 腸肝循環は拡散と能動輸送を含みます。
Question 36 of 40
Which of the following is true about the secretion from the exocrine pancreas?
a. It has a pH of 7.0-8.0, providing an appropriate pH for action of the pancreatic digestive enzymes
b. It is stimulated by the presence of HCO3- in the duodenum
c. Pancreatic enzyme secretion is increased by secretin
d. Its total secretion is the sum of all different stimuli when occurring at once
Answer: a. It has a pH of 7.0-8.0, providing an appropriate pH for action of the pancreatic digestive enzymes
解説: 膵外分泌物はpH7.0〜8.0で、膵酵素の働きに最適です。
- b. Stimulated by the presence of HCO3-: 膵分泌はHCO3-の存在ではなく、酸性の内容物によって刺激されます。
- c. Increased by secretin: セクレチンは水分とHCO3-の分泌を刺激しますが、酵素分泌には直接関与しません。
- d. Total secretion is sum of all stimuli: 各刺激が同時に発生しても、分泌は単純な合計にはなりません。
Question 37 of 40
A disaccharide popularly known as cane sugar which splits into a molecule of fructose and glucose:
a. Glucose
b. Sucrose
c. Maltose
d. Lactose
Answer: b. Sucrose
解説: **スクロース(Sucrose)**は、一般的にサトウキビ糖と呼ばれ、フルクトースとグルコースに分解されます。
- a. Glucose: グルコースは単糖です。
- c. Maltose: マルトースは二分子のグルコースから成ります。
- d. Lactose: ラクトースはグルコースとガラクトースに分解されます。
Question 38 of 40
Which of the following would NOT occur if saliva is absent?
a. Difficulty in swallowing solid food even when it is eaten along with large amounts of water
b. Dental caries
c. Proliferation of pathogenic bacteria in the mouth
d. Malabsorption
Answer: d. Malabsorption
解説: 唾液がないと、飲み込みや口腔内の健康に問題が生じますが、腸内での吸収(malabsorption)には直接影響しません。
- a. Difficulty in swallowing: 唾液は食物の滑りを助けます。
- b. Dental caries: 唾液は虫歯を防ぎます。
- c. Proliferation of pathogenic bacteria: 唾液の抗菌作用により、病原菌の繁殖を抑えます。
Question 39 of 40
Digestive enzyme for carbohydrate digestion secreted by the parotid glands:
a. Pancreatic α-amylase
b. Lingual lipase
c. α-Dextrinase
d. Salivary α-amylase
Answer: d. Salivary α-amylase
解説: 耳下腺は**唾液α-アミラーゼ(salivary α-amylase)**を分泌し、炭水化物の初期消化を行います。
- a. Pancreatic α-amylase: これは膵臓から分泌されます。
- b. Lingual lipase: これは脂肪消化に関与します。
- c. α-Dextrinase: これは小腸で働きます。
Question 40 of 40
The lack of pancreatic juice in the duodenum may lead to the following, EXCEPT:
a. Feces with a low specific gravity leading to floating of stools
b. A tendency for feces to putrefy
c. A decrease in the fat content of the feces
d. The presence of undigested meat fibers in the stool
Answer: c
Lack of pancreatic juice: Pancreatic juice contains digestive enzymes essential for breaking down fats, proteins, and carbohydrates in the duodenum. Without it, digestion and absorption of these nutrients are significantly impaired.
Option (a): Without pancreatic enzymes, fats are not properly digested, leading to steatorrhea (fatty stools), which have a low specific gravity and tend to float.
Option (b): Undigested food in the intestines due to enzyme deficiency can lead to putrefaction, as bacteria break down the undigested material, resulting in foul-smelling stools.
Option (c): A decrease in fat content in the feces is incorrect. In fact, the fat content of the stool increases because undigested fats are excreted rather than absorbed.
Option (d): Without proper protein-digesting enzymes, undigested meat fibers may be found in the stool, as proteins are not adequately broken down.
ADDITIONAL

1. Achalasia(アカラシア)
アカラシアは、食道下部の筋肉(下部食道括約筋)が適切に弛緩しないために食道から胃への食物の移動が困難になる疾患です。通常、食物が飲み込まれるとこの括約筋がリラックスして胃に食物を送りますが、アカラシアではこの機能が障害され、食道に食物が滞留しやすくなります。原因は不明で、食道の神経の変性が関与していると考えられています。症状には、嚥下困難、胸部痛、逆流などがあります。
2. Sprue(スプルー)
スプルーは、消化管の特に小腸が栄養素を適切に吸収できなくなる吸収不良症候群の一種です。主にセリアック病(グルテンに対する免疫反応が小腸の絨毛を損傷するもの)や熱帯性スプルー(熱帯地方で見られる吸収不良症候群)などを指すことがあります。症状には、下痢、体重減少、栄養不足、疲労などが含まれ、治療には原因に応じた食事制限や抗生物質が使用されることがあります。
3. Megacolon(メガコロン)
メガコロンは、腸の一部または全体が異常に拡張している状態を指します。先天性の場合、ヒルシュスプルング病と呼ばれ、腸の一部に神経が存在しないため、正常な蠕動運動が起こらず、便が溜まって腸が拡張します。後天性メガコロンの原因には、慢性的な便秘、感染症、薬剤などが挙げられます。症状としては、便秘、腹部膨満、腹痛があり、重症の場合には手術が必要になることもあります。
4. Flatus(フラトゥス)
フラトゥスとは、腸内に蓄積されたガスが肛門から排出される現象、つまり「おなら」を指します。腸内での細菌による発酵や、食物の消化過程で発生するガス(主に窒素、酸素、二酸化炭素、メタンなど)が原因です。健康な腸の働きの一部であり、通常は特に問題視されませんが、過度のガス発生は消化不良や特定の食物に対する感受性が関係していることがあります。
アセス2(22nd Oct 2024)
Question 1 of 20
The stomach:
a. Peristaltic contractions start from the pyloric region
b. Contraction waves pass over it at a rate of about ten per minute
c. Relaxes when food is ingested so that there is little increase in intra-gastric pressure
d. Motility increases when fat enters the duodenum
Answer: d
Question 2 of 20
Which of the following changes occurs during defecation?
a. External anal sphincter is contracted
b. Rectal smooth muscle is contracted
c. Internal anal sphincter is contracted
d. Intra-abdominal pressure is lower than when at rest
Answer: b. Rectal smooth muscle is contracted
解説: 排便時には直腸の平滑筋が収縮し、便が押し出されます。
- a. External anal sphincter is contracted: 排便時には外肛門括約筋が弛緩します。
- c. Internal anal sphincter is contracted: 内肛門括約筋も排便時には弛緩します。
- d. Intra-abdominal pressure is lower than when at rest: 排便時には腹圧が上昇します。
Question 3 of 20
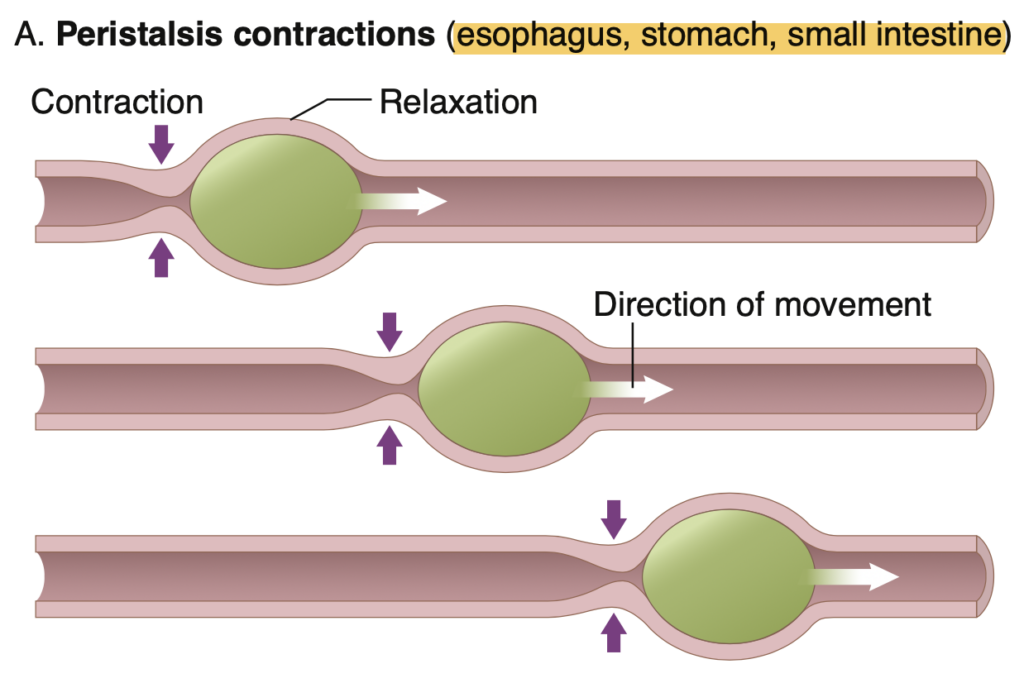
Peristalsis of the small intestine:
a. Involves relaxation of circular and longitudinal smooth muscle simultaneously throughout the small intestine
b. Is coordinated by the central nervous system (CNS)
c. Mixes the food bolus
d. Involves contraction of circular smooth muscle behind the food bolus and relaxation of circular smooth muscle in front of the bolus
Answer: c
Question 4 of 20
Which of the examples of intestinal motility does NOT match with the appropriate stimulus?
a. Gastrocolic reflex – distention of the viscus wall
b. Receptive relaxation – release of gastric inhibitory peptide
c. Peristalsis – release of motilin
d. Contraction of the gallbladder – release of cholecystokinin
Answer: b. Receptive relaxation – release of gastric inhibitory peptide
解説: 受容性弛緩(Receptive relaxation)は、胃が食物を受け入れる際に起こるが、ガストリック・インヒビトリー・ペプチド(GIP)は関与しません。GIPは膵臓に関連しています。
- a. Gastrocolic reflex – distention of the viscus wall: 胃の拡張は大腸反射を引き起こします。
- c. Peristalsis – release of motilin: モチリンは蠕動運動を促進します。
- d. Contraction of the gallbladder – release of cholecystokinin: コレシストキニン(CCK)は胆嚢を収縮させます。
Question 5 of 20
Layers of the intestinal wall from the inner surface going outward:
a. Mucosa, submucosa, longitudinal smooth muscle, circular smooth muscle, serosa
b. Serosa, submucosa, longitudinal smooth muscle, circular smooth muscle, mucosa
c. Serosa, longitudinal smooth muscle, circular smooth muscle, submucosa, mucosa
d. Mucosa, submucosa, circular smooth muscle, longitudinal smooth muscle, serosa
Answer: a

Question 6 of 20
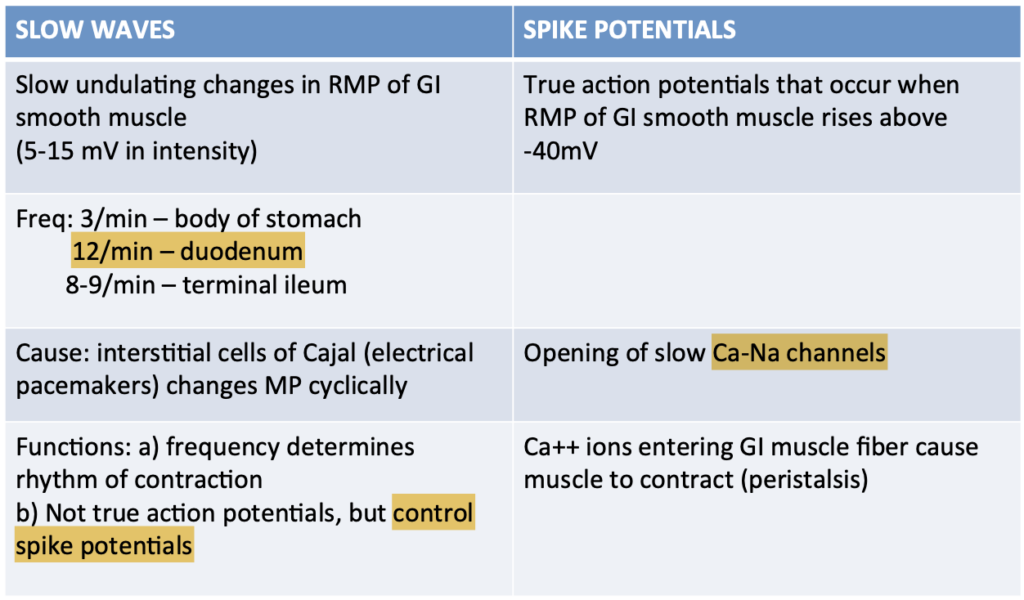
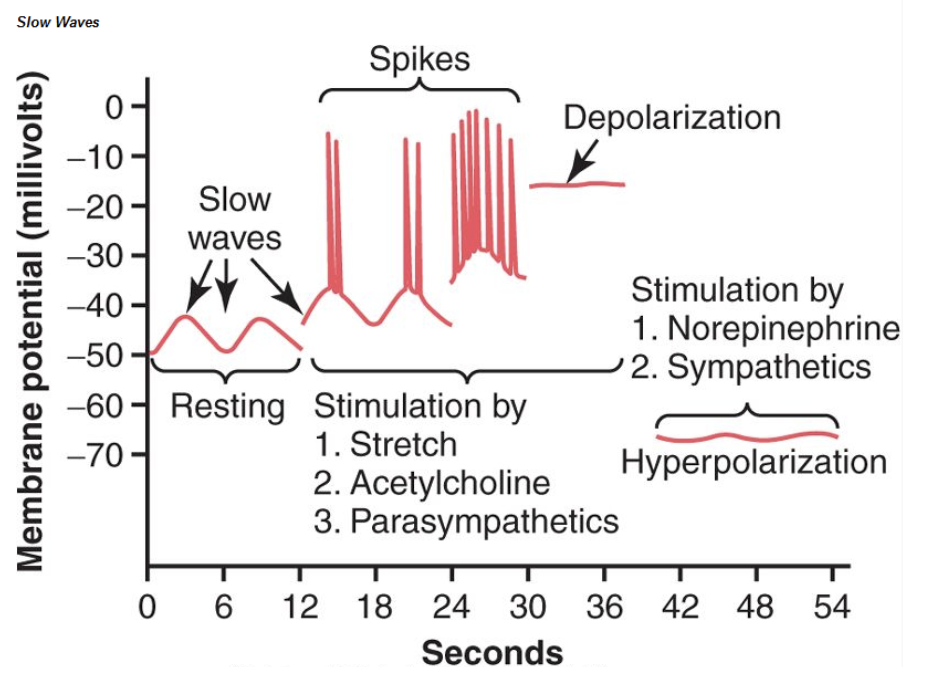
Gastrointestinal contractions develop when the resting membrane potential of the GI smooth muscles become more positive than:
a. -30 mvolts
b. -40 mvolts
c. -10 mvolts
d. -20 mvolts
Answer: b. -40 mvolts
解説: 胃腸の平滑筋の収縮は、静止膜電位が-40 mVより正になると始まります。これにより活動電位が発生し、筋収縮が引き起こされます。
Question 7 of 20
The more potent signals controlling the rate of gastric emptying are coming from the:
a. Pyloric region
b. Duodenum
c. Esophagus
d. Body of the stomach
Answer: b. Duodenum
解説: 胃内容物の排出速度を最も強力に制御する信号は、十二指腸から発せられます。十二指腸が酸性度や脂肪含量に応じて排出速度を調整します。
Question 8 of 20
Defecation is a reflex action:
a. Whose efferent limb travels mainly in sympathetic autonomic nerves
b. Which is more likely to be initiated just before a meal than just after it
c. Whose afferent limb carries impulses from stretch receptors in the rectal wall
d. Which cannot be voluntarily inhibited or facilitated
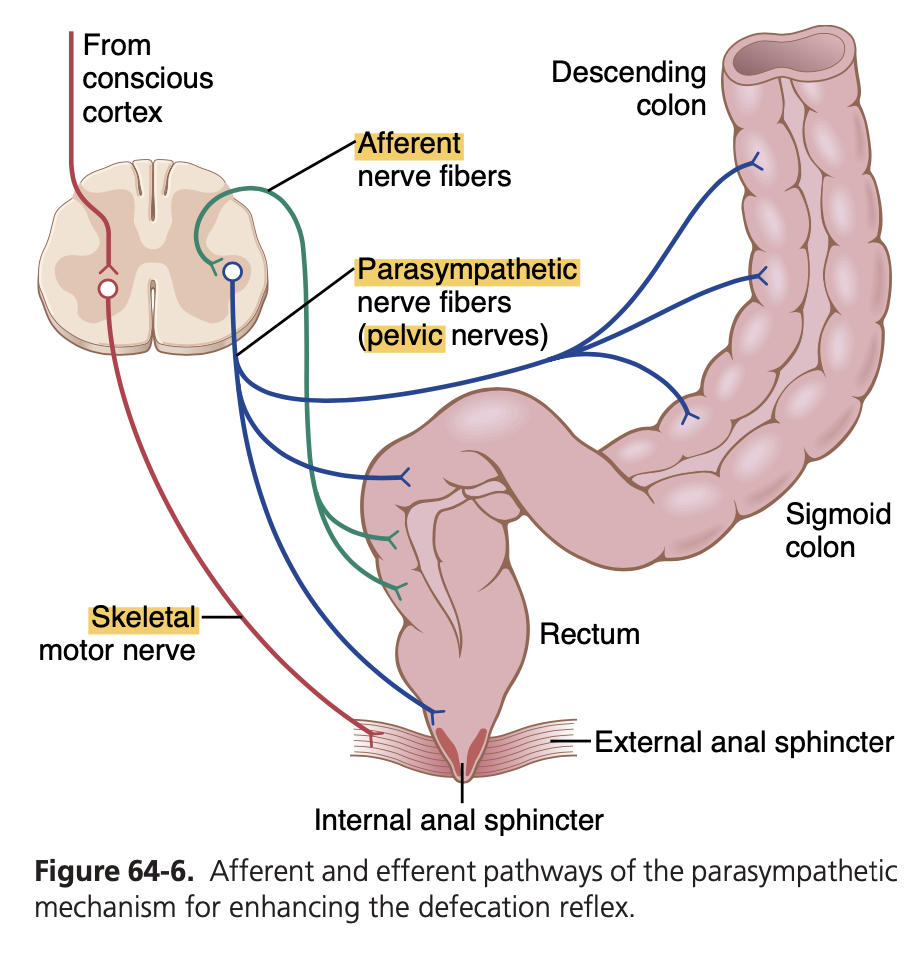
Answer: c. Whose afferent limb carries impulses from stretch receptors in the rectal wall
解説: 排便反射は、直腸壁の伸展受容体からのインパルスが感覚神経を介して伝達されることで始まります。
- a. Sympathetic autonomic nerves: 排便反射の遠心路は主に副交感神経です。
- b. Initiated just before a meal: 食後に始まることが多いです。
- d. Cannot be voluntarily inhibited: 自発的に制御可能です。
Question 9 of 20
Which of the following is not true about the swallowing reflex?
a. It has its reflex centers in the cervical segments of the spinal cord.
b. It includes inhibition of respiration.
c. It is dependent on intrinsic nerve networks in the esophagus.
d. It is initiated by a voluntary act.
Answer: a. It has its reflex centers in the cervical segments of the spinal cord
解説: 嚥下反射の中心は延髄にあり、頸髄にはありません。
- b. Inhibition of respiration: 嚥下中は呼吸が抑制されます。
- c. Dependent on intrinsic nerve networks: 食道の神経ネットワークに依存します。
- d. Initiated by a voluntary act: 嚥下は自発的な行動で開始されます。
Question 10 of 20
A patient is referred to a gastroenterologist because of persistent difficulties with swallowing. Endoscopic examination reveals that the lower esophageal sphincter fails to fully open as the bolus reaches it, and a diagnosis of achalasia is made. Which stage of swallowing failed in this condition?
a. Pharyngeal stage
b. Intestinal stage
c. Voluntary stage
d. Esophageal stage
Answer: d. Esophageal stage
解説: アカラシアでは、食道括約筋が十分に開かず、食道の蠕動が正常に機能しないため、食道段階の嚥下が失敗します。
- a. Pharyngeal stage: 咽頭段階ではなく、問題は食道にあります。
- b. Intestinal stage: 腸段階は嚥下とは無関係です。
- c. Voluntary stage: 自発的段階は嚥下の開始に関与しますが、この問題には関与しません。

Question 11 of 20
In infants, defecation often follows a meal. The cause of colonic contractions in this situation is:
a. The enterogastric reflex
b. Increased circulating levels of CCK
c. Histamine
d. The gastrocolic reflex
Answer: d. The gastrocolic reflex
解説: 幼児で食事後に排便が起こるのは、**胃結腸反射(gastrocolic reflex)**が原因です。この反射は胃の拡張により結腸の運動が刺激されることによって起こります。
- a. Enterogastric reflex: これは胃の抑制に関連します。
- b. Increased circulating levels of CCK: CCKは胆嚢の収縮や膵酵素の分泌を刺激しますが、排便には直接関与しません。
- c. Histamine: ヒスタミンは主に胃酸分泌に関与します。
Question 12 of 20
Slow waves in small intestinal smooth muscle cells are:
a. Tonic contractions
b. Action potentials
c. Oscillating resting membrane potentials
d. Phasic contractions
Answer: c. Oscillating resting membrane potentials
解説: 小腸の平滑筋における遅波(slow waves)は、**振動する静止膜電位(oscillating resting membrane potentials)**であり、これが活動電位と収縮を引き起こします。
- a. Tonic contractions: 遅波自体は収縮を引き起こしません。
- b. Action potentials: 活動電位は収縮を引き起こしますが、遅波ではありません。
- d. Phasic contractions: フェーシック収縮は活動電位に続く収縮です。
Question 13 of 20
During swallowing, entry of food into the trachea is prevented by:
a. Closure of the glottis
b. Palatopharyngeal folds folding medially
c. Relaxation of upper esophageal sphincter
d. Elevation of soft palate
Answer: a. Closure of the glottis
解説: 嚥下時に食物が気管に入るのを防ぐ主な機構は**声門の閉鎖(closure of the glottis)**です。これにより食物が気道に入らず食道に入ります。
- b. Palatopharyngeal folds folding medially: これは嚥下の一部ですが、主に食物が鼻腔に入るのを防ぎます。
- c. Relaxation of upper esophageal sphincter: これは食物が食道に入ることを許容しますが、気管に入るのを防ぐ機構ではありません。
- d. Elevation of soft palate: 軟口蓋の挙上は食物が鼻腔に入るのを防ぎます。
Question 14 of 20
A 50-year-old man comes to see his clinician complaining of severe epigastric pain, frequent heartburn, and unexplained weight loss of 20 lb over a 6-month period. He claims to have obtained no relief from over-the-counter H2 antihistamine drugs. He is referred to a gastroenterologist, and upper endoscopy reveals erosions and ulcerations in the proximal duodenum and an increased output of gastric acid in the fasting state. The patient is most likely to have a tumor secreting which of the following hormones?
a. Secretin
b. Motilin
c. Somatostatin
d. Gastrin
Answer: c
ソマトスタチン (somatostatin) は、主に内分泌系に関わるホルモンで、以下のような様々な機能を持っています:
成長ホルモンの抑制: ソマトスタチンは、下垂体前葉から分泌される成長ホルモン(GH)の分泌を抑制します。このため、成長や代謝に関連するプロセスの調節に関与しています。
消化器系ホルモンの抑制: ソマトスタチンは、胃、十二指腸、膵臓などから分泌される多くの消化ホルモンの分泌を抑制します。具体的には、インスリン、グルカゴン、ガストリン、コレシストキニンなどのホルモンの分泌を抑制し、消化機能の調整を行います。
胃酸分泌の抑制: ソマトスタチンは胃からの酸の分泌を抑制し、消化機能に影響を与えます。また、膵臓からの酵素分泌も抑制し、全体的に消化活動を抑制する働きを持っています。
神経系での役割: ソマトスタチンは中枢神経系でも見られ、神経伝達物質として機能し、神経活動や神経細胞の過剰な興奮を抑える効果があります。
インスリンとグルカゴンの分泌調整: ソマトスタチンは膵臓のランゲルハンス島から分泌され、血糖値の調節に関与するインスリンとグルカゴンの分泌を抑制する役割を持ちます。
ソマトスタチンは、これらの様々なシステムで抑制的に作用するため、ホメオスタシス(体内の安定状態)の維持に重要な役割を果たしています。
Question 15 of 20
In the colon:
a. Fecal transit time is about 7 days
b. Excess motility causes more absorption and constipation
c. The combined contractions of the circular and longitudinal strips of muscle cause the unstimulated portion of the large intestine to bulge outward into baglike sacs
d. A greater volume of water is absorbed than in the small intestine
Answer: c. The combined contractions of the circular and longitudinal strips of muscle cause the unstimulated portion of the large intestine to bulge outward into baglike sacs
解説: 大腸の縦走筋と輪状筋の収縮は、大腸の袋状の構造である**ハウストラ(haustra)**を形成します。
- a. Fecal transit time is about 7 days: 大腸の便通過時間は通常1-2日です。
- b. Excess motility causes more absorption and constipation: 過剰な運動性は便の排出を早め、下痢を引き起こします。
- d. Greater volume of water is absorbed than in the small intestine: 小腸が水の大部分を吸収します。
Question 16 of 20
Regarding neural control of GI function, which of the following controls mainly gastrointestinal secretion and local blood flow?
a. Mucosal plexus
b. Myenteric plexus
c. Meissner’s plexus
d. Auerbach’s plexus
Answer: c. Meissner’s plexus
解説: **マイスナー神経叢(Meissner’s plexus)**は消化管の分泌と局所血流の制御に主に関与します。
- a. Mucosal plexus: 存在しない構造です。
- b. Myenteric plexus (Auerbach’s plexus): 筋層間神経叢は主に蠕動運動を制御します。
- d. Auerbach’s plexus: これも筋層間神経叢で、運動を制御します。
Question 17 of 20
Movements in the colon:
a. Mixing movements occur as mass movements
b. Propulsive movements appear as haustrations
c. The proximal half of the colon is concerned principally with storage, the distal half with absorption
d. Distention of the stomach and duodenum after a meal initiates mass movement facilitated by gastrocolic and duodenocolic reflexes respectively
Answer: d. Distention of the stomach and duodenum after a meal initiates mass movement facilitated by gastrocolic and duodenocolic reflexes respectively
解説: 食後に胃や十二指腸が拡張すると、**胃結腸反射(gastrocolic reflex)**や十二指腸結腸反射(duodenocolic reflex)により大腸の大量運動が促進されます。
- a. Mixing movements occur as mass movements: 大量運動は推進運動であり、混和運動ではありません。
- b. Propulsive movements appear as haustrations: ハウストラは主に混和運動に関与します。
- c. Proximal colon is for storage: 近位結腸は主に吸収、遠位結腸は貯蔵に関与します。
Question 18 of 20
The basic propulsive movement in the GIT is known as:
a. Emulsification
b. Spike contraction
c. Mixing
d. Peristalsis
Answer: d. Peristalsis
解説: 消化管の基本的な推進運動は**蠕動(peristalsis)**です。
- a. Emulsification: 乳化は脂肪消化に関係します。
- b. Spike contraction: これは活動電位による収縮を指しますが、推進運動ではありません。
- c. Mixing: これは混和運動です。
Question 19 of 20
Motility recordings in a patient with signs of bacterial overgrowth of the small intestine indicate an abnormal pattern of motility in the fasting state that is characterized by a lack of the normal periodic bursts of gastric and intestinal contractions. This patient is likely to demonstrate abnormal secretion of which of the following hormones?
a. Secretin
b. Motilin
c. CCK (Cholecystokinin)
d. Gastrin
Answer: b. Motilin
解説: モチリン(Motilin)は空腹時に消化管の蠕動波を調整し、**移動性複合運動(MMC)**を促進します。モチリンの欠乏は腸内細菌の過剰増殖につながることがあります。
Question 20 of 20
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of cholecystokinin (CCK)?
a. CCK inhibits gastric emptying and stimulates gallbladder contraction
b. CCK stimulates both functions of the exocrine pancreas – HCO3- secretion and digestive enzyme secretion
c. CCK is released by the K-cells of the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
d. CCK has 5 identical C-terminal amino acids with gastrin, hence CCK has gastrin-like properties
Answer: c. CCK is released by the K-cells of the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
解説: コレシストキニン(CCK)はI細胞によって分泌され、K細胞では分泌されません。
- a. CCK inhibits gastric emptying: 正しいです。
- b. CCK stimulates pancreatic secretion: 正しいです。
- d. CCK has similar amino acids to gastrin: 正しいです。
ブロック
Question 136 of 185
A 25-year-old female presented to your clinic with weight loss, dysphagia, chest pain, and regurgitation of food. Work-up revealed an enlarged esophagus. The pathophysiologic basis of which of the following conditions is associated with damage to the myenteric plexus in the esophagus?
a) Megacolon
b) Sprue
c) Achalasia
d) None of the above
e) Hirschsprung’s Disease
Answer: c. Achalasia
解説: アカラシア(Achalasia)は、食道の蠕動不全および下部食道括約筋の弛緩不全によって引き起こされます。この病態は、食道の**筋層間神経叢(myenteric plexus)**が損傷していることに関連しています。
- a. Megacolon: 大腸に影響する疾患で、食道ではありません。
- b. Sprue: セリアック病などの吸収不良症候群を指します。
- e. Hirschsprung’s Disease: 大腸に影響を及ぼす疾患です。
Question 137 of 185
A 42-year-old woman complaining of gnawing pain in the stomach is diagnosed with Chronic Gastritis. Which of the following findings is consistent with the diagnosis?
a) Polycythemia
b) None of the above
c) Pernicious anemia
d) Steatorrhea
e) Hyperchlorhydria
Answer: c. Pernicious anemia
解説: 慢性胃炎は、胃の壁細胞による内因子の産生減少につながり、ビタミンB12の吸収不良を引き起こします。これが**悪性貧血(Pernicious anemia)**につながることがあります。
- a. Polycythemia: 赤血球の過剰産生は胃炎とは関連しません。
- d. Steatorrhea: 脂肪便は消化不良の結果ですが、胃炎と直接関連しません。
- e. Hyperchlorhydria: 胃酸分泌過剰は慢性胃炎では一般的ではありません。
Question 138 of 185
Severe sprue leads to:
a) Osteomalacia
b) Polycythemia
c) A hypercoagulable state
d) Obesity
e) None of the above
Answer: a. Osteomalacia
解説: **重度のセリアック病(sprue)**は、ビタミンDの吸収不良を引き起こし、**骨軟化症(Osteomalacia)**につながる可能性があります。
- b. Polycythemia: 吸収不良とは関連がありません。
- c. Hypercoagulable state: 吸収不良は凝固亢進状態を引き起こしません。
- d. Obesity: 吸収不良は体重減少につながります。
Question 139 of 185
A 35-year-old man was admitted for abdominal pain with vomiting that has lasted for 3 days. Initial tests reveal expelling acidic vomitus and arterial blood gases show an alkaline pH. An intestinal obstruction is suspected. Where would one suspect the obstruction to be located?
a) Beyond the stomach
b) Pylorus
c) Proximal half of large intestine
d) Below the duodenum
e) All of the above
Answer: b. Pylorus
解説: **幽門部(Pylorus)**に閉塞があると、胃内容物が排出されず、酸性の嘔吐が続き、代謝性アルカローシスを引き起こすことがあります。
- a. Beyond the stomach: 胃を超える閉塞では嘔吐の酸性度が低下する可能性があります。
- c. Proximal half of large intestine: 大腸閉塞は通常酸性の嘔吐を引き起こしません。
- d. Below the duodenum: ここでの閉塞はアルカローシスを引き起こす可能性は低いです。
Question 140 of 185
A 23-year-old female medical student was complaining of nausea and vomiting while riding a bus. Vomiting of this type was initiated by:
a) Stimulating receptors in the vestibular labyrinth of the inner ear
b) Decreasing gastrointestinal motility
c) An irritative stimulus in the gastrointestinal tract
d) Directly stimulating the chemoreceptor trigger zone
e) All of the above
Answer: a
Explanation (日本語での解説):
この問題は、乗り物酔い(motion sickness)に関連する吐き気と嘔吐の原因を問うています。乗り物酔いは、内耳の前庭系にある受容体が刺激されることによって引き起こされます。前庭迷路(vestibular labyrinth)は、身体のバランスや位置を感知する役割を担い、乗り物の動きによってこれらの受容体が過剰に刺激されると、吐き気や嘔吐が引き起こされます。
各選択肢の解説:
- a) Stimulating receptors in the vestibular labyrinth of the inner ear: 正しい選択肢です。内耳の前庭迷路は乗り物酔いを引き起こす主要な場所で、ここでの受容体が刺激されることで吐き気が生じます。
- b) Decreasing gastrointestinal motility: 誤りです。胃腸運動の低下は嘔吐を直接引き起こすものではなく、むしろ消化不良などに関連することが多いです。
- c) An irritative stimulus in the gastrointestinal tract: 誤りです。胃腸への刺激は食中毒や消化不良による嘔吐に関連しますが、乗り物酔いの原因ではありません。
- d) Directly stimulating the chemoreceptor trigger zone: 誤りです。化学受容器引き金帯(chemoreceptor trigger zone, CTZ)は毒素や薬物に反応して嘔吐を引き起こしますが、乗り物酔いは主に前庭系の刺激によって発生します。
- e) All of the above: 誤りです。正しい答えは「a」のみであり、他の選択肢は乗り物酔いに直接関係していません。
Question 141 of 185
A 42-year-old woman is diagnosed with a gastrin-secreting tumor of the pancreas. Which of the following findings is consistent with the diagnosis?
a) Decreased level of serum gastrin
b) Increased absorption of dietary lipids
c) Peptic ulcer disease
d) All of the above
e) Decreased parietal cell mass
Answer: c. Peptic ulcer disease
解説: ガストリノーマでは、過剰なガストリン分泌により胃酸が過剰に生成され、**消化性潰瘍(peptic ulcer disease)**が発生します。
- a. Decreased level of serum gastrin: ガストリンは増加します。
- b. Increased absorption of dietary lipids: ガストリノーマとは関連しません。
- e. Decreased parietal cell mass: 壁細胞の量は増加します。
Question 142 of 185
Most common site of peptic ulcer formation:
a) Lesser curvature
b) Greater curvature
c) Pylorus
d) Cardia
e) None of the above
Answer: a. Lesser curvature
解説: 消化性潰瘍は通常、**胃の小彎部(lesser curvature)**に最もよく発生します。
- b. Greater curvature: ここに潰瘍ができることは稀です。
- c. Pylorus: 幽門も潰瘍ができる場所ですが、小彎部が最も一般的です。
- d. Cardia: カーディアでは稀です。
Question 143 of 185
A 34-year-old male patient was diagnosed with ulcerative colitis on endoscopy. Ulcerative colitis is characterized as:
a) Decreased colonic secretion leading to constipation
b) None of the above
c) Decreased motility of the ulcerated colon with mass movements occurring less than normal
d) A self-limiting condition in which the ulcers will heal over time
e) A disease in which extensive areas of the walls of the large intestine become inflamed and ulcerated
Answer: e. A disease in which extensive areas of the walls of the large intestine become inflamed and ulcerated
解説: 潰瘍性大腸炎は、大腸の広範囲の炎症と潰瘍が特徴です。
- a. Decreased colonic secretion: 通常は下痢が見られます。
- c. Decreased motility: 運動性は正常または増加します。
- d. Self-limiting: 潰瘍性大腸炎は自己限定性の病態ではありません。
Question 144 of 185
Bile:
a) Contains enzymes required for the digestion of fat
b) All are correct
c) Salts make cholesterol more water-soluble
d) Pigments contain iron
e) Contains unconjugated bilirubin
Answer: c. Salts make cholesterol more water-soluble
解説: 胆汁塩はコレステロールをより水溶性にするため、脂肪の消化吸収を助けます。
- a. Contains enzymes for fat digestion: 胆汁には酵素が含まれていません。
- b. All are correct: すべてが正しいわけではありません。
- d. Pigments contain iron: 胆汁色素には鉄は含まれていません。
- e. Contains unconjugated bilirubin: 胆汁中のビリルビンは抱合型です。
Question 145 of 185
The liver is the principal site for:
a) Storage of vitamin C
b) Synthesis of vitamin B12
c) Synthesis of plasma globulins
d) All of the above
e) Synthesis of plasma albumin
Answer: e. Synthesis of plasma albumin
解説: 肝臓は主に血漿アルブミンを合成する場所です。
- a. Storage of vitamin C: 肝臓はビタミンCの主な貯蔵場所ではありません。
- b. Synthesis of vitamin B12: ビタミンB12の合成は行われません。
- c. Synthesis of plasma globulins: 肝臓は一部のグロブリンを合成しますが、アルブミンが主な生成物です。
Question 146 of 185
The cause of jaundice is likely to be:
a) Bile duct obstruction, if the urine is paler than normal
b) Haemolysis, if the prothrombin level is below normal
c) All of the above
d) Haemolysis, if the urine is darker than normal
e) Liver disease, if albumin is low and bilirubin mainly unconjugated
Answer: b
Question 147 of 185
Diminished liver function may result in an increase in the following EXCEPT:
a) Size of male breasts
b) Tendency to bleed
c) Albumin to globulin ratio in the blood
d) Level of unconjugated bilirubin in the blood
e) None of the above
Answer: e
Question 148 of 185
What is the effect of sympathetic stimulation on alimentary tract glandular secretion rate?
a) Sympathetic stimulation alone slightly increases secretion
b) No effect
c) All of the above
d) In the face of parasympathetic stimulation, superimposed sympathetic stimulation increases the secretion
e) Sympathetic stimulation leads to glandular vasodilation leading to a decreased secretion
Answer: d
Question 149 of 185
Salivary secretion:
a) Is increased when touch receptors in the mouth are stimulated
b) All of the above
c) From different salivary glands has a similar composition
d) Contains the most important enzymes for the digestion of carbohydrates
e) Is decreased when vomiting is imminent
Answer: a. Is increased when touch receptors in the mouth are stimulated
解説: 唾液分泌は口腔内の接触受容体が刺激されると増加しますが、他の選択肢は不正確です。
- b. All of the above: すべてが正しいわけではありません。
- c. From different salivary glands has a similar composition: 各腺の組成は異なります。
- d. Contains the most important enzymes for carbohydrate digestion: 唾液には炭水化物消化酵素が含まれますが、最も重要ではありません。
- e. Decreased when vomiting is imminent: 嘔吐時には通常唾液分泌が増加します。
Question 150 of 185
When parietal cells are stimulated, they secrete:
a) None of the above
b) HCl and pepsinogen
c) HCl and HCO3-
d) HCl and intrinsic factor
Answer: d
Question 151 of 185
A 25-year-old male with acute gastritis was taking omeprazole as prescribed by his physician. The basis for the proton pump inhibitor, omeprazole’s inhibition of gastric H+ secretion is that it blocks the main driving force for hydrochloric acid secretion by the parietal cells, which is the:
a) Na-K ATPase pump
b) All of the above
c) Na-Ca pump
d) H-K ATPase pump
e) Na pump
Answer: d. H-K ATPase pump
解説: オメプラゾールは壁細胞のH-K ATPaseポンプを阻害し、胃酸分泌を抑制します。
- a. Na-K ATPase pump: これは異なる細胞プロセスに関与します。
- c. Na-Ca pump: これは胃酸分泌には関与しません。
- e. Na pump: これはHCl分泌に直接関与しません。
Question 152 of 185
Cholecystokinin (CCK) stimulates:
a) Gastric emptying
b) Hydrochloric acid secretion
c) Contraction of the gallbladder and relaxation of the sphincter of Oddi
d) Pancreatic HCO3- secretion
e) All of the above
Answer: c. Contraction of the gallbladder and relaxation of the sphincter of Oddi
解説: コレシストキニン(CCK)は胆嚢の収縮とオッディ括約筋の弛緩を引き起こします。
- a. Gastric emptying: CCKは胃排出を遅らせます。
- b. Hydrochloric acid secretion: CCKは胃酸分泌を刺激しません。
- d. Pancreatic HCO3- secretion: CCKは主に酵素分泌を刺激します。
Question 153 of 185
Intestinal secretions contain:
a) Enzymes that inactivate pancreatic proteolytic enzymes
b) Enzymes that hydrolyze monosaccharides
c) All of the above
d) Enzymes that hydrolyze disaccharides
Answer: d. Enzymes that hydrolyze disaccharides
解説: 小腸の分泌物には、二糖類を加水分解する酵素が含まれます。
- a. Enzymes that inactivate pancreatic proteolytic enzymes: これは不正確です。
- b. Enzymes that hydrolyze monosaccharides: モノ糖の加水分解酵素は存在しません。
Question 154 of 185
Pancreatic secretion:
a) All of the above
b) In response to secretin secretion is low in bicarbonate
c) Contains enzymes that convert disaccharides to monosaccharides
d) Contains enzymes that digest neutral fat to glycerol and fatty acids
e) In response to acid in the duodenum is scanty but rich in enzymes
Answer: d. Contains enzymes that digest neutral fat to glycerol and fatty acids
解説: 膵液には中性脂肪をグリセロールと脂肪酸に分解する酵素が含まれます。
- b. Low in bicarbonate: セクレチンに応答してHCO3-が増加します。
- c. Enzymes for disaccharides: 膵臓は主に脂肪やタンパク質を分解します。
Question 155 of 185
A 40-year-old male patient with a duodenal ulcer is treated successfully with the drug cimetidine. The basis for cimetidine’s inhibition of gastric H+ secretion is that it:
a) Enhances the action of acetylcholine (ACh) on parietal cells
b) All of the above
c) Blocks muscarinic receptors on parietal cells
d) Blocks Histamine2 receptors on parietal cells
e) Blocks H+, K+-adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase)
Answer: d. Blocks Histamine2 receptors on parietal cells
解説: シメチジンはH2受容体を遮断することにより、胃酸分泌を抑制します。
- a. Enhances the action of acetylcholine: シメチジンはAChには影響を与えません。
- c. Blocks muscarinic receptors: これはシメチジンの作用ではありません。
- e. Blocks H+, K+-ATPase: プロトンポンプ阻害薬はH+,K+-ATPaseを阻害しますが、シメチジンは異なる機構です。
Question 156 of 185
Which of the following is the site of secretion of Hydrochloric acid?
a) Gastric fundus
b) Gastric antrum
c) Ileum
d) Duodenum
e) All of the above
Answer: a. Gastric fundus
解説: **塩酸(HCl)は胃底部(gastric fundus)**の壁細胞(parietal cells)によって分泌されます。
- b. Gastric antrum: 幽門部では塩酸は分泌されません。
- c. Ileum: 回腸では塩酸は分泌されません。
- d. Duodenum: 十二指腸では塩酸は分泌されません。
Question 157 of 185
Factors which help to prevent stomach mucosal damage due to backleak of HCl:
a) All of the above
b) Protective action of aspirin
c) Thick viscid alkaline mucus secreted by mucous cells
d) Gap junctions between epithelial cells
Answer: c. Thick viscid alkaline mucus secreted by mucous cells
解説: 胃の粘膜を塩酸から保護するために粘膜細胞が分泌する厚くて粘稠なアルカリ性の粘液が重要です。
- b. Protective action of aspirin: アスピリンは実際には胃粘膜に対して有害です。
- d. Gap junctions: ギャップ結合は保護に直接関与しません。
- a. All of the above: すべてが正しいわけではありません。
Question 158 of 185
The stomach:
a) Relaxes when food is ingested so that there is little rise in intra-gastric pressure
b) Peristaltic contractions start from the pyloric region
c) All of the above
d) Is responsible for absorbing about 10 percent of the ingested food
e) Motility increases when fat enters the duodenum
Answer: a. Relaxes when food is ingested so that there is little rise in intra-gastric pressure
解説: 胃は食物が入ると弛緩し、胃内圧の上昇を抑えます(受容性弛緩)。脂肪が十二指腸に入ると胃運動は低下します。
- b. Peristaltic contractions start from the pyloric region: 蠕動運動は胃全体で起こります。
- d. Absorption of food: 胃は主に吸収ではなく、食物の消化を行います。
- e. Motility increases when fat enters the duodenum: 脂肪が十二指腸に入ると運動性は低下します。
Question 159 of 185
Bile salts:
a) Are reabsorbed mainly in the upper small intestine
b) Inhibit bile secretion by the liver
c) Have a characteristic molecule, part water-soluble and part fat-soluble
d) Are derived from proteins
e) All of the above
Answer: c. Have a characteristic molecule, part water-soluble and part fat-soluble
解説: **胆汁酸塩(bile salts)は両親媒性(部分的に水溶性、部分的に脂溶性)**で、脂肪の乳化に役立ちます。
- a. Reabsorbed in upper small intestine: 胆汁酸塩は回腸で再吸収されます。
- b. Inhibit bile secretion: 胆汁酸塩は胆汁の分泌を促進します。
- d. Derived from proteins: 胆汁酸塩はコレステロール由来です。
Question 160 of 185
In the small intestine:
a) Glucose absorption is dependent on sodium absorption
b) Absorption of calcium occurs mainly in the terminal ileum
c) All of the above
d) Vitamin B12 is absorbed mainly in the jejunum
e) Water absorption is independent on the active absorption of sodium and glucose
Answer: a. Glucose absorption is dependent on sodium absorption
解説: 小腸でのグルコースの吸収は、ナトリウムの共輸送によって促進されます。
- b. Calcium absorption in terminal ileum: カルシウムは主に十二指腸で吸収されます。
- d. Vitamin B12 absorption: ビタミンB12は回腸で吸収されます。
- e. Water absorption is independent of sodium and glucose: 水の吸収はナトリウムとグルコースの吸収に依存します。
Question 161 of 185
Absorption of dietary fat:
a) Involves fat uptake by both the lymphatic and blood capillaries
b) Is required for normal bone development
c) Is required for normal blood clotting
d) All of the above
Answer: a
Question 162 of 185
Urobilinogen is:
a) Highly insoluble
b) Converted into the dark pigment, urobilin, on exposure to air
c) Formed in the reticuloendothelial system from bilirubin
d) Excreted mainly in the urine
e) All of the above
Answer: b. Converted into the dark pigment, urobilin, on exposure to air
解説: ウロビリノーゲンは空気に触れるとウロビリンに変換され、尿を暗くします。
- a. Highly insoluble: ウロビリノーゲンは水に可溶です。
- c. Formed from bilirubin in reticuloendothelial system: ウロビリノーゲンは腸内で形成されます。
- d. Excreted mainly in urine: 一部は尿中に排泄されますが、主に糞便中です。
Question 163 of 185
Surgical removal of 90 percent of the small intestine may cause a decrease in the following EXCEPT:
a) All are correct
b) Body weight
c) Bone mineralization (osteomalacia)
d) Blood haemoglobin level
e) The fat content of the stools
Answer: e. The fat content of the stools
解説: 腸の大部分を切除すると、吸収不良により体重や血中ヘモグロビンが減少しますが、便中の脂肪含量は増加します。
Question 164 of 185
Absorption of glucose by intestinal mucosal cells:
a) Takes place mainly in the ileum
b) Is enhanced by blockade of active sodium transport in the cells
c) Relies on a carrier mechanism in the cell membrane
d) Involves the same carriers that are used for the absorption of fructose
e) All of the above
Answer: c. Relies on a carrier mechanism in the cell membrane
解説: グルコースの吸収は、細胞膜内のキャリアメカニズムに依存しています。フルクトースとは異なるキャリアを使用します。
- a. Mainly in the ileum: グルコースは主に十二指腸と空腸で吸収されます。
- b. Enhanced by blockade of sodium transport: ナトリウム輸送の阻害はグルコース吸収を減少させます。
- d. Same carriers as fructose: グルコースとフルクトースは異なる輸送キャリアを使用します。
Question 165 of 185
Which of the following characterizes protein digestion?
a) For pepsin to cause digestion of proteins, the pH of the stomach must be above 5.0
b) More than 99% of the final protein digestive products absorbed are individual amino acids
c) All proteins are digested all the way to their constituent amino acids by the pancreatic juices
d) Trypsin initiates the process of protein digestion in meats
Answer: b. More than 99% of the final protein digestive products absorbed are individual amino acids
解説: 99%以上のタンパク質の最終的な消化生成物はアミノ酸として吸収されます。
- a. Pepsin’s optimal pH: ペプシンはpH 1.5-2.0で最適に機能します。
- c. Pancreatic juices digest all proteins: タンパク質は胃と腸でも部分的に消化されます。
- d. Trypsin initiates digestion: タンパク質の消化は胃で開始されます。
Question 166 of 185
The basic process of digestion involves which of the following chemical reactions?
a) Hydrolysis
b) All of the above
c) Polymerization
d) Condensation
e) Reduction
Answer: a. Hydrolysis
解説: 消化の基本的な化学反応は、**水解反応(hydrolysis)**です。これは大きな分子が水分子の作用によって分解される反応です。
- c. Polymerization: ポリマーの形成は消化に関与しません。
- d. Condensation: 凝縮反応は消化の逆過程です。
- e. Reduction: 還元反応は消化には関係しません。
Question 167 of 185
Spike potentials:
a) Basic Electrical Rhythm
b) Intensity varies between 5 & 15 mV
c) True action potentials
d) Occurs when RMP is more negative than -40 mV
e) All of the above
Answer: d
Question 168 of 185
The Meissner’s nerve plexus is in this layer of the intestinal wall:
a) Submucosa
b) None of the above
c) Muscular layer
d) Mucosa
e) Serosa
Answer: a. Submucosa
解説: **マイスナー神経叢(Meissner’s plexus)は粘膜下層(submucosa)**に位置し、消化管の分泌や局所の血流を調整します。
Question 169 of 185
Local nervous system of the GIT residing in the muscular and submucosal layers:
a) Sympathetics
b) Parasympathetics
c) Enteric Nervous System
d) Autonomic Nervous System
e) All of the above
Answer: c. Enteric Nervous System
解説: **消化管の局所神経系(Enteric Nervous System)**は筋層および粘膜下層に位置し、消化管の運動と分泌を独立して制御します。
Question 170 of 185
Regarding autonomic control of the GIT:
a) Parasympathetic stimulation inhibits activity
b) All of the above
c) Sympathetic fibers function especially to execute the defecation reflexes
d) Sacral parasympathetics originate in the S2-S4 segments of the spinal cord
e) Anal regions are better supplied with sympathetic fibers than other intestinal areas
Answer: d. Sacral parasympathetics originate in the S2-S4 segments of the spinal cord
解説: **仙骨副交感神経(S2-S4)**は直腸や肛門括約筋を支配します。副交感神経刺激は通常消化管の活動を促進し、交感神経は抑制します。
Question 171 of 185
This gastrointestinal reflex’s stimulus originates from the gut, then to the brain stem, and then back to the GIT:
a) Secretion
b) Defecation
c) Enterogastric
d) Peristalsis
e) All of the above
Answer: b
Question 172 of 185
Pancreatic bicarbonate secretion is increased when this hormone is secreted by the “S” cells of the duodenum in response to stimuli associated with the presence of acid in the duodenum:
a) Motilin
b) Cholecystokinin
c) All are correct
d) Gastrin
e) Secretin
Answer: e. Secretin
解説: セクレチン(Secretin)は十二指腸の”S”細胞から分泌され、膵臓の重炭酸塩分泌を刺激して酸を中和します。
Question 173 of 185
Hormone secreted by I cells in the mucosa of the duodenum and jejunum mainly in response to digestive products of fat, fatty acids, and monoglycerides in the intestinal contents and strongly contracts the gallbladder:
a) Gastrin
b) Motilin
c) Secretin
d) All are correct
e) Cholecystokinin
Answer: e. Cholecystokinin
解説: コレシストキニン(CCK)はI細胞から分泌され、胆嚢収縮と膵臓酵素分泌を促進します。
Question 174 of 185
The myenteric reflex of peristalsis and directional movement of peristaltic waves toward the anus:
a) Peristaltic reflex
b) Law of the Gut
c) Receptive relaxation
d) All are correct
e) Defecation Reflex
Answer: d
Question 175 of 185
Gastrin:
a) Is secreted by the “G” cells of the stomach in response to stimuli associated with ingestion
b) Is secreted during fasting to increase gastrointestinal motility
c) Promotes gallbladder contraction
d) Is also known as glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide
e) All are correct
Answer: a. Is secreted by the “G” cells of the stomach in response to stimuli associated with ingestion
解説: ガストリン(Gastrin)は胃のG細胞から分泌され、胃酸分泌を促進します。
- b. Is secreted during fasting: ガストリンは空腹時ではなく、食物摂取時に分泌されます。
- c. Promotes gallbladder contraction: 胆嚢収縮は主にCCKによって促進されます。
- d. Glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide: これはGIPであり、ガストリンとは異なります。
Question 176 of 185
Mastication involves which nerve?
a) None of the above
b) Trigeminal nerve
c) Trochlear nerve
d) Vagus nerve
e) Facial nerve
Answer: b. Trigeminal nerve
解説: **咀嚼(Mastication)は主に三叉神経(Trigeminal nerve, CN V)**によって支配されています。この神経が咀嚼筋の運動を制御します。
Question 177 of 185
Which of the following is not true about the swallowing reflex?
a) Is dependent on intrinsic nerve networks in the esophagus
b) Includes inhibition of respiration.
c) Is initiated by a voluntary act.
d) Has its reflex centers in the cervical segments of the spinal cord.
e) All of the above
Answer: d. Has its reflex centers in the cervical segments of the spinal cord
解説: 嚥下反射の中枢は延髄にあります。したがって、頸髄セグメントには嚥下の反射中枢はありません。
Question 178 of 185
A 60-year-old man underwent colon surgery for removal of a tumor in the gastrointestinal tract. Which of the following would be expected to increase after surgical removal of the duodenum?
a) Secretion of CCK
b) Contraction of the gallbladder
c) All of the above
d) Gastric emptying
e) Secretion of secretin
Answer: d. Gastric emptying
解説: 十二指腸の切除により、胃内容物の速やかな排出が促進されますが、セクレチンやCCKの分泌は抑制されます。
Question 179 of 185
Gastroesophageal sphincter:
a) All of the above
b) Helps to prevent significant reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus
c) Remains tonically constricted at 10 mmHg intraluminal pressure
d) Also known as the upper esophageal sphincter
e) Its receptive relaxation occurs during the peristaltic wave of the esophagus
Answer: b. Helps to prevent significant reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus
解説: **下部食道括約筋(Gastroesophageal sphincter)**は胃内容物の逆流を防ぎます。
- d. Upper esophageal sphincter: 下部食道括約筋は下部に位置し、上部括約筋とは異なります。
- e. Receptive relaxation: 下部食道括約筋は主に逆流防止に関与します。
Question 180 of 185
Increased peristaltic activity in the ileum and emptying of ileal contents into the cecum occurring immediately after a meal:
a) Peritoneointestinal reflex
b) Gastroileal reflex
c) Gastroenteric reflex
d) Renointestinal reflex
e) All of the above
Answer: b. Gastroileal reflex
解説: **胃回腸反射(Gastroileal reflex)**は、食事後に回腸内容物が盲腸に排出される反射です。
Question 181 of 185
Peristaltic waves in the small intestine:
a) Faster in the distal intestine and slower in the proximal
b) Spreads out the chyme along the intestinal mucosa
c) All of the above
d) Normally strong and die out after traveling 15 cm
e) Progresses chyme toward the pylorus
Answer: b. Spreads out the chyme along the intestinal mucosa
解説: 蠕動波は、小腸内の食物内容物(キーム)を腸粘膜に沿って広げ、吸収を促進します。
Question 182 of 185
Defecation is a reflex action:
a) Whose afferent limb carries impulses from stretch receptors in the colon.
b) Which cannot be voluntarily inhibited or facilitated.
c) Which is more likely to be initiated just after a meal than just before it.
d) Whose efferent limb travels mainly in sympathetic autonomic nerves.
e) All are correct
Answer: c
Question 183 of 185
In the colon:
a) Fecal transit time is faster than the peristaltic movements in the small intestine
b) Mucus is secreted to lubricate the fecal contents.
c) A greater volume of water is absorbed than in the small intestine.
d) Fecal transit time is normally about 7 days.
e) All of the above
Answer: b. Mucus is secreted to lubricate the fecal contents
解説: 大腸では粘液が分泌され、糞便の移動を助けます。
- a. Fecal transit time: 大腸での糞便の移動は、小腸よりもゆっくりです。
- c. Water absorption: 小腸が大部分の水分を吸収します。
- d. Fecal transit time is about 7 days: 通常は1〜2日です。
Question 184 of 185
A modified type of peristalsis characterized by the formation of a constrictive ring in response to a distended point in the GIT, then rapidly, the 20 or more centimeters of colon distal to the constrictive ring lose their haustrations and instead contract as a unit:
a) Primary esophageal peristalsis
b) All of the above
c) Mass movements
d) Secondary esophageal peristalsis
e) Gastric constrictor waves
Answer: c. Mass movements
解説: **大量移動(Mass movements)**は、大腸で強力な蠕動が起こり、一度に大部分が移動します。
Question 185 of 185
Which of the following changes occurs during defecation?
a) Intra-abdominal pressure is lower than when at rest
b) External anal sphincter is contracted
c) Internal anal sphincter is relaxed
d) Rectal smooth muscle is relaxed
e) All of the above
Answer: c. Internal anal sphincter is relaxed
解説: 排便時には、内肛門括約筋が弛緩し、直腸の収縮が起こります。
自作問題(50問、22nd Oct 2024)
Question 1
What is the primary cause of slow waves in GI smooth muscle?
a. Hormones secreted by the adrenal glands
b. Acetylcholine released from parasympathetic nerves
c. Interstitial cells of Cajal
d. Continuous spike potentials
Answer: c. Interstitial cells of Cajal
解説:
腸管平滑筋におけるslow waves(緩徐波)は、カハールの介在細胞(interstitial cells of Cajal)によって引き起こされます。この細胞は電気的なペースメーカーの役割を果たし、膜電位を周期的に変化させます。他の選択肢について説明すると、選択肢aのホルモンは、腸の電気的活動に直接関与していません。選択肢bのアセチルコリンは、主に興奮性のニューロンから分泌される神経伝達物質であり、膜電位を直接的に制御することはありません。選択肢dの連続的なスパイク電位は、収縮の発生を制御しますが、slow waves自体を引き起こす要因ではありません。

Question 2
What is the resting membrane potential (RMP) of GI smooth muscle?
a. -40 mV
b. -56 mV
c. 0 mV
d. -70 mV
Answer: b. -56 mV
解説:
GI平滑筋の静止膜電位(RMP)は-56 mVです。この値は細胞がどれだけ興奮しやすいかを決定し、平滑筋がどのようにして活動電位を発生させるかに影響します。他の選択肢について、選択肢aの-40 mVは活動電位が発生する臨界値に近いですが、静止状態ではありません。選択肢cの0 mVは通常の生理的条件下では存在しません。選択肢dの-70 mVは神経細胞などの他の細胞の静止膜電位に近いですが、GI平滑筋では見られません。

Question 3
Which of the following does NOT contribute to depolarization of GI smooth muscle?
a. Stretching of muscle
b. Acetylcholine release
c. Norepinephrine release
d. GI hormones
Answer: c. Norepinephrine release
解説:
ノルエピネフリン(norepinephrine)は、交感神経によって放出される神経伝達物質で、主に過分極を引き起こし、膜電位をより負の方向に変化させるため、筋肉の興奮性を低下させます。選択肢a、b、dはすべて脱分極を引き起こし、筋肉の興奮性を高めます。depolarizationは正の方向へ変化する。

Question 4
Which ions primarily enter the GI smooth muscle during spike potentials?
a. Sodium (Na+)
b. Potassium (K+)
c. Calcium (Ca++)
d. Chloride (Cl-)
Answer: c. Calcium (Ca++)
解説:
スパイク電位の際にGI平滑筋に入る主なイオンはカルシウムイオン(Ca++)です。これにより、筋繊維が収縮します。選択肢aのナトリウムは活動電位に関与しますが、主に神経細胞での役割です。選択肢bのカリウムは主に再分極に関与します。選択肢dの塩化物イオンは膜電位の維持に寄与しますが、スパイク電位とは関係が薄いです。

Question 5
What type of neurotransmitter is acetylcholine in the GI system?
a. Inhibitory
b. Excitatory
c. Neutral
d. Hormonal
Answer: b. Excitatory
解説:
アセチルコリン(acetylcholine)は、消化管において主に興奮性の神経伝達物質として作用し、平滑筋の収縮を促進します。他の選択肢について、選択肢aの抑制性の神経伝達物質は主に交感神経で見られます。選択肢cの中立という神経伝達物質は存在しません。選択肢dのホルモンは別のカテゴリーです。
Question 6
What is the primary function of slow waves in GI smooth muscle?
a. Trigger action potentials directly
b. Control the rhythm of contractions
c. Cause muscle fibers to relax
d. Stimulate hormone release
Answer: b. Control the rhythm of contractions
解説:
Slow wavesは、消化管平滑筋の収縮のリズムを制御する役割を果たしています。これ自体は真の活動電位ではありませんが、スパイク電位を制御し、最終的に収縮のタイミングを決定します。選択肢aは誤りで、slow waves自体は直接的に活動電位を引き起こしません。選択肢cは、slow wavesが筋繊維を弛緩させるわけではなく、むしろリズムを整えます。選択肢dのホルモン分泌に直接関与するわけでもありません。
Question 8
What causes tonic contraction in some GI smooth muscles?
a. Continuous spike potentials
b. Periodic hyperpolarization
c. Increased potassium entry
d. Reduced calcium concentration
Answer: a. Continuous spike potentials
解説:
トニック収縮は、連続したスパイク電位が引き金となり、長時間にわたり持続する部分的な収縮状態を引き起こします。選択肢bの周期的な過分極や選択肢cのカリウムの流入増加は、筋収縮を抑制する方向に働きます。選択肢dのカルシウム濃度の減少も筋収縮を弱めます。

Question 9
Which neurotransmitter is NOT typically secreted by enteric neurons?
a. Acetylcholine
b. Norepinephrine
c. Dopamine
d. Glutamate
Answer: d. Glutamate
解説:
腸管神経系は、アセチルコリン、ノルエピネフリン、ドーパミンなど多くの神経伝達物質を分泌しますが、グルタミン酸(glutamate)は腸管神経系で主要な神経伝達物質ではありません。他の選択肢はすべて腸管神経系での役割を持っています。
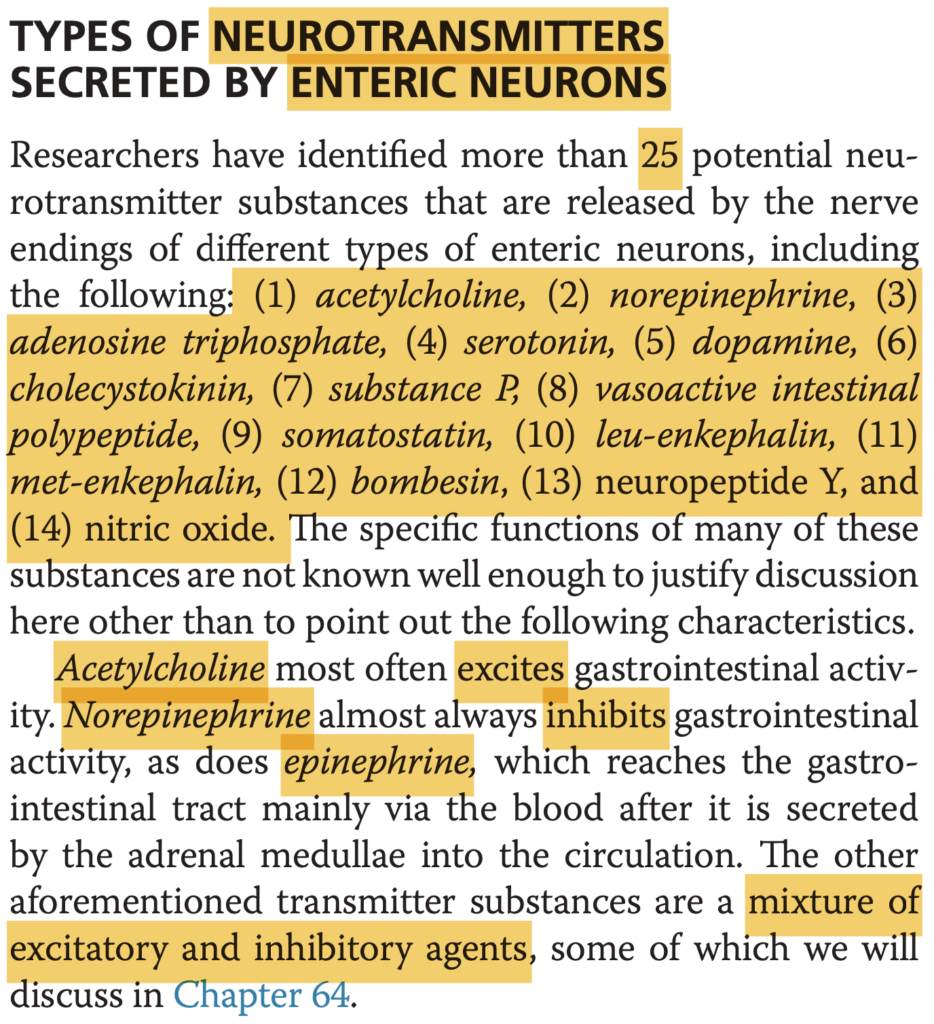
Question 1
Which reflex involves the communication from the gut to the prevertebral sympathetic ganglia and back to the gastrointestinal tract (GIT)?
a. Gastrocolic reflex
b. Pain reflex
c. Defecation reflex
d. Peristaltic reflex
Answer: a. Gastrocolic reflex
解説:
Gastrocolic reflexは、消化管から交感神経節(prevertebral sympathetic ganglia)を経由して消化管に戻る反射です。この反射は、胃が食物で満たされると大腸の運動を促進します。他の選択肢について、選択肢bとcの痛み反射および排便反射は脊髄や脳幹を経由して消化管に影響を与える反射です。選択肢dの蠕動反射(Peristaltic reflex)は消化管内の局所反射であり、外部の神経を介しません。

Question 2
What type of movement in the gastrointestinal tract keeps the intestinal contents thoroughly mixed?
a. Propulsive movements
b. Peristaltic movements
c. Mixing movements
d. Gastrocolic movements
Answer: c. Mixing movements
解説:
Mixing movementsは、腸の内容物を常にしっかりと混合させる役割を果たします。これにより、消化酵素が食物に均等に作用し、吸収が効率的に行われます。選択肢aの推進運動(Propulsive movements)は食物を前方に送る運動です。選択肢bの蠕動運動(Peristaltic movements)は食物を移動させる運動です。選択肢dのgastrocolic movementsは大腸の運動に関連しています。


Question 3
Which neurotransmitter is responsible for increasing GI blood flow during parasympathetic stimulation?
a. Norepinephrine
b. Acetylcholine
c. Dopamine
d. Serotonin
Answer: b. Acetylcholine
解説:
副交感神経の刺激時に放出されるアセチルコリン(Acetylcholine)は、消化管の血流を増加させ、腺の分泌を促進します。他の選択肢について、選択肢aのノルエピネフリンは交感神経刺激時に放出され、血流を減少させます。選択肢cのドーパミンや選択肢dのセロトニンは、主に中枢神経系に関与し、直接的な消化管血流の調整には関わりません。
Question 4
What is the “Law of the Gut”?
a. Peristaltic reflex and reverse movement
b. Peristaltic reflex and anal direction
c. Mixing reflex and gastric direction
d. Gastrocolic reflex and oral direction
Answer: b. Peristaltic reflex and anal direction
解説:
“Law of the Gut”とは、蠕動反射が肛門方向にのみ進むという法則です。これにより、食物や消化物は消化管全体を通して一方向に進むことが保証されます。選択肢aの逆方向やcの胃方向、dの口方向は間違っています。


Question 5
Which of the following is NOT a vasodilator substance that increases blood flow during GI activity?
a. Cholecystokinin (CCK)
b. Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP)
c. Norepinephrine
d. Gastrin
Answer: c. Norepinephrine
解説:
ノルエピネフリンは血管を収縮させ、血流を減少させる交感神経系の神経伝達物質です。他の選択肢であるCCK、VIP、ガストリンは、血管拡張を引き起こし、消化活動中に消化管の血流を増加させます。
Question 6
What are the primary functions of propulsive movements in the gastrointestinal tract?
a. To mix intestinal contents
b. To cause the food to move forward at an appropriate rate
c. To increase glandular secretion
d. To decrease the rate of digestion
Answer: b. To cause the food to move forward at an appropriate rate
解説:
Propulsive movementsの主な機能は、食物が消化管を前方に適切な速度で進むようにすることです。これにより、消化と吸収が適切に行われます。他の選択肢について、選択肢aの混合運動は消化酵素と食物を混ぜる役割があります。選択肢cの腺分泌は運動の結果ではなく、神経刺激の影響によります。選択肢dは誤りです。
Question 7
Which reflex is integrated entirely within the gut wall’s enteric nervous system?
a. Gastrocolic reflex
b. Pain reflex
c. Defecation reflex
d. Local inhibitory effects
Answer: d. Local inhibitory effects
解説:
消化管壁内の腸管神経系によって完全に統合される反射には、局所的な抑制効果(Local inhibitory effects)があります。他の選択肢について、選択肢aのgastrocolic reflexは交感神経節を経由します。選択肢bとcの痛み反射および排便反射は、脊髄や脳幹を経由します。

Question 8
Which substance is released by GI glands and acts as a vasodilator during GI activity?
a. Bradykinin
b. Norepinephrine
c. Serotonin
d. Dopamine
Answer: a. Bradykinin
解説:
ブレイジキニン(Bradykinin)は、消化管活動中に血管を拡張させ、血流を増加させる物質です。選択肢bのノルエピネフリンは血管収縮を引き起こします。選択肢cとdは、血管拡張には直接関与しません。

Question 9
What happens when oxygen concentration decreases during GI activity?
a. Vasodilation due to increased adenosine
b. Vasoconstriction due to increased norepinephrine
c. Decreased blood flow
d. Increased acetylcholine release
Answer: a. Vasodilation due to increased adenosine
解説:
酸素濃度が減少すると、アデノシン(adenosine)の増加により血管が拡張し、血流が増加します。他の選択肢について、選択肢bのノルエピネフリンは酸素濃度に関わらず血管収縮を引き起こします。選択肢cの血流減少や選択肢dのアセチルコリン分泌の増加は、酸素濃度の低下に関連しません。

Question 10
What is the effect of sympathetic stimulation on GI blood flow?
a. Increases blood flow
b. Decreases blood flow
c. Causes autoregulatory escape
d. Causes vasodilation
Answer: b. Decreases blood flow
解説:
交感神経刺激は、消化管の血流を減少させます。血管収縮を引き起こし、一時的に血流が低下します。選択肢aの血流増加や選択肢dの血管拡張は、副交感神経刺激によるものです。選択肢cの自律調節的脱出(autoregulative escape)は、血流が元に戻ろうとするメカニズムですが、これは血流が減少した後のことです。
Question 1
Which hormone is primarily responsible for stimulating gastric acid secretion?
a. Secretin
b. Gastrin
c. Cholecystokinin
d. Motilin
Answer: b. Gastrin
解説:
ガストリン(Gastrin)は、胃酸分泌を刺激する主要なホルモンです。ガストリンは胃のG細胞から分泌され、胃酸の分泌を促進し、粘膜の成長も刺激します。選択肢aのセクレチンは、胃酸分泌を抑制し、主に膵臓の重炭酸イオン分泌を促します。選択肢cのコレシストキニン(Cholecystokinin)は胆嚢収縮を刺激し、消化酵素の分泌を促進します。選択肢dのモチリン(Motilin)は主に消化管の運動を促進します。

Question 2
Which hormone is responsible for inhibiting gastric emptying and stimulating gallbladder contraction?
a. Gastrin
b. Secretin
c. Cholecystokinin
d. Gastric inhibitory peptide
Answer: c. Cholecystokinin
解説:
コレシストキニン(Cholecystokinin)は、胆嚢の収縮を促進し、消化酵素の分泌を刺激するだけでなく、胃の排出を抑制します。選択肢aのガストリンは胃酸分泌を促進し、胃の排出に影響を与えません。選択肢bのセクレチンは主に膵臓の重炭酸イオン分泌を刺激し、選択肢dのガストリック・インヒビトリ・ペプチドは主にインスリンの分泌を刺激します。


Question 3
Which hormone stimulates insulin release in response to carbohydrate intake?
a. Gastrin
b. Secretin
c. Gastric inhibitory peptide
d. Motilin
Answer: c. Gastric inhibitory peptide
解説:
ガストリック・インヒビトリ・ペプチド(Gastric inhibitory peptide, GIP)は、炭水化物や脂肪の摂取に応じてインスリンの分泌を刺激します。選択肢aのガストリンは主に胃酸分泌を刺激し、選択肢bのセクレチンは膵臓の重炭酸分泌を刺激します。選択肢dのモチリンは主に消化管の運動を調整します。

Question 4
Which hormone is released by S cells in response to acid in the duodenum and stimulates bicarbonate secretion?
a. Gastrin
b. Secretin
c. Cholecystokinin
d. Motilin
Answer: b. Secretin
解説:
セクレチン(Secretin)は、酸性条件に反応して十二指腸のS細胞から分泌され、膵臓や胆管からの重炭酸イオンの分泌を促進します。これは、腸内の酸性環境を中和するためです。選択肢aのガストリンは胃酸分泌を促進します。選択肢cのコレシストキニンは主に消化酵素の分泌を促進し、選択肢dのモチリンは消化管の運動を調整します。

Question 5
Which hormone stimulates both gastric and intestinal motility?
a. Gastrin
b. Secretin
c. Cholecystokinin
d. Motilin
Answer: d. Motilin
解説:
モチリン(Motilin)は胃と腸の運動を刺激し、特に食間の腸の運動を促進します。他の選択肢について、選択肢aのガストリンは主に胃酸分泌を刺激します。選択肢bのセクレチンや選択肢cのコレシストキニンは主に消化液の分泌に関与します。


Question 6
Which hormone is released by K cells in the duodenum and jejunum in response to fat and carbohydrate intake?
a. Gastrin
b. Secretin
c. Gastric inhibitory peptide
d. Cholecystokinin
Answer: c. Gastric inhibitory peptide
解説:
ガストリック・インヒビトリ・ペプチド(Gastric inhibitory peptide, GIP)は十二指腸と空腸のK細胞から脂肪や炭水化物の摂取に応じて分泌されます。他の選択肢について、選択肢aのガストリンは主に胃酸分泌を刺激します。選択肢bのセクレチンは酸性環境に応答し、選択肢dのコレシストキニンは主に脂肪とタンパク質に応答します。
Question 7
What is the main stimulus for the release of motilin?
a. Protein
b. Fat
c. Acid
d. Nerve stimulation
Answer: d. Nerve stimulation
解説:
モチリン(Motilin)は主に神経刺激によって分泌され、消化管の運動を促進します。他の選択肢について、選択肢aのタンパク質や選択肢bの脂肪、選択肢cの酸は、主に他のホルモン(ガストリン、コレシストキニン、セクレチン)の分泌を促します。
Question 8
Which hormone primarily inhibits gastric acid secretion and stimulates pancreatic bicarbonate secretion?
a. Gastrin
b. Secretin
c. Cholecystokinin
d. Gastric inhibitory peptide
Answer: b. Secretin
解説:
セクレチン(Secretin)は、胃酸の分泌を抑制し、膵臓から重炭酸を分泌させることで、腸内の酸性環境を中和します。選択肢aのガストリンは胃酸分泌を刺激し、選択肢cのコレシストキニンは主に消化酵素の分泌を促します。選択肢dのGIPも胃酸分泌を抑制しますが、インスリン分泌の刺激が主な作用です。
Question 9
What is the primary site of gastrin secretion?
a. G cells of the antrum, duodenum, and jejunum
b. I cells of the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
c. S cells of the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
d. K cells of the duodenum and jejunum
Answer: a. G cells of the antrum, duodenum, and jejunum
解説:
ガストリン(Gastrin)は、幽門部(antrum)や十二指腸、空腸のG細胞から分泌されます。他の選択肢について、選択肢bのI細胞はコレシストキニンを、選択肢cのS細胞はセクレチンを、選択肢dのK細胞はGIPを分泌します。
Question 10
Which hormone primarily stimulates pancreatic enzyme secretion and inhibits gastric emptying?
a. Secretin
b. Cholecystokinin
c. Gastric inhibitory peptide
d. Motilin
Answer: b. Cholecystokinin
解説:
コレシストキニン(Cholecystokinin)は、膵酵素の分泌を刺激し、同時に胃の排出を抑制します。選択肢aのセクレチンは膵重炭酸分泌を刺激し、選択肢cのGIPは主にインスリンの分泌を刺激します。選択肢dのモチリンは主に消化管の運動を刺激します。
Question 1
Which cranial nerve is primarily responsible for the motor control of the muscles involved in mastication?
a. CN VII
b. CN V
c. CN X
d. CN XII
Answer: b. CN V
解説:
咀嚼に関与する筋肉は主に三叉神経(CN V)の運動枝によって制御されています。この神経は顎の動きを制御し、食物を口の中で砕くのに重要です。選択肢aの顔面神経(CN VII)は顔の表情筋を制御します。選択肢cの迷走神経(CN X)は消化管の他の部分に関連し、選択肢dの舌下神経(CN XII)は主に舌の運動を制御します。

Question 2
What is the primary purpose of chewing (mastication)?
a. To decrease the surface area of food
b. To prevent food from passing through the digestive tract too quickly
c. To increase the surface area for digestive enzymes to act on
d. To mix saliva with food for taste
Answer: c. To increase the surface area for digestive enzymes to act on
解説:
咀嚼の主な目的は、消化酵素が効率的に作用できるように食物の表面積を増やすことです。また、食物をより小さく砕くことで、消化管を傷つけないようにします。選択肢aの表面積を減少させるのではなく増やし、選択肢bやdは咀嚼の副次的な効果に過ぎません。

Question 3
Which reflex is responsible for the rhythmic movement of the jaw during chewing?
a. Gag reflex
b. Stretch reflex
c. Pain reflex
d. Cough reflex
Answer: b. Stretch reflex
解説:
咀嚼中の下顎のリズミカルな動きは伸張反射(Stretch reflex)によって引き起こされます。食物が口に入ると咀嚼筋の活動が抑制され、下顎が下がりますが、その後筋肉が伸展されると反射的に収縮し、顎が再び上がります。他の選択肢であるgag reflexやpain reflexは咀嚼には関係ありません。


Question 4
Which stage of swallowing is voluntary?
a. Pharyngeal stage
b. Esophageal stage
c. Voluntary stage
d. Laryngeal stage
Answer: c. Voluntary stage
解説:
嚥下の最初の段階である「voluntary stage」は、意識的に行われるもので、舌が食物を後方に押し出す動作が含まれます。選択肢aとbの咽頭段階(pharyngeal stage)と食道段階(esophageal stage)は自動的に行われます。選択肢dの喉頭段階は存在しません。

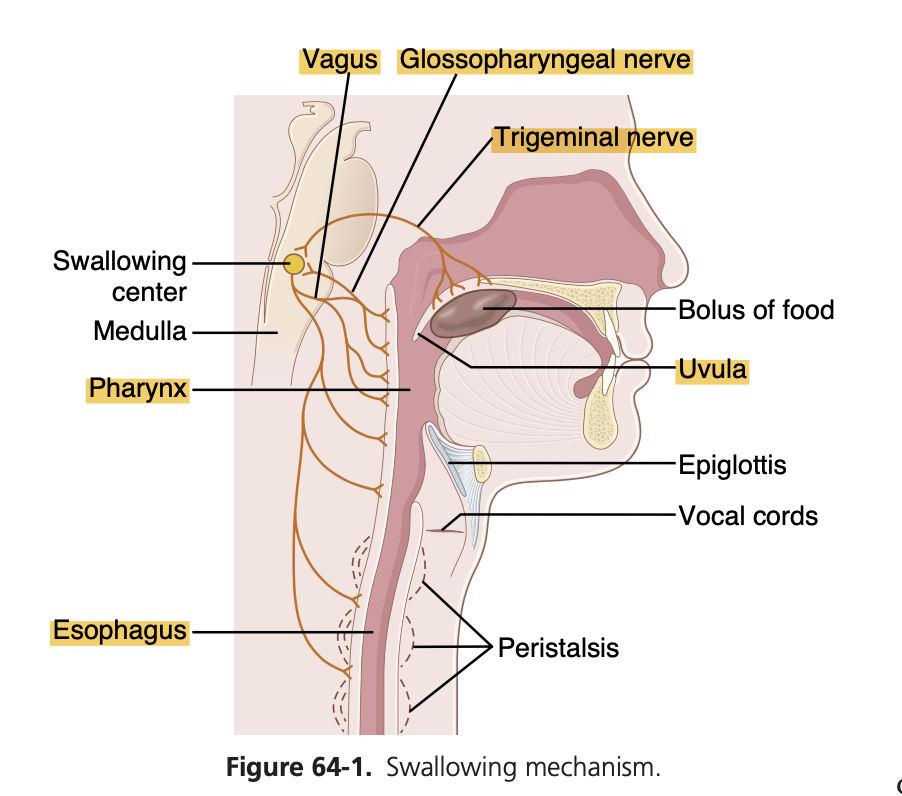
Question 5
During swallowing, which structure seals off the nasal passage to prevent food from entering the nose?
a. Epiglottis
b. Soft palate
c. Vocal cords
d. Pharyngeal muscles
Answer: b. Soft palate
解説:
嚥下中、軟口蓋(soft palate)が鼻腔を閉じ、食物が鼻に入らないようにします。他の選択肢について、選択肢aの喉頭蓋(epiglottis)は気管を閉じ、選択肢cの声帯(vocal cords)は窒息を防ぎます。選択肢dの咽頭筋(pharyngeal muscles)は食物を咽頭から食道に押し下げます。

Question 6
Which nerves are involved in the sensory initiation of the pharyngeal stage of swallowing?
a. CN V and CN VII
b. CN IX and CN X
c. CN V and CN IX
d. CN X and CN XII
Answer: c. CN V and CN IX
解説:
咽頭段階の嚥下を開始する感覚情報は、三叉神経(CN V)と舌咽神経(CN IX)によって伝達されます。この情報は延髄の嚥下中枢に送られます。他の選択肢の神経は、嚥下に関連する他の運動機能や制御を担っていますが、感覚入力に直接関与しているのはCN VとCN IXです。

Question 7
What effect does swallowing have on respiration?
a. Increases respiration rate
b. Halts respiration for a brief moment
c. Stimulates the respiratory center in the brain
d. Has no effect on respiration
Answer: b. Halts respiration for a brief moment
解説:
嚥下中、呼吸中枢は一時的に抑制され、呼吸は短時間停止します。これにより、食物が気管に入らないようにします。他の選択肢について、選択肢aのように呼吸速度が増加することはなく、選択肢cも誤りです。選択肢dの「影響がない」というのは間違いです。

Question 8
Which cranial nerves are involved in the motor control of the pharyngeal stage of swallowing?
a. CN V, IX, X, XII
b. CN VII, IX, X
c. CN V, VII, X
d. CN IX, X, XI
Answer: a. CN V, IX, X, XII
解説:
咽頭段階の嚥下の運動制御には、三叉神経(CN V)、舌咽神経(CN IX)、迷走神経(CN X)、および舌下神経(CN XII)が関与しています。これらの神経は、食物を咽頭から食道に送り込むための筋肉を制御しています。他の選択肢は、嚥下に直接関与していない神経も含んでいます。
Question 9
What is the role of the esophageal stage of swallowing?
a. Voluntary movement of food from the pharynx to the esophagus
b. Reflexive movement of food into the stomach
c. Closing of the vocal cords
d. Sealing of the nasal passages
Answer: b. Reflexive movement of food into the stomach
解説:
食道段階(esophageal stage)は、反射的に食道を通じて食物を胃に送り込む段階です。選択肢aは咽頭段階の役割であり、選択肢cは声帯の閉鎖、選択肢dは軟口蓋による鼻腔の封鎖に関係しています。
Question 10
Which cranial nerve controls the movement of the tongue during swallowing?
a. CN IX
b. CN XII
c. CN X
d. CN V
Answer: b. CN XII
解説:
舌の運動は舌下神経(CN XII)によって制御されます。この神経は、嚥下の最初の段階で舌が食物を押し出す運動を制御します。選択肢aの舌咽神経(CN IX)は咽頭の運動を制御し、選択肢cの迷走神経(CN X)は消化管全体の調整に関与しています。選択肢dの三叉神経(CN V)は主に咀嚼に関与しています。
Question 1
What occurs during the receptive relaxation of the stomach?
a. The stomach contracts in anticipation of food
b. The stomach relaxes ahead of food arriving from the esophagus
c. Peristalsis starts in the stomach
d. The stomach closes to prevent food from entering
Answer: b. The stomach relaxes ahead of food arriving from the esophagus
解説:
「receptive relaxation」は、食物が食道から胃に移動する前に、胃が食物を受け入れるために弛緩する現象です。この反応は蠕動運動に先立ち、主に腸間神経系(myenteric inhibitory neurons)によって調節されます。選択肢aは誤りで、弛緩の代わりに収縮は行われません。選択肢cの蠕動運動は食物が胃に到達した後に発生します。選択肢dは胃が閉じるのではなく、食物を受け入れるために弛緩します。


Question 2
What is the primary function of hunger contractions in the stomach?
a. To prepare the stomach for digestion
b. To increase the release of gastric acid
c. To cause intense contractions after prolonged fasting
d. To propel food into the small intestine
Answer: c. To cause intense contractions after prolonged fasting
解説:
「hunger contractions」は、数時間以上食物がない場合に胃で発生する強い収縮で、しばしば空腹感を伴います。選択肢aのように消化の準備のためではなく、選択肢bの胃酸の分泌増加とも関係ありません。選択肢dの小腸への食物の送り出しは、胃の排出段階で起こりますが、空腹収縮の目的ではありません。

Question 3
Which reflex helps to slow gastric emptying when the duodenum is overloaded?
a. Gastrocolic reflex
b. Enterogastric reflex
c. Peristaltic reflex
d. Gastroileal reflex
Answer: b. Enterogastric reflex
解説:
「enterogastric reflex」は、十二指腸が過負荷になると、胃の排出を遅らせる反射です。これにより、十二指腸が消化と吸収を処理する時間が確保されます。選択肢aのgastrocolic reflexは胃の充満が大腸の運動を促進する反射です。選択肢cとdの反射は、蠕動運動や小腸の動きを調整しますが、胃の排出を抑制するわけではありません。

Question 4
What is the main purpose of peristaltic rush in the small intestine?
a. To slow down the passage of chyme
b. To enhance nutrient absorption
c. To rapidly clear irritative contents during infections
d. To stimulate the release of digestive enzymes
Answer: c. To rapidly clear irritative contents during infections
解説:
「peristaltic rush」は、感染症や腸内の強い刺激がある場合に、小腸を迅速に掃除し、内容物を大腸に送り込むための強力で急速な蠕動運動です。選択肢aの内容物の速度を遅くするのではなく、逆に急速に移動させます。選択肢bの栄養吸収を促進する目的はありません。選択肢dの消化酵素の分泌は蠕動運動とは直接関係がありません。

Question 5
Which reflex inhibits ileal peristalsis when there is pressure in the cecum?
a. Gastroileal reflex
b. Ileocecal sphincter reflex
c. Enterogastric reflex
d. Defecation reflex
Answer: b. Ileocecal sphincter reflex
解説:
「ileocecal sphincter reflex」は、盲腸に圧力や化学的刺激があると、回腸の蠕動運動を抑制し、回盲弁を閉じる反射です。これにより、内容物が大腸に入り過ぎないように制御されます。選択肢aのgastroileal reflexは胃の動きが回腸の蠕動運動を促進しますが、盲腸の圧力には関係しません。選択肢cのenterogastric reflexや選択肢dのdefecation reflexもこの現象には関係がありません。
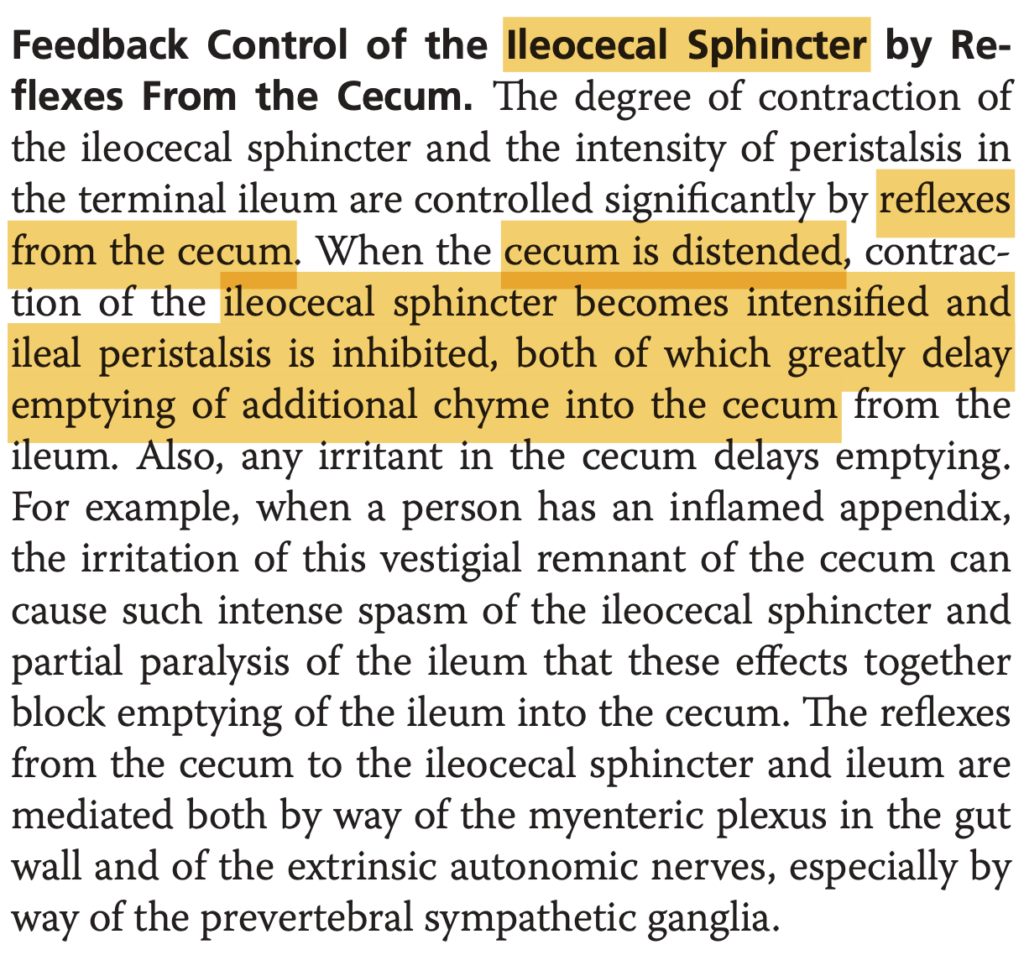
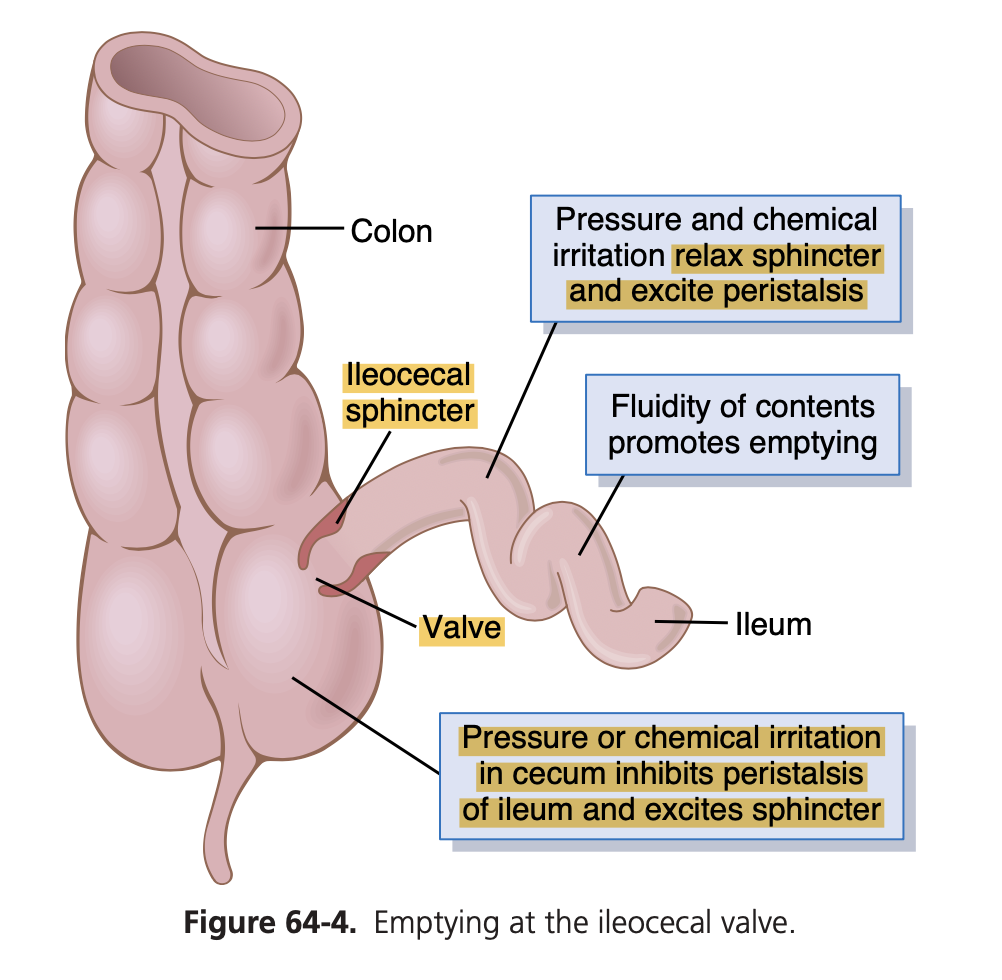
Question 6
Which movements are responsible for forming the characteristic “haustrations” in the colon?
a. Propulsive movements
b. Mass movements
c. Circular and longitudinal muscle contractions
d. Peristaltic rush
Answer: c. Circular and longitudinal muscle contractions
解説:
「haustrations」は、大腸の円形筋と縦走筋の収縮によって形成される袋状の構造です。これにより、大腸内の内容物が適切に混合され、吸収が促進されます。選択肢aやbの推進運動や質量運動は、内容物を前方に移動させますが、haustrationsには関与しません。選択肢dの蠕動ラッシュは小腸での現象です。

Question 7
Which reflex stimulates mass movements in the colon after eating?
a. Gastrocolic reflex
b. Enterogastric reflex
c. Peristaltic reflex
d. Vesicointestinal reflex
Answer: a. Gastrocolic reflex
解説:
「gastrocolic reflex」は、食事後に大腸での質量運動(mass movements)を引き起こす反射です。これにより、食事の摂取が大腸の運動を刺激し、排便が促進されます。選択肢bのenterogastric reflexは胃の排出を抑制します。選択肢cのperistaltic reflexやdのvesicointestinal reflexは大腸での質量運動には関係していません。
Question 8
What type of movement is responsible for the mass propulsion of fecal material in the colon?
a. Haustrations
b. Peristaltic rush
c. Mass movements
d. Propulsive movements
Answer: c. Mass movements
解説:
「mass movements」は、大腸内の糞便を一括して下方に押し進める運動です。この運動は、1日に1〜3回発生し、特に食事後に顕著になります。選択肢aのhaustrationsは混合運動であり、選択肢bのperistaltic rushは小腸で見られる急速な蠕動です。選択肢dの推進運動は小腸での通常の蠕動運動です。


Question 9
Which reflex can inhibit bowel activity as a result of bladder irritation?
a. Renointestinal reflex
b. Vesicointestinal reflex
c. Gastrocolic reflex
d. Peritoneointestinal reflex
Answer: b. Vesicointestinal reflex
解説:
「vesicointestinal reflex」は、膀胱の刺激が腸の活動を抑制する反射です。選択肢aのrenointestinal reflexは腎臓の刺激に関連し、選択肢cのgastrocolic reflexは食事後の大腸運動に関連します。選択肢dのperitoneointestinal reflexは腹膜刺激による腸活動の抑制を指します。

Question 10
Which autonomic reflex can cause intestinal paralysis in response to peritoneal irritation?
a. Gastroileal reflex
b. Defecation reflex
c. Peritoneointestinal reflex
d. Vesicointestinal reflex
Answer: c. Peritoneointestinal reflex
解説:
「peritoneointestinal reflex」は、腹膜の刺激により腸の活動が強く抑制され、場合によっては腸麻痺(intestinal paralysis)を引き起こすことがあります。他の選択肢は腸活動の抑制に直接関係していません。


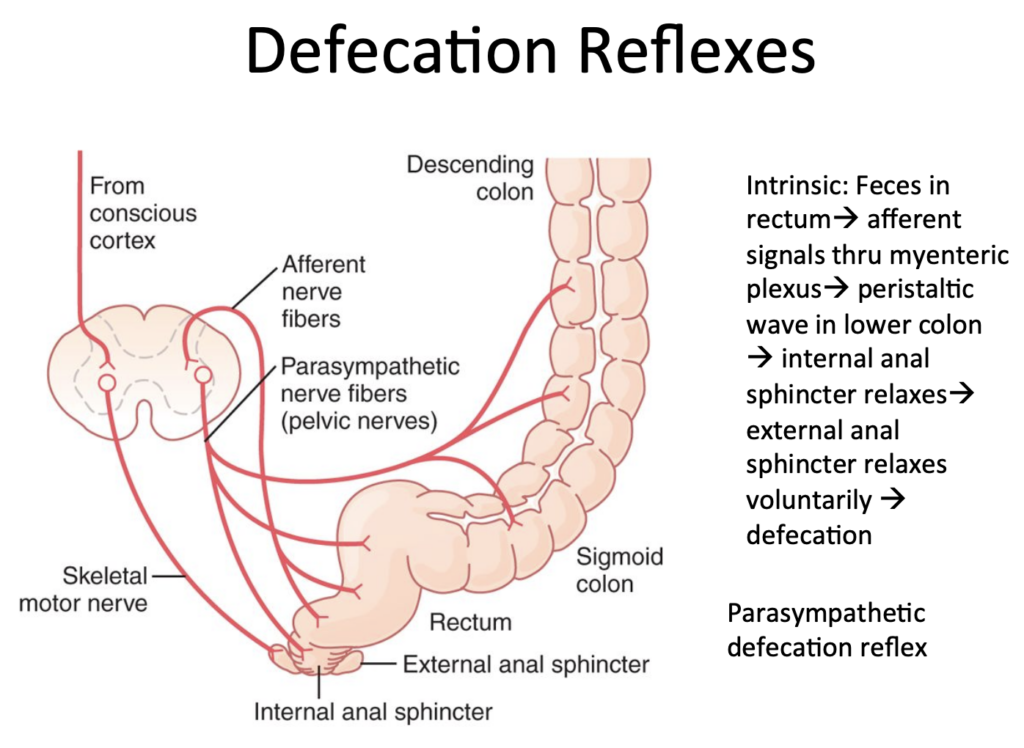
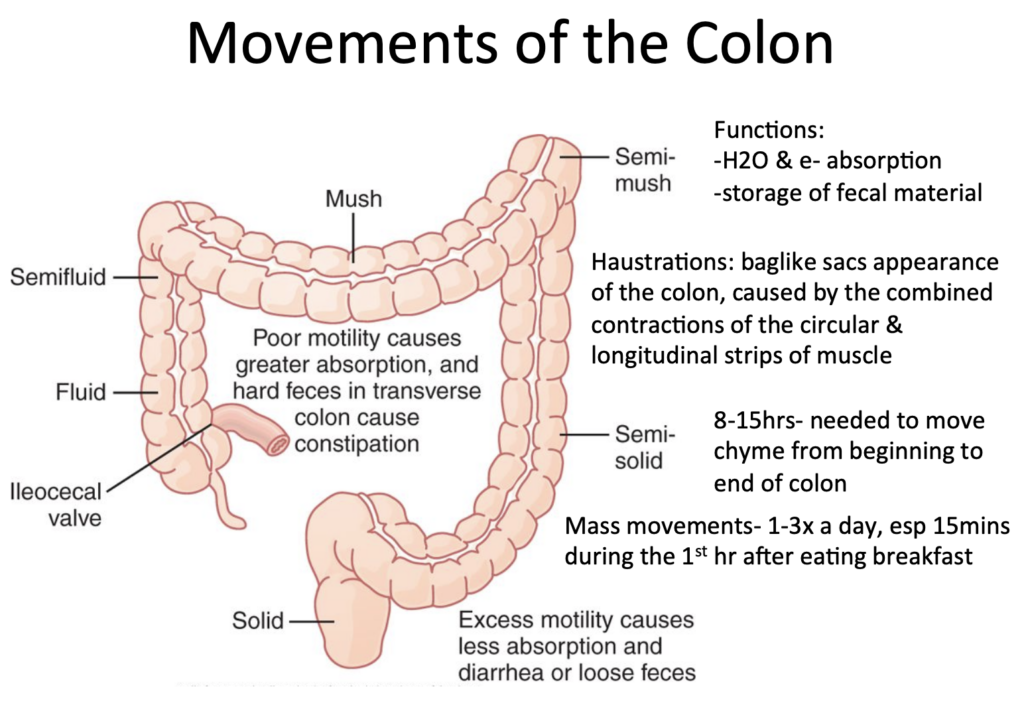


コメント