Contents
- 1 アセス(22nd Oct 2024)
- 1.1 Question 1
- 1.2 Question 2
- 1.3 Question 3
- 1.4 Question 4
- 1.5 Question 5(ミス)
- 1.6 Question 6 of 25
- 1.7 Question 7 of 25(ミス)
- 1.8 Question 8 of 25(ミス)
- 1.9 Question 9 of 25
- 1.10 Question 10 of 25
- 1.11 Question 11 of 25
- 1.12 Question 12 of 25
- 1.13 Question 13 of 25
- 1.14 Question 14 of 25(ミス)
- 1.15 Question 15 of 25
- 1.16 Question 16 of 25
- 1.17 Question 17 of 25
- 1.18 Question 18 of 25
- 1.19 Question 19 of 25
- 1.20 Question 20 of 25
- 1.21 Question 21 of 25
- 1.22 Question 22 of 25
- 1.23 Question 23 of 25
- 1.24 Question 24 of 25
- 1.25 Question 25 of 25(ミス)
- 2 アセス
- 2.1 Question 1
- 2.2 Question 2
- 2.3 Question 3
- 2.4 Question 4
- 2.5 Question 5
- 2.6 Question 6
- 2.7 Question 7
- 2.8 Question 8
- 2.9 Question 9
- 2.10 Question 10
- 2.11 Question 11
- 2.12 Question 12
- 2.13 Question 13
- 2.14 Question 14
- 2.15 Question 15
- 2.16 Question 16
- 2.17 Question 17
- 2.18 Question 18
- 2.19 Question 19
- 2.20 Question 20
- 2.21 Question 21
- 2.22 Question 22
- 2.23 Question 23
- 2.24 Question 24
- 2.25 Question 25
- 3 追加(教科書の問題からCh 15,16)
- 4 追加(スライドから)
- 4.1 Question 1
- 4.2 Question 2
- 4.3 Question 3
- 4.4 Question 4
- 4.5 Question 5
- 4.6 Question 6
- 4.7 Question 7
- 4.8 Question 8
- 4.9 Question 9
- 4.10 Question 10
- 4.11 Question 1
- 4.12 Question 2
- 4.13 Question 3
- 4.14 Question 4
- 4.15 Question 5
- 4.16 Question 6
- 4.17 Question 7
- 4.18 Question 8
- 4.19 Question 9
- 4.20 Question 10
- 4.21 Question 1
- 4.22 Question 2
- 4.23 Question 3
- 4.24 Question 4
- 4.25 Question 5
- 4.26 Question 6
- 4.27 Question 7
- 4.28 Question 8
- 4.29 Question 9
- 4.30 Question 10
- 5 ブロック
- 5.1 Question 1
- 5.2 Question 2
- 5.3 Question 3
- 5.4 Question 4
- 5.5 Question 5
- 5.6 Question 6
- 5.7 Question 7
- 5.8 Question 8
- 5.9 Question 9
- 5.10 Question 10
- 5.11 Question 11
- 5.12 Question 12
- 5.13 Question 13
- 5.14 Question 14
- 5.15 Question 15
- 5.16 Question 16
- 5.17 Question 17
- 5.18 Question 18
- 5.19 Question 19
- 5.20 Question 20
- 5.21 Question 21
- 5.22 Question 22
- 5.23 Question 23
- 6 自作70問(22nd Oct 2024)
アセス(22nd Oct 2024)
Question 1
Which layer contains the lining epithelium?
a. Serosa
b. Muscularis externa
c. Submucosa
d. Mucosa
Answer: d. Mucosa
解説:
粘膜(Mucosa)は消化管の内側を覆う最も内側の層で、上皮細胞(lining epithelium)を含んでいます。これらの細胞は栄養吸収や病原体からの防御を行う重要な役割を果たします。また、粘膜は固有層(lamina propria)と粘膜筋板(muscularis mucosa)を含むため、柔軟性が高く、消化管の運動にも関与します。
他の選択肢の解説:
- Serosa(漿膜): 外側の保護層であり、腹膜の一部として他の臓器と接触しますが、上皮細胞を含みません。
- Muscularis externa(筋層): 消化管の平滑筋から成り、蠕動運動や食物の輸送を助けますが、上皮組織は含まれていません。
- Submucosa(粘膜下層): 粘膜の下層で、血管や神経が存在し、支持組織としての役割を果たしますが、上皮細胞は含まれていません。
Question 2
What is the innermost layer of the GI Tract called?
a. Serosa
b. Submucosa
c. Mucosa
d. Muscularis externa
Answer: c. Mucosa
解説:
粘膜(Mucosa)は消化管の最も内側に位置し、上皮細胞、固有層、および粘膜筋板で構成されます。食物の消化と吸収に直接関与し、保護機能も果たします。この層は、異物の侵入を防ぐ物理的な障壁を提供し、消化酵素や粘液を分泌します。
他の選択肢の解説:
- Serosa(漿膜): 外膜で、腹膜に覆われた領域で見られます。
- Submucosa(粘膜下層): 粘膜と筋層の間にある結合組織の層で、栄養を供給する血管を含んでいますが、消化管の最内層ではありません。
- Muscularis externa(筋層): 消化管の平滑筋で、食物の移動を助ける蠕動運動を引き起こします。
Question 3
Which type of papillae on the tongue is NOT well developed in humans?
a. Filiform papillae
b. Fungiform papillae
c. Foliate papillae
d. All of the above
Answer: b
Question 4
What is the outer layer of the GI Tract called when it is abutting another organ?
a. Muscularis externa
b. Serosa
c. Mucosa
d. Adventitia
Answer: d. Adventitia
解説:
消化管の外側が他の臓器と接触している場合、その部分は「外膜(Adventitia)」と呼ばれます。これは、消化管を他の臓器と固定する結合組織の一種です。腹膜に覆われない部分で主に見られます。
他の選択肢の解説:
- Muscularis externa(筋層): 食物の移動を助けるための平滑筋から成り、外膜ではありません。
- Serosa(漿膜): 消化管の腹膜に覆われた部分に存在する外層です。
- Mucosa(粘膜): 内層の一部で、外側の構造には関与しません。
Question 5(ミス)
Which layer contains the Muscularis mucosa?
a. Muscularis externa
b. Submucosa
c. Mucosa
d. Serosa
Answer: c
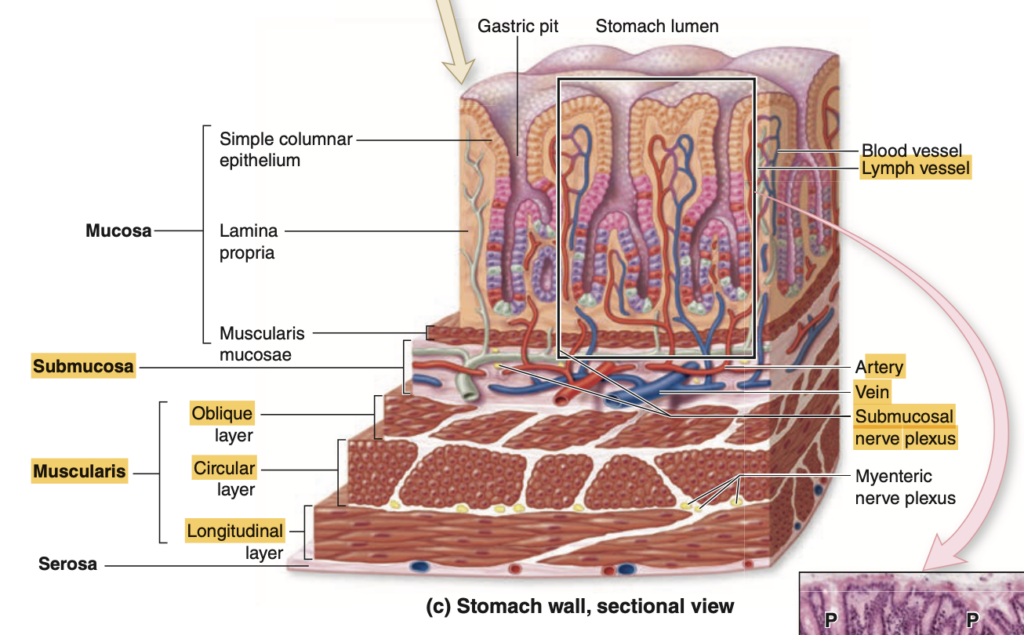
Question 6 of 25
What are the finger-like projections of the mucosa that are seen in the Small Intestine?
a. Villi
b. Plicae Circulares
c. Crypts of Lieberkuhn
d. Striated Border
a. Villi
Explanation:
- Villi are finger-like projections of the mucosa in the small intestine, which increase the surface area for absorption of nutrients.
- Plicae Circulares are large circular folds of the mucosa and submucosa that also aid in increasing the surface area but are much larger and involve the entire wall.
- Crypts of Lieberkuhn are glandular structures located between the villi and are involved in secreting intestinal juices.
- Striated Border refers to the microvilli on the surface of the epithelial cells lining the villi, also contributing to increased surface area for absorption but on a much smaller scale.
Question 7 of 25(ミス)
Which layer consists of only a single layer of epithelial cells and underlying connective tissue?
a. Serosa
b. Mucosa
c. Adventitia
d. Submucosa
Answer: a. Serosa
解説:
漿膜(Serosa)は、単層の上皮細胞(中皮細胞)とその下の結合組織からなる薄い層で、消化管の外側を覆っています。この層は主に消化管を保護し、他の臓器との摩擦を減らす役割を果たします。
他の選択肢の解説:
- Mucosa(粘膜): 多層の構造を持ち、上皮細胞、固有層、粘膜筋板で構成されています。
- Adventitia(外膜): 他の臓器と接する部分に存在する結合組織で、単層の上皮細胞はありません。
- Submucosa(粘膜下層): 粘膜の下に位置する結合組織層で、神経や血管を含んでいます。
Question 8 of 25(ミス)
Where is the masticatory mucosa found?
a. Hard Palate
b. Underside of the Tongue
c. Soft Palate
d. Lips
Answer: a. Hard Palate
解説:
咀嚼粘膜(Masticatory mucosa)は硬口蓋(Hard Palate)と歯肉に存在し、咀嚼の際の摩擦や圧力に耐えるために角化した上皮を持ちます。
他の選択肢の解説:
- Underside of the Tongue(舌の裏側): ここには非角化粘膜が見られます。
- Soft Palate(軟口蓋): ここも非角化粘膜で、咀嚼粘膜とは異なります。
- Lips(唇): 唇の内側は非角化粘膜ですが、外側には皮膚があります。
Question 9 of 25
Which cells secrete Hydrochloric Acid?
a. Oxyntic cells
b. Parietal cells
c. Both a and b
d. Chief Cells
Answer: c. Both a and b
解説:
塩酸(Hydrochloric Acid)は壁細胞(Parietal cells)とも呼ばれるオキシンティック細胞(Oxyntic cells)によって胃の壁から分泌されます。この酸は胃のpHを下げ、消化を助けるとともに病原体を殺菌します。
他の選択肢の解説:
- Chief Cells(主細胞): ペプシノーゲン(Pepsinogen)を分泌しますが、塩酸の分泌には関与しません。
Question 10 of 25
What is the surface layer of the Masticatory Mucosa composed of?
a. Non-Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium
b. Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium
c. Simple Squamous Epithelium
d. Both a and b
Answer: b. Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium
解説:
咀嚼粘膜(Masticatory mucosa)の表層は角化重層扁平上皮(Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium)で構成され、咀嚼による摩擦に対する耐性を高めます。
他の選択肢の解説:
- Non-Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium(非角化重層扁平上皮): 舌の裏側や口唇の内側に見られます。
- Simple Squamous Epithelium(単層扁平上皮): これは血管や体腔を覆う薄い上皮で、咀嚼粘膜には見られません。
- Both a and b: 咀嚼粘膜には主に角化上皮が見られるため、この選択肢は誤りです。
Question 11 of 25
What surrounds the pulp cavity?
a. Dentin
b. Enamel
c. Dental pulp
d. Cementum
Answer: a. Dentin
解説:
象牙質(Dentin)は歯髄腔(pulp cavity)を取り囲む組織で、歯全体の構造を支えます。象牙質は骨に似た硬組織で、歯髄(pulp)を保護します。
他の選択肢の解説:
- Enamel(エナメル質): 歯の表面を覆う非常に硬い外層で、象牙質の上にあります。
- Dental pulp(歯髄): 歯の中心にある組織で、神経や血管を含んでいますが、象牙質には含まれません。
- Cementum(セメント質): 歯根を覆う硬い組織で、歯を歯槽骨に固定します。
Question 12 of 25
Which layer of the alimentary tract contains the lamina propria?
a. Muscular externa
b. Submucosa
c. Serosa
d. Mucosa
Answer: d. Mucosa
解説:
固有層(Lamina propria)は粘膜(Mucosa)の一部であり、結合組織から構成され、血管、神経、リンパ組織が含まれます。この層は粘膜の保護と栄養供給を助けます。
他の選択肢の解説:
- Muscular externa(筋層): 消化管の運動を担当する層で、固有層は含まれません。
- Submucosa(粘膜下層): 粘膜の下層で、結合組織を多く含みますが、固有層はありません。
- Serosa(漿膜): 消化管の外層で、滑らかな表面を提供し、固有層は含まれません。
Question 13 of 25
Which type of papillae on the Tongue is mushroom shaped?
a. Filiform papillae
b. Fungiform papillae
c. Foliate papillae
d. None of the above
Answer: b. Fungiform papillae
解説:
茸状乳頭(Fungiform papillae)は、舌の先端や側面に見られ、きのこ(mushroom)のような形をしています。これらの乳頭には味蕾が含まれ、味覚を感知する役割を持っています。
他の選択肢の解説:
- Filiform papillae(糸状乳頭): 舌全体を覆い、触覚に関与しますが、味蕾は含まれません。
- Foliate papillae(葉状乳頭): 舌の側面に存在しますが、茸状形状ではありません。
- None of the above(以上のいずれでもない): 誤りです。茸状乳頭が正解です。
Question 14 of 25(ミス)
Where are Peyer’s Patches located?
a. Esophagus
b. Small intestine
c. Large intestine
d. Stomach
Answer: b. Small intestine
解説:
パイエル板(Peyer’s patches)は、小腸の特に回腸(ileum)に集中するリンパ組織で、免疫防御に重要な役割を果たします。異物や病原体に対する免疫応答を促進します。
他の選択肢の解説:
- Esophagus(食道): パイエル板は見られません。
- Large intestine(大腸): 大腸にもリンパ組織がありますが、パイエル板ほど集中していません。
- Stomach(胃): 胃にはパイエル板が存在しません。
Question 15 of 25
Which cells secrete intrinsic factor?
a. Parietal cells
b. Oxyntic cells
c. Chief cells
d. Both a and b
Answer: d. Both a and b
解説:
内因子(Intrinsic factor)は、壁細胞(Parietal cells)、またはオキシンティック細胞(Oxyntic cells)と呼ばれる細胞から分泌されます。内因子はビタミンB12の吸収を助けるため、欠乏すると悪性貧血を引き起こします。
他の選択肢の解説:
- Parietal cells(壁細胞): 壁細胞は内因子を分泌する主要な細胞です。
- Oxyntic cells(オキシンティック細胞): 壁細胞の別名であり、内因子を分泌します。
- Chief cells(主細胞): 主細胞はペプシノーゲンを分泌しますが、内因子の分泌には関与しません。
Question 16 of 25
What are mucous surface cells?
a. Stratified Squamous epithelium
b. Simple Squamous epithelium
c. Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
d. Simple Columnar Epithelium
Answer: d. Simple Columnar Epithelium
解説:
粘液表面細胞(Mucous surface cells)は、単層円柱上皮(Simple Columnar Epithelium)からなり、胃の内壁を覆います。これらの細胞は粘液を分泌し、胃酸から胃の粘膜を保護する役割を果たします。
他の選択肢の解説:
- Stratified Squamous epithelium(重層扁平上皮): 食道や皮膚に見られますが、胃にはありません。
- Simple Squamous epithelium(単層扁平上皮): 血管内皮や体腔を覆う上皮であり、粘液表面細胞とは異なります。
- Simple Cuboidal Epithelium(単層立方上皮): 腺や尿細管に見られますが、胃粘膜には存在しません。
Question 17 of 25
Which type of papillae on the tongue does NOT contain taste buds?
a. Filiform papillae
b. Fungiform papillae
c. Foliate papillae
d. All of the Above
Answer: a. Filiform papillae
解説:
糸状乳頭(Filiform papillae)は舌全体に広がっていますが、味蕾を持たないため、味覚には関与しません。これらの乳頭は主に食物の取り扱いを助け、触覚に関与します。
他の選択肢の解説:
- Fungiform papillae(茸状乳頭): 味蕾を含み、特に甘味の感知に役立ちます。
- Foliate papillae(葉状乳頭): 味蕾を含み、特に幼少期に発達しています。
- All of the Above: 誤りです。糸状乳頭以外は味蕾を持ちます。
Question 18 of 25
Which is the smallest type of tongue papillae?
a. Filiform papillae
b. None of the above
c. Foliate Papillae
d. Fungiform Papillae
Answer: a. Filiform papillae
解説:
糸状乳頭(Filiform papillae)は舌の表面を覆う最も小さな乳頭で、主に触覚を担当します。これらの乳頭は舌のざらつきを生み出し、食物の処理を助けます。
他の選択肢の解説:
- Foliate Papillae(葉状乳頭): 比較的大きく、舌の側面に見られます。
- Fungiform Papillae(茸状乳頭): 大きめで、味覚に関与します。
- None of the above(以上のいずれでもない): 正解ではありません。糸状乳頭が最小です。
Question 19 of 25
Which type of papillae on the tongue is the most abundant?
a. All of the Above
b. Foliate Papillae
c. Fungiform Papillae
d. Filiform Papillae
Answer: d. Filiform papillae
解説:
糸状乳頭(Filiform papillae)は舌全体に最も多く存在し、食物の摩擦を助けます。これらの乳頭は触覚に関与し、味蕾を持ちません。
他の選択肢の解説:
- Foliate Papillae(葉状乳頭): 舌の側面に限られ、数量は少ないです。
- Fungiform Papillae(茸状乳頭): 数は少なく、舌の先端に集中します。
- All of the Above: 全ての乳頭が豊富に存在するわけではありません。糸状乳頭が最も豊富です。
Question 20 of 25
What covers the visible portion of a tooth?
a. Cementum
b. Enamel
c. Dental Pulp
d. Dentin
Answer: b. Enamel
解説:
エナメル質(Enamel)は、歯冠(visible portion of a tooth)を覆う非常に硬い層で、人体の中で最も硬い組織です。これにより、咀嚼中の摩耗から歯を保護します。
他の選択肢の解説:
- Cementum(セメント質): 歯根を覆い、歯を歯槽骨に固定する役割を果たします。
- Dental Pulp(歯髄): 歯の中心にあり、神経と血管を含む柔らかい組織です。
- Dentin(象牙質): エナメル質の下にあり、歯全体の形状と構造を支えますが、表面を覆いません。
Question 21 of 25
What covers the part of the tooth that is embedded within the jaw?
a. Cementum
b. Enamel
c. Dental Pulp
d. Dentin
Answer: a. Cementum
解説:
セメント質(Cementum)は、歯の根の部分を覆い、歯を顎骨に固定します。セメント質はエナメル質より柔らかいですが、歯根膜とともに歯を安定させるための重要な役割を果たします。
他の選択肢の解説:
- Enamel(エナメル質): 歯冠を覆う層で、歯の根には存在しません。
- Dental Pulp(歯髄): 歯の中心にある柔らかい組織で、神経や血管を含みますが、外層を構成しません。
- Dentin(象牙質): 歯の内部にあり、セメント質の下で歯の形状を支えますが、根の表面にはなりません。
Question 22 of 25
Which organ has a mucosa lined by Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
a. Esophagus
b. Small Intestine
c. Large Intestine
d. Rectum
Answer: a. Esophagus
解説:
食道の粘膜は非角化重層扁平上皮(Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium)で覆われています。これにより、食べ物が通過する際の摩擦に耐えることができます。
他の選択肢の解説:
- Small Intestine(小腸): 小腸の粘膜は単層円柱上皮で覆われており、吸収機能に特化しています。
- Large Intestine(大腸): 大腸の粘膜も円柱上皮を持ち、粘液を分泌します。
- Rectum(直腸): 直腸の粘膜は部分的に扁平上皮に移行しますが、主に円柱上皮です。
Question 23 of 25
What are the folds of the Stomach called?
a. Rugae
b. Taeniae coli
c. Gastric pits
d. Plicae circulares
Answer: a. Rugae
解説:
胃のヒダ(Rugae)は、胃が空のときに粘膜と筋層が折りたたまれてできる構造です。これにより、胃の容量が拡張したときに滑らかになります。
他の選択肢の解説:
- Taeniae coli(結腸ひも): 大腸の平滑筋の帯で、胃には存在しません。
- Gastric pits(胃小窩): 胃の内壁にあるくぼみで、消化液を分泌する腺の開口部です。
- Plicae circulares(輪状ヒダ): 小腸に見られるヒダで、胃には存在しません。
Question 24 of 25
Which layer contains the Meissner’s Plexus?
a. Submucosa
b. Muscularis externa
c. Mucosa
d. Serosa
Answer: a. Submucosa
解説:
マイスナー神経叢(Meissner’s plexus)は粘膜下層(Submucosa)に存在し、主に消化管の血流と粘膜の活動を調節する役割を果たします。
他の選択肢の解説:
- Muscularis externa(筋層): アイエルバッハ神経叢(Auerbach’s plexus)が含まれています。
- Mucosa(粘膜): マイスナー神経叢は含まれません。
- Serosa(漿膜): 外層であり、神経叢はありません。
Question 25 of 25(ミス)
Which layer contains the Auerbach’s Plexus?
a. Mucosa
b. Submucosa
c. Serosa
d. Muscularis externa
Answer: d. Muscularis externa
解説:
アイエルバッハ神経叢(Auerbach’s plexus)は、筋層(Muscularis externa)に存在し、蠕動運動を制御します。この神経叢は、消化管全体の筋肉の協調運動を助け、食物の移動を促進します。
他の選択肢の解説:
- Mucosa(粘膜): アイエルバッハ神経叢はここには存在しません。
- Submucosa(粘膜下層): マイスナー神経叢が存在する層です。
- Serosa(漿膜): 神経叢は含まれていません。
アセス
Question 1
A 20-year-old man noted progressive swelling on the left side of the face over the past year. On physical examination, there is painless swelling in the region of the Left Posterior Mandible. The lesion is surgically excised with wide margins. Examination revealed benign findings on a background of predominantly mucous acini. Which is the gland affected?
a. Parotid gland
b. Submandibular gland
c. Minor Salivary gland
d. Sublingual gland
Answer: a
Explanation:
The parotid gland is the largest of the salivary glands and is located near the posterior mandible, where the swelling is noted. The parotid gland contains both serous and mucous acinar cells, though predominantly serous acini. However, benign tumors in the parotid gland can occasionally show a background of mucous acini as well.
A painless, progressive swelling in the parotid region is commonly associated with benign parotid tumors, such as pleomorphic adenomas, which are the most common benign salivary gland tumors. These tumors typically grow slowly and are usually painless. Surgical excision with wide margins is the standard treatment approach to prevent recurrence.
Other salivary glands (such as the submandibular or sublingual glands) are less likely to be involved given the location (posterior mandible) and the predominance of mucous acini in the examination findings.
Question 2
A 52-year-old woman who works as a cashier has had increasing malaise and nausea for the past 2 weeks. On physical examination, she had icterus and mild Right Upper Quadrant tenderness. A liver biopsy was done which showed necrosis and inflammation in the triangular region consisting of apices of the neighboring central veins. Which part of the liver is affected?
a. Classical Lobule
b. Portal triad
c. Space of Disse
d. Portal Lobule
Answer: d. Portal Lobule
解説: 肝臓の門脈小葉(portal lobule)は、隣接する中心静脈の頂点を囲む三角形領域として定義され、ここで壊死と炎症が観察されました。
- a. Classical Lobule: 古典的肝小葉は中心静脈を中心にした六角形の構造です。
- b. Portal triad: 門脈三つ組は肝動脈、門脈、胆管で構成されますが、壊死の領域ではありません。
- c. Space of Disse: ディッセ腔は肝細胞と類洞の間の微小領域です。
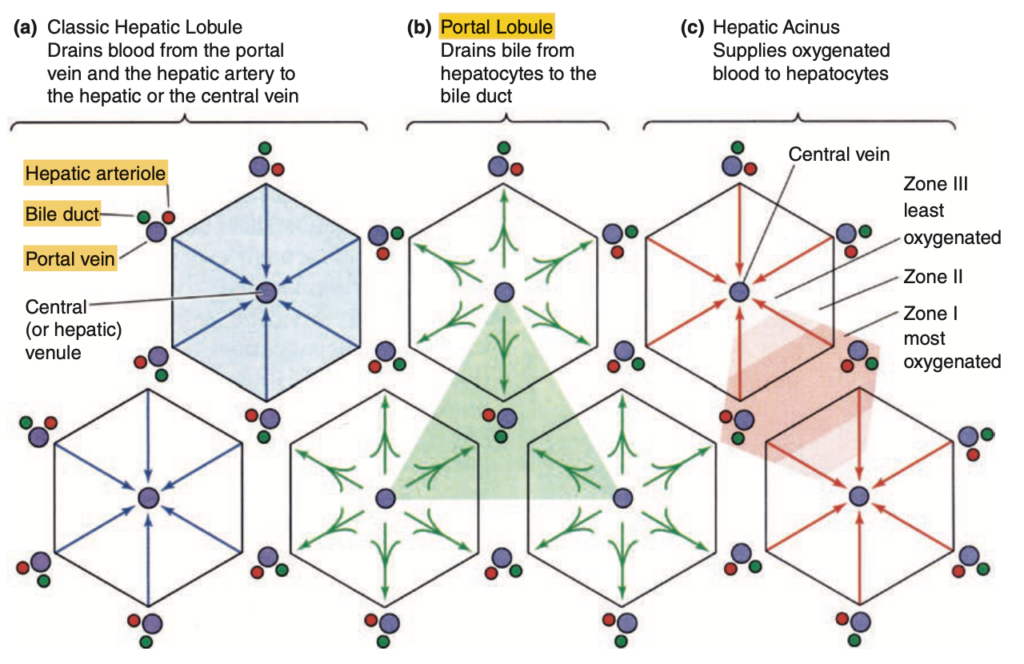
Junqueira’s Basic Histology: Text and Atlas, Fifteenth Edition
Studies of liver microanatomy, physiology, and pathology have given rise to three related ways to view the liver’s organization, which emphasize different aspects of hepatocyte activity.
(a) The classic lobule concept offers a basic understanding of the structure-function relationship in liver organization and emphasizes the endocrine function of hepatocytes as blood flows past them toward the central vein.
(b) The portal lobule emphasizes the hepatocytes’ exocrine function and the flow of bile from regions of three classic lobules toward the bile duct in the portal triad at the center here. The area drained by each bile duct is roughly triangular.
(c) The hepatic acinus concept emphasizes the different oxygen and nutrient contents of blood at different distances along the
sinusoids, with blood from each portal area supplying cells in two or more classic lobules. Major activity of each hepatocyte is determined by its location along the oxygen/nutrient gradient: periportal cells of zone I get the most oxygen and nutrients and show metabolic activity generally different from the pericentral hepatocytes of zone III, exposed to the lowest oxygen and nutri- ent concentrations. Many pathologic changes in the liver are best understood from the point of view of liver acini.
(Used with permission from Boron WF, Boulpaep EL. Medical Physiology: A Cellular and Molecular Approach. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier, 2005.)
Question 3
Which of the following is NOT a component of the Portal Triad?
a. Portal Vein
b. Lymph vessel
c. Hepatic Artery
d. Biliary Tree
Answer: b. Lymph vessel
解説: 門脈三つ組(portal triad)は、門脈、肝動脈、および胆管(biliary tree)から構成されます。リンパ管はこの三つ組の一部ではありません。
- a. Portal Vein: 門脈は三つ組の一部です。
- c. Hepatic Artery: 肝動脈も三つ組に含まれます。
- d. Biliary Tree: 胆管も含まれます。
Question 4
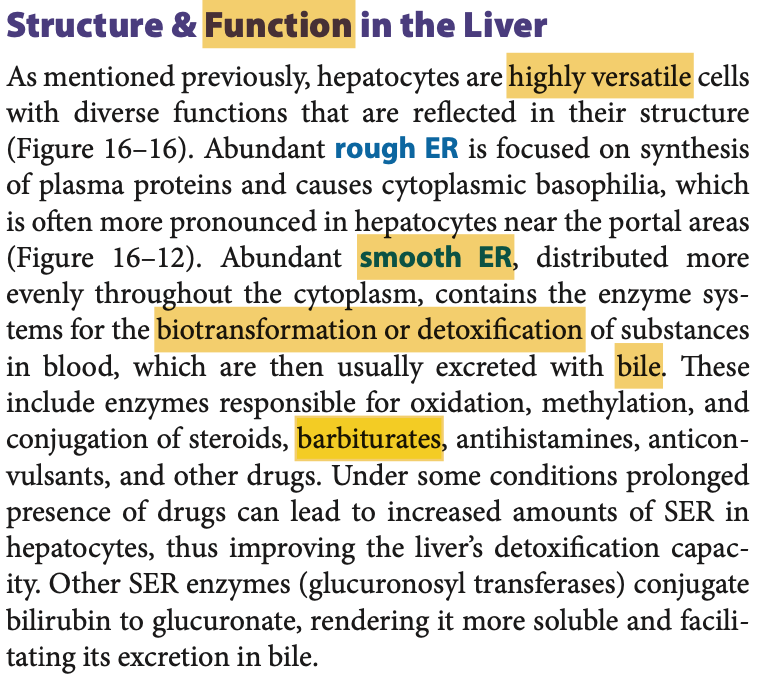
Hepatocytes detoxify barbiturates using Cytochrome p-450 enzymes. Where are these enzymes mainly found?
a. Lysosomes
b. Golgi apparatus
c. Smooth ER
d. Proteasomes
Answer: c. Smooth ER
解説: 肝細胞は滑面小胞体(smooth ER)に存在するシトクロムP450酵素を利用して、バルビツール酸系薬物の解毒を行います。
- a. Lysosomes: リソソームは異化作用に関与しますが、解毒には関与しません。
- b. Golgi apparatus: ゴルジ装置は細胞内の物質輸送に関与します。
- d. Proteasomes: プロテアソームはタンパク質の分解に関与します。
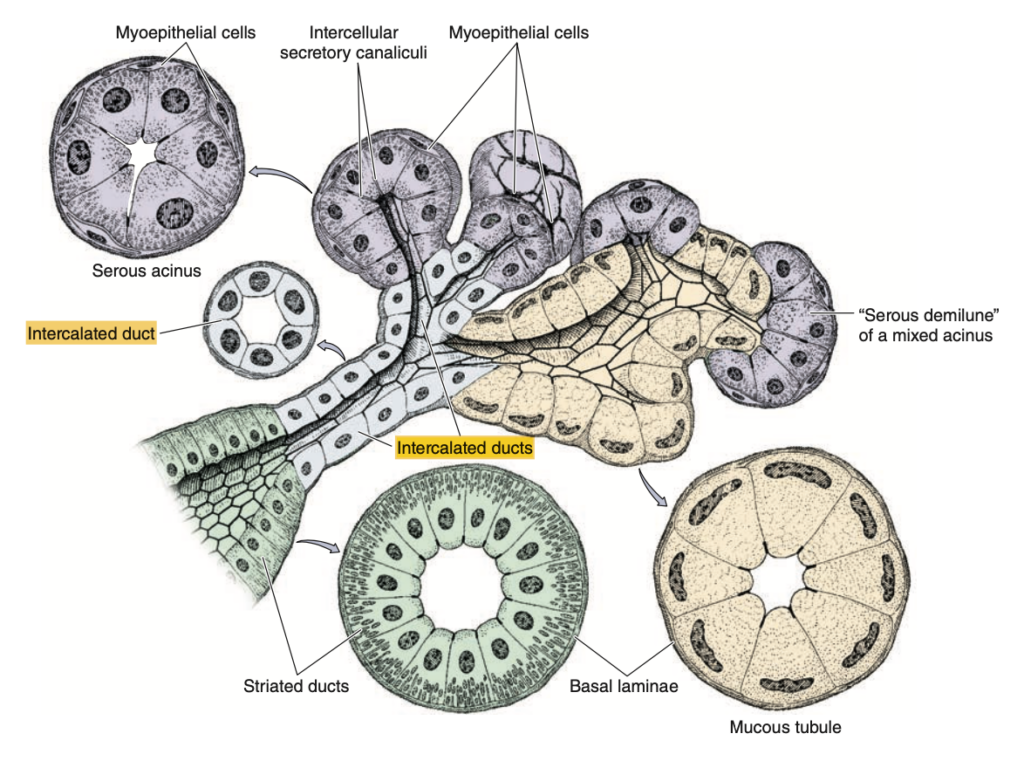
Question 5
A 76-year-old man has been bothered by pain in the left side of the face for two weeks. On physical examination, there is a tender area of swelling 4 cm in diameter beneath the skin, anterior to the left auricle. Laboratory shows defective delivery of bicarbonate ions into the primary secretion. Which ducts are affected in this case?
a. Acinar ducts
b. Luminal Ducts
c. Intercalated ducts
d. Striated Ducts
Answer: c
Explanation:
インターローブ間導管(Intercalated ducts)はアシニで始まり、初期分泌物に重炭酸イオン(HCO₃⁻)を供給する重要な役割を果たします。これにより、唾液がアルカリ性に近づき、口腔内の酸中和を助けます。この患者の症状および重炭酸イオン供給の欠陥は、耳下腺や顎下腺のインターローブ間導管の異常が示唆され、耳の前にある腫脹部位も耳下腺の位置に一致します。線条導管(Striated ducts)は主にナトリウムや塩化物の再吸収に関与し、bicarbonateの供給を直接的に行う役割ではありません。

Question 6
What is the lining epithelium of the Gallbladder?
a. Simple columnar with convoluted folds in its full state
b. Simple columnar epithelium with brush border
c. Simple columnar with a richly vascularized lamina propria
d. Simple columnar epithelium with goblet cells
Answer: b
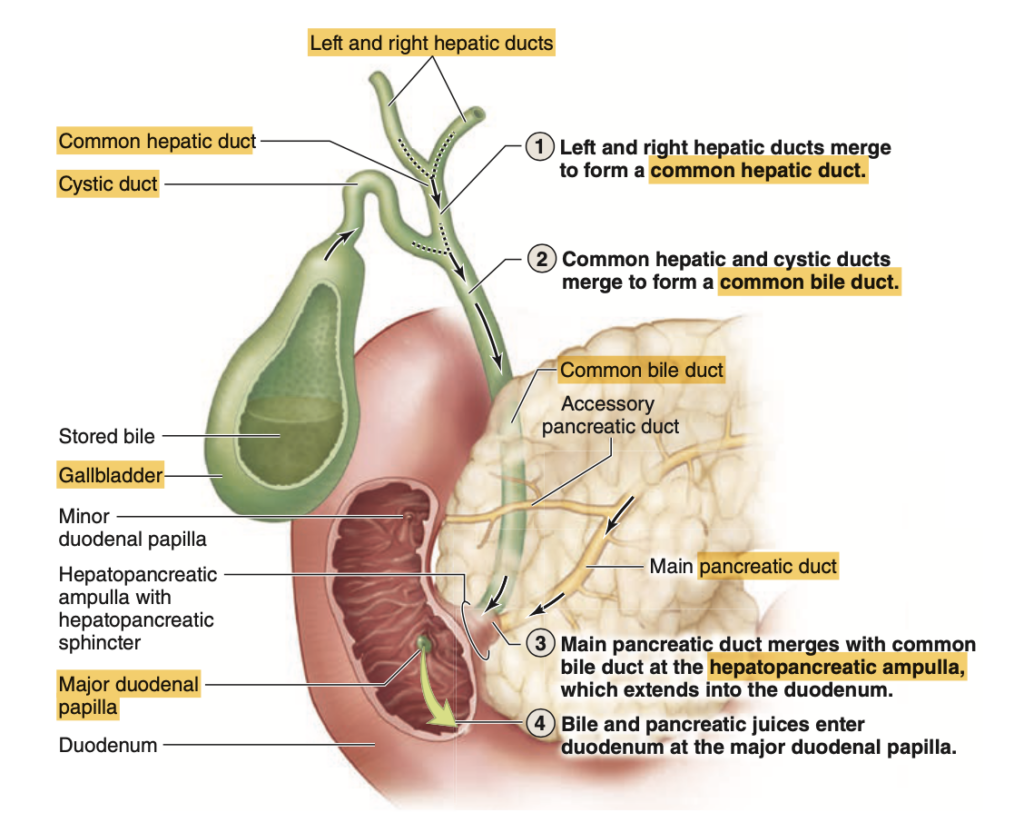

Question 7
A 63-year-old man who had worsening congestive heart failure with cardiac dysrhythmias suddenly died of pneumonia. An autopsy of his pancreas is grossly small and fibrotic. Microscopic examination shows extensive atrophy of the cells which inhibit release of exocrine pancreatic secretions. What cells are affected in this condition?
a. A cells
b. PP cells
c. D cells
d. B cells
Answer: b. PP cells
解説: PP細胞は膵臓の外分泌分泌を抑制する役割を持ち、これらが萎縮することで膵外分泌が阻害されます。
- a. A cells: A細胞はグルカゴンを分泌します。
- c. D cells: D細胞はソマトスタチンを分泌します。
- d. B cells: B細胞はインスリンを分泌します。
Question 8
Which of the following structures secrete enzymes that help in the digestion of lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates?
a. Zymogen granules
b. PP cells
c. Pancreatic acinus
d. Acinar cells
e. All of the above
Answer: e. All of the above
解説: ジモゲン顆粒(zymogen granules)、膵腺房(pancreatic acinus)、腺房細胞(acinar cells)はすべて、消化酵素を分泌する役割を果たしています。
- a. Zymogen granules: 酵素前駆体を含む顆粒です。
- b. PP cells: これも膵臓の分泌に関与します。
- c. Pancreatic acinus: 腺房は消化酵素を生成します。
- d. Acinar cells: 腺房細胞も消化酵素を分泌します。
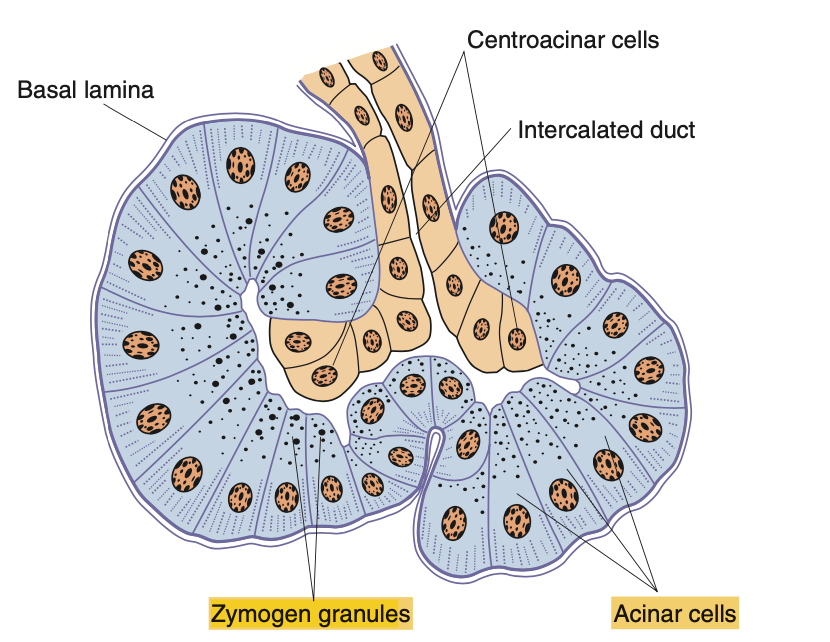
Question 9
A 23-year-old male medical student was rushed to the ER and found dead upon arrival. When his close friends were interviewed, they noted that the patient had been binge drinking the night prior to his demise. An autopsy was performed. What organ should be taken in for further examination as cause of death?
a. Pancreas
b. Liver
c. Gallbladder
d. Stomach
Answer: a. Pancreas
解説: アルコール乱用は急性膵炎を引き起こす可能性があり、膵臓の急性炎症が死因の可能性があります。
- b. Liver: 肝臓もアルコールに影響されますが、急性死の原因とは異なります。
- c. Gallbladder: 胆嚢は通常、急性アルコール乱用に関連しません。
- d. Stomach: 胃は直接の原因ではありません。
Question 10
A diamond-shaped region encompassing triangular sections of two adjacent classic liver lobules.
a. Classic Liver Lobule
b. Hepatic Acinus of Rappaport
c. Hepatic triad
d. Portal lobule
Answer: b. Hepatic Acinus of Rappaport
解説: ラッポポートの肝小葉(hepatic acinus of Rappaport)は、隣接する肝小葉の領域をダイヤモンド形に含む構造です。
- a. Classic Liver Lobule: これは六角形の構造です。
- c. Hepatic triad: これは門脈三つ組です。
- d. Portal lobule: これは三角形の構造です。
Question 11
The liver diagram divided the liver into three zones on the basis of the proximity of the hepatocytes to the incoming blood.
a. Portal triad with emphasis on the common bile duct
b. Portal triad
c. Classic liver lobule
d. Acini of Rappaport
Answer: a
Question 12
Functional unit of a Salivary Gland is made up of the following:
a. Acini only
b. Intercalated duct + Acinar gland
c. Intercalated ducts + Striated duct
d. Intercalated duct + Striated Duct + Acinar cells
Answer: d
The functional unit of a salivary gland is the salivon, which is composed of acini (or acinar cells) and a series of ducts that transport and modify saliva. Here’s a breakdown of the components within the salivon:
- Acini: The acini are clusters of secretory cells that produce the primary saliva. They are typically either serous acini, which secrete a watery, enzyme-rich fluid, or mucous acini, which produce a viscous, mucin-rich secretion. Some glands contain mixed acini with both serous and mucous cells.
- Intercalated Ducts: These small ducts originate from the acini and are the first segment in the duct system. Intercalated ducts may add bicarbonate ions to the saliva, which helps neutralize acids.
- Striated Ducts: Following the intercalated ducts, striated ducts further modify saliva by reabsorbing sodium and chloride ions and secreting potassium and bicarbonate. This process adjusts the electrolyte composition of the saliva.
- Excretory Ducts: These larger ducts collect saliva from the striated ducts and transport it to the oral cavity.
Question 13
Which of the following is TRUE of Semi Demilunes?
a. Some mucous cells may be capped with serous cells
b. Serous cells make up the majority of the cells
c. Often arranged in an elongated circular structure with a flattened or round lumen
d. Serous cells stain lighter than Mucous cells
Answer: a. Some mucous cells may be capped with serous cells
解説: 半月形(demilunes)は、粘液細胞の上に漿液細胞が覆い被さる形で存在します。
- b. Serous cells make up the majority: 漿液細胞が多数を占めるわけではありません。
- c. Arranged in a circular structure: 長円形ではなく、半月形です。
- d. Serous cells stain lighter: 漿液細胞は通常、粘液細胞よりも濃く染色されます。
Question 14
Which of the following layers covers most of the Gallbladder?
a. Serosa
b. Mucosa
c. Epithelium
d. Adventitia
Answer: a. Serosa
解説: 胆嚢の大部分は漿膜(serosa)で覆われています。
- b. Mucosa: 粘膜は内部層です。
- c. Epithelium: 上皮は最内層です。
- d. Adventitia: 腹膜後の領域には外膜(adventitia)が存在しますが、大部分ではありません。
Question 15
Which of the following is NOT a content of the Space of Disse?
a. The short microvilli of Hepatocytes
b. Elastic fibers which maintain the architecture of the Sinusoids
c. Occasional Non-myelinated nerve fibers
d. Stellate fat-storing cells or Ito cells
Answer: b. Elastic fibers which maintain the architecture of the Sinusoids
解説: ディッセ腔(Space of Disse)は、肝細胞の短い微絨毛、星状細胞(Ito細胞)、および非有髄神経線維を含みますが、弾性線維は含まれていません。
- a. Microvilli of Hepatocytes: 微絨毛はディッセ腔に存在します。
- c. Non-myelinated nerve fibers: これは時折見られる要素です。
- d. Stellate fat-storing cells or Ito cells: これらはディッセ腔の主な細胞成分です。
Space of Disse(ディッセ腔)
Space of Disseは、肝臓の肝細胞(hepatocytes)と血管内皮細胞(sinusoidal endothelial cells)との間に存在する狭い隙間です。この空間は、肝細胞と血液との間の物質交換を促進する重要な場所です。
- 位置: ディッセ腔は肝細胞板(hepatocyte plates)と肝類洞(sinusoids)との間に位置し、微小な空間です。
- 機能:
- 物質交換: 血液からの栄養素、酸素、ホルモン、そして肝細胞からの分泌物がディッセ腔を介して交換されます。
- リンパ生成: この空間にはリンパ液が流入し、肝臓内のリンパ流を形成します。これにより、老廃物や過剰なタンパク質が除去されます。
- 細胞成分: ディッセ腔には、Ito細胞(星状細胞)やクッパー細胞(肝マクロファージ)が見られます。
Ito細胞(伊藤細胞、星状細胞または脂肪蓄積細胞)
Ito細胞(伊藤細胞)は、肝臓のディッセ腔に位置する特殊な細胞で、脂肪滴内にビタミンAを蓄える役割を持っています。
- 位置と構造: 伊藤細胞はディッセ腔内に分布し、星状の形をしています。細胞質内にはビタミンAを蓄える脂肪滴が含まれます。
- 機能:
- ビタミンAの蓄積: 伊藤細胞はビタミンAを脂肪滴として蓄え、必要に応じて放出します。ビタミンAは視力や免疫機能に重要な役割を果たします。
- 細胞外マトリックスの生成: 正常な条件下では、伊藤細胞は細胞外マトリックスの成分を生成し、肝臓の組織構造をサポートします。
- 線維化の役割: 肝障害(例:慢性肝炎や肝硬変)に応答して伊藤細胞が活性化し、膠原繊維(コラーゲン)を過剰に生成することで、肝臓の線維化が進行します。これにより、正常な肝機能が低下し、肝硬変へと進展します。
Question 16
A 11-year-old boy has experienced multiple bouts of severe abdominal pain for the past 6 years, but no other medical problems. Sudden loss of weight is also noted. On examination, his pancreas is grossly small and fibrotic. Laboratory examination shows a high glucose level due to a defect in the production of insulin. What insulin-producing cells are affected in this condition?
a. D cells
b. A cells
c. B cells
d. PP Cells
Answer: c. B cells
解説: インスリンを分泌する膵臓のβ細胞(B cells)が影響を受けています。これにより、血糖値が高くなります。
- a. D cells: D細胞はソマトスタチンを分泌します。
- b. A cells: A細胞はグルカゴンを分泌します。
- d. PP Cells: PP細胞は膵ポリペプチドを分泌します。
Question 17
A 21-year-old woman comes to the physician because she is concerned about a lump on the left side of her mandible that has remained the same size for the past year. Physical examination shows a painless, movable 2 cm nodule with no other pertinent findings. Microscopic examination shows keratin debris in a background of purely serous acini. What gland is affected?
a. Parotid gland
b. Minor Salivary Gland
c. Submandibular gland
d. Sublingual gland
Answer: a. Parotid gland
解説: 耳下腺(parotid gland)は、主に漿液性腺房を持つ唾液腺であり、腫瘤の位置や所見から最も関与する可能性があります。
- b. Minor Salivary Gland: これらは通常、口腔内に位置します。
- c. Submandibular gland: 顎下腺は混合腺であり、漿液性のみではありません。
- d. Sublingual gland: 舌下腺は主に粘液性です。
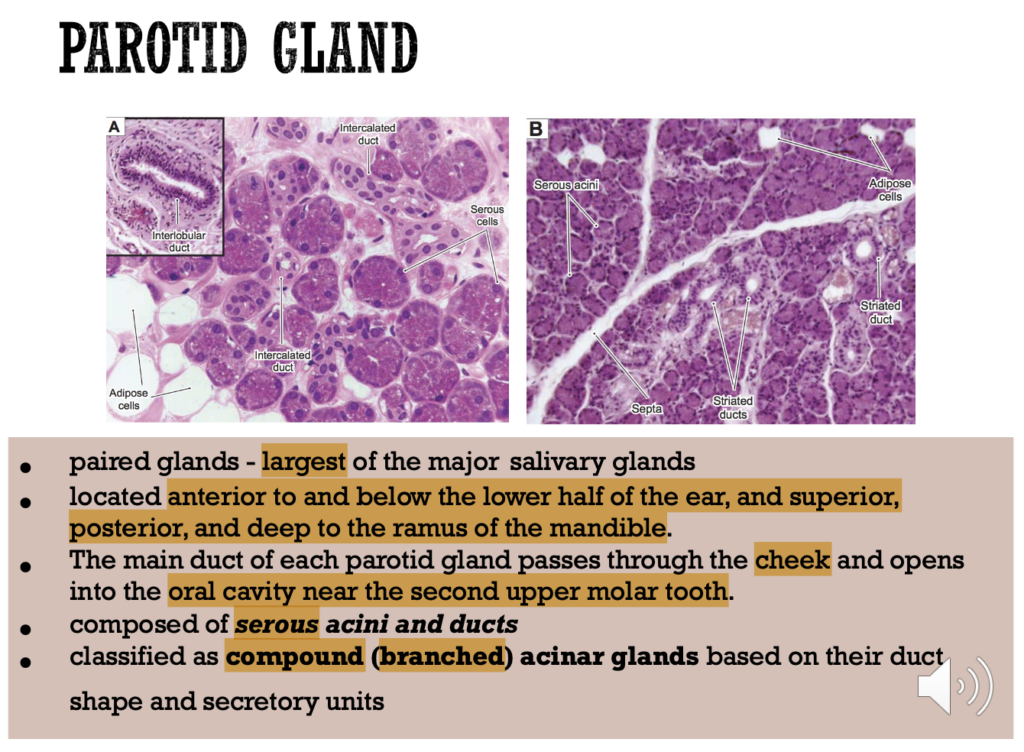
Question 18
Which of the following is TRUE of Liver Sinusoids?
a. Sinusoidal capillaries that arise at the periphery of a lobule and run between adjacent plates of hepatocytes
b. Display fenestrations with Basal laminae
c. They are lined by simple columnar cells that have large discontinuities between them
d. They relay and transmit blood from the vessels in the Portal areas and deliver it to the central vein
Answer: a
Explanation:
Liver sinusoids are specialized capillaries located within the liver lobules. They arise at the periphery of each lobule, where blood from the portal vein and hepatic artery enters, and they run between plates of hepatocytes, allowing nutrients and oxygen to be exchanged.
- Option a is correct because sinusoids do run between hepatocyte plates, facilitating the exchange of materials.
- Option b is incorrect because sinusoids have discontinuous endothelium with no basal lamina, which allows for free exchange of large molecules.
- Option c is incorrect because the lining cells are simple squamous endothelial cells, not columnar, with large gaps allowing for the easy passage of proteins and cells.
- Option d is incorrect because, while sinusoids do drain into the central vein, they do not “relay” blood; rather, they serve as channels for blood flow within the lobule and allow for exchange before reaching the central vein.
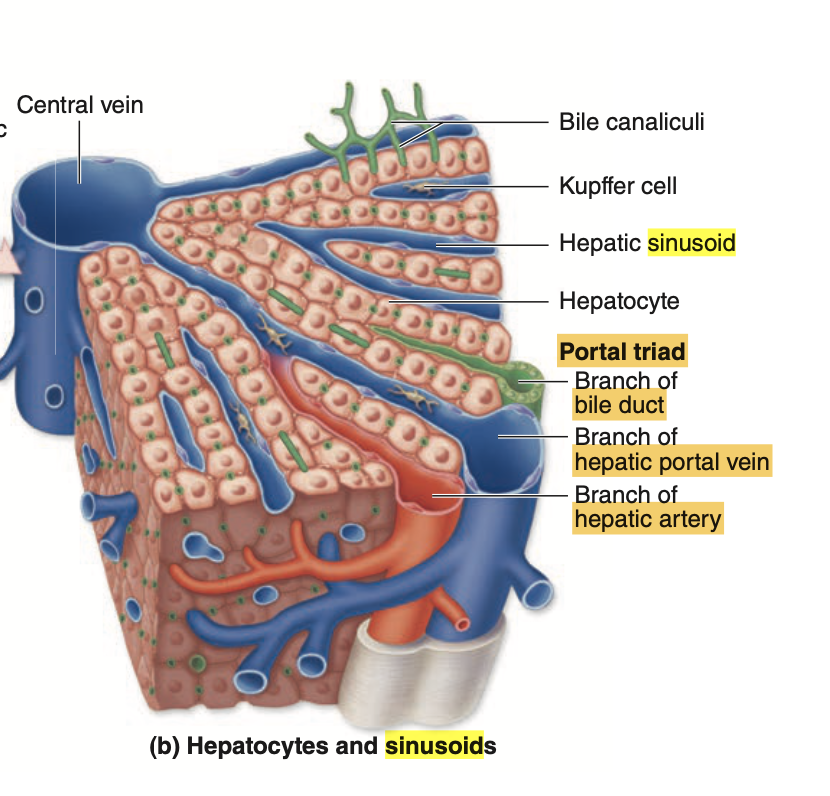
**Hepatic sinusoid(肝類洞)**は、肝臓内に存在する特殊な毛細血管の一種で、肝細胞(hepatocytes)と血液との間で物質交換を行う重要な場所です。肝類洞は通常の毛細血管とは異なる特徴を持ち、肝臓の効率的な機能に必要不可欠です。
特徴
- 構造: 肝類洞は肝小葉の中を走り、中央静脈(central vein)に向かって放射状に分布しています。類洞は肝細胞板(hepatocyte plates)の間を通り、肝細胞と直接接触するように配置されています。
- 内皮: 肝類洞の内皮細胞は「不連続性内皮(discontinuous endothelium)」と呼ばれ、内皮細胞の間に隙間が多く存在し、基底膜(basal lamina)が欠如しています。これにより、血液中のタンパク質や栄養素が容易に肝細胞へと浸透できます。
- Kupffer細胞: 肝類洞内には、クッパー細胞(Kupffer cells)と呼ばれる特殊なマクロファージが存在し、古い赤血球の破壊や細菌・異物の捕食を行います。
- Ito細胞(星状細胞): 類洞の外側のディッセ腔には、ビタミンAを蓄積する伊藤細胞(Ito cells)が存在しています。
機能
- 物質交換: 肝類洞は、血液と肝細胞の間で酸素、栄養素、ホルモン、老廃物などの物質交換を行います。内皮が不連続であるため、タンパク質や大きな分子も自由に通過しやすく、肝臓が効率的に血液を浄化できます。
- 解毒と代謝: 肝類洞を通る血液は、肝細胞によって毒素や老廃物が処理されます。この過程で血液は解毒され、肝臓はエネルギーを供給する代謝物を産生します。
流れ
肝門脈(portal vein)と肝動脈(hepatic artery)からの血液は、肝小葉の外周から肝類洞に流れ込み、中央静脈へと運ばれます。この流れにより、肝細胞は血液から栄養素を取り込み、同時に代謝産物を放出します。
Question 19
Which of the following organelles are found abundantly in the Liver?
a. RER
b. SER
c. Golgi Apparatus
d. All of the Above
Answer: d. All of the Above
解説: 肝細胞には、粗面小胞体(RER)、滑面小胞体(SER)、およびゴルジ装置が豊富に存在し、タンパク質合成や解毒に関与しています。
肝細胞(hepatocytes)は、代謝、解毒、合成などの多機能を持つ細胞であり、それを支えるために、粗面小胞体(Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum, RER)、滑面小胞体(Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum, SER)、および**ゴルジ装置(Golgi Apparatus)**が豊富に存在しています。それぞれの構造が肝細胞でどのように機能しているかを解説します。
1. 粗面小胞体(RER)
- 構造と特徴: 粗面小胞体は、表面にリボソームが付着しているため「粗面」と呼ばれます。リボソームが付いているため、タンパク質合成に特化しています。
- 役割: 肝細胞では、RERが**血漿タンパク質(例えばアルブミン、凝固因子など)**を合成する役割を果たしています。これらのタンパク質は血液中でさまざまな機能を担い、肝臓で生成されます。
- 代謝酵素の合成: 肝細胞は代謝に関連する酵素も大量に合成するため、RERが発達していることが重要です。
2. 滑面小胞体(SER)
- 構造と特徴: 滑面小胞体は、リボソームが付着していないため「滑面」と呼ばれ、RERよりも滑らかな表面を持っています。
- 役割: SERは脂質やステロイドホルモンの合成、解毒作用に関与しています。
- 解毒作用: SERには、薬物やアルコールなどの有害物質を無毒化する酵素(例えばシトクロムP450酵素群)が含まれており、これにより肝臓は体内の解毒機能を担っています。
- 脂質代謝: SERは胆汁酸の合成やコレステロールの代謝にも関与しており、これらは消化やホルモンの合成に不可欠です。
3. ゴルジ装置
- 構造と特徴: ゴルジ装置は、RERで合成されたタンパク質や脂質が修飾され、パッケージングされる場所です。
- 役割:
- タンパク質の修飾と輸送: 肝細胞がRERで生成した血漿タンパク質や酵素は、ゴルジ装置に送られて糖鎖の付加やフォールディング(折りたたみ)といった修飾が行われます。
- 分泌物のパッケージング: 修飾されたタンパク質は、ゴルジ装置によって小胞にパッケージングされ、細胞外へ分泌されます。
- 胆汁の分泌: ゴルジ装置も胆汁の成分の分泌に関与しており、肝細胞で生成された胆汁成分を小胞にまとめて、胆細管へ送り出します。
Question 20
The connective tissue layer of the gallbladder is made of?
a. Dense Irregular CT
b. Dense Regular CT
c. Dense Irregular Collagenous CT
d. Dense Regular Collagenous CT
Answer: c. Dense Irregular Collagenous CT
解説: 胆嚢の結合組織層は、密性不規則膠原線維結合組織(dense irregular collagenous connective tissue)からなります。これは、強度と柔軟性を提供します。
- a. Dense Irregular CT: 膠原線維を含まない結合組織では不十分です。
- b. Dense Regular CT: 規則的な結合組織は特定の方向に限定されます。
- d. Dense Regular Collagenous CT: 規則的な膠原線維結合組織は柔軟性が低いです。
胆嚢の結合組織層が密性不規則膠原線維結合組織(dense irregular collagenous connective tissue)で構成されている理由は、その構造が胆嚢の機能に必要な「強度」と「柔軟性」を提供するためです。この結合組織の性質は以下の点で重要です。
- 強度の提供
密性不規則膠原線維結合組織は、コラーゲン線維が不規則に配向しているため、あらゆる方向からの機械的な応力に耐えることができます。胆嚢は消化過程で収縮と拡張を繰り返し、胆汁を小腸に排出する役割があるため、これらの機械的なストレスに耐えられる強度が必要です。 - 柔軟性の提供
コラーゲン線維が不規則に配置されていることで、結合組織は構造的に頑丈でありながらも柔軟性を持っています。これにより、胆嚢はその容量に応じて伸縮でき、胆汁を適切に蓄え、排出することが可能になります。また、柔軟性は胆嚢が収縮する際に破裂や損傷を防ぐためにも必要です。 - 結合組織層の保護作用
胆嚢の結合組織層は、内側にある粘膜と外側の筋肉層を支持し、炎症や損傷に対する保護役も果たしています。この層が胆嚢全体の安定性を保つことで、内臓の正常な機能を維持しています。
このように、密性不規則膠原線維結合組織は、胆嚢がその役割を果たすために不可欠な支持と保護を提供していると言えます。
Question 21
A 75-year-old male was brought to the Emergency Department presenting with abdominal distention and jaundice. Work-up included a liver biopsy. Abnormality in bile flow is suspected. Which part of the liver should the pathologist examine?
a. Portal Triad with emphasis on the Common Bile Duct
b. Acini of Rappaport
c. Portal lobule
d. Classic liver lobule
Answer: c
Question 22
A 44-year-old woman has noticed increasingly severe generalized pruritus(瘙痒感) for the past 8 months. Serum levels of alkaline phosphatase and cholesterol are elevated. A liver biopsy showed defective phagocytic cells in the liver sinusoids. What specific cells are defective in the patient?
a. Kupffer cells
b. Astrocytic cells
c. Alveolar pneumocytes
d. Dendritic cells
Answer: a. Kupffer cells
解説: クッパー細胞(Kupffer cells)は肝臓の類洞内に存在する貪食細胞であり、異物や病原体の除去に関与します。これらの細胞が機能不全であると、肝臓の免疫防御が低下します。
- b. Astrocytic cells: 星状細胞は脳に存在し、肝臓とは関係がありません。
- c. Alveolar pneumocytes: 肺胞上皮細胞は肺に存在します。
- d. Dendritic cells: 樹状細胞は主に免疫系に関与しますが、肝臓の類洞には通常見られません。
クッパー細胞(Kupffer cells)は、肝臓に存在する特化型マクロファージであり、主に血液中の病原体や異物、不必要な細胞片を除去する役割を持っています。これらの細胞は肝臓のシヌソイド(毛細血管様の血管)内の内皮に付着しており、血流中の異物を効率よく検出し、捕捉することができます。
クッパー細胞の機能と役割
- 病原体の捕捉・除去
クッパー細胞は、血流に乗って肝臓に入ってきた細菌やウイルス、異常細胞を捕捉し、貪食(ファゴサイトーシス)と呼ばれる過程で取り込み、分解します。これにより、全身に病原体が広がるのを防ぐ初期防衛ラインの役割を果たしています。 - 老廃物や異物の除去
血流中の古くなった赤血球や異常な血球、細胞片を貪食し、体内の循環を維持します。特に脾臓と並び、血液中の老化細胞を除去する重要な機能を担っています。 - 炎症反応の調節
クッパー細胞は免疫反応の一部として炎症性サイトカインを分泌し、他の免疫細胞を活性化させたり、炎症反応を調節したりすることで、感染や損傷に対する体の防御をサポートします。 - 抗原提示機能
クッパー細胞は抗原提示細胞(APC)としても機能し、取り込んだ病原体の断片を細胞表面で提示することで、T細胞などの適応免疫系を刺激し、免疫応答を誘導します。
肝臓における免疫と恒常性の維持
肝臓は消化管から直接血液が流入するため、腸内から流れ込む細菌や毒素などの異物に曝されやすい臓器です。クッパー細胞はこれらの異物を処理し、体全体の免疫系に影響が及ばないようにするため、恒常性の維持に重要な役割を担っています。また、過剰な免疫反応を防ぐため、クッパー細胞は必要以上の炎症反応を抑制する役割も持っています。
Question 23
A 56-year-old man from Shanghai, China has experienced fatigue and a 10-kg weight loss over the past 3 months. Physical examination yields a 10 cm mass affecting the supply of oxygen-rich blood from the abdominal aorta to the liver. Which vessel of the liver blood flow is affected?
a. Common Bile Ducts
b. Hepatic artery
c. Portal Triad
d. Portal Vein
Answer: b. Hepatic artery
解説: 肝動脈(Hepatic artery)は酸素を豊富に含む血液を肝臓に供給します。この動脈が影響を受けると、肝臓への酸素供給が不足します。
- a. Common Bile Ducts: 胆管は血液供給に関与しません。
- c. Portal Triad: 門脈三つ組には肝動脈が含まれますが、特定の影響は肝動脈にあります。
- d. Portal Vein: 門脈は栄養に富んだ血液を供給しますが、酸素供給は肝動脈が担当します。
Question 24
A 57-year-old vendor has been bothered by pain in the right side of the face for three weeks. On physical examination, there is a tender area of swelling 10 cm in diameter beneath the skin, anterior to the right auricle. Laboratory shows defective removal of sodium and chloride ions from the luminal fluid. Which ducts are affected in this case?
a. Acinar Ducts
b. Luminal Ducts
c. Intercalated Ducts
d. Striated Ducts
Answer: d. Striated Ducts
解説: 線条管(Striated ducts)は唾液腺でナトリウムや塩化物イオンの再吸収を行い、唾液の調整に関与します。この機能が損なわれると、電解質の異常が生じます。
- a. Acinar Ducts: 腺房導管は主に初期の分泌物を運びます。
- b. Luminal Ducts: これは存在しない構造です。
- c. Intercalated Ducts: 介在導管は主に水の輸送に関与しますが、電解質には直接関与しません。
Question 25
A 26-year-old female was rushed to the Emergency Department due to increased abdominal pain. Pain was colicky with a scale of 9/10. Chronic Calculous Cholecystitis was suspected after thorough work-up and ultrasonographic studies. One should expect absence of which histologic layer on the organ’s pathologic report?
a. Serosa
b. Submucosa
c. Adventitia
d. Mucosa
Answer: b
胆嚢の表皮細胞(上皮細胞)は、以下の層構造で構成されています。
- 粘膜上皮(Mucosal Epithelium)
- 単層円柱上皮(Simple Columnar Epithelium):胆嚢の内腔表面を覆う細胞で、胆汁の吸収や分泌を行います。これらの細胞は、微絨毛(Microvilli)を持ち、表面積を増やすことで効率的な吸収を助けます。
- 粘膜固有層(Lamina Propria)
- 上皮の直下に存在する結合組織の層で、血管やリンパ管が豊富に存在します。粘膜固有層には、免疫細胞や細胞外基質が含まれており、胆嚢の保護や栄養供給を支えています。
- 筋層(Muscularis)
- 平滑筋(Smooth Muscle)の層で、胆嚢の収縮と胆汁の排出を行う役割を持ちます。特に、食事摂取後に胆嚢が収縮し、胆汁を十二指腸に排出します。
- 外膜(Serosa)
- 胆嚢の最外層で、主に結合組織から成り、胆嚢を保護します。この層は腹腔内の他の臓器ともつながっています。
胆嚢には一般的に**粘膜下層(submucosa)**は存在しません。通常、胆嚢の組織構造は以下のように簡略化されており、粘膜上皮、粘膜固有層、筋層、外膜から構成されています。
多くの消化器官には粘膜下層があり、血管や神経、リンパ組織が豊富に存在しますが、胆嚢はこの層が欠如しているため、直接粘膜固有層と筋層が接しているのが特徴です。この構造が胆嚢の柔軟な収縮運動に寄与していると考えられます。
追加(教科書の問題からCh 15,16)
Ch15
Question 1
問題文: In which of the following structures of the oral cavity would taste buds be localized in the highest concentration?
a. Fungiform papillae
b. Gingiva
c. Filiform papillae
d. Ventral surface of the tongue
e. Vallate papillae
Answer: e. Vallate papillae
Explanation:
味蕾(taste buds)は、特に「有郭乳頭」(Vallate papillae)に多く存在し、舌の奥に集中しています。有郭乳頭は他の乳頭よりも大きく、多くの味蕾が集中しているため、味覚の感知において重要な役割を果たします。その他の選択肢について、茸状乳頭(a)は味蕾を含んでいますが、量は有郭乳頭より少なく、歯肉(b)や糸状乳頭(c)、舌の腹側(d)は味蕾をほとんど含まないため、誤りです。
Question 2
問題文: Certain antibiotic therapies slow the replacement of the cells lining the small intestine. This may cause the loss of what tissue type?
a. Ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium
b. Simple cuboidal epithelium
c. Simple columnar epithelium
d. Pseudostratified columnar epithelium with stereocilia
e. Stratified squamous, nonkeratinized epithelium
Answer: c. Simple columnar epithelium
Explanation:
小腸は「単層円柱上皮」(simple columnar epithelium)で覆われており、抗生物質療法によりこの上皮細胞の再生が遅れると、消化・吸収能力が低下します。aの「線毛擬多層円柱上皮」やdの「ステレオシリア付き擬多層円柱上皮」は呼吸器系などに見られ、bの「単層立方上皮」は主に腺や管の内壁に見られます。また、eの「非角化重層扁平上皮」は口腔や食道に見られるため、誤りです。
Question 3
問題文: The teniae coli of the large intestine represent an organ-specific specialization of which layer of the intestinal tract wall?
a. Epithelium
b. Lamina propria
c. Muscularis mucosa
d. Muscularis externa
e. Serosa
Answer: d. Muscularis externa
Explanation:
大腸の「結腸ひも」(teniae coli)は、腸壁の筋層に特有の構造であり、主に「外筋層」(muscularis externa)で形成されています。これは結腸全体を収縮させるためのもので、他の消化管には見られない特徴です。他の選択肢について、上皮(a)や固有層(b)、粘膜筋板(c)は大腸に特有の特徴ではなく、漿膜(e)は腹腔内の他の臓器でも見られるため誤りです。
Question 4
問題文: Which of the following would most likely result from a reduction in the number of Paneth cells?
a. Thinning of the glycocalyx
b. Reduced breakdown of fats
c. Elevated levels of undigested proteins
d. Decreased mucus in the intestine
e. Increased number of intestinal bacteria
Answer: e. Increased number of intestinal bacteria
Explanation:
パネート細胞(Paneth cells)は小腸の腸陰窩にあり、抗菌ペプチドを分泌して腸内の微生物バランスを保っています。この細胞数が減少すると、腸内の細菌数が増加するリスクがあります。他の選択肢について、aのグリコカリックスの薄化やbの脂肪分解、cのタンパク質未消化、dの粘液減少には直接関与しません。
Question 5
問題文: A medical student on a rotation in the pathology laboratory is given an unlabeled microscope slide with tissue provided by a gastroenterologist from a cancer patient she is attending. The mucosa and submucosa are poorly preserved, with only the thick muscularis well-stained, showing striated fibers. The slide most likely shows a biopsy of which region of the GI tract?
a. Pyloric sphincter
b. Esophagus
c. Colon
d. Corpus of the stomach
e. Ileum
Answer: b. Esophagus
Explanation:
食道は筋層が厚く、特に上部において横紋筋(striated muscle)を含むため、標本で観察された横紋構造と一致します。他の選択肢である幽門括約筋(a)や大腸(c)、胃の本体(d)、回腸(e)には横紋筋が見られないか、極めて少ないため誤りです。
Question 6
問題文: Diarrhea may result if which of the following organs fails to carry out its role in absorbing water from the feces?
a. Anal canal
b. Cecum
c. Colon
d. Jejunum
e. Duodenum
Answer: c. Colon
Explanation:
大腸(Colon)は水分を再吸収することで便の硬さを調整しています。大腸が正常に機能しない場合、水分が吸収されずに下痢を引き起こします。他の選択肢であるaの肛門管やbの盲腸、dの空腸、eの十二指腸は、水分吸収が主要な機能ではありません。
Question 7
問題文: Which of the following is true of the absorptive cells of the small intestine?
a. Also called enteroendocrine cells
b. Have many microvilli covering their basal surfaces
c. Absorb lipids by active transport
d. Synthesize triglycerides from absorbed lipids
e. Undergo mitosis at tips of villi and are sloughed off into crypts
Answer: d. Synthesize triglycerides from absorbed lipids
Explanation:
小腸の吸収細胞(腸細胞)は、吸収した脂質をトリグリセリドに合成し、リンパ管に輸送します。他の選択肢について、aの内分泌細胞とは異なり、bの基底面ではなく頂端に微絨毛が密集しています。cの脂質吸収は拡散で行われ、eの細胞分裂は腸陰窩で行われます。
Question 8
問題文: A 52-year-old man is diagnosed with a carcinoid after an appendectomy. The enteroendocrine cells producing this disorder differ from goblet cells in which of the following?
a. The direction of release of secretion
b. The use of exocytosis for release of secretory product
c. Their presence in the small and large intestines
d. The origin from a crypt stem cell
e. Their location in a simple columnar epithelium
Answer: a. The direction of release of secretion
Explanation:
腸内分泌細胞は基底膜側に向かってホルモンを分泌し、ゴブレット細胞は腸管内腔側に粘液を分泌します。bのエキソサイトーシスやcの腸内での存在、dの陰窩幹細胞起源、eの単層円柱上皮内の存在は両細胞に共通しています。
Question 9
問題文: A 14-month-old girl is brought to the pediatric dentistry clinic because her erupted deciduous teeth are opalescent with fractured and chipped surfaces. X-rays reveal bulb-shaped crowns, thin roots, and enlarged central cavities. Tissue immediately surrounding one tooth’s central cavity is biopsied and prepared for histology, which reveals irregular, widely spaced tubules. Which of the following applies to this irregular tissue layer?
a. It has a composition similar to that of bone and is produced by cells similar in appearance to osteocytes.
b. It is formed on a noncollagenous matrix that is resorbed after mineralization by the same cells that secreted it.
c. It contains abundant nerves, microvasculature, and loose connective tissue.
d. It consists of mineralized collagen secreted by cells derived from the neural crest.
e. It is the site of inflammation in diabetic patients and is sensitive to vitamin C deficiency.
Answer: d. It consists of mineralized collagen secreted by cells derived from the neural crest
Explanation:
乳歯の異常がみられるこの患者は象牙質(dentin)に異常があり、象牙質は神経堤由来の細胞によって分泌される鉱化コラーゲンで構成されています。他の選択肢は骨組織(a)、歯のセメント質(b)、歯髄(c)や歯肉(e)に該当するため誤りです。
Question 10
問題文: A 39-year-old woman presents with dyspnea, fatigue, pallor, tachycardia, anosmia, and diarrhea. Laboratory results are: hematocrit 32% (normal 36.1%-44.3%), MCV 102 fL (normal 78-98 fL), 0.3% reticulocytes (normal 0.5%-2.0%), 95 pg/mL vitamin B12 (normal 200-900 pg/mL), and an abnormal stage I of the Schilling test. Autoantibodies are detected against a cell type located in one region of the GI tract. In which regions would those cells be found?
a. Esophagus
b. Body of the stomach
c. Pyloric region of the stomach
d. Cardiac region of the stomach
e. Duodenum
Answer: b. Body of the stomach
Explanation:
ビタミンB12欠乏による貧血は、壁細胞(parietal cells)に対する自己抗体が原因で発生し、これらの細胞は胃体部に集中しています。他の選択肢である食道(a)、幽門(c)、胃の噴門部(d)、十二指腸(e)には壁細胞は存在しません。
Ch 16
Question 1
問題文: In a liver biopsy from a long-time drug user, which of the following hepatocyte organelles would be expected to be more extensive than normal?
a. Rough endoplasmic reticulum
b. Golgi apparatus
c. Lysosomes
d. Peroxisomes
e. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Answer: e. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Explanation:
長期にわたり薬物を使用している患者の場合、肝細胞内で薬物の解毒や代謝が頻繁に行われるため、滑面小胞体(Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum; SER)が拡張することが予想されます。SERは薬物の解毒を行う酵素を含んでおり、薬物使用により活性が増加します。他の選択肢が誤っている理由としては、粗面小胞体(a)はタンパク質合成に関わり、ゴルジ体(b)はタンパク質の修飾や分泌に関与するため、薬物の解毒に関連性が低く、リソソーム(c)やペルオキシソーム(d)は主に細胞の老廃物処理や脂質代謝に関わるため、薬物使用に特有の増加は起こりにくいです。
Question 2
問題文: Which description is true of pancreatic zymogens?
a. Are packaged for secretion in the SER
b. Are synthesized on free ribosomes
c. Are inactive until they reach the duodenal lumen
d. Are stored in the basal cytoplasm of acinar cells
e. Are produced by cuboidal cells lining the pancreatic duct
Answer: c. Are inactive until they reach the duodenal lumen
Explanation:
膵臓で作られる酵素前駆体(zymogens)は、膵臓内で活性化されると自身の組織を損傷する恐れがあるため、不活性状態で分泌され、十二指腸に到達するまで活性化されません。この仕組みで自己消化が防がれています。他の選択肢について、aは粗面小胞体(RER)でパッケージされ、bの自由リボソームで合成されることはなく、dのように基底ではなく頂端側に小胞として蓄えられます。また、eの膵管内の立方上皮細胞によって生成されるのではなく、腺房細胞で産生されます。
Question 3
問題文: Which process increases in response to parasympathetic stimulation of the salivary glands?
a. Volume of secretion
b. Cell division in secretory acini
c. Mucus content of saliva
d. Inorganic salts content of saliva
e. Cell division in interlobular ducts
Answer: a. Volume of secretion
Explanation:
副交感神経の刺激により、唾液腺の分泌量が増加し、消化に必要な唾液の分泌が促進されます。その他の選択肢である細胞分裂(b, e)は副交感神経の刺激とは直接関係がなく、唾液の粘液含有量(c)や無機塩(d)の増減は副交感神経刺激による分泌量の変化に伴うものです。
Question 4
問題文: Which feature is unique to the exocrine pancreas?
a. Insulin-secreting β cells
b. Centroacinar cells
c. Predominately serous secretory cells
d. Striated interlobular ducts
e. Striated intralobular ducts
Answer: b. Centroacinar cells
Explanation:
外分泌膵に特徴的な構造として、腺房中心細胞(Centroacinar cells)が挙げられ、これは膵臓に特有の細胞です。他の選択肢について、インスリン分泌β細胞(a)は内分泌膵のランゲルハンス島に存在し、主に漿液性分泌細胞(c)は唾液腺にも見られます。また、条線導管(d, e)は唾液腺に存在する特徴であり、膵臓では見られません。
Question 5
問題文: Which description is true of the bile canaliculi?
a. Are bordered directly by endothelial cells
b. Are part of the portal triad
c. Are surrounded by the hepatic sinusoids
d. Lumens are entirely sealed by junctional complexes
e. Normally contain some blood plasma
Answer: d. Lumens are entirely sealed by junctional complexes
Explanation:
胆小管は隣接する肝細胞の間に存在し、接合複合体(junctional complexes)によって完全に密閉されています。この構造により、胆汁の漏出が防がれ、効率的に胆嚢へと輸送されます。他の選択肢について、胆小管は内皮細胞(a)で直接縁取られることはなく、門脈三つ組(b)の一部でもありません。また、血漿(e)が胆汁中に含まれることもありません。
Question 6
問題文: Which description is true of the gallbladder?
a. Dilutes bile
b. Absorbs bile
c. Secretes mucus
d. Has a thick submucosa
e. Is covered entirely by serosa
Answer: c. Secretes mucus
Explanation:
胆嚢は粘液を分泌し、胆汁の粘度を保つのに役立っています。胆嚢の粘膜上皮細胞から分泌される粘液は、胆汁が濃縮される際に粘膜を保護する役割も担います。その他の選択肢について、aの胆汁の希釈は胆嚢の機能ではなく、むしろ胆汁を濃縮します。bの胆汁の吸収も主な役割ではなく、dの厚い粘膜下層(submucosa)は胆嚢には存在しません。また、eの漿膜(serosa)は一部のみで、全体を覆っているわけではありません。
Question 7
問題文: Which description is true for the hepatic space of Disse?
a. Is surrounded by the hepatic sinusoid
b. Contents flow toward the central vein
c. Is directly contacted by hepatocytes
d. Lumen sealed by junctional complexes
e. Contents empty into canals of Hering lined by cholangiocytes
Answer: c. Is directly contacted by hepatocytes
Explanation:
Disse腔(Space of Disse)は肝細胞と肝洞(hepatic sinusoid)の間に存在し、肝細胞が直接接触しています。ここで、栄養分や酸素が血液から肝細胞に供給されます。他の選択肢について、aの「肝洞に囲まれている」と表現すると、肝細胞との直接接触が示されません。bの「中央静脈への流れ」は血流の方向を示しますが、Disse腔の機能ではありません。dのような接合複合体で密閉されているわけでもなく、eのようにチャンネルであるHering管に直接流入するものでもありません。
Question 8
問題文: A 50-year-old woman presents to the family medicine clinic. She admits to drinking a six-pack of beer each day with a little more intake on weekends. Laboratory tests show elevated alanine aminotransferase/serum glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (AST/SGOT). Her sclerae appear jaundiced, and her serum bilirubin is 2.5 mg/dL (normal 0.3-1.9 mg/dL). A biopsy shows hepatic fibrosis with significant loss of normal lobular structure. Jaundice is most likely to result when the proper location or orientation of what hepatic structures is disrupted?
a. Central veins
b. Spaces of Disse
c. Kupffer cells
d. Hepatocytes
e. Merging sinusoids
Answer: d. Hepatocytes
Explanation:
黄疸はビリルビンが血中に蓄積することで引き起こされ、肝細胞が障害されるとビリルビンの処理が滞り、血中濃度が上昇します。選択肢aの中心静脈、bのDisse腔、cのクッパー細胞やeの結合部となる肝洞はビリルビン代謝に直接関与しないため、黄疸の原因となりにくいです。
Question 9
問題文: A 48-year-old woman is referred to an allergy and rheumatology specialist with itching eyes, dryness of the mouth, difficulty swallowing, loss of the sense of taste, hoarseness, fatigue, and swollen parotid glands. She reports increasing joint pain over the past 2 years. She complains of frequent mouth sores. Laboratory tests show a positive antinuclear antibody (ANA) and rheumatoid factor (RF) levels of 70 U/mL (normal < 60 U/mL) by the nephelometric method. A parotid gland biopsy shows inflammatory infiltrates in the interlobular connective tissue with damage to the acinar cells and striated ducts. In this case, resorption of which of the following will be most altered by destruction of those ducts?
a. Na+
b. HO2-
c. HCO3-
d. Cl-
e. Ca2+
Answer: a. Na+
Explanation:
耳下腺における縞状導管(striated duct)は、主にNa+の再吸収を担っています。これが破壊されると、Na+の調整機能が失われ、電解質バランスが崩れます。bの過酸化物やcのHCO3-、dのCl-、eのCa2+は、耳下腺の機能での主な再吸収対象とは異なります。
Question 10
問題文: A young child presents with hepatomegaly and renomegaly, failure to thrive, stunted growth, and hypoglycemia. A deficiency in glucose-6-phosphatase is identified, and the diagnosis of von Gierke disease is made. What cellular structures would be expected to accumulate in hepatocytes during progression of this disorder?
a. Chylomicrons
b. Glycogen granules
c. Mitochondria
d. Zymogen granules
e. Ribosomes
Answer: b. Glycogen granules
Explanation:
Von Gierke病はグルコース-6-ホスファターゼ欠損により、グリコーゲンが分解されず肝細胞内に蓄積します。選択肢aのカイロミクロンは脂肪輸送、cのミトコンドリアはエネルギー生産、dの酵素前駆体やeのリボソームはタンパク質合成に関与しており、グリコーゲン蓄積の直接の原因とはなりません。
追加(スライドから)
Question 1
Question: Which of the following structures are responsible for producing bicarbonate ions in the primary secretion of salivary glands?
a. Acini
b. Mucous cells
c. Intercalated ducts
d. Striated ducts
Answer: c. Intercalated ducts
Explanation:
インターローブ間の導管は、アシニで始まり、重炭酸イオン(HCO₃⁻)を初期分泌物に追加する役割を持っています。これにより、唾液がアルカリ性に近づき、消化管での酸中和に役立ちます。選択肢dの線条導管は、ナトリウム(Na⁺)と塩化物(Cl⁻)を取り除き、HCO₃⁻とカリウム(K⁺)を追加しますが、これは二次的な唾液分泌の段階です。アシニ(選択肢a)は初期唾液生成に関連し、ムチンを分泌するムチン細胞(選択肢b)は構造的には唾液に直接重炭酸を供給しません。
※「Acini(腺房)」とは、さまざまな腺に見られる小さな球状または袋状の構造で、分泌機能を持つ細胞の集合体を指します。主に以下のような特徴と役割を持っています。
Question 2
Question: What is the functional unit of all salivary glands?
a. Lobules and ducts
b. Mucous cells and ducts
c. Acini and ducts
d. Striated ducts and acini
Answer: c. Acini and ducts
Explanation:
唾液腺の機能単位は、アシニ(腺房)と導管で構成され、唾液の生成とその導入を行います。アシニはタンパク質や酵素を分泌する小さな球状構造であり、導管はそれを口腔に運ぶための経路です。他の選択肢は部分的な要素ですが、完全な機能単位ではありません。
Question 3
Question: Which cells in the salivary glands are organized in cylindrical tubules and contain hydrophilic mucins in their granules?
a. Serous cells
b. Mucous cells
c. Acinar cells
d. Ion-transferring cells
Answer: b. Mucous cells
Explanation:
ムチン細胞は円柱状の構造で、疎水性のムチンを含む顆粒が多く、粘液分泌を行います。円柱状で圧縮された核が特徴です。セロース細胞(選択肢a)はピラミッド型でタンパク質を分泌しますが、ムチンは含まれません。イオン輸送細胞(選択肢d)は、塩類を交換する働きがあり、粘液生成に関与しません。
Question 4
Question: Which duct is responsible for actively removing sodium and chloride ions from the luminal fluid?
a. Excretory ducts
b. Striated ducts
c. Intercalated ducts
d. Mucous tubules
Answer: b. Striated ducts
Explanation:
線条導管はナトリウムと塩化物イオンを除去し、唾液の電解質組成を調整します。これは主にNa⁺ポンプによって行われ、唾液を希釈します。インターローブ間導管(選択肢a)やムチン細胞(選択肢d)はこのプロセスに関与しません。
Question 5
Question: What is the primary role of the acinar cells in the salivary glands?
a. To produce enzymes and other proteins
b. To secrete mucins
c. To exchange ions
d. To transport saliva
Answer: a. To produce enzymes and other proteins
Explanation:
アシニ細胞は酵素やタンパク質の分泌を主な役割とし、唾液の消化能力を高めます。ムチン細胞(選択肢b)は粘液を分泌し、イオン交換(選択肢c)は線条導管によって行われます。
Question 6
Question: Which of the following is a paired major salivary gland?
a. Gallbladder
b. Parotid gland
c. Pancreas
d. Liver
Answer: b. Parotid gland
Explanation:
唾液腺には主な3種類の大唾液腺があり、そのうちの一つが耳下腺(Parotid gland)です。膵臓(選択肢c)や肝臓(選択肢d)は消化液を生成しますが、唾液腺ではありません。
Question 7
Question: What type of cells are pyramidal in shape and have round nuclei in the salivary glands?
a. Mucous cells
b. Acinar cells
c. Serous cells
d. Intercalated duct cells
Answer: c. Serous cells
Explanation:
セロース細胞はピラミッド型で、タンパク質分泌に適した形状を持っています。ムチン細胞(選択肢a)は円柱状で、インターローブ間導管細胞(選択肢d)は構造的に異なります。
Question 8
Question: Which ducts converge in each lobule to form interlobular ducts?
a. Striated ducts
b. Mucous tubules
c. Intercalated ducts
d. Excretory ducts
Answer: a. Striated ducts
Explanation:
線条導管は各小葉内で収束し、インターローブ間導管を形成します。これにより唾液がより大きな導管に移行します。他の選択肢は唾液の直接排出に関与しません。
Question 9
Question: Which cells contain apical granules with hydrophilic mucins in the salivary glands?
a. Striated duct cells
b. Serous cells
c. Mucous cells
d. Acinar cells
Answer: c. Mucous cells
Explanation:
ムチン細胞は疎水性ムチンを含む顆粒を持ち、粘液を生成します。セロース細胞(選択肢b)はタンパク質分泌を行いますが、ムチンは含まれません。
Question 10
Question: What component of the salivary glands initiates the formation of striated ducts?
a. Acini
b. Mucous tubules
c. Excretory ducts
d. Intercalated ducts
Answer: d. Intercalated ducts
Explanation:
インターローブ間導管はアシニで始まり、線条導管を形成する役割を果たします。
Question 1
Question: Which of the following is the largest of the major salivary glands and located anterior to and below the lower half of the ear?
a. Submandibular glands
b. Sublingual glands
c. Parotid glands
d. Minor salivary glands
Answer: c. Parotid glands
Explanation:
耳下腺(Parotid gland)は、三大唾液腺の中で最大であり、耳の下および前方に位置しています。この腺はセロース腺房で構成され、二次上顎臼歯近くの頬を通して唾液を口腔内に導きます。他の選択肢(a.顎下腺、b.舌下腺)は、パロチッド腺よりも小さく、位置も異なります。
Question 2
Question: What type of secretory cells make up the majority of the sublingual glands?
a. Only serous cells
b. Only mucous cells
c. Mostly serous cells with some mucous cells
d. Mostly mucous cells with some serous cells
Answer: d. Mostly mucous cells with some serous cells
Explanation:
舌下腺は主に粘液細胞で構成されており(約60%)、少数のセロース細胞も含まれています。これは、舌下腺の粘液分泌に特徴があり、他の唾液腺と異なります。選択肢aやcは顎下腺や耳下腺の特徴とされ、適切ではありません。
Question 3
Question: What classification is given to the submandibular gland based on its duct shape and secretory units?
a. Compound acinar gland
b. Simple tubular gland
c. Compound tubulo-acinar gland
d. Compound alveolar gland
Answer: c. Compound tubulo-acinar gland
Explanation:
顎下腺は複合管状腺房腺(Compound tubulo-acinar gland)に分類され、セロース細胞と少数のムチン細胞を含みます。他の選択肢(aやd)は耳下腺や他の腺に適用されます。
Question 4
Question: Which of the following conditions is a benign tumor most commonly found in the parotid gland?
a. Squamous cell carcinoma
b. Sialadenitis
c. Pleomorphic adenoma
d. Acute pancreatitis
Answer: c. Pleomorphic adenoma
Explanation:
多形腺腫(Pleomorphic adenoma)は耳下腺に最も多く見られる良性腫瘍です。約80%が耳下腺の浅部葉で発生します。選択肢aの扁平上皮がんは悪性腫瘍、選択肢bの唾液腺炎は感染症、dの急性膵炎は膵臓の炎症です。
Question 5
Question: In which gland are serous demilunes found at the distal end of mucous tubuloalveolar secretory units?
a. Parotid gland
b. Pancreas
c. Submandibular gland
d. Minor salivary glands
Answer: c. Submandibular gland
Explanation:
顎下腺では、粘液分泌単位の末端にセロース半月(serous demilunes)が見られます。これは粘液細胞に蓋をする形で存在します。他の選択肢(aの耳下腺やbの膵臓)には該当しません。
Question 6
Question: Which salivary gland duct drains saliva into the oral cavity at the sublingual caruncles?
a. Parotid gland duct
b. Minor salivary gland duct
c. Sublingual gland duct
d. Submandibular gland duct
Answer: d. Submandibular gland duct
Explanation:
顎下腺の主導管は舌小帯両側の舌下小丘で口腔に唾液を排出します。これは耳下腺(選択肢a)や舌下腺(選択肢c)の導管とは異なり、特定の排出位置があります。
Question 7
Question: Which disease is associated with painful swelling of the salivary glands often caused by bacterial infection or ductal obstruction?
a. Pleomorphic adenoma
b. Squamous cell carcinoma
c. Sialadenitis
d. Acute pancreatitis
Answer: c. Sialadenitis
Explanation:
唾液腺炎(Sialadenitis)は唾液腺の炎症で、石(唾石症)による導管の閉塞や細菌感染(例:Staphylococcus aureus)によることが多く、痛みを伴います。aやbは腫瘍、dは膵臓の疾患で異なります。
Question 8
Question: Which pancreatic cells secrete enzymes through zymogen granules that assist in the digestion of lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates?
a. Islet cells
b. Acinar cells
c. Duct cells
d. Mucous cells
Answer: b. Acinar cells
Explanation:
膵臓の腺房細胞は、脂質、タンパク質、炭水化物の消化を助ける酵素を含むジモーゲングラニュールを分泌します。アイレット細胞(選択肢a)は内分泌ホルモンを分泌し、導管細胞(選択肢c)は排出のみを担います。
Question 9
Question: Which condition is characterized by severe abdominal pain and elevated pancreatic enzymes like amylase and lipase?
a. Pleomorphic adenoma
b. Sialadenitis
c. Acute pancreatitis
d. Squamous cell carcinoma
Answer: c. Acute pancreatitis
Explanation:
急性膵炎は、上腹部の激しい痛みとアミラーゼやリパーゼの上昇を特徴とする膵臓の炎症です。他の選択肢は腫瘍や唾液腺の炎症で、膵炎には該当しません。
Question 10
Question: Which of the following is a malignant neoplasm of the oral cavity, most commonly occurring on the lateral aspect of the tongue?
a. Pleomorphic adenoma
b. Sialadenitis
c. Squamous cell carcinoma
d. Adenocarcinoma
Answer: c. Squamous cell carcinoma
Explanation:
扁平上皮がんは口腔内で最も一般的な悪性腫瘍であり、しばしば舌の側面に発生します。他の選択肢(aの多形腺腫)は良性腫瘍で、唾液腺炎(選択肢b)は感染による炎症です。
Question 1
Question: What is the primary structural unit of the liver that is hexagonal in shape and contains a central vein at its core?
a. Hepatic acinus
b. Portal lobule
c. Classic liver lobule
d. Bile canaliculi
Answer: c. Classic liver lobule
Explanation:
クラシカル肝小葉(Classic liver lobule)は六角柱の形を持ち、その中心に中央静脈があります。この構造は肝細胞の放射状配置と血管の配置に基づいており、肝臓の基本的な組織単位です。他の選択肢は、異なる肝臓の構造概念に関連しています。
Question 2
Question: What are the main components of a portal triad found at the corners of a liver lobule?
a. Hepatic artery, bile canaliculi, central vein
b. Hepatic artery, bile duct, portal vein
c. Portal vein, hepatic vein, lymphatic vessel
d. Bile duct, central vein, hepatic artery
Answer: b. Hepatic artery, bile duct, portal vein
Explanation:
門脈三つ組(Portal triad)は、肝小葉の角に位置し、門脈、肝動脈、胆管から成ります。これらの構成要素は血液と胆汁の流れを管理するために重要であり、他の選択肢に含まれる中央静脈やリンパ管は含まれていません。
Question 3
Question: Which cell type in the liver is specialized for vitamin A storage?
a. Kupffer cells
b. Hepatocytes
c. Ito cells (stellate cells)
d. Endothelial cells
Answer: c. Ito cells (stellate cells)
Explanation:
伊藤細胞(Ito cells)は星状の脂肪蓄積細胞で、主にビタミンAの貯蔵に特化しています。他の選択肢(a. Kupffer細胞)は肝臓のマクロファージで、ビタミンの蓄積には関与していません。
Question 4
Question: What is the function of the gallbladder?
a. Produces bile
b. Stores and concentrates bile
c. Synthesizes plasma proteins
d. Breaks down red blood cells
Answer: b. Stores and concentrates bile
Explanation:
胆嚢は胆汁を貯蔵し、濃縮する役割を持っています。他の選択肢(aやc)は肝臓の機能であり、赤血球の分解(d)は脾臓や肝臓内の他の細胞が関与しています。
Question 5
Question: Which structure is responsible for carrying bile from the liver and connecting to the gallbladder?
a. Cystic duct
b. Common bile duct
c. Common hepatic duct
d. Hepatic artery
Answer: c. Common hepatic duct
Explanation:
総肝管(Common hepatic duct)は肝臓から胆汁を運び、胆嚢へ接続します。胆嚢管(a)は胆嚢に直接接続し、総胆管(b)は胆嚢から十二指腸へ胆汁を運びます。
Question 6
Question: What type of epithelium lines the mucosa of the gallbladder?
a. Simple cuboidal
b. Stratified squamous
c. Simple columnar
d. Pseudostratified columnar
Answer: c. Simple columnar
Explanation:
胆嚢の粘膜は単層円柱上皮で構成されており、濃縮された胆汁を効率的に保持できるように構造が形成されています。他の選択肢は、異なる器官や部位で見られる上皮組織です。
Question 7
Question: Which condition is characterized by an excess of bilirubin in the blood, leading to a yellowish pigmentation in the skin and eyes?
a. Sialadenitis
b. Gallstones
c. Jaundice
d. Acute pancreatitis
Answer: c. Jaundice
Explanation:
黄疸(Jaundice)は血中のビリルビン過剰により皮膚や眼が黄変する症状で、これは肝機能不全や胆道閉塞などで引き起こされます。他の選択肢は、肝臓や胆嚢には関連しません。
Question 8
Question: In a liver acinus, which zone contains hepatocytes that are closest to the blood supply and thus receive the highest oxygen concentration?
a. Zone 1
b. Zone 2
c. Zone 3
d. Portal area
Answer: a. Zone 1
Explanation:
肝小葉の区分であるアシナスでは、Zone 1が動脈に最も近く、高い酸素濃度を得られる場所です。Zone 3(選択肢c)は血流から遠く、酸素が不足するため、細胞壊死のリスクが高まります。
Question 9
Question: Which of the following describes the lining cells of intrahepatic bile ductules?
a. Simple squamous cells
b. Cuboidal cells with dark, round nuclei
c. Pseudostratified columnar cells
d. Columnar cells with microvilli
Answer: b. Cuboidal cells with dark, round nuclei
Explanation:
肝内胆管は立方細胞で裏打ちされ、暗色の丸い核が特徴的です。これは胆汁の流れに関係しており、他の選択肢にある細胞形態は肝内胆管に適合しません。
Question 10
Question: What are the two primary types of gallstones?
a. Bilirubin stones and cholesterol stones
b. Calcium stones and cholesterol stones
c. Pigment stones and cholesterol stones
d. Oxalate stones and pigment stones
Answer: c. Pigment stones and cholesterol stones
Explanation:
胆石にはコレステロール結石と色素結石の2種類があり、それぞれの成因や構成が異なります。他の選択肢は、胆石の主な分類には含まれません。
ブロック
Question 1
What is the finger-like projection of mucosa that is seen in the small intestine?
a. Striated border
b. Plicae Circulares
c. Crypts of Lieberkühn
d. Villi
Answer: d. Villi
解説: 小腸の粘膜には指状の突起である絨毛(villi)が見られ、吸収面積を増加させます。
- a. Striated border: これは絨毛に見られる微絨毛の層です。
- b. Plicae Circulares: これは小腸の円形のヒダです。
- c. Crypts of Lieberkühn: これは腸腺(intestinal glands)です。
Question 2
What is the outer layer of the GI tract called when it is abutting another organ?
a. Mucosa
b. Muscularis Externa
c. Adventitia
d. Serosa
Answer: c. Adventitia
解説: 他の臓器に接している場合、消化管の外層は外膜(adventitia)と呼ばれます。
- a. Mucosa: これは最内層です。
- b. Muscularis Externa: これは筋層です。
- d. Serosa: 漿膜は外膜と区別され、腹膜で覆われた領域にあります。
Question 3
Where is the masticatory mucosa found?
a. Hard Palate
b. Tongue underside
c. Soft Palate
d. Lips
Answer: a. Hard Palate
解説: 咀嚼粘膜(masticatory mucosa)は硬口蓋(hard palate)や歯肉に見られます。
- b. Tongue underside: これは裏側に存在する粘膜です。
- c. Soft Palate: 軟口蓋は粘膜に覆われていますが、咀嚼粘膜ではありません。
- d. Lips: 唇の粘膜は異なります。
Question 4
What is the surface layer of masticatory mucosa composed of?
a. Non-Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
b. Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
c. Simple Squamous epithelium
d. Both a and b
Answer: b
Question 5
What is the innermost layer of the GI tract?
a. Serosa
b. Sub-Mucosa
c. Muscularis externa
d. Mucosa
Answer: d. Mucosa
解説: 粘膜(mucosa)は消化管の最内層で、消化吸収に関与します。
- a. Serosa: これは最外層の漿膜です。
- b. Sub-Mucosa: これは粘膜の下にある組織です。
- c. Muscularis externa: これは筋層で、消化管の動きに関与します。
Question 6
Which type of papillae is not well developed in humans?
a. Filiform papillae
b. Fungiform papillae
c. Foliate papillae
d. None of the above
Answer: c. Foliate papillae
解説: 葉状乳頭(foliate papillae)はヒトではあまり発達していませんが、一部の動物ではよく発達しています。
- a. Filiform papillae: 糸状乳頭は最も一般的です。
- b. Fungiform papillae: 茸状乳頭は舌の先端に見られます。
Question 7
What covers the visible portion of the tooth?
a. Dentine
b. Cementum
c. Enamel
d. Dental Pulp
Answer: c. Enamel
解説: エナメル質(enamel)は歯の可視部分を覆い、最も硬い体組織です。
- a. Dentine: 象牙質はエナメル質の下にあります。
- b. Cementum: セメント質は歯の根部を覆います。
- d. Dental Pulp: 歯髄は歯の内部にあります。
Question 8
What covers the tooth that is embedded within the jaw?
a. Cementum
b. Dentine
c. Dental Pulp
d. Enamel
Answer: a. Cementum
解説: セメント質(cementum)は顎骨に埋まっている歯の部分を覆っています。
- b. Dentine: 象牙質はセメント質の内側にあります。
- c. Dental Pulp: 歯髄は歯の内部にあります。
- d. Enamel: エナメル質は歯の外側で、根部にはありません。
Question 9
What surrounds the pulp cavity?
a. Dental Pulp
b. Cementum
c. Dentine
d. Enamel
Answer: c. Dentine
解説: 象牙質(dentine)は歯髄腔(pulp cavity)を取り囲む組織です。
- a. Dental Pulp: 歯髄は象牙質に囲まれています。
- b. Cementum: セメント質は根部を覆いますが、歯髄腔には関与しません。
- d. Enamel: エナメル質は歯冠部分を覆いますが、歯髄腔は囲みません。
Question 10
Which is the smallest papillae on the tongue?
a. Filiform papillae
b. Fungiform papillae
c. Foliate papillae
d. None of the above
Answer: a. Filiform papillae
解説: 糸状乳頭(filiform papillae)は舌の最も小さな乳頭で、舌の大部分を覆います。
- b. Fungiform papillae: 茸状乳頭は比較的大きく、舌の先端にあります。
- c. Foliate papillae: 葉状乳頭は側面にありますが、ヒトではあまり発達していません。
Question 11
Which layer contains the lamina propria?
a. Submucosa
b. Muscularis externa
c. Mucosa
d. Serosa
Answer: c. Mucosa
解説: 粘膜(mucosa)は、内層である粘膜固有層(lamina propria)を含み、これが結合組織を形成します。
- a. Submucosa: これは粘膜の下の層です。
- b. Muscularis externa: これは筋肉層です。
- d. Serosa: これは外層であり、結合組織を含んでいますが、粘膜固有層はありません。
Question 12
What is the mucus surface cells?
a. Simple squamous epithelium
b. Simple columnar epithelium
c. Stratified squamous epithelium
d. Simple cuboidal epithelium
Answer: b. Simple columnar epithelium
解説: 粘液分泌細胞は、単層円柱上皮(simple columnar epithelium)として胃や腸に存在します。
- a. Simple squamous epithelium: 単層扁平上皮は通常、血管や体腔を覆います。
- c. Stratified squamous epithelium: 重層扁平上皮は皮膚や口腔内に見られます。
- d. Simple cuboidal epithelium: 単層立方上皮は腺に見られます。
Question 13
Where are the Peyer’s patches located?
a. Small intestine
b. Esophagus
c. Large intestine
d. Stomach
Answer: a. Small intestine
解説: パイエル板(Peyer’s patches)は小腸の特に回腸に位置するリンパ組織です。
- b. Esophagus: 食道にはパイエル板はありません。
- c. Large intestine: 大腸にはパイエル板はありませんが、リンパ組織は存在します。
- d. Stomach: 胃にはパイエル板は存在しません。
Question 14
Which layers contain the muscularis mucosa?
a. Serosa
b. Submucosa
c. Mucosa
d. Muscularis externa
Answer: c. Mucosa
解説: 筋層板(muscularis mucosa)は粘膜の一部で、粘膜の動きを助けます。
- a. Serosa: 漿膜は外層です。
- b. Submucosa: 粘膜下層には筋層板は含まれていません。
- d. Muscularis externa: これは主に消化管の運動を担う外層の筋肉です。
Question 15
Which layer contains the muscularis mucosa?
a. Serosa
b. Submucosa
c. Mucosa
d. Muscularis externa
Answer: c. Mucosa
解説: 筋層板(muscularis mucosa)は粘膜(mucosa)内に存在し、粘膜の収縮に関与します。
Question 16
What is the lining epithelium of the first part of the esophagus?
a. Simple cuboidal with goblet cells
b. Simple columnar epithelium
c. Stratified squamous epithelium non-keratinized
d. Stratified squamous epithelium, keratinized
Answer: c. Stratified squamous epithelium non-keratinized
解説: 食道の最初の部分は、非角化重層扁平上皮(non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium)で覆われています。
- a. Simple cuboidal with goblet cells: これは腺の構造に見られます。
- b. Simple columnar epithelium: 胃や腸に見られます。
- d. Stratified squamous epithelium, keratinized: 角化重層扁平上皮は皮膚に見られます。
Question 17
Which layer contains the Meissner’s plexus?
a. Muscularis externa
b. Mucosa
c. Submucosa
d. Serosa
Answer: c. Submucosa
解説: マイスナー神経叢(Meissner’s plexus)は、粘膜下層(submucosa)に位置し、腸管の分泌と局所的な運動を調整します。
- a. Muscularis externa: これはアウエルバッハ神経叢が存在する層です。
- b. Mucosa: 粘膜には神経叢はありません。
- d. Serosa: 漿膜には神経叢は存在しません。
Question 18
Which of the following is NOT a content of the Space of Disse?
a. Stellate fat-storing cells or Ito cells
b. Elastic fibers which maintain the architecture of sinusoids
c. The short microvilli of hepatocytes
d. Occasional non-myelinated nerve fibers
Answer: b. Elastic fibers which maintain the architecture of sinusoids
解説: ディッセ腔(Space of Disse)には、星状細胞(Ito cells)、肝細胞の微絨毛、無髄神経線維が含まれますが、弾性線維は含まれていません。
- a. Stellate fat-storing cells or Ito cells: これらはディッセ腔に存在します。
- c. The short microvilli of hepatocytes: 肝細胞の微絨毛はディッセ腔に伸びています。
- d. Occasional non-myelinated nerve fibers: 無髄神経線維は時折存在します。
Question 19
The connective tissue layer of the gallbladder is made of?
a. Dense regular collagenous CT
b. Dense irregular collagenous CT
c. Dense irregular CT
d. Dense regular CT
Answer: b. Dense irregular collagenous CT
解説: 胆嚢の結合組織層は、密性不規則膠原線維結合組織(dense irregular collagenous connective tissue)で構成されています。
- a. Dense regular collagenous CT: これは靭帯や腱に見られます。
- c. Dense irregular CT: これは一般的な結合組織のタイプですが、膠原線維が主です。
- d. Dense regular CT: 規則的な結合組織は筋肉と骨に関連しています。
Question 20
Which of the following is true of semi-demilunes?
a. Serous cells make up the majority of the cells
b. Some mucous cells may be capped with serous cells
c. Serous cells stain lighter than mucous cells
d. Often arranged in an elongated circular structure with a flattened or round lumen
Answer: b. Some mucous cells may be capped with serous cells
解説: 半月形(demilunes)は、粘液細胞の上に漿液細胞が覆う形で存在します。
- a. Serous cells make up the majority of the cells: 粘液細胞が多く存在することもあります。
- c. Serous cells stain lighter than mucous cells: 漿液細胞は通常、粘液細胞よりも濃く染まります。
- d. Often arranged in an elongated circular structure: 半月形は長円形には配置されません。
Question 21
Which of the following structures secrete enzymes that help in digestion of lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates?
a. Pancreatic acinus
b. Kiemmel Wilston
c. Acinar cells
d. Zymogen granules
Answer: a
Question 22
Which of the following layers covers most of the gallbladder?
a. Mucosa
b. Serosa
c. Adventitia
d. Epithelium
Answer: b. Serosa
解説: 胆嚢の大部分は漿膜(serosa)で覆われていますが、一部は外膜(adventitia)に覆われています。
- a. Mucosa: 粘膜は内層です。
- c. Adventitia: 外膜は他の臓器と接触する部分で見られます。
- d. Epithelium: 上皮は内層に存在します。
Question 23
Hepatocytes detoxify barbiturates using cytochrome P-450 enzymes. Where are these enzymes mainly found?
a. Proteasomes
b. Smooth ER
c. Golgi apparatus
d. Lysosomes
Answer: b. Smooth ER
解説: シトクロムP450酵素は滑面小胞体(smooth ER)に主に存在し、薬物の解毒に関与しています。
- a. Proteasomes: プロテアソームはタンパク質分解に関与します。
- c. Golgi apparatus: ゴルジ装置は細胞の輸送に関与します。
- d. Lysosomes: リソソームは異化作用に関与しますが、解毒には関与しません。
自作70問(22nd Oct 2024)
Question 1
What type of epithelium is found in the gingiva and hard palate?
a. Nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium
b. Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
c. Simple squamous epithelium
d. Transitional epithelium
Answer: b. Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
解説:
歯茎(gingiva)および硬口蓋(hard palate)は、外部の刺激や摩擦に対して保護するために角化している重層扁平上皮(keratinized stratified squamous epithelium)で覆われています。選択肢aのnonkeratinized stratified squamous epitheliumは、口腔内の柔らかい部分、例えば頬や軟口蓋に見られます。cのsimple squamous epitheliumは、血管や内壁に見られる単層の上皮で、口腔内では存在しません。dのtransitional epitheliumは、主に尿路系に特有で、口腔内には存在しません。

Question 2
What type of papillae is the most numerous on the dorsal surface of the tongue?
a. Fungiform papillae
b. Filiform papillae
c. Foliate papillae
d. Circumvallate papillae
Answer: b. Filiform papillae
解説:
舌の背側(dorsal surface)には、短く狭い角化したフィリフォーム乳頭(filiform papillae)が最も多く存在します。これらは味覚芽を持たない一方、食べ物の感覚的な触知に役立ちます。選択肢aのfungiform papillaeは、比較的少数で軽度に角化しており、時々味覚芽を含みます。cのfoliate papillaeは舌の側面にあり、幼児期には味覚芽を持ちますが、2歳を過ぎると徐々に減少します。dのcircumvallate papillaeは8~12個の大きな乳頭で、味覚芽を含むものの数は限られています。

Question 3
Which structure in the oral cavity lacks keratinization?
a. Gingiva
b. Hard palate
c. Soft palate
d. Vermilion zone
Answer: c. Soft palate
解説:
軟口蓋(soft palate)は非角化(nonkeratinized)重層扁平上皮で覆われており、柔軟で可動性の高い部分です。aのgingivaとbのhard palateは、摩擦からの保護が必要なため角化しています。dのvermilion zoneは薄く角化した重層扁平上皮で、唾液や汗腺が欠如しています。
Question 4
Which part of the tooth is responsible for producing enamel?
a. Odontoblasts
b. Cementoblasts
c. Ameloblasts
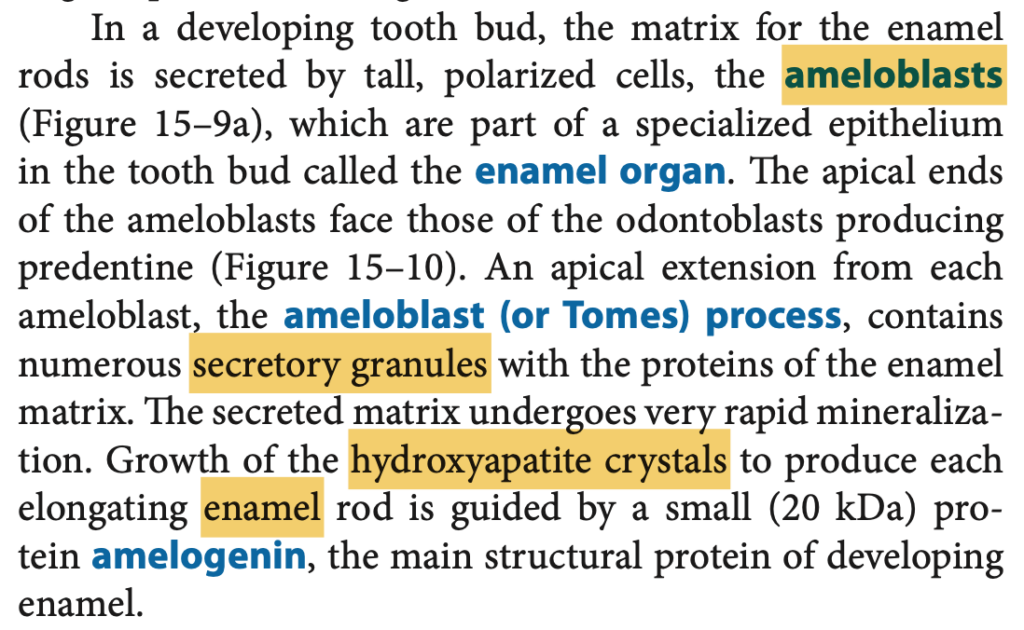
d. Fibroblasts
Answer: c. Ameloblasts
解説:
エナメル質(enamel)は、アメロブラスト(ameloblasts)によって形成され、非常に硬い組織でカルシウムハイドロキシアパタイトの含有率が96%です。aのodontoblastsは象牙質(dentin)を生成します。bのcementoblastsは歯の根部を覆うセメント質(cementum)を作り、dのfibroblastsは主に結合組織の成分を作りますが、歯の硬い部分を生成する役割はありません。
Question 5
What type of epithelium is found on the inner surface of the lips?
a. Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
b. Nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium
c. Simple squamous epithelium
d. Transitional epithelium
Answer: b. Nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium
解説:
唇の内側は、非角化重層扁平上皮(nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium)で覆われています。これは柔軟で唾液腺を含んでいるため、食事中や会話時の動きを助けます。aのkeratinized stratified squamous epitheliumは、外側や硬い口腔部分に見られ、より強固な保護を提供します。cのsimple squamous epitheliumは口腔内ではなく、主に血管内膜で見られる単層上皮です。dのtransitional epitheliumは主に尿路に存在します。
Question 6
What is the function of the periodontal ligaments?
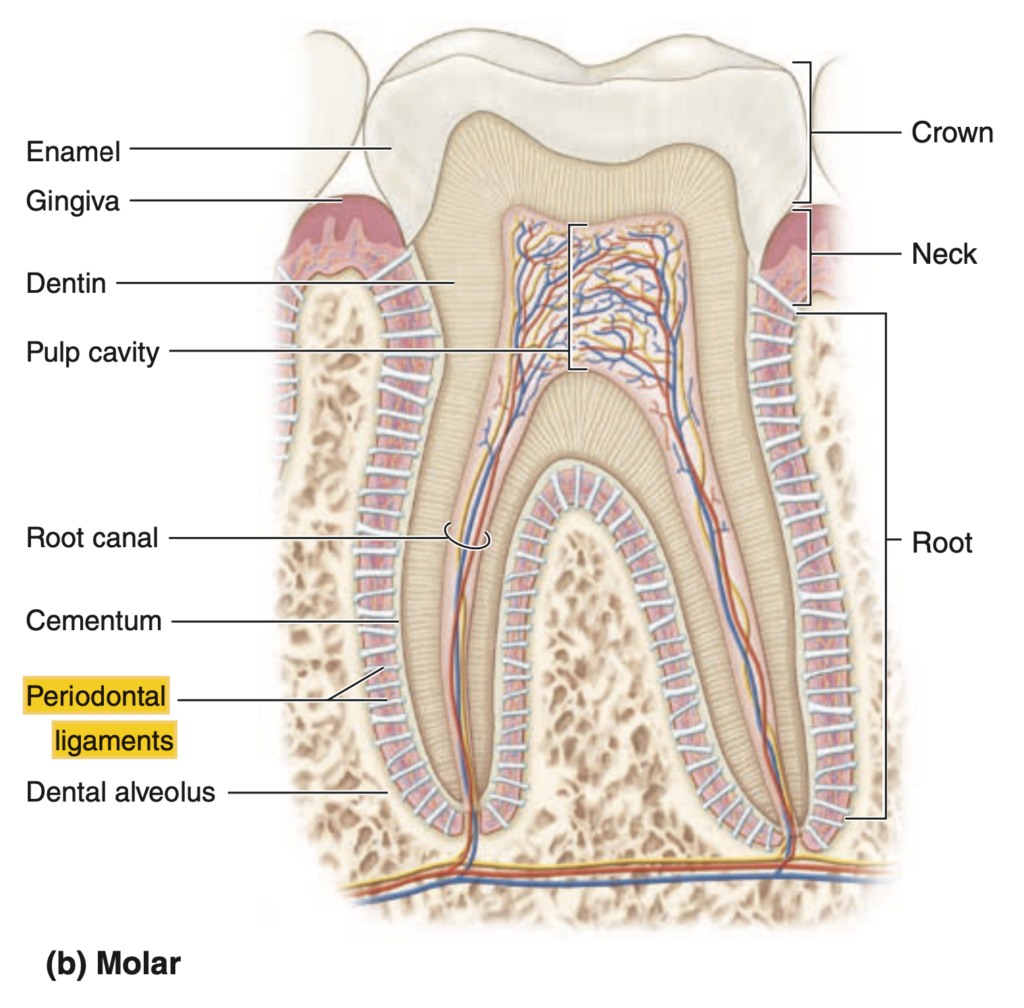
a. To produce enamel
b. To hold the tooth to the jawbone
c. To produce cementum
d. To protect the pulp cavity
Answer: b. To hold the tooth to the jawbone
解説:
歯根膜(periodontal ligaments)は、歯を顎の骨に固定する役割を持ち、歯の安定性と耐久性を提供します。aのエナメル質はアメロブラストによって作られ、cのセメント質はセメントブラストによって生成されます。dの歯髄腔(pulp cavity)は、血管と神経により維持され、特定の組織によって保護されていますが、歯根膜の役割ではありません。
Question 7
Which papillae are responsible for taste sensation and are located just anterior to the sulcus terminalis?
a. Filiform papillae
b. Fungiform papillae
c. Circumvallate papillae
d. Foliate papillae
Answer: c. Circumvallate papillae
解説:
サーカムバレート乳頭(circumvallate papillae)は、V字型の溝であるsulcus terminalisの直前に位置し、味覚芽を多数含むため、味覚の認識に重要な役割を果たします。aのfiliform papillaeは味覚芽を持たず、触感に寄与します。bのfungiform papillaeは、舌の先端付近にあり、時々味覚芽を含みます。dのfoliate papillaeは側面にありますが、味覚芽は幼少期にのみ活発です。


Question 8
What structure separates the anterior two-thirds of the tongue from the posterior one-third?
a. Vermilion zone
b. Sulcus terminalis
c. Filiform papillae
d. Circumvallate papillae
Answer: b. Sulcus terminalis
解説:
舌の前方2/3と後方1/3は、V字状の溝であるsulcus terminalisによって分けられます。この構造は、舌の機能的および発生学的な区分に関与しています。aのvermilion zoneは唇に関連し、cとdの乳頭(papillae)は舌の表面にありますが、舌の区分には関与しません。
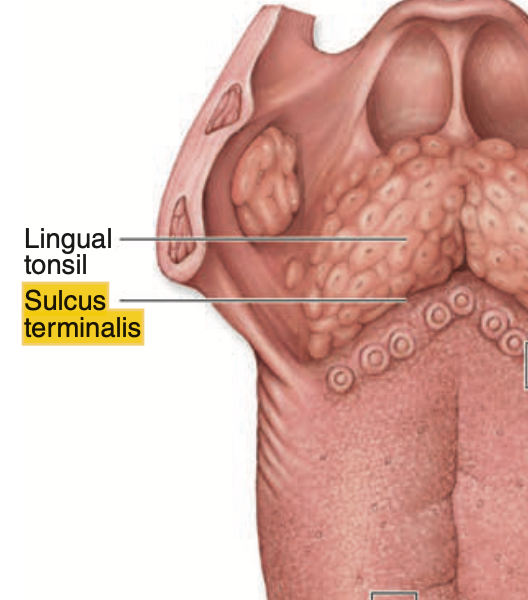
Question 9
Which of the following is true regarding filiform papillae?
a. They are the least numerous type of papillae
b. They contain taste buds
c. They are highly keratinized structures
d. They are mushroom-shaped structures
Answer: c. They are highly keratinized structures
解説:
フィリフォーム乳頭(filiform papillae)は非常に角化した構造で、触覚的な感覚を助けますが、味覚芽を含んでいません。aの「最も少ない」ではなく、実際には舌の乳頭の中で最も多く存在します。bの選択肢は誤りで、味覚に関与しない点が特徴です。dの「キノコ型」構造は、フンジフォーム乳頭(fungiform papillae)に関連しています。
Question 10
What tissue type covers the root of the tooth?
a. Enamel
b. Dentin
c. Cementum
d. Pulp
Answer: c. Cementum
解説:
歯の根(root)はセメント質(cementum)によって覆われており、歯を顎の骨に固定する歯根膜に接続しています。aのエナメル質(enamel)は歯の冠部を覆い、bの象牙質(dentin)はエナメル質やセメント質の内側にあります。dの歯髄(pulp)は、歯の中心に位置し、神経と血管で構成されていますが、歯を覆う組織ではありません。
Question 11
How many permanent teeth does an adult human typically have?
a. 28
b. 32
c. 24
d. 36
Answer: b. 32
解説:
成人の通常の歯列には32本の永久歯があり、それぞれの顎の各象限に8本ずつ存在します。aの28本は親知らずを除いた場合の本数であり、cの24本は通常の本数ではありません。dの36本は実際の人間の歯の本数を超えています。
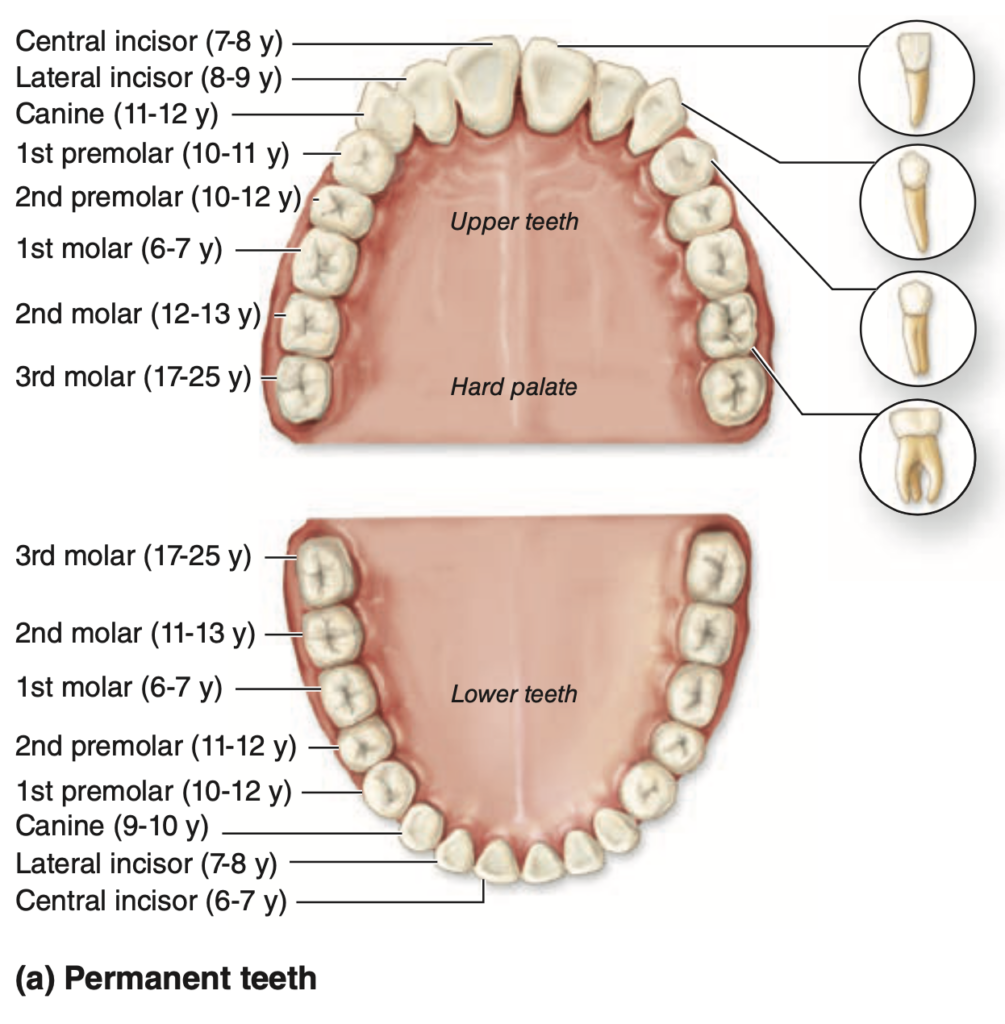
Question 12
Which part of the tooth contains well-vascularized and well-innervated mesenchymal connective tissue?
a. Enamel
b. Dentin
c. Cementum
d. Pulp cavity
Answer: d. Pulp cavity
解説:
歯髄腔(pulp cavity)は、豊富な血管と神経を含む間葉系結合組織で満たされています。この部分は歯の生存と感覚に重要な役割を果たしています。aのエナメル質、bの象牙質、cのセメント質はすべて硬い歯の組織であり、血管や神経を含んでいません。
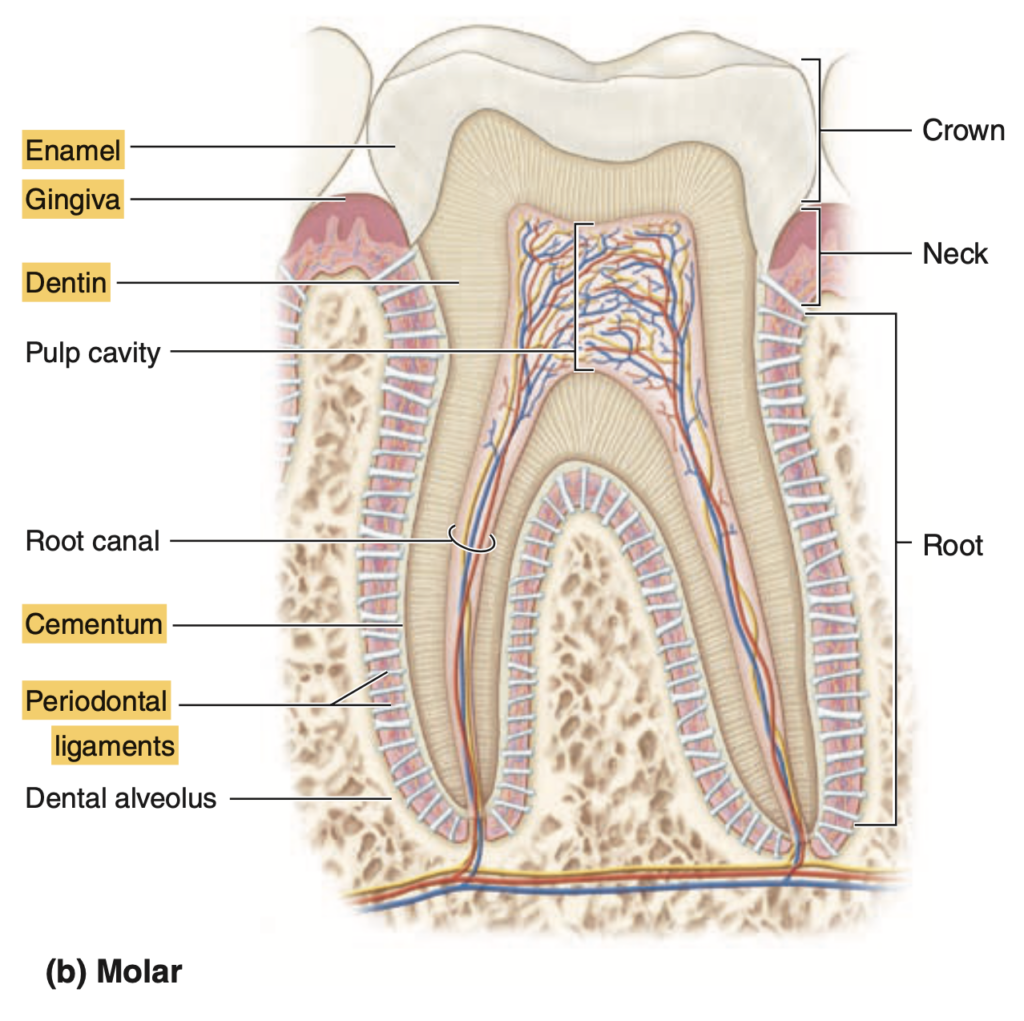
Question 13
Which of the following statements about dentin is true?
a. It is harder than enamel
b. It is produced by ameloblasts
c. It is 70% calcium hydroxyapatite
d. It contains no collagen
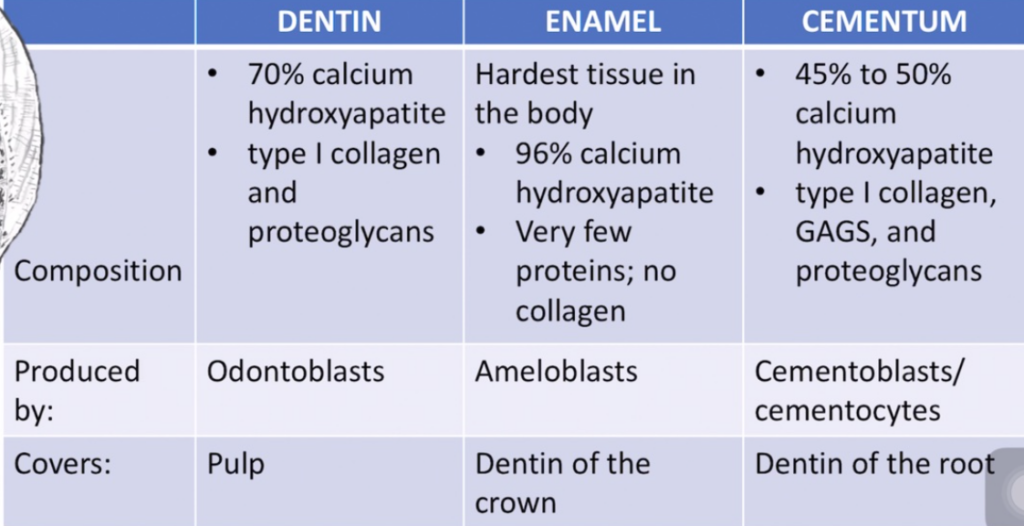
Answer: c. It is 70% calcium hydroxyapatite
解説:
象牙質(dentin)は70%のカルシウムハイドロキシアパタイトを含み、他にもタイプIコラーゲンやプロテオグリカンを含む構造で、歯の内側の主な硬い組織です。aは誤りで、エナメル質の方が硬く、dentinは比較的柔らかいです。bは誤りで、象牙質はオドントブラスト(odontoblasts)によって生成され、dの選択肢も誤りで、象牙質にはコラーゲンが豊富に含まれています。

Question 14
Which papillae degenerate shortly after the second year of life?
a. Filiform papillae
b. Fungiform papillae
c. Foliate papillae
d. Circumvallate papillae
Answer: c. Foliate papillae
解説:
葉状乳頭(foliate papillae)は幼少期に発達しますが、2歳を過ぎると徐々に味覚芽が退化します。aのfiliform papillaeは味覚に関与せず、触覚的な役割を果たします。bのfungiform papillaeは味覚を感じる乳頭の1つであり、dのcircumvallate papillaeも味覚芽を多く含みますが、いずれも寿命による退化は見られません。
Question 15
Which structure in the lips lacks salivary and sweat glands?
a. Vermilion zone
b. Inner surface
c. Outer surface
d. Gingiva
Answer: a. Vermilion zone
解説:
唇の紅色縁(vermilion zone)は、唾液腺や汗腺を持たないため、乾燥しやすく、他の部分に比べて特別なケアが必要です。bの内側表面は非角化しており、唾液腺を含みます。cの外側表面は角化しており、毛包や汗腺を含んでいます。dのgingivaは唇ではなく歯茎の部分であり、選択肢の文脈には適していません。

Question 16
Which tissue is responsible for covering the crown of the tooth?
a. Cementum
b. Enamel
c. Dentin
d. Pulp
Answer: b. Enamel
解説:
エナメル質(enamel)は、歯冠(crown)を覆う最も外側の層で、体内で最も硬い組織です。aのcementumは歯根を覆い、cのdentinは歯の内部にあり、dのpulpは歯の中心部で血管や神経を含んでいますが、歯冠を覆うものではありません。
Question 17
What type of glands are found on the outer surface of the lips?
a. Salivary glands
b. Sweat glands and sebaceous glands
c. Taste buds
d. None
Answer: b. Sweat glands and sebaceous glands
解説:
唇の外側表面には、汗腺(sweat glands)と皮脂腺(sebaceous glands)があり、これらの腺は皮膚を保湿し、保護する役割を果たします。aの唾液腺(salivary glands)は唇の内側や口腔内に存在します。cの味覚芽(taste buds)は唇には存在せず、舌に見られます。
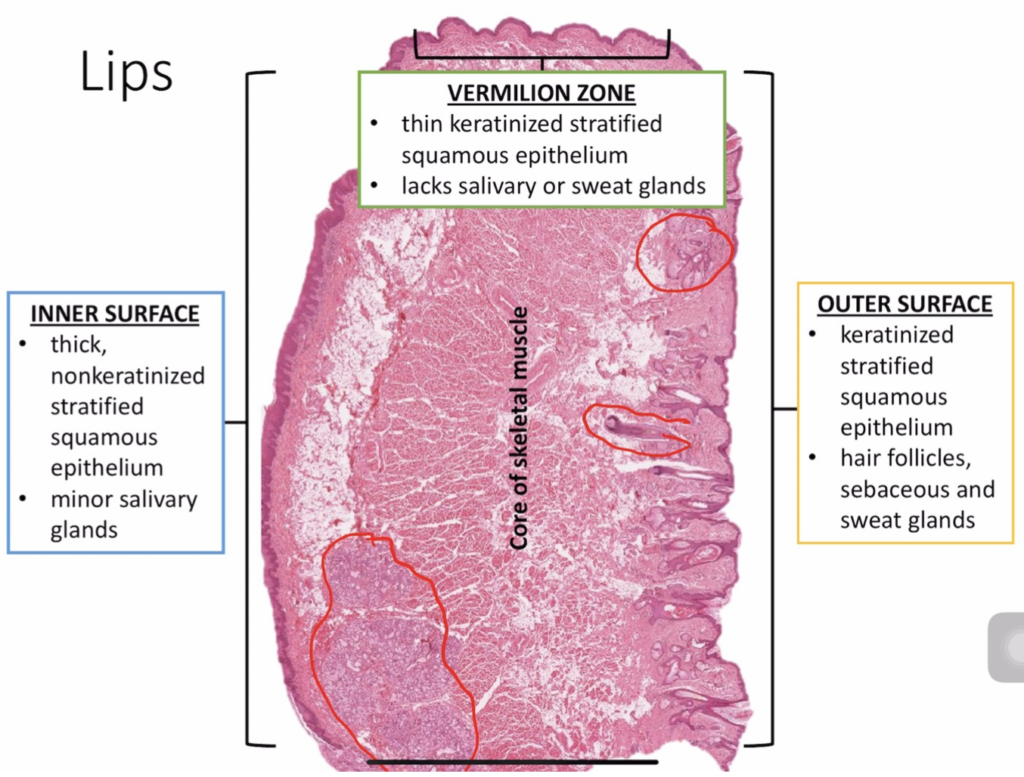
Question 18
Which structure contains hair follicles?
a. Inner surface of the lips
b. Vermilion zone
c. Outer surface of the lips
d. Dorsal surface of the tongue
Answer: c. Outer surface of the lips
解説:
唇の外側表面には毛包(hair follicles)が含まれ、汗腺や皮脂腺も存在します。これにより、外界からの保護が提供されます。aの唇の内側表面やbの紅色縁(vermilion zone)には毛包は存在しません。dの舌の背側(dorsal surface)も毛包を持たず、乳頭や味覚芽が主に存在しています。
Question 19
Which type of papillae is mushroom-shaped and lightly keratinized?
a. Filiform papillae
b. Fungiform papillae
c. Circumvallate papillae
d. Foliate papillae
Answer: b. Fungiform papillae
解説:
フンジフォーム乳頭(fungiform papillae)は、キノコ型の構造を持ち、軽度に角化しており、時折味覚芽を含みます。aのフィリフォーム乳頭(filiform papillae)は角化が強く、味覚芽を含んでいません。cのサーカムバレート乳頭(circumvallate papillae)は大きな乳頭であり、舌の後方に配置されています。dの葉状乳頭(foliate papillae)は舌の側面にありますが、幼少期に味覚芽が活発で、その後退化します。
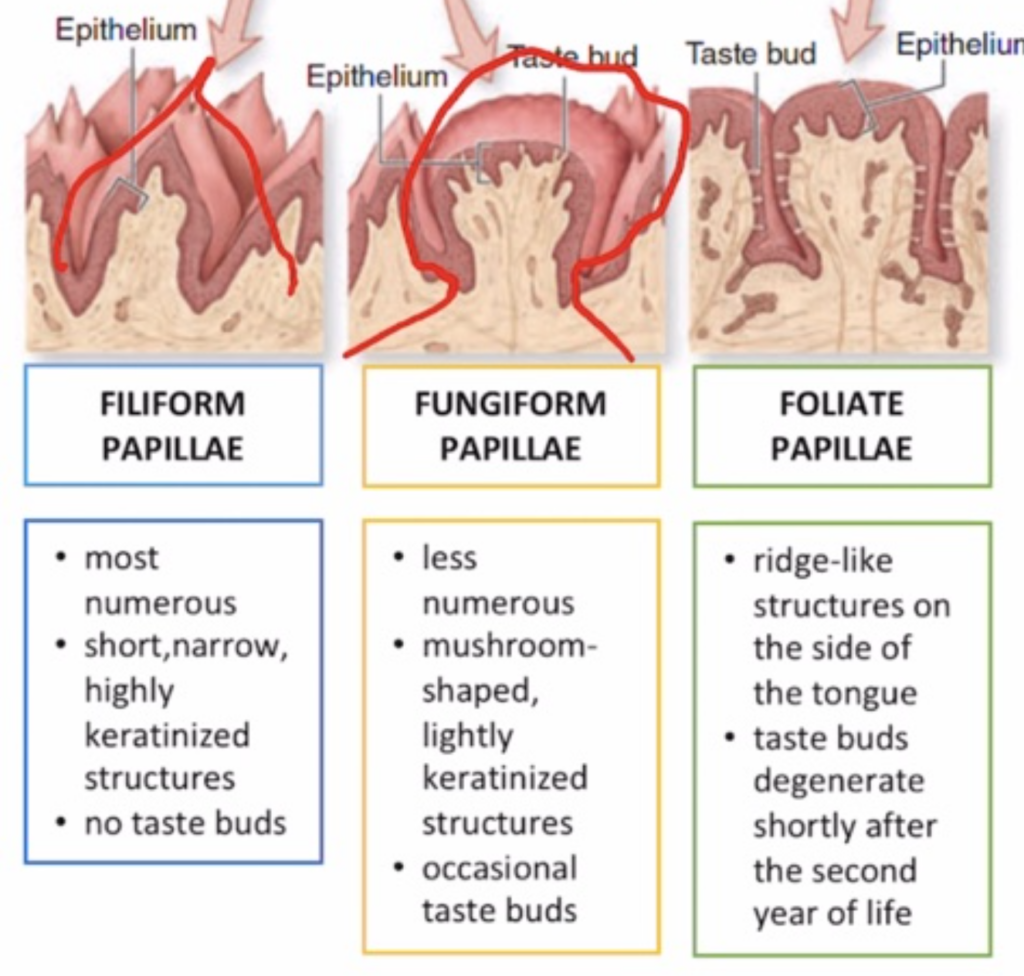
Question 20
What is the primary function of odontoblasts?
a. To produce enamel
b. To produce dentin
c. To produce cementum
d. To produce pulp tissue
Answer: b. To produce dentin
解説:
オドントブラスト(odontoblasts)は象牙質(dentin)を生成する細胞で、歯の内側を構成する重要な組織を形成します。aのエナメル質はアメロブラスト(ameloblasts)によって生成され、cのセメント質はセメントブラスト(cementoblasts)によって作られます。dの選択肢は、歯髄組織に関連する役割を持ちません。
Question 1
Which layer of the digestive tract contains the lining epithelium, lamina propria, and muscularis mucosae?
a. Mucosa
b. Submucosa
c. Muscularis
d. Serosa
Answer: a. Mucosa
解説:
消化管の粘膜(mucosa)は、最も内側に位置し、被覆上皮(lining epithelium)、固有層(lamina propria)、および粘膜筋板(muscularis mucosae)で構成されています。bのsubmucosaは密な結合組織を含み、cのmuscularisは平滑筋層で、dのserosaは外側の層で構成されています。
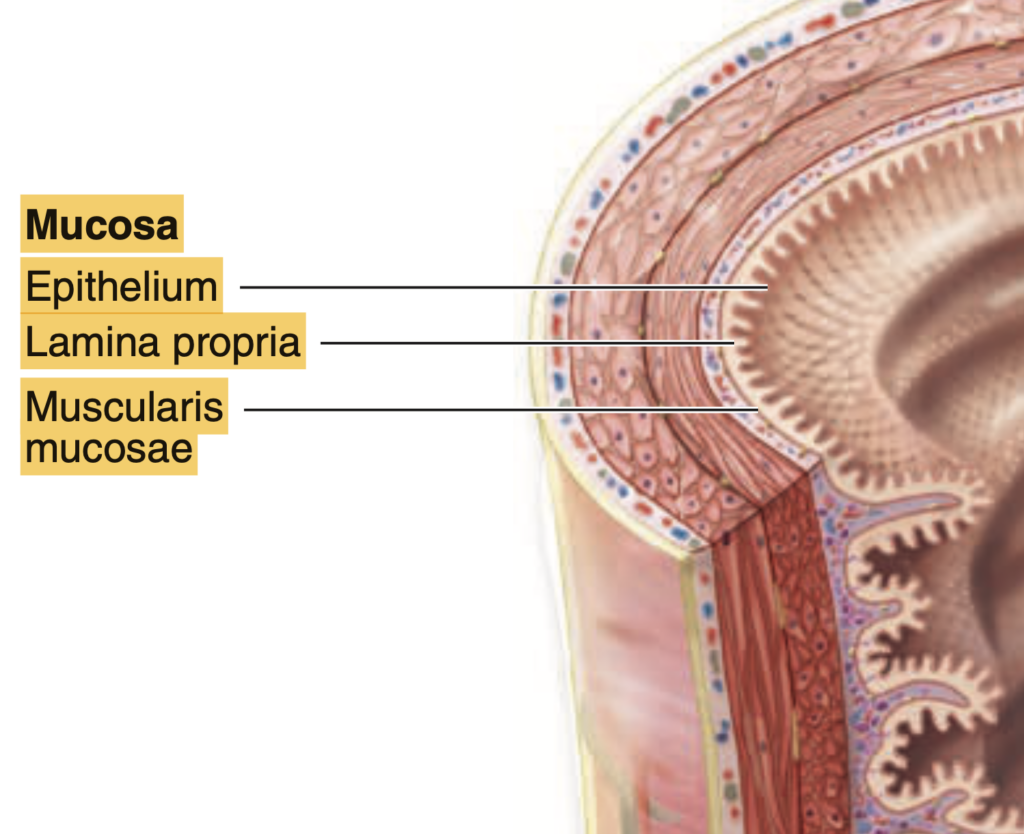
Question 2
Which layer of the digestive tract contains the submucosal (Meissner) plexus?
a. Mucosa
b. Submucosa
c. Muscularis
d. Serosa
Answer: b. Submucosa
解説:
Submucosaには、Meissnerの神経叢(submucosal plexus)が含まれ、消化管の腺の分泌や血流の調整に関与しています。aのmucosaは内層であり、cのmuscularisはAuerbachの神経叢を持っています。dのserosaは外層で、神経叢は含みません。

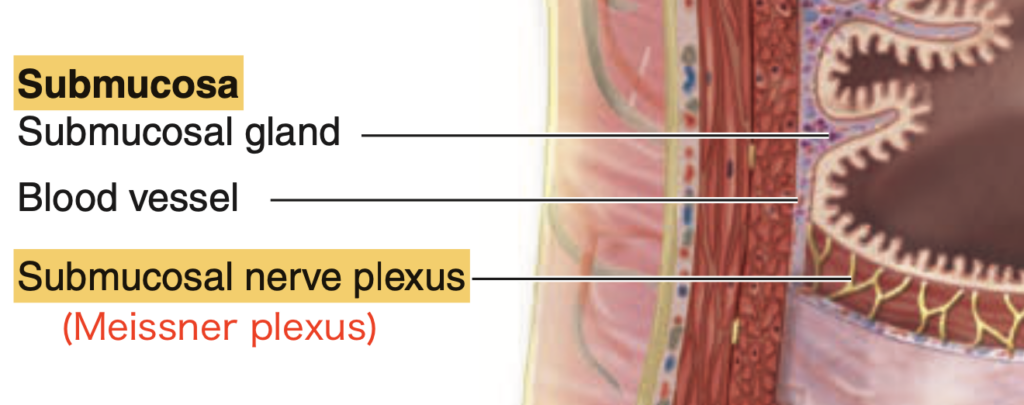
Question 3
What type of epithelium lines the esophagus?
a. Simple columnar epithelium
b. Nonkeratinizing stratified squamous epithelium
c. Simple squamous epithelium
d. Transitional epithelium
Answer: b. Nonkeratinizing stratified squamous epithelium
解説:
食道は、非角化重層扁平上皮(nonkeratinizing stratified squamous epithelium)で覆われ、食物の摩擦から保護します。aのsimple columnar epitheliumは胃の粘膜に見られ、cのsimple squamous epitheliumは血管内皮などに存在します。dのtransitional epitheliumは主に尿路で見られます。
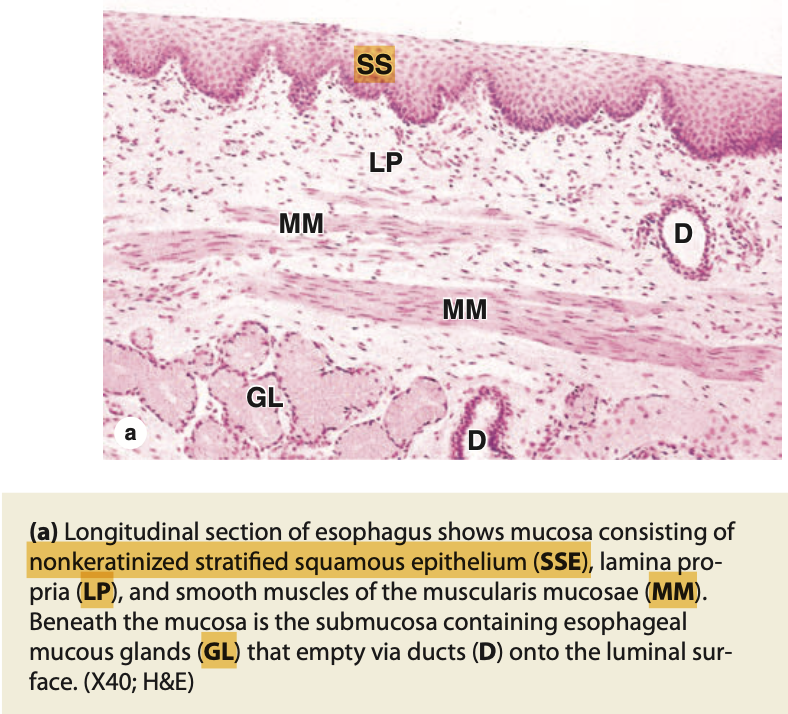

Question 4
What type of muscle is found in the proximal (upper) one-third of the esophagus?
a. Skeletal muscle
b. Smooth muscle
c. Cardiac muscle
d. Mixed skeletal and smooth muscle
Answer: a. Skeletal muscle
解説:
食道の上部1/3は骨格筋(skeletal muscle)で構成されており、嚥下運動を自発的に制御できます。bのsmooth muscleは下部1/3に見られ、dの混合筋は中部1/3に存在します。cのcardiac muscleは心臓にのみ存在します。

Question 5
What is the primary function of the esophageal cardiac glands?
a. Secretion of mucus
b. Production of digestive enzymes
c. Secretion of hydrochloric acid
d. Secretion of bicarbonate
Answer: a. Secretion of mucus
解説:
食道の心臓腺(esophageal cardiac glands)は、酸性環境からの保護のために粘液を分泌します。bの消化酵素やcの塩酸、dの重炭酸は胃や腸で見られる分泌物であり、食道の心臓腺とは関係がありません。
Question 6
Which part of the stomach secretes intrinsic factor and hydrochloric acid?
a. Mucous neck cell
b. Chief cell
c. Parietal cell
d. G cell
Answer: c. Parietal cell
解説:
壁細胞(parietal cell)は、胃の内因子(intrinsic factor)と塩酸(HCl)を分泌します。内因子はビタミンB12の吸収に必要であり、HClは消化のための酸性環境を提供します。aのmucous neck cellは酸性の粘液を分泌し、bのchief cellはペプシノーゲンとリパーゼを分泌します。dのG cellはガストリンを分泌します。

**内因子(Intrinsic Factor)は、胃の壁細胞(Parietal cells)またはオキシンティック細胞(Oxyntic cells)**から分泌される糖タンパク質で、ビタミンB12(コバラミン)の吸収に必要な非常に重要な物質です。
内因子の役割
内因子は、ビタミンB12と結合することで、ビタミンB12が小腸(特に回腸)で吸収されるのを助けます。ビタミンB12は、DNA合成や赤血球の成熟に重要な役割を果たすため、内因子が不足するとビタミンB12欠乏症が生じ、結果として**悪性貧血(Pernicious anemia)**などの深刻な健康問題が引き起こされます。
内因子の分泌過程
- 壁細胞は胃の**体部(body)や底部(fundus)**に主に存在し、内因子と同時に塩酸(HCl)も分泌します。
- ビタミンB12は通常、食物の中に含まれており、胃内で分泌される酵素によってタンパク質から解離されます。
- 解離されたビタミンB12は、内因子と結合し、この複合体が回腸で特定の受容体を介して吸収されます。
内因子が不足する理由
- 自己免疫性疾患: 免疫系が壁細胞や内因子自体を攻撃する場合、内因子の分泌が減少し、ビタミンB12の吸収が妨げられることがあります。これが悪性貧血の原因の一つです。
- 胃の切除手術: 胃の一部や全体を切除した場合、壁細胞の数が減少するため、内因子の分泌も減少します。
内因子はビタミンB12の吸収に不可欠であり、その欠乏は重篤な影響を及ぼすため、正常な消化機能を保つ上で非常に重要な物質です。
Question 7
What type of epithelium lines the stomach?
a. Simple columnar epithelium
b. Nonkeratinizing stratified squamous epithelium
c. Transitional epithelium
d. Simple squamous epithelium
Answer: a. Simple columnar epithelium
解説:
胃は単層円柱上皮(simple columnar epithelium)で覆われており、これが胃の粘膜に深い陥凹を作り、胃酸や酵素を分泌します。bのnonkeratinizing stratified squamous epitheliumは食道に見られ、cのtransitional epitheliumは尿路で、dのsimple squamous epitheliumは血管内皮で見られます。


Question 8
Which part of the digestive tract contains both skeletal and smooth muscle?
a. Proximal esophagus
b. Middle esophagus
c. Distal esophagus
d. Stomach
Answer: b. Middle esophagus
解説:
食道の中部1/3は骨格筋と平滑筋の両方を含んでおり、嚥下運動が上部から下部へ移行するための移行区間です。aの上部1/3は骨格筋のみ、cの下部1/3は平滑筋のみです。dの胃は完全に平滑筋で構成されています。
Question 9
What are the folds of mucosa and submucosa in the stomach called?
a. Rugae
b. Villi
c. Crypts
d. Folds of Kerckring
Answer: a. Rugae
解説:
胃の粘膜と粘膜下層には、胃壁が伸展したときに拡大するためのヒダ(rugae)が存在します。bのvilliは腸の小さな突起であり、cのcryptsは腸に見られる腺のくぼみ、dのfolds of Kerckringは小腸の輪状ヒダです。
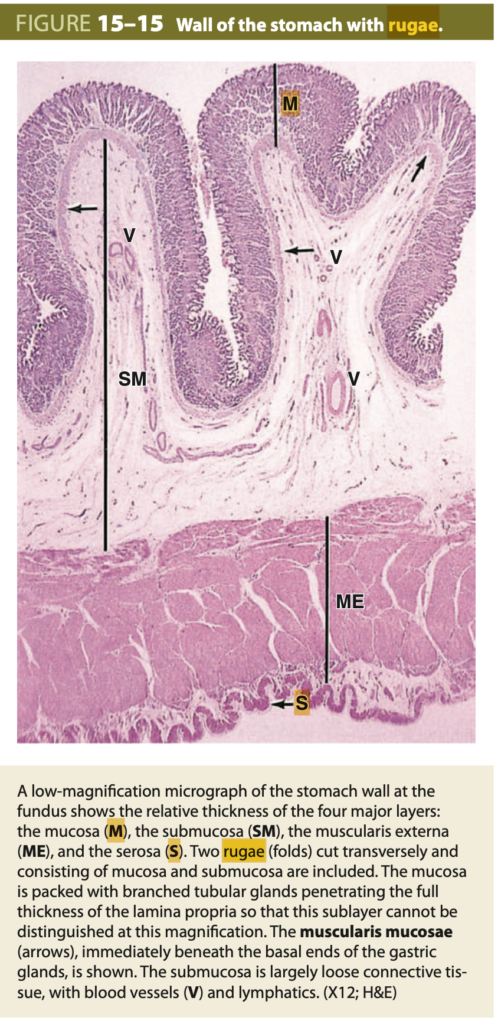
Question 10
What is the function of chief cells in the stomach?
a. Secretion of pepsinogen and gastric lipase
b. Secretion of hydrochloric acid
c. Secretion of intrinsic factor
d. Secretion of mucus
Answer: a. Secretion of pepsinogen and gastric lipase
解説:
主細胞(chief cells)は、ペプシノーゲンと胃リパーゼを分泌します。ペプシノーゲンは酸性環境下でペプシンに変換され、タンパク質の消化に寄与します。bのHClは壁細胞によって分泌され、cの内因子も壁細胞によるものです。dの粘液は粘液細胞によって分泌されます。

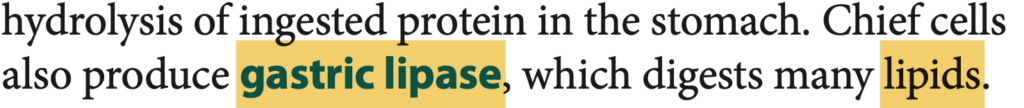
Question 11
What type of cells in the stomach secrete gastrin into the blood?
a. Parietal cells
b. Chief cells
c. G cells
d. Mucous neck cells
Answer: c. G cells
解説:
G細胞はガストリンを分泌し、これにより胃酸の分泌が刺激されます。aのparietal cellsはHClを分泌し、bのchief cellsはペプシノーゲンを分泌し、dのmucous neck cellsは酸性の粘液を分泌します。

Question 12
Which layer of the digestive tract contains the myenteric (Auerbach) plexus?
a. Mucosa
b. Submucosa
c. Muscularis
d. Serosa
Answer: c. Muscularis
解説:
Auerbachの神経叢(myenteric plexus)は、消化管の筋層(muscularis)に位置し、消化管の運動を調整します。aのmucosaやbのsubmucosaにはこの神経叢は含まれておらず、dのserosaは最も外側の層です。
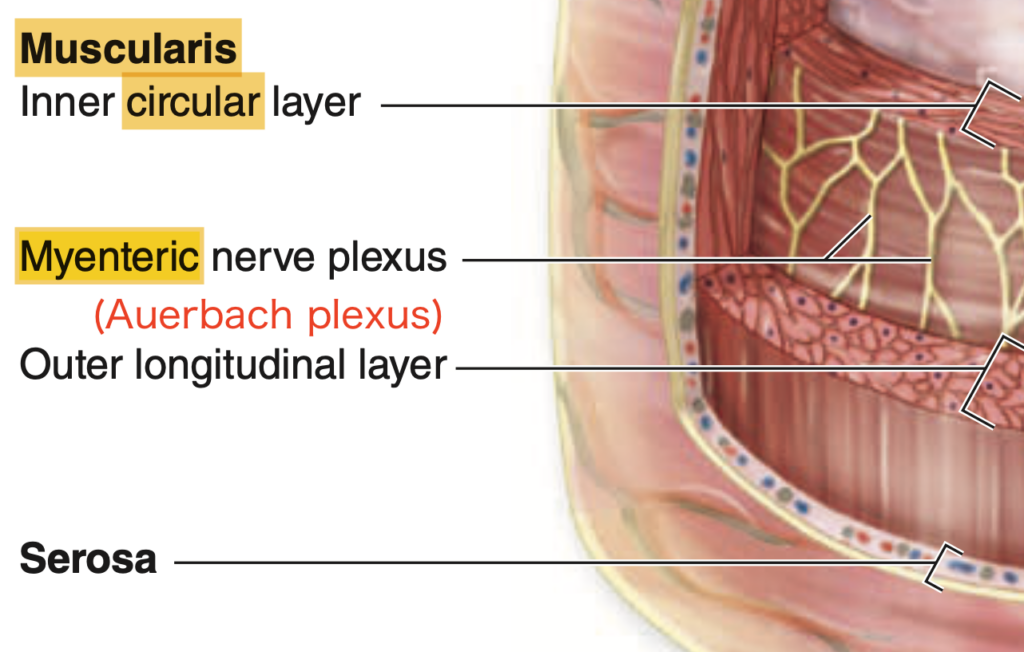
Question 13
What structure is responsible for producing acidic fluid in the stomach?
a. Mucous neck cells
b. Parietal cells
c. Chief cells
d. G cells
Answer: a. Mucous neck cells
解説:
粘液頸細胞(mucous neck cells)は、酸性の粘液を分泌し、胃の内容物を潤滑し保護します。bのparietal cellsはHClを分泌し、cのchief cellsはペプシノーゲンを分泌し、dのG cellsはガストリンを分泌します。
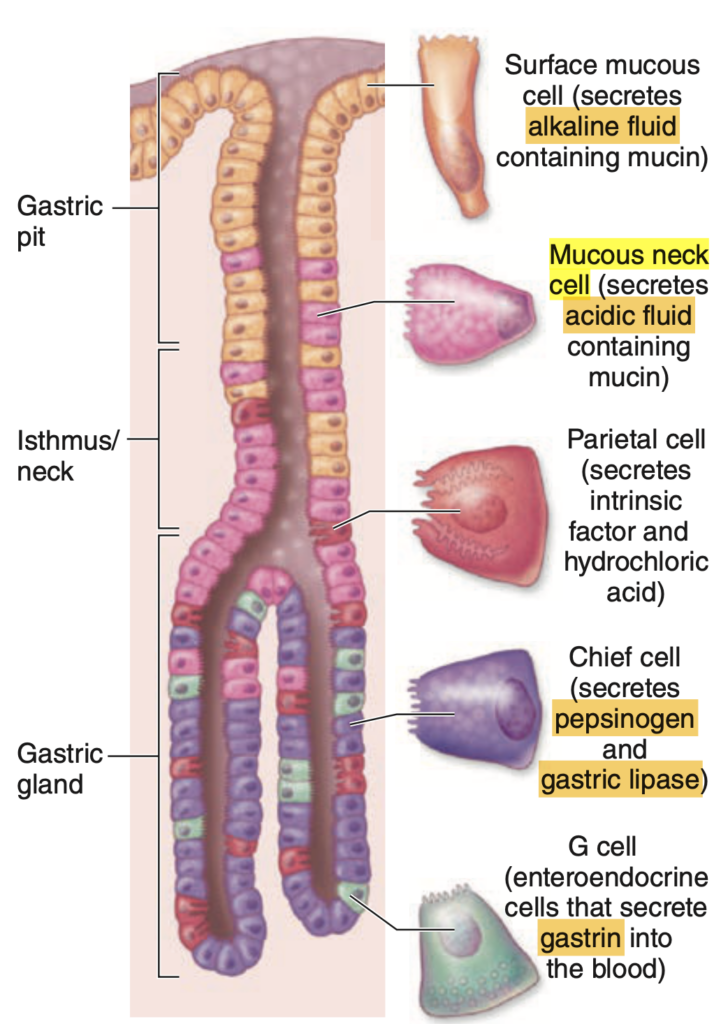
Question 14
Which region of the stomach is closest to the esophagus?
a. Fundus
b. Cardia
c. Body
d. Pylorus
Answer: b. Cardia
解説:
Cardiaは食道に最も近い胃の部分で、食道からの内容物を受け入れます。aのfundusは上部に位置し、cのbodyは胃の主要な部分です。dのpylorusは小腸に最も近い部分です。
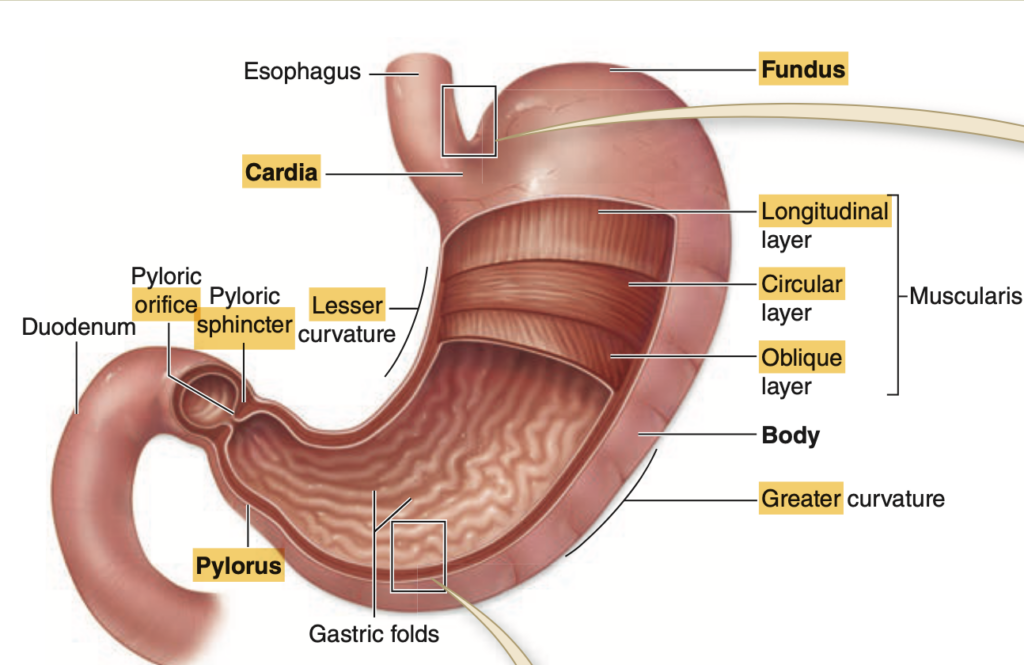
Question 15
Which region of the stomach is closest to the pyloric sphincter?
a. Fundus
b. Cardia
c. Body
d. Pylorus
Answer: d. Pylorus
解説:
幽門(pylorus)は胃の出口に位置し、小腸の十二指腸へとつながっています。aのfundusは胃の上部、bのcardiaは食道に最も近い部分で、cのbodyは胃の中央にあります。したがって、幽門は小腸に最も近い部分です。
Question 16
Which of the following cells in the stomach is responsible for secreting hydrochloric acid?
a. Parietal cells
b. Chief cells
c. G cells
d. Mucous neck cells
Answer: a. Parietal cells
解説:
壁細胞(parietal cells)は胃の酸性環境を作るために塩酸(HCl)を分泌します。bのchief cellsはペプシノーゲンや胃リパーゼを分泌し、cのG cellsはガストリンを分泌します。dのmucous neck cellsは粘液を分泌しますが、酸性の液体ではありません。
Question 17
What is the function of the submucosal (Meissner) plexus?
a. Controls the secretions of the digestive tract
b. Controls the muscular contractions of the digestive tract
c. Absorbs nutrients from digested food
d. Produces mucus in the digestive tract
Answer: a. Controls the secretions of the digestive tract
解説:
Meissnerの神経叢(submucosal plexus)は、消化管の腺の分泌や血管の動きを調節します。bのAuerbach(myenteric )の神経叢は筋肉の収縮を制御します。cは腸の機能で、栄養吸収に関連しています。dの粘液分泌は腺や細胞の働きであり、神経叢自体ではありません。
Question 18
Which of the following regions of the stomach contains the majority of gastric glands?
a. Cardia
b. Pylorus
c. Body
d. Fundus
Answer: c. Body
解説:
胃の中央部であるボディ(body)は、胃酸や酵素を分泌するための多数の胃腺を含んでいます。aのcardiaとbのpylorusには比較的少数の胃腺が存在し、dのfundusも胃腺は含んでいますが、数はボディほど多くありません。

Question 19 ★
What type of connective tissue is primarily found in the submucosa layer?
a. Loose connective tissue
b. Dense connective tissue
c. Adipose tissue
d. Reticular connective tissue
Answer: b. Dense connective tissue
解説:
粘膜下層(submucosa)は主に密な結合組織(dense connective tissue)で構成され、血管や神経、腺を支えています。aのloose connective tissueは一般に粘膜の固有層に見られ、cのadipose tissueは脂肪組織で、消化管の層には少ないです。dのreticular connective tissueはリンパ系に関連しています。
Question 20
Which part of the digestive tract contains both serosa and adventitia?
a. Esophagus
b. Stomach
c. Small intestine
d. Large intestine
Answer: a. Esophagus
解説:
食道の遠位部(distal 1-2cm)は漿膜(serosa)で覆われていますが、他の部分は周囲の構造物にしっかりと接続するために外膜(adventitia)を持ちます。bの胃やcの小腸、dの大腸は主に漿膜で覆われています。
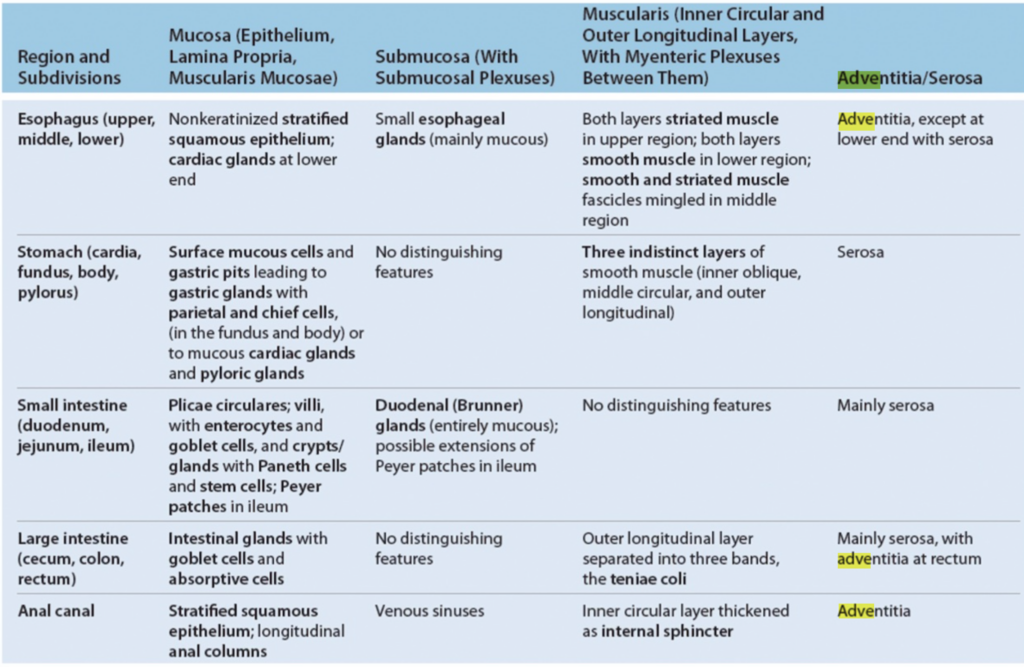
Question 1 ★
Which hormone is produced by D cells and inhibits the secretion of other nearby DNES cells?
a. Gastrin
b. Somatostatin
c. Cholecystokinin (CCK)
d. Secretin
Answer: b. Somatostatin
解説:
D細胞はソマトスタチンを分泌し、他のDNES(diffuse neuroendocrine system)細胞の分泌を抑制します。aのガストリンはG細胞から分泌され、胃酸分泌を刺激します。cのCCKはI細胞から分泌され、膵臓酵素や胆嚢収縮を促します。dのセクレチンはS細胞から分泌され、膵臓や胆道からの重炭酸塩の分泌を促進します。
Question 2
Which cells produce gastrin and are primarily located in the pylorus?
a. D cells
b. G cells
c. K cells
d. Mo cells
Answer: b. G cells
解説:
G細胞は胃の幽門(pylorus)に多く存在し、ガストリンを分泌して胃酸の分泌を促進します。aのD細胞はソマトスタチンを分泌し、cのK細胞はGIP(Gastric inhibitory polypeptide)を分泌します。dのMo細胞はモチリンを分泌し、胃の排出を促します。
Question 3 ★
Which hormone, produced by EC cells, increases gut motility?
a. Somatostatin
b. Secretin
c. Serotonin
d. Cholecystokinin (CCK)
Answer: c. Serotonin
解説:
EC細胞はセロトニンを分泌し、腸の運動(gut motility)を促進します。aのソマトスタチンは分泌を抑制し、bのセクレチンは膵臓と胆道からの重炭酸塩分泌を促進し、dのCCKは膵臓酵素の分泌と胆嚢収縮を促進しますが、直接的な腸運動促進の役割はありません。
Question 4
Which hormone, produced by I cells, promotes pancreatic enzyme secretion and gallbladder contraction?
a. Gastrin
b. Cholecystokinin (CCK)
c. Glucagon-like peptide (GLP-1)
d. Motilin
Answer: b. Cholecystokinin (CCK)
解説:
I細胞はCCK(Cholecystokinin)を分泌し、膵臓からの消化酵素分泌と胆嚢収縮を促進します。aのガストリンは胃酸分泌を刺激し、cのGLP-1はインスリン分泌を促進し、dのモチリンは腸管運動を調整します。
Question 5 ★
Which cells in the duodenum and jejunum secrete gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP)?
a. I cells
b. K cells
c. D cells
d. G cells
Answer: b. K cells
解説:
K細胞は十二指腸と空腸に存在し、GIP(Gastric inhibitory polypeptide)を分泌してインスリン分泌を促進します。aのI細胞はCCKを分泌し、cのD細胞はソマトスタチンを分泌し、dのG細胞はガストリンを分泌します。
Question 6
Which hormone, produced by L cells in the ileum and colon, promotes insulin secretion?
a. Gastrin
b. Glucagon-like peptide (GLP-1)
c. Secretin
d. Neurotensin
Answer: b. Glucagon-like peptide (GLP-1)
解説:
L細胞はGLP-1(Glucagon-like peptide-1)を分泌し、インスリンの分泌を促進します。aのガストリンは胃酸分泌を刺激し、cのセクレチンは膵臓と胆道からの重炭酸塩分泌を促進し、dのニューロテンシンは胃酸分泌を抑制します。
Question 7
Which hormone, produced by S cells, stimulates the secretion of bicarbonate from the pancreas and bile ducts?
a. Somatostatin
b. Secretin
c. Cholecystokinin (CCK)
d. Serotonin
Answer: b. Secretin
解説:
S細胞はセクレチンを分泌し、膵臓および胆管からの重炭酸塩の分泌を刺激して胃酸の中和を助けます。aのソマトスタチンは分泌を抑制し、cのCCKは膵酵素の分泌と胆嚢収縮を促し、dのセロトニンは腸の運動を促進します。
Question 8 ★
Which hormone, produced by L cells in the ileum and colon, is involved in the absorption of water and electrolytes in the large intestine?
a. Peptide YY
b. Gastrin
c. Motilin
d. Neurotensin
Answer: a. Peptide YY
解説:
L細胞はペプチドYY(Peptide YY)を分泌し、大腸での水分と電解質の吸収を促進します。bのガストリンは胃酸分泌を刺激し、cのモチリンは腸管の運動を調整し、dのニューロテンシンは胃酸分泌を抑制します。
Question 9
Which hormone, produced by Mo cells, increases gut motility and stimulates stomach emptying?
a. Cholecystokinin (CCK)
b. Motilin
c. Secretin
d. Gastrin
Answer: b. Motilin
解説:
Mo細胞はモチリンを分泌し、胃の排出を刺激し、腸の蠕動運動を促進します。aのCCKは膵酵素と胆嚢収縮を促し、cのセクレチンは膵臓と胆道からの重炭酸塩分泌を促し、dのガストリンは胃酸分泌を刺激します。
Question 10 ★
Which hormone, produced by N cells in the ileum, inhibits gastric acid secretion?
a. Somatostatin
b. Secretin
c. Neurotensin
d. Peptide YY
Answer: c. Neurotensin
解説:
N細胞はニューロテンシンを分泌し、胃酸分泌を抑制します。aのソマトスタチンも分泌を抑制しますが、S細胞が分泌します。bのセクレチンは重炭酸塩分泌を刺激し、dのペプチドYYは水分と電解質の吸収を促進します。

Question 1 ★
Which of the following layers is absent in the submucosa of the stomach?
a. Glands
b. Blood vessels
c. Nerves
d. Lymphoid tissue
Answer: a. Glands
解説:
胃の粘膜下層(submucosa)には腺(glands)は存在しません。他の組織層とは異なり、胃では粘膜下層に腺が含まれないため、選択肢aが正しいです。選択肢bの血管やcの神経は、粘膜下層に存在し、dのリンパ組織も存在しますが、腺は存在しません。
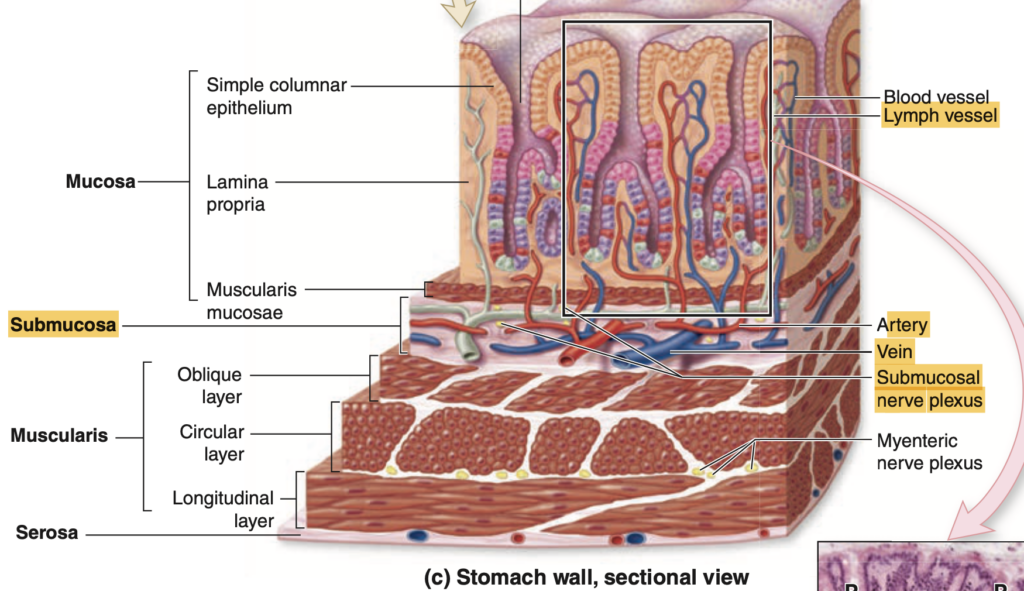
Question 2
How many layers of muscle are found in the muscularis of the stomach?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
Answer: c. 3
解説:
胃の筋層(muscularis)は3層の平滑筋で構成されています。それぞれ、内斜筋(inner oblique)、中輪状筋(middle circular)、外縦筋(outer longitudinal)です。これにより、胃の内容物を効果的に混ぜたり、移動させたりすることができます。選択肢aとbは正しくなく、dは胃には存在しない層の数です。
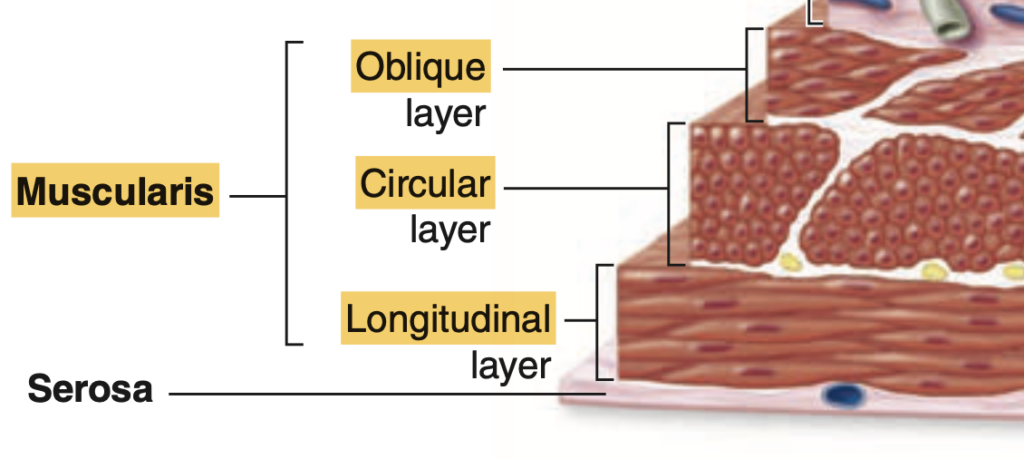
Question 3
Which of the following is a unique feature of the small intestine’s mucosa?
a. Plicae circulares
b. Taenia coli
c. Haustra
d. Appendices epiploicae
Answer: a. Plicae circulares
解説:
小腸の粘膜には、輪状ヒダ(plicae circulares)があり、消化吸収を助けるために表面積を増やしています。bのtaenia coliとcのhaustraは大腸に見られ、dのappendices epiploicaeは大腸の横行結腸とS状結腸に存在します。

Question 4 ★
Which glands are found in the lamina propria of the duodenum?
a. Brunner’s glands
b. Peyer’s patches
c. Gastric glands
d. Esophageal glands
Answer: a. Brunner’s glands
解説:
Brunner腺は十二指腸の固有層(lamina propria)に存在し、粘液を分泌して胃酸を中和し、腸の粘膜を保護します。bのPeyer’s patchesは回腸に見られるリンパ組織で、cの胃腺は胃に存在し、dの食道腺は食道に存在します。
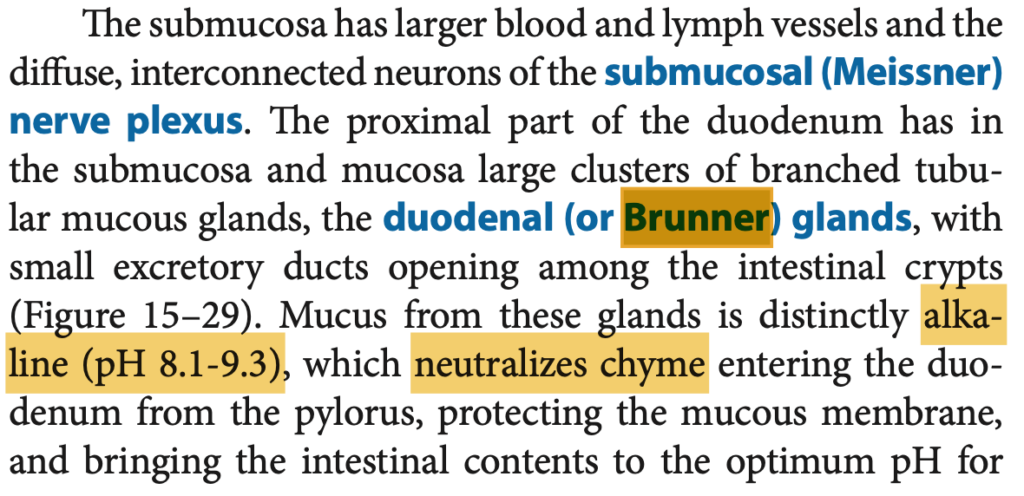

Question 5 ★
Which of the following cells in the small intestine is responsible for absorption?
a. Goblet cells
b. Enterocytes
c. Paneth cells
d. Enteroendocrine cells
Answer: b. Enterocytes
解説:
腸細胞(enterocytes)は小腸の主な吸収細胞であり、栄養素の吸収を行います。aのgoblet cellsは粘液を分泌し、cのPaneth cellsは抗菌物質を分泌し、dのenteroendocrine cellsはホルモンを分泌しますが、栄養吸収に関与するのはenterocytesです。


Question 6
Which feature is unique to the large intestine and is formed by the outer layer of the muscularis?
a. Plicae circulares
b. Taenia coli
c. Villi
d. Brunner’s glands
Answer: b. Taenia coli
解説:
大腸の外側の筋層は3つの幅広い縦の筋帯であるtaenia coliに凝縮され、これが大腸に特有のハウストラ(sacculations、袋状の膨らみ)を形成します。aのplicae circularesは小腸に、cのvilliも小腸に存在し、dのBrunner’s glandsは十二指腸にあります。

Question 7
Which type of epithelium lines the mucosa of the large intestine?
a. Stratified squamous epithelium
b. Simple columnar epithelium
c. Simple squamous epithelium
d. Transitional epithelium
Answer: b. Simple columnar epithelium
解説:
大腸の粘膜は単層円柱上皮(simple columnar epithelium)で覆われ、ゴブレット細胞を含み、粘液を分泌して大腸内容物を潤滑します。aの重層扁平上皮は食道や肛門管に見られ、cの単層扁平上皮は主に血管内皮に、dの移行上皮は尿路に見られます。
Question 8 ★
Which of the following structures is a characteristic feature of the transverse and sigmoid colon?
a. Peyer’s patches
b. Appendices epiploicae
c. Villi
d. Gastric pits
Answer: b. Appendices epiploicae
解説:
横行結腸とS状結腸の外側には脂肪が充填された小さなポケットである「腹膜付属物」(appendices epiploicae)が存在します。aのPeyer’s patchesは回腸に見られ、cのvilliは小腸に存在し、dの胃小窩(gastric pits)は胃に見られます。
Question 9
Which of the following segments of the digestive tract contains both inner circular and outer longitudinal muscle layers, with the outer layer condensed into taenia coli?
a. Small intestine
b. Stomach
c. Large intestine
d. Esophagus
Answer: c. Large intestine
解説:
大腸の筋層は内側の輪状筋と外側の縦筋で構成されており、外側の筋はtaenia coliとして凝縮されています。aの小腸やbの胃も筋層がありますが、大腸特有の特徴ではありません。dの食道もこの特徴を持ちません。
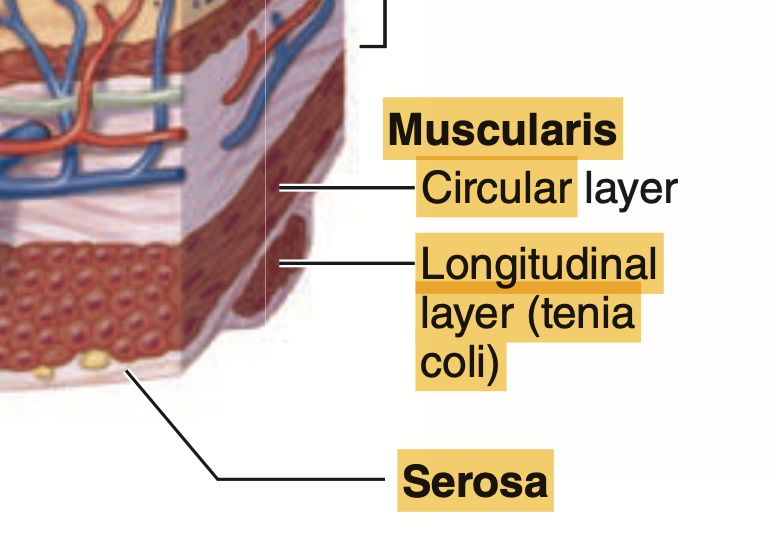
Question 10
Which of the following is a function of the goblet cells in the large intestine?
a. Absorption of nutrients
b. Secretion of digestive enzymes
c. Secretion of mucus
d. Production of bile
Answer: c. Secretion of mucus
解説:
ゴブレット細胞は大腸で粘液を分泌し、糞便の移動を滑らかにします。aの栄養吸収は腸細胞(colonocytes)によって行われ、bの消化酵素分泌は主に胃や膵臓で行われます。dの胆汁の生成は肝臓で行われます。
Question 11
Which structure is responsible for forming sacculations (haustra) in the large intestine?
a. Inner circular muscle layer
b. Taenia coli
c. Villi
d. Plicae circulares
Answer: b. Taenia coli
解説:
Taenia coliは大腸の筋層の外側の3つの筋帯であり、これが収縮することで袋状の膨らみ(haustra)を形成します。aの内側の輪状筋は腸全体で見られ、cのvilliは小腸に、dのplicae circularesは小腸の輪状ヒダです。
Question 12 ★
Which type of epithelium is found in the mucosa of the anal canal?
a. Simple columnar epithelium
b. Stratified squamous epithelium
c. Transitional epithelium
d. Simple squamous epithelium
Answer: b. Stratified squamous epithelium
解説:
肛門管の粘膜は重層扁平上皮(stratified squamous epithelium)で覆われ、摩擦に対する耐性を持っています。aの単層円柱上皮は小腸や大腸で見られ、cの移行上皮は尿路に、dの単層扁平上皮は主に血管内皮に見られます。
Question 13
Which glands are found in the submucosa of the duodenum?
a. Brunner’s glands
b. Peyer’s patches
c. Gastric glands
d. Esophageal glands
Answer: a. Brunner’s glands
解説:
Brunner腺は十二指腸の粘膜下層(submucosa)にあり、粘液を分泌して酸を中和し、腸粘膜を保護します。bのPeyer’s patchesは回腸に見られ、cの胃腺は胃に、dの食道腺は食道に存在します。
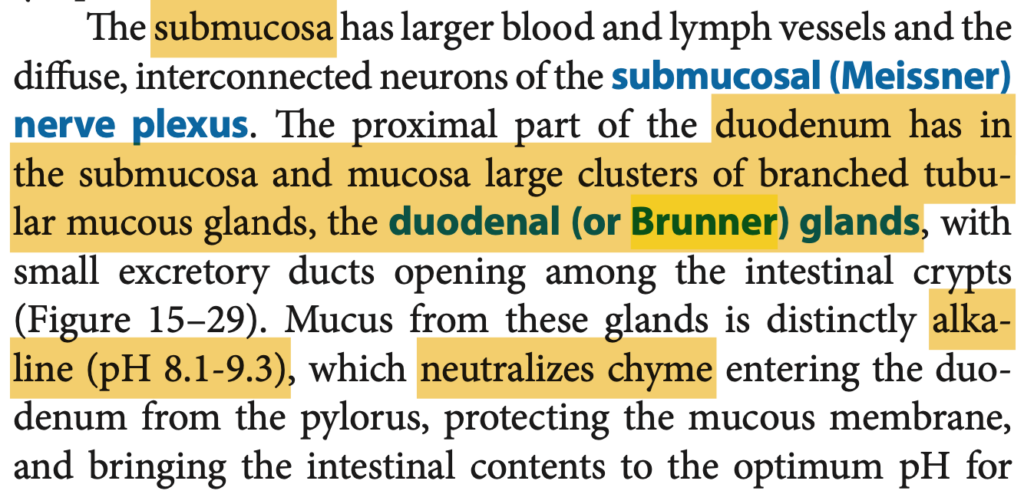

Question 14
Which feature of the small intestine increases the surface area for absorption?
a. Plicae circulares
b. Taenia coli
c. Haustra
d. Appendices epiploicae
Answer: a. Plicae circulares
解説:
小腸の輪状ヒダ(plicae circulares)は、粘膜の表面積を増やして吸収効率を高める役割を果たします。bのtaenia coliとcのhaustraは大腸に関連し、dのappendices epiploicaeは横行結腸とS状結腸に見られます。
Question 15 ★
What is the function of Paneth cells in the small intestine?
a. Secretion of mucus
b. Absorption of nutrients
c. Secretion of antimicrobial peptides
d. Production of digestive enzymes
Answer: c. Secretion of antimicrobial peptides
解説:
Paneth細胞は小腸に存在し、抗菌ペプチドを分泌して腸内の微生物バランスを保つ役割を果たします。aの粘液分泌はゴブレット細胞によって行われ、bの栄養吸収は腸細胞(enterocytes)によって行われ、dの消化酵素は主に膵臓から分泌されます。

Question 16
Which part of the large intestine is responsible for forming and storing feces before defecation?
a. Cecum
b. Rectum
c. Ascending colon
d. Transverse colon
Answer: b. Rectum
解説:
直腸(rectum)は排便前に糞便を形成し、保存する役割を果たします。aの盲腸(cecum)は大腸の最初の部分であり、cの上行結腸やdの横行結腸は主に水分と電解質の吸収に関与します。
Question 17 ★
Which cells in the small intestine are responsible for hormone secretion?
a. Enterocytes
b. Goblet cells
c. Enteroendocrine cells
d. Paneth cells
Answer: c. Enteroendocrine cells
解説:
内分泌細胞(enteroendocrine cells)はホルモンを分泌し、消化の調節に重要な役割を果たします。aのenterocytesは栄養吸収を行い、bのgoblet cellsは粘液を分泌し、dのPaneth cellsは抗菌物質を分泌します。
Question 18 ★
Which of the following best describes the muscularis layer of the small intestine?
a. Inner oblique, middle circular, outer longitudinal
b. Inner circular, outer longitudinal
c. Inner circular, middle oblique, outer longitudinal
d. Only circular muscle
Answer: b. Inner circular, outer longitudinal
解説:
小腸の筋層(muscularis)は内輪筋(inner circular)と外縦筋(outer longitudinal)から構成されています。この二重構造により、腸の蠕動運動が可能になります。選択肢aとcは胃の筋層に見られる構造であり、dは誤りです。
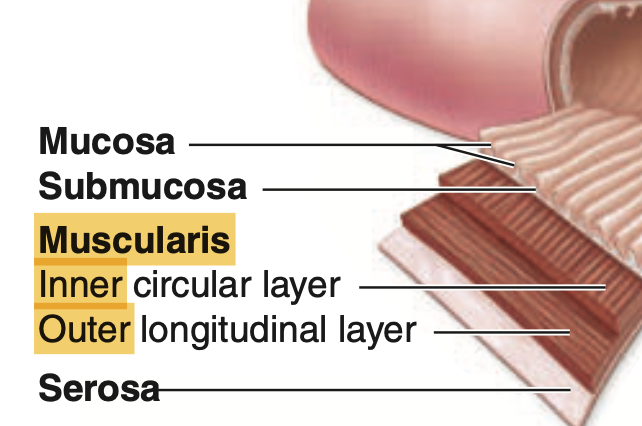
Question 19
Which of the following is NOT found in the large intestine?
a. Taenia coli
b. Haustra
c. Plicae circulares
d. Goblet cells
Answer: c. Plicae circulares
解説:
輪状ヒダ(plicae circulares)は小腸に見られ、大腸には存在しません。aのtaenia coliやbのhaustraは大腸の特徴であり、dのgoblet cellsは大腸で粘液を分泌します。
Question 20
Which structure helps to control defecation in the anal canal?
a. Haustra
b. Internal anal sphincter
c. Taenia coli
d. Appendices epiploicae
Answer: b. Internal anal sphincter
解説:
内肛門括約筋(internal anal sphincter)は排便を制御するための重要な平滑筋層です。aのhaustraやcのtaenia coliは大腸の特徴であり、dのappendices epiploicaeは横行結腸とS状結腸に存在しますが、排便の制御には関与していません。
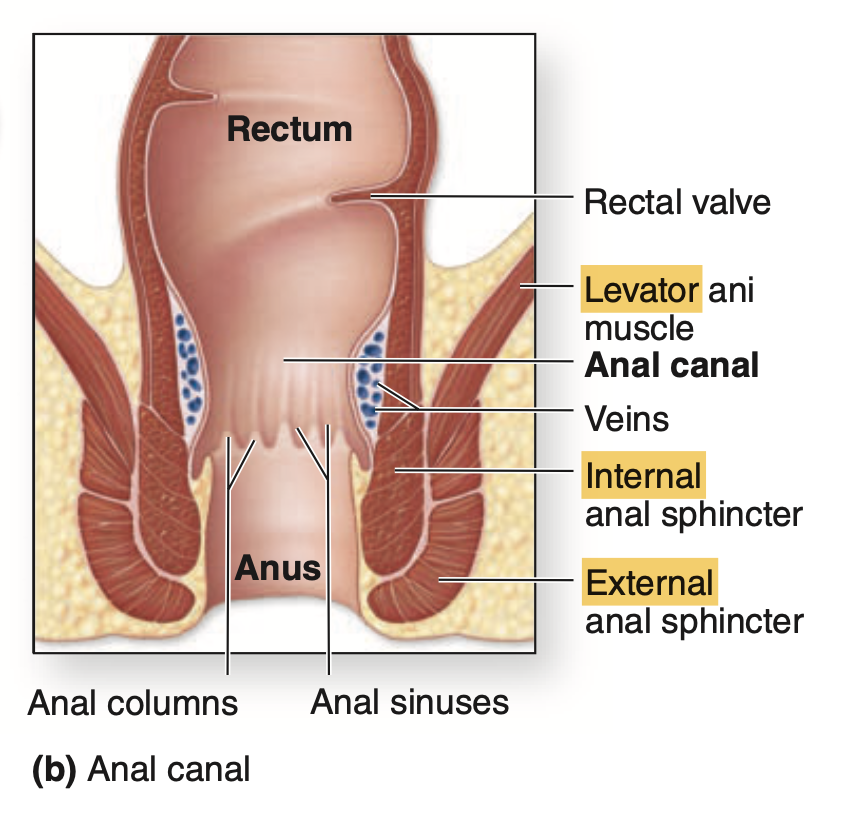
内肛門括約筋 (Internal Anal Sphincter)
- 神経支配: 自律神経系(autonomic nervous system)によって制御されています。具体的には、交感神経と副交感神経が関与します。
- 交感神経(Sympathetic Nervous System): 内肛門括約筋を収縮させ、肛門を閉じる役割を担います。交感神経の支配は、**下腹神経(hypogastric nerve)**を通じて行われます。交感神経は排便を抑制し、肛門を閉じた状態に保つ働きがあります。
- 副交感神経(Parasympathetic Nervous System): 内肛門括約筋を弛緩させ、排便を促進します。副交感神経の支配は、**骨盤神経(pelvic nerve)**を介して行われます。副交感神経が作用すると、筋肉が弛緩して肛門が開き、便が排出される準備が整います。
外肛門括約筋 (External Anal Sphincter)
- 神経支配: 随意神経(somatic nervous system)によって制御されています。これは、自分の意思でコントロールできる骨格筋であるため、体性神経系が関与しています。
- 陰部神経(Pudendal Nerve): 外肛門括約筋は、主に**陰部神経(S2-S4)**の支配を受けています。この神経は、外肛門括約筋を随意的に収縮させたり弛緩させたりすることを可能にします。これにより、排便を意識的にコントロールすることができ、必要に応じて肛門を閉じたり開いたりすることができます。
機能的な協調
排便の際、まず副交感神経が内肛門括約筋を弛緩させますが、外肛門括約筋は陰部神経を介して随意的に収縮することができるため、排便のタイミングを調整できます。このように、自律神経と随意神経の協調が肛門括約筋の働きを制御しています。


コメント