Contents
- 1 ブロック(呼吸)
- 1.1 Question 1:
- 1.2 Question 2:
- 1.3 Question 3:
- 1.4 Question 4:
- 1.5 Question 5:
- 1.6 Question 6:
- 1.7 Question 7:
- 1.8 Question 8:
- 1.9 Question 9:
- 1.10 Question 10:
- 1.11 Question 12:
- 1.12 Question 13:
- 1.13 Question 14:
- 1.14 Question 15:
- 1.15 Question 16:
- 1.16 Question 17:
- 1.17 Question 18:
- 1.18 Question 19:
- 1.19 Question 20:
- 1.20 Question 21:
- 1.21 Question 22:
- 1.22 Question 23:
- 1.23 Question 24:
- 1.24 Question 25:
- 1.25 Question 26:
- 1.26 Question 27:
- 1.27 Question 28:
- 1.28 Question 29:
- 1.29 Question 30:
- 1.30 Question 31:
- 1.31 Question 32:
- 1.32 Question 33:
- 1.33 Question 34:
- 1.34 Question 35:
- 1.35 Question 36:
- 1.36 Question 37:
- 1.37 Question 38:
- 1.38 Question 39:
- 1.39 Question 40:
- 1.40 Question 41:
- 1.41 Question 42:
- 1.42 Question 43:
- 1.43 Question 44:
- 1.44 Question 45:
- 1.45 Question 46:
- 1.46 Question 47:
- 1.47 Question 48:
- 1.48 Question 49:
- 1.49 Question 50:
- 2 PPTより自作(細胞障害、細胞死、適応)
- 2.1 Question 1:
- 2.2 Question 2:
- 2.3 Question 3:
- 2.4 Question 4:
- 2.5 Question 5:
- 2.6 Question 6:
- 2.7 Question 7:
- 2.8 Question 8:
- 2.9 Question 9:
- 2.10 Question 10:
- 2.11 Question 11:
- 2.12 Question 12:
- 2.13 Question 13:
- 2.14 Question 14:
- 2.15 Question 15:
- 2.16 Question 16:
- 2.17 Question 17:
- 2.18 Question 18:
- 2.19 Question 19:
- 2.20 Question 20:
- 3 アセス(呼吸)
- 3.1 Question 1:
- 3.2 Question 2:
- 3.3 Question 3:
- 3.4 Question 4:
- 3.5 Question 5:
- 3.6 Question 6:
- 3.7 Question 7:
- 3.8 Question 8:
- 3.9 Question 9:
- 3.10 Question 10:
- 3.11 Question 11:
- 3.12 Question 12:
- 3.13 Question 13:
- 3.14 Question 14:
- 3.15 Question 15:
- 3.16 Question 16:
- 3.17 Question 17:
- 3.18 Question 18:
- 3.19 Question 19:
- 3.20 Question 20:
- 3.21 Question 21:
- 3.22 Question 22:
- 3.23 Question 23:
- 3.24 Question 24:
- 3.25 Question 25:
- 4 自作問題(呼吸:ナバスカス)
- 4.1 Question 1:
- 4.2 Question 2:
- 4.3 Question 3:
- 4.4 Question 4:
- 4.5 Question 5:
- 4.6 Question 6:
- 4.7 Question 7:
- 4.8 Question 8:
- 4.9 Question 9:
- 4.10 Question 10:
- 4.11 Question 11:
- 4.12 Question 12:
- 4.13 Question 13:
- 4.14 Question 14:
- 4.15 Question 15:
- 4.16 Question 16:
- 4.17 Question 17:
- 4.18 Question 18:
- 4.19 Question 19:
- 4.20 Question 20:
ブロック(呼吸)
Question 1:
A 12-year-old boy presents with a history of coughing, wheezing, and repeated episodes of difficulty breathing. Laboratory results show an elevated serum IgE level and peripheral blood eosinophilia, concomitant with asthma. Which of the following cells is responsible for removing inhaled dust, bacteria, and particulate matter trapped in the pulmonary surfactant?
- A) Alveolar macrophages
- B) Dust cells
- C) Mononuclear phagocytes
- D) All of the above
Answer: D) All of the above
Explanation (日本語): 肺胞マクロファージ(alveolar macrophages)は、「塵細胞(dust cells)」とも呼ばれ、単核食細胞系に属する細胞です。これらの細胞は、吸入された塵、細菌、その他の異物を取り込み、肺の防御機構に貢献しています。これにより、肺サーファクタントに捕捉された異物を除去し、肺を清浄に保つ役割を果たします。したがって、これらすべてが正解となります。
Question 2:
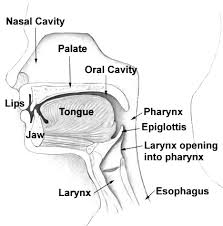
Which of the following parts of the pharynx is lined by respiratory epithelium?
- A) Nasopharynx
- B) Oropharynx
- C) Laryngopharynx
- D) None of the above
Answer: A) Nasopharynx
Explanation (日本語): 鼻咽頭(nasopharynx)は呼吸器上皮で覆われています。この上皮は、多列線毛円柱上皮(pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium)であり、粘液産生細胞(goblet cells)を含んでいます。この構造は、空気中の異物や病原体を捕捉し、咳や嚥下によって体外へ排出する機能を持っています。口咽頭(oropharynx)および喉頭咽頭(laryngopharynx, Hypopharynx)は重層扁平上皮(stratified squamous epithelium)で覆われており、異なる機能を持っています。
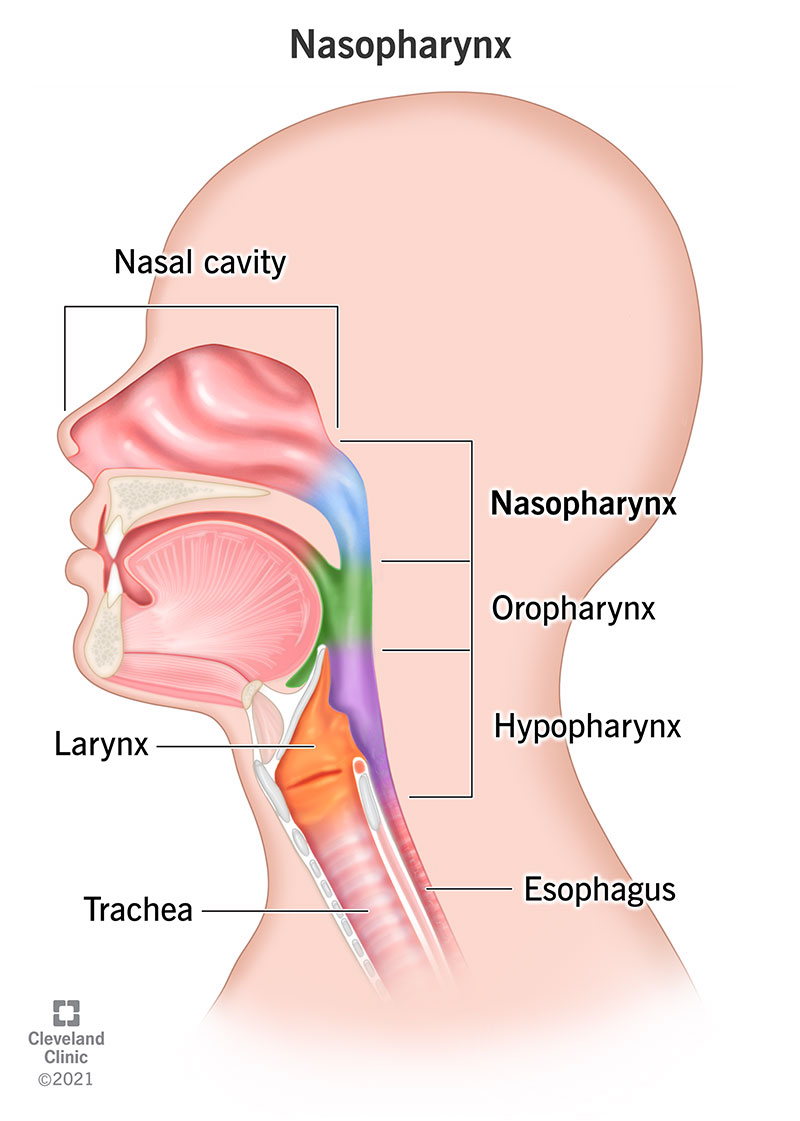
| 部位 | 上皮の種類 | 特徴 |
|---|---|---|
| 鼻咽頭 (Nasopharynx) | 多列線毛円柱上皮 (Pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium) | 杯細胞 (Goblet cells) を含み、異物を捕捉して排出 |
| 口咽頭 (Oropharynx) | 重層扁平上皮 (Stratified squamous epithelium) | 機械的ストレスに対する保護 (Protects against mechanical stress) |
| 喉頭咽頭 (Laryngopharynx, Hypopharynx) | 重層扁平上皮 (Stratified squamous epithelium) | 機械的ストレスに対する保護 (Protects against mechanical stress) |
Question 3:
A 42-year-old man comes to the physician due to a history of increasing shortness of breath. Physical examination reveals a 1 cm laceration in the posterior portion of the vestibule. What is the lining epithelium of this affected area?
- A) Simple squamous epithelium
- B) Stratified squamous epithelium
- C) Pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium with goblet cells
- D) Cuboidal epithelium
Answer: C) Pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium with goblet cells
Explanation (日本語): 鼻前庭部の後部は、主に多列線毛円柱上皮(pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium)と杯細胞(goblet cells)で覆われています。この上皮は、吸入した異物を捕捉し、線毛の運動によって排出する機能を持っています。一方、鼻前庭の外部は重層扁平上皮(stratified squamous epithelium)で覆われていますが、後部になると呼吸器上皮が見られます。
| 部位 | 上皮の種類 | 特徴 |
|---|---|---|
| 鼻前庭の外部 (Anterior part) | 重層扁平上皮 (Stratified squamous epithelium) | 機械的ストレスに対する保護 (Protects against mechanical stress) |
| 鼻前庭の後部 (Posterior part) | 多列線毛円柱上皮 (Pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium) | 杯細胞 (Goblet cells) を含み、異物を捕捉し排出 (Traps and removes foreign particles) |
Question 4:
Which of the following is a correct association?
- A) Terminal bronchioles: simple squamous epithelium
- B) Alveolar ducts: pseudostratified columnar epithelium
- C) Respiratory bronchioles: simple cuboidal epithelium
- D) Intrapulmonary bronchi: pseudostratified columnar epithelium with goblet cells
Answer: D) Intrapulmonary bronchi: pseudostratified columnar epithelium with goblet cells
Explanation (日本語): 肺内気管支(intrapulmonary bronchi)は、多列線毛円柱上皮(pseudostratified columnar epithelium)で覆われ、杯細胞(goblet cells)を含んでいます。この構造は、気道に入った異物を線毛の運動により排除する役割を果たします。一方、終末細気管支(terminal bronchioles)は単層立方上皮(simple cuboidal epithelium)で覆われ、線毛を持つClara細胞も見られます。
| 構造 | 上皮の種類 |
|---|---|
| 終末細気管支 (Terminal bronchioles) | 単層扁平上皮 (Simple squamous epithelium), 線毛を持つClara細胞 |
| 肺胞管 (Alveolar ducts) | 多列線毛円柱上皮 (Pseudostratified columnar epithelium) |
| 呼吸細気管支 (Respiratory bronchioles) | 単層立方上皮 (Simple cuboidal epithelium), Clara細胞 |
| 肺内気管支 (Intrapulmonary bronchi) | 杯細胞を含む多列線毛円柱上皮 (Pseudostratified columnar epithelium with goblet cells) |
Question 5:
A 35-year-old pregnant woman in her third trimester experiences severe hypogastric pain and irregular abdominal contractions. She is given a dose of steroids to prevent neonatal hyaline membrane disease. Which cells are likely underdeveloped in this condition?
- A) Type I pneumocytes
- B) Type II pneumocytes
- C) Clara cells
- D) Dust cells
Answer: B) Type II pneumocytes
Explanation (日本語): ヒアリン膜病(hyaline membrane disease)は、未熟児に見られる呼吸窮迫症候群の一種であり、主に肺サーファクタントを分泌するII型肺胞上皮細胞(type II pneumocytes)の未発達が原因です。サーファクタントの不足により、肺胞が適切に膨張できず、呼吸困難が生じます。ステロイドはこれらの細胞の成熟を促進し、呼吸窮迫のリスクを軽減します。
Question 6:
A 55-year-old man has experienced increasing respiratory difficulty for the past 18 months. A chest radiograph shows diffuse interstitial disease with no masses or hilar adenopathy. A biopsy reveals a blockage at the root of the lung extending along the bronchial tree. Which major blood vessel is likely affected?
- A) Pulmonary artery
- B) Pulmonary vein
- C) Bronchial artery
- D) Superior vena cava
Answer: A) Pulmonary artery
Explanation (日本語): 肺動脈(pulmonary artery)は、肺へ酸素を取り込む前の静脈血を運ぶ主要な血管です。このケースでは、肺門(root of the lung)に沿って広がる病変が見られ、肺動脈が影響を受ける可能性が高いです。気管支動脈(bronchial artery)は肺への酸素化された血液の供給を担当しており、肺動脈ほど広範囲には影響しません。
Question 7:
A 40-year-old man presents with an increasing cough and hemoptysis for 2 weeks. A chest radiograph shows consolidation in the upper right lobe. The pathology reads squamous cell carcinoma. What is the typical lining epithelium of the bronchi before this pathological change?
- A) Simple squamous epithelium
- B) Pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium with goblet cells
- C) Simple cuboidal epithelium
- D) Stratified squamous epithelium
Answer: B) Pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium with goblet cells
Explanation (日本語): 気管支(bronchi)は、通常多列線毛円柱上皮(pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium)で覆われ、杯細胞(goblet cells)が粘液を分泌します。扁平上皮癌(squamous cell carcinoma)は、これらの正常な上皮細胞が癌化し、扁平上皮に変化することで発生します。この変化により、上皮の保護機能が損なわれます。
Question 8:
Which of the following structures is involved in gas exchange?
- A) Terminal bronchioles
- B) Alveoli
- C) Trachea
- D) Nasal cavity
Answer: B) Alveoli
Explanation (日本語): ガス交換が行われる主な部位は肺胞(alveoli)です。肺胞は、非常に薄い単層扁平上皮で覆われ、酸素と二酸化炭素の交換が可能です。終末細気管支(terminal bronchioles)は気道の導管部に属し、ガス交換には直接関与していません。
Question 9:
What type of connective tissue is present in the interalveolar septum?
- A) Dense regular connective tissue
- B) Elastic fibers and reticular fibers
- C) Adipose tissue
- D) Cartilage
Answer: B) Elastic fibers and reticular fibers
Explanation (日本語): 肺胞中隔(interalveolar septum)は、弾性線維(elastic fibers)と網状線維(reticular fibers)から成る結合組織を含んでいます。これにより肺胞の伸展性と弾性が保たれ、呼吸運動に対応できます。他の選択肢は、肺胞中隔には見られない組織です。
Question 10:
Which of the following epithelium covers the laryngeal surface of the epiglottis?
- A) Simple squamous epithelium
- B) Stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium
- C) Pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium
- D) Simple cuboidal epithelium
Answer: C) Pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium
Explanation (日本語): 喉頭蓋(epiglottis)の喉頭側は、多列線毛円柱上皮(pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium)で覆われています。一方、喉頭蓋の他の側(舌側)は非角化重層扁平上皮(stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium)で覆われ、機械的保護を提供します。これらの異なる上皮は、異なる機能に適応しています。
| 部位 | 上皮の種類 | 機能 |
|---|---|---|
| 喉頭側 (Laryngeal side) | 多列線毛円柱上皮 (Pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium) | 異物の捕捉と排出 (Trapping and removal of particles) |
| 舌側 (Lingual side) | 非角化重層扁平上皮 (Stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium) | 機械的保護 (Mechanical protection) |
Question 12:
Which of the following is true of type II pneumocytes?
- A) They form the blood-gas barrier
- B) They secrete surfactant
- C) They have phagocytic capabilities
- D) They are also called dust cells
Answer: B) They secrete surfactant
Explanation (日本語): II型肺胞上皮細胞(type II pneumocytes)は、肺サーファクタント(pulmonary surfactant)を分泌します。このサーファクタントは、肺胞の表面張力を低下させ、呼吸時に肺胞が容易に膨張できるようにします。I型肺胞上皮細胞(type I pneumocytes)はガス交換に直接関与し、塵細胞(dust cells)は肺胞マクロファージの別名です。
Question 13:
Clara cells are found in the following structures, except:
- A) Terminal bronchioles
- B) Respiratory bronchioles
- C) Intrapulmonary bronchi
- D) None of the above
Answer: C) Intrapulmonary bronchi
Explanation (日本語): Clara細胞(現在は「クラブ細胞」とも呼ばれる)は、主に終末細気管支(terminal bronchioles)や呼吸細気管支(respiratory bronchioles)で見られます。これらの細胞は、肺の防御機構に関与し、サーファクタント様物質を分泌します。一方、肺内気管支(intrapulmonary bronchi)では、クラブ細胞は見られず、ここでは主に杯細胞と線毛円柱上皮が存在します。

Question 14:
Which of the following parts of the respiratory system does not participate in gas exchange?
- A) Alveolar sac
- B) Alveoli
- C) Interalveolar septum
- D) Terminal bronchioles
Answer: D) Terminal bronchioles
Explanation (日本語): 終末細気管支(terminal bronchioles)は、導管部の一部であり、ガス交換には直接関与していません。ガス交換は主に肺胞(alveoli)や肺胞嚢(alveolar sacs)、そして肺胞中隔(interalveolar septum)で行われます。終末細気管支は、ガスが肺に到達するための通路として機能しますが、酸素と二酸化炭素の交換は行われません。
Question 15:
What type of epithelium lines the olfactory region?
- A) Simple squamous epithelium
- B) Stratified squamous epithelium
- C) Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
- D) Simple cuboidal epithelium
Answer: C) Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Explanation (日本語): 嗅上皮(olfactory epithelium)は、鼻腔の嗅覚を司る部分に存在し、多列線毛円柱上皮(pseudostratified columnar epithelium)で構成されています。この上皮には、嗅細胞(olfactory cells)、支持細胞(sustentacular cells)、基底細胞(basal cells)などの特殊な細胞が含まれています。これらの細胞が協力して嗅覚を感知します。
Question 16:
A 64-year-old man who is a chain smoker presents with a chronic cough and a 5-kg weight loss over the past 3 months. A chest radiograph shows a cavitation within a lesion near the right hilum. Which of the following would not be a normal characteristic of alveoli?
- A) Pouch-like invaginations in the walls of respiratory bronchioles
- B) Pores of Kohn
- C) Lined by simple squamous epithelium
- D) Contains capillary networks for gas exchange
Answer: A) Pouch-like invaginations in the walls of respiratory bronchioles
Explanation (日本語): 肺胞(alveoli)は、単層扁平上皮(simple squamous epithelium)で覆われ、ガス交換に適した構造をしています。Kohnの孔(pores of Kohn)は、肺胞間で空気を循環させる役割を持つ開口部です。一方で、呼吸細気管支(respiratory bronchioles)はガス交換の一部に関与しますが、肺胞の特徴である「ポーチ状のくぼみ」を持つわけではありません。
Question 17:
Which of the following structures synthesize pulmonary surfactants?
- A) Type I pneumocytes
- B) Type II pneumocytes
- C) Alveolar macrophages
- D) Clara cells
Answer: B) Type II pneumocytes
Explanation (日本語): II型肺胞上皮細胞(type II pneumocytes)は、肺サーファクタントを合成・分泌する役割を持っています。サーファクタントは肺胞の表面張力を低減し、肺胞が潰れないようにします。I型肺胞上皮細胞(type I pneumocytes)はガス交換を担い、Clara細胞は終末細気管支で防御物質を分泌しますが、サーファクタントを生成しません。
Question 18:
Which of the following parts of the respiratory system contain seromucous glands?
- A) Submucosa of the trachea
- B) Alveolar sacs
- C) Terminal bronchioles
- D) Respiratory bronchioles
Answer: A) Submucosa of the trachea
Explanation (日本語): 気管(trachea)の粘膜下層(submucosa)には、粘液と漿液を分泌する漿液粘液腺(seromucous glands)が存在します。これらの腺は、気道を潤し、異物の排出を助ける役割を持っています。肺胞嚢(alveolar sacs)や終末細気管支(terminal bronchioles)にはこれらの腺は見られません。
Question 19:
Which of the following structures does not contain goblet cells?
- A) Nasal cavity
- B) Trachea
- C) Terminal bronchioles
- D) Intrapulmonary bronchi
Answer: C) Terminal bronchioles
Explanation (日本語): 杯細胞(goblet cells)は、気道に粘液を分泌する細胞で、鼻腔(nasal cavity)、気管(trachea)、肺内気管支(intrapulmonary bronchi)に存在します。しかし、終末細気管支(terminal bronchioles)では、Clara細胞が存在し、杯細胞は見られません。Clara細胞は粘液の分泌ではなく、防御物質の分泌を行います。
Question 20:
Which of the following structures contain elastic cartilage?
- A) Epiglottis
- B) Thyroid cartilage
- C) Cricoid cartilage
- D) Corniculate cartilage
Answer: A) Epiglottis
Explanation (日本語): 喉頭蓋(epiglottis)は、弾性軟骨(elastic cartilage)で構成されています。これにより、弾力性があり、飲み込む際に気道を覆う柔軟な動きが可能です。甲状軟骨(thyroid cartilage)や輪状軟骨(cricoid cartilage)は硝子軟骨(hyaline cartilage)でできています。コーニキュレート軟骨(corniculate cartilage)も弾性軟骨に分類されますが、問題の他の選択肢とは異なる役割を持っています。
| 軟骨の種類 | 特徴 | 繊維の構成 | 位置 | 具体例 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 硝子軟骨 (Hyaline Cartilage) | 柔軟で弾力性があり、表面が滑らか | コラーゲン (Collagen) | 関節の表面、肋軟骨、気管、喉頭 | 甲状軟骨 (Thyroid Cartilage)、環状軟骨 (Cricoid Cartilage)、下部喉頭蓋軟骨 (Lower Arytenoids) |
| 弾性軟骨 (Elastic Cartilage) | 高い柔軟性を持ち、弾性繊維を多く含む | 弾性繊維 (Elastic Fibers) とコラーゲン (Collagen) | 喉頭蓋、外耳、耳管 (咽頭と耳を繋ぐ管) | 喉頭蓋 (Epiglottis)、小角軟骨 (Corniculate Cartilage)、喉頭の先端 (Tip of Arytenoids) |
| 線維軟骨 (Fibrocartilage) | 高い圧縮力と張力に耐える能力があり、厚いコラーゲン層を持つ | 厚いコラーゲン繊維 (Thick Collagen Fibers) | 椎間板、膝の半月板、恥骨結合 | 半月板 (Knee Menisci)、椎間板の髄核 (Annulus Fibrosis of Intervertebral Discs) |
Question 21:
The pharyngeal tonsil, which is a collection of lymphoid follicles, is located in which layer of the organ?
- A) Epithelium
- B) Lamina propria
- C) Submucosa
- D) Adventitia
Answer: B) Lamina propria
Explanation (日本語): 咽頭扁桃(pharyngeal tonsil)は、リンパ濾胞が集まった構造で、粘膜固有層(lamina propria)に位置しています。粘膜固有層は、粘膜の上皮下に存在し、免疫反応に重要なリンパ組織が豊富です。咽頭扁桃は特に上咽頭に存在し、感染防御の役割を果たします。
Question 22:
Which of the following is true of the blood-gas barrier in the lungs?
- A) It is formed by the alveolar macrophages
- B) It prevents oxygen from entering the capillaries
- C) It facilitates the diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide
- D) It is primarily composed of type II pneumocytes
Answer: C) It facilitates the diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide
Explanation (日本語): 血液-ガス障壁(blood-gas barrier)は、肺胞と毛細血管の間にあり、酸素と二酸化炭素の効率的なガス交換を可能にします。主にI型肺胞上皮細胞(type I pneumocytes)と毛細血管内皮から成り、非常に薄い構造が特徴です。酸素は肺胞から血液中に拡散し、二酸化炭素は逆方向に拡散します。
Question 23:
A 56-year-old man with ischemic heart disease undergoes coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Two days postoperatively, he experiences increasing respiratory difficulty. A biopsy reveals a stricture at the terminal bronchiole. What is the lining epithelium of the affected area?
- A) Simple cuboidal epithelium with Clara cells
- B) Pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium
- C) Stratified squamous epithelium
- D) Simple squamous epithelium
Answer: A) Simple cuboidal epithelium with Clara cells
Explanation (日本語): 終末細気管支(terminal bronchioles)は、単層立方上皮(simple cuboidal epithelium)で覆われ、Clara細胞(クラブ細胞)が存在します。Clara細胞は、サーファクタント様物質を分泌し、気道を保護する役割を果たしています。この部位の上皮は、より上位の気道とは異なり、多列線毛上皮や杯細胞は見られません。
Question 24:
Which of the following parts of the respiratory system does not contain goblet cells?
- A) Trachea
- B) Nasal cavity
- C) Terminal bronchioles
- D) Intrapulmonary bronchi
Answer: C) Terminal bronchioles
Explanation (日本語): 杯細胞(goblet cells)は、鼻腔(nasal cavity)や気管(trachea)、肺内気管支(intrapulmonary bronchi)で見られ、粘液を分泌して気道を潤します。しかし、終末細気管支(terminal bronchioles)では、杯細胞の代わりにClara細胞が存在し、気道の保護や修復に関与します。
| 位置(Location) | 説明(Description) |
|---|---|
| 鼻腔(Nasal Cavity) | 鼻腔の粘膜に存在し、吸い込まれる空気に含まれる異物を捕捉し、鼻腔内を潤滑します。異物を除去するために繊毛運動と連携して粘液を外に排出します。 |
| 気管(Trachea) | 気管の粘膜に豊富に存在し、粘液を分泌して気管を保護し、吸入した異物(例えば、埃や微生物)を捕捉します。粘液と繊毛運動により異物を上部呼吸器へ運び、排出されやすくします。 |
| 気管支(Bronchi) | 大気管支(large bronchi)で杯細胞が多く、気道を潤滑し、異物や病原体の侵入を防ぎます。気管支粘膜の保護とともに、細菌やウイルスからの防御を補助します。 |
| 細気管支(Bronchioles) | 杯細胞は主に大気管支で見られますが、細気管支の一部にも存在します。細気管支においても、粘液を分泌して気道を保護する機能を果たします。ただし、細気管支では杯細胞の数が少なくなります。 |
肺内気管支における杯細胞の存在
- 大気管支(Large bronchi): 肺内の大きな気管支には多くの杯細胞が存在し、粘液を分泌して気道を潤滑し、異物の除去を助けます。この部分では杯細胞は比較的豊富に見られ、気管に似た機能を果たしています。
- 細気管支に向かうにつれて: 肺内気管支から細気管支に進むと、杯細胞の数は減少します。特に末梢の細気管支では杯細胞はほとんど存在せず、代わりにクララ細胞(Clara cells, 現在ではクラブ細胞とも呼ばれる)が増加し、気道の保護と修復、そして粘液分泌の代わりに表面活性物質を分泌します。
杯細胞が存在する範囲
- 杯細胞が多く存在する領域: 鼻腔、気管、主気管支、葉気管支(lobar bronchi)、区域気管支(segmental bronchi)。
- 杯細胞が減少する領域: 細気管支(bronchioles)ではほとんど見られず、終末細気管支(terminal bronchioles)や呼吸細気管支(respiratory bronchioles)にはほぼ存在しません。
したがって、杯細胞は肺内気管支には存在しますが、末梢に向かうとその数は減少し、代わりにクララ細胞が役割を担うことになります。
Question 25:
Which of the following correctly describes the epithelium covering the laryngeal surface of the epiglottis?
- A) Simple squamous epithelium
- B) Stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium
- C) Pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium
- D) Simple cuboidal epithelium
Answer: C) Pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium
Explanation (日本語): 喉頭蓋(epiglottis)の喉頭側は、多列線毛円柱上皮(pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium)で覆われています。この上皮は、気道に入る異物を捕捉し、線毛の動きで排出する役割を果たしています。一方で、喉頭蓋の舌側は、非角化重層扁平上皮(stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium)で覆われ、機械的保護を提供します。
Question 26:
Which of the following structures is classified as a serous gland?
- A) Bowman’s gland
- B) Goblet cells
- C) Mucous glands of the submucosa
- D) Sebaceous glands
Answer: A) Bowman’s gland
Explanation (日本語): Bowman腺(Bowman’s gland)は、嗅覚系に関与する嗅上皮に存在する漿液腺(serous gland)です。これらの腺は嗅上皮を洗い流し、嗅覚を新しい匂い刺激に対して敏感に保つために必要です。他の選択肢である杯細胞(goblet cells)や粘液腺(mucous glands)は粘液を分泌するものであり、皮脂腺(sebaceous glands)は皮脂を分泌します。
Question 27:
A 55-year-old woman undergoes a health maintenance examination. Her physician suggests checking the respiratory portion of her respiratory system. Which of the following would not be included in this check?
- A) Alveoli
- B) Alveolar sacs
- C) Respiratory bronchioles
- D) Intrapulmonary bronchioles
Answer: D) Intrapulmonary bronchioles
Explanation (日本語): 呼吸器系の「呼吸部(respiratory portion)」には、肺胞(alveoli)、肺胞嚢(alveolar sacs)、呼吸細気管支(respiratory bronchioles)が含まれ、これらはガス交換に直接関与しています。一方で、肺内細気管支(intrapulmonary bronchioles)は主に空気を導く役割を果たし、ガス交換には関与していません。そのため、呼吸器系の検査には含まれません。
Question 28:
Which type of connective tissue is present in the interalveolar septum?
- A) Dense regular connective tissue
- B) Elastic fibers and reticular fibers
- C) Adipose tissue
- D) Cartilage
Answer: B) Elastic fibers and reticular fibers
Explanation (日本語): 肺胞中隔(interalveolar septum)は、弾性線維(elastic fibers)と網状線維(reticular fibers)から成る結合組織でできており、これにより肺胞の柔軟性と弾力性が保たれます。これにより、呼吸運動に伴う肺の膨張と収縮をサポートします。その他の選択肢である密性結合組織(dense regular connective tissue)や軟骨(cartilage)、脂肪組織(adipose tissue)は、肺胞中隔には見られません。
Question 29:
Which of the following structures mark the transition from the conducting to the respiratory portion of the respiratory system?
- A) Trachea
- B) Terminal bronchioles
- C) Respiratory bronchioles
- D) Alveoli
Answer: C) Respiratory bronchioles
Explanation (日本語): 呼吸細気管支(respiratory bronchioles)は、呼吸器系の「導管部(conducting portion)」から「呼吸部(respiratory portion)」への移行点を示します。この部分では、気道の構造がガス交換可能な肺胞に変わっていきます。終末細気管支(terminal bronchioles)は導管部の一部であり、ガス交換には関与しません。
Question 30:
Which of the following statements is not true of Clara cells?
- A) They secrete surfactant
- B) They are found in terminal bronchioles
- C) They detoxify harmful substances
- D) They divide to regenerate bronchiolar epithelium
Answer: A) They secrete surfactant
Explanation (日本語): Clara細胞(現在は「クラブ細胞」とも呼ばれる)は、主に終末細気管支(terminal bronchioles)で見られ、防御物質の分泌や有害物質の解毒、気管支上皮の再生に関与します。ただし、サーファクタントの分泌を行うのはII型肺胞上皮細胞(type II pneumocytes)であり、Clara細胞ではありません。
Question 31:
Which specific structure facilitates the surgical resection of lung tissue in cases of lung disease?
- A) Alveolar ducts
- B) Pulmonary lobules
- C) Bronchopulmonary segments
- D) Terminal bronchioles
Answer: C) Bronchopulmonary segments
Explanation (日本語): 気管支肺区域(bronchopulmonary segments)は、肺の独立した機能単位であり、それぞれが独自の気管支と血管供給を持っています。これにより、病変がある場合、肺全体ではなく特定の区域のみを切除する外科的手術が可能となります。この構造により、周囲の健康な肺組織を保存しながら病変部を安全に除去できます。
Question 32:
Which of the following structures contain elastic cartilage?
- A) Corniculate cartilage
- B) Thyroid cartilage
- C) Cricoid cartilage
- D) Arytenoid cartilage
Answer: A) Corniculate cartilage
Explanation (日本語): 角軟骨(corniculate cartilage)は、弾性軟骨(elastic cartilage)でできており、喉頭の機能に関与しています。弾性軟骨は、柔軟で可動性が必要な部位に存在します。甲状軟骨(thyroid cartilage)、輪状軟骨(cricoid cartilage)、および披裂軟骨(arytenoid cartilage)は主に硝子軟骨(hyaline cartilage)で構成されています。
Question 33:
Which of the following are not characteristics of secondary bronchi?
- A) Spiraling smooth muscle bundles
- B) Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
- C) Presence of goblet cells
- D) Seromucous glands are found in the mucosa
Answer: D) Seromucous glands are found in the mucosa
Explanation (日本語): 二次気管支(secondary bronchi)の特徴には、多列線毛円柱上皮(pseudostratified columnar epithelium)や杯細胞(goblet cells)、そして螺旋状に配置された平滑筋が含まれます。しかし、漿液粘液腺(seromucous glands)は粘膜下層(submucosa)に位置しており、粘膜には存在しません。
Question 34:
A 35-year-old pregnant woman in her early third trimester presents with severe hypogastric pain and irregular contractions. She is administered steroids to prevent neonatal hyaline membrane disease. Which cells are likely underdeveloped in such cases?
- A) Type I pneumocytes
- B) Type II pneumocytes
- C) Clara cells
- D) Alveolar macrophages
Answer: B) Type II pneumocytes
Explanation (日本語): 新生児のヒアリン膜病(hyaline membrane disease)は、II型肺胞上皮細胞(type II pneumocytes)の発達不足が原因であり、サーファクタントが不足することで呼吸困難を引き起こします。ステロイドは、これらの細胞の発達を促進し、肺が適切に膨張できるようにするため、早産児における呼吸窮迫症候群の予防に使用されます。
Question 35:
Which of the following is considered the most distal part of the conducting portion of the respiratory system?
- A) Terminal bronchioles
- B) Respiratory bronchioles
- C) Alveolar ducts
- D) Alveolar sacs
Answer: A) Terminal bronchioles
Explanation (日本語): 終末細気管支(terminal bronchioles)は、呼吸器系の「導管部(conducting portion)」の最遠部に位置し、ガス交換には直接関与していません。この部分から下流にある呼吸細気管支(respiratory bronchioles)や肺胞導管(alveolar ducts)は「呼吸部(respiratory portion)」に属し、実際のガス交換が行われます。
Question 36:
Which of the following is true of primary bronchioles?
- A) Lined by simple squamous epithelium
- B) Lined by pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium with goblet cells
- C) Lined by cuboidal epithelium with Clara cells
- D) Contain no smooth muscle
Answer: B) Lined by pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium with goblet cells
Explanation (日本語): 一次細気管支(primary bronchioles)は、多列線毛円柱上皮(pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium)で覆われ、杯細胞(goblet cells)を含んでいます。これにより、粘液が分泌され、異物を捕捉して気道から排出する役割を果たします。終末細気管支や呼吸細気管支は、Clara細胞を含む単層立方上皮で覆われています。
Question 37:
A 64-year-old man with a history of smoking presents with a persistent cough and a 5-kg weight loss over 3 months. A bronchoscopy shows a defect in his alveoli. Which of the following would not be a characteristic finding in normal alveoli?
- A) Pores of Kohn
- B) Type II pneumocytes
- C) Capillary networks for gas exchange
- D) Thick walls made of cartilage
Answer: D) Thick walls made of cartilage
Explanation (日本語): 正常な肺胞(alveoli)は、非常に薄い壁でできており、酸素と二酸化炭素の効率的なガス交換が可能です。Kohnの孔(pores of Kohn)は肺胞間の空気循環を助け、II型肺胞上皮細胞(type II pneumocytes)はサーファクタントを分泌します。肺胞には軟骨組織は存在せず、壁が厚くなることは病的な変化です。
Question 38:
Which of the following structures contain alveolar pores?
- A) Respiratory bronchioles
- B) Terminal bronchioles
- C) Alveoli
- D) Intrapulmonary bronchi
Answer: C) Alveoli
Explanation (日本語): Kohnの孔(pores of Kohn)は、肺胞(alveoli)に存在し、隣接する肺胞間で空気の交換を可能にします。これにより、気道が閉塞した場合でも、別の経路を通じて酸素を供給できます。呼吸細気管支や終末細気管支にはこれらの孔は存在しません。
Question 39:
Which of the following causes contraction of pulmonary smooth muscles?
- A) Parasympathetic fibers
- B) Sympathetic fibers
- C) Type I pneumocytes
- D) Alveolar macrophages
Answer: A) Parasympathetic fibers
Explanation (日本語): 副交感神経線維(parasympathetic fibers)は、気道平滑筋の収縮を引き起こし、気管支収縮(bronchoconstriction)を引き起こします。これにより、気道が狭まり、空気の流れが制限されます。一方、交感神経(sympathetic fibers)は気管支拡張(bronchodilation)を引き起こし、気道を広げます。
Question 40:
Which of the following cells have phagocytic capabilities within the alveoli?
- A) Type I pneumocytes
- B) Clara cells
- C) Alveolar macrophages
- D) Type II pneumocytes
Answer: C) Alveolar macrophages
Explanation (日本語): 肺胞マクロファージ(alveolar macrophages)、または「塵細胞(dust cells)」は、肺胞内で異物や細菌を取り込み、体外に排出する役割を果たします。これにより、肺の防御機能を維持し、感染や炎症を防ぎます。I型およびII型肺胞上皮細胞はガス交換やサーファクタントの分泌に関与しますが、貪食能は持っていません。
Question 41:
Which of the following are not characteristics of secondary bronchi?
- A) Presence of pseudostratified columnar epithelium
- B) Presence of smooth muscle bundles
- C) Contains seromucous glands in the submucosa
- D) Contains type II pneumocytes
Answer: D) Contains type II pneumocytes
Explanation (日本語): 二次気管支(secondary bronchi)は、多列線毛円柱上皮(pseudostratified columnar epithelium)で覆われ、平滑筋や漿液粘液腺(seromucous glands)を含むのが特徴です。しかし、II型肺胞上皮細胞(type II pneumocytes)は肺胞に存在し、サーファクタントを分泌します。したがって、II型肺胞上皮細胞は二次気管支には存在しません。
1. 一次気管支(Primary Bronchi)
- 別名: 主気管支(Main Bronchi)
- 位置: 気管(trachea)から左右に分岐する最初の気管支です。気管が胸部に入った後、左右の肺に向かって分岐します。
- 右主気管支(Right Primary Bronchus): 右肺へ入ります。右主気管支は比較的短く、太く、傾斜が急です。
- 左主気管支(Left Primary Bronchus): 左肺へ入ります。左主気管支は長く、やや狭く、傾斜が緩やかです。
- 機能: 吸い込まれた空気を左右の肺へ運びます。
2. 二次気管支(Secondary Bronchi)
- 別名: 葉気管支(Lobar Bronchi)
- 位置: 一次気管支が肺に入った後、左右の肺のそれぞれの肺葉(lobe)へ分岐します。
- 右肺には3つの葉(上葉、中葉、下葉)があります。そのため、右二次気管支は3本に分かれます。
- 左肺には2つの葉(上葉、下葉)があります。そのため、左二次気管支は2本に分かれます。
- 機能: 各肺葉に空気を供給し、空気がさらに細かい気管支に分かれる準備をします。
3. 三次気管支(Tertiary Bronchi)
- 別名: 区域気管支(Segmental Bronchi)
- 位置: 二次気管支がさらに細かく分岐し、肺の各機能的単位である肺区域(bronchopulmonary segments)に空気を供給します。
- 右肺には10の肺区域があり、それに応じて10本の三次気管支があります。
- 左肺には8〜10の肺区域があり、それに応じた三次気管支が存在します。
- 機能: 肺の各区域に空気を供給し、ガス交換が行われる肺胞に最終的に空気を届けます。
全体の構造と機能
- 一次気管支(Primary Bronchi): 気管から直接分かれ、左右の肺に空気を供給。
- 二次気管支(Secondary Bronchi): 肺葉ごとに空気を供給。
- 三次気管支(Tertiary Bronchi): 肺区域に空気を供給。
これらの気管支は、段階的に細かく分岐しながら空気を末端の気管支(bronchioles)に運び、最終的には肺胞(alveoli)でのガス交換を可能にします。
また、杯細胞(goblet cells)は主に一次気管支や二次気管支に豊富に存在しますが、三次気管支ではその数が減少します。
Question 42:
Which of the following statements is histologically correct about the epiglottis?
- A) The connective tissue layer contains several mucous glands
- B) It is lined by simple cuboidal epithelium
- C) The laryngeal surface is covered by stratified squamous epithelium
- D) It contains no cartilage
Answer: A) The connective tissue layer contains several mucous glands
Explanation (日本語): 喉頭蓋(epiglottis)の結合組織層には、多くの粘液腺(mucous glands)が存在し、喉頭蓋を潤し、保護する役割を果たします。喉頭蓋の喉頭側は、多列線毛円柱上皮(pseudostratified columnar epithelium)で覆われ、舌側は重層扁平上皮(stratified squamous epithelium)で覆われています。また、喉頭蓋には弾性軟骨(elastic cartilage)が含まれています。
Question 43:
Which of the following is true of the blood-gas barrier?
- A) It prevents carbon dioxide from entering the alveoli
- B) It is formed by the alveolar epithelium and capillary endothelium
- C) It is primarily composed of type II pneumocytes
- D) It allows only oxygen to diffuse across
Answer: B) It is formed by the alveolar epithelium and capillary endothelium
Explanation (日本語): 血液-ガス障壁(blood-gas barrier)は、肺胞上皮(主にI型肺胞上皮細胞)と毛細血管の内皮細胞で構成されており、酸素と二酸化炭素が効率的に拡散できるようになっています。この非常に薄い構造により、酸素は肺胞から血液中に、二酸化炭素は逆に血液から肺胞へと拡散します。
Question 44:
Which of the following types of epithelium covers the laryngeal surface of the epiglottis?
- A) Simple squamous epithelium
- B) Stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium
- C) Pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium
- D) Simple cuboidal epithelium
Answer: C) Pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium
Explanation (日本語): 喉頭蓋(epiglottis)の喉頭側は多列線毛円柱上皮(pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium)で覆われており、異物を捕捉して喉頭から排出する機能を持っています。舌側は重層扁平上皮(stratified squamous epithelium)で覆われ、保護機能を果たします。異なる部分で異なる種類の上皮が見られます。
Question 45:
Which type of connective tissue is present in the interalveolar septum?
- A) Dense regular connective tissue
- B) Elastic fibers and reticular fibers
- C) Adipose tissue
- D) Hyaline cartilage
Answer: B) Elastic fibers and reticular fibers
Explanation (日本語): 肺胞中隔(interalveolar septum)には、弾性線維(elastic fibers)と網状線維(reticular fibers)が存在し、肺の伸展性や弾性を保つ役割を果たします。これにより、肺胞は呼吸運動に対応して効率よく膨張・収縮できるようになっています。他の結合組織(密性結合組織や軟骨、脂肪組織)は中隔には見られません。
Question 46:
Type II pneumocytes are also known as:
- A) Dust cells
- B) Clara cells
- C) Septal cells
- D) Goblet cells
Answer: C) Septal cells
Explanation (日本語): II型肺胞上皮細胞(type II pneumocytes)は「中隔細胞(septal cells)」とも呼ばれ、サーファクタントを分泌することで肺胞の表面張力を低減し、呼吸時の肺胞の膨張を助けます。塵細胞(dust cells)は肺胞マクロファージであり、異物の貪食を行います。Clara細胞は終末細気管支に存在し、防御物質を分泌します。
Question 47:
Which of the following structures mark the transition from the conducting portion to the respiratory portion of the respiratory system?
- A) Terminal bronchioles
- B) Alveolar ducts
- C) Respiratory bronchioles
- D) Alveoli
Answer: C) Respiratory bronchioles
Explanation (日本語): 呼吸細気管支(respiratory bronchioles)は、導管部(conducting portion)から呼吸部(respiratory portion)への移行を示す構造です。呼吸細気管支は、気道の構造に肺胞が含まれ始める部分であり、ガス交換が可能となります。終末細気管支(terminal bronchioles)は導管部に属し、ガス交換には直接関与しません。
Question 48:
Clara cells are found in the following structures, except:
- A) Respiratory bronchioles
- B) Terminal bronchioles
- C) Intrapulmonary bronchi
- D) None of the above
Answer: C) Intrapulmonary bronchi
Explanation (日本語): Clara細胞は、主に終末細気管支(terminal bronchioles)や呼吸細気管支(respiratory bronchioles)で見られ、防御物質の分泌や修復に関与しています。一方で、肺内気管支(intrapulmonary bronchi)にはClara細胞は存在せず、ここでは主に杯細胞(goblet cells)と線毛円柱上皮が見られます。
**Intrapulmonary bronchi(肺内気管支)は、肺内に存在する気管支の総称です。気管支は、気管から左右の肺に入った後、細かく分岐していきますが、そのうち、肺の中に入った気管支が「intrapulmonary bronchi」と呼ばれます。これに対して、肺外に位置する気管支(一次気管支)はextrapulmonary bronchi(肺外気管支)**と呼ばれます。
Intrapulmonary bronchiの位置
- **一次気管支(Primary Bronchi)**の肺内部分:
- 一次気管支が左右の肺に入り、肺門(hilum)を越えて肺の内部に入る部分から「intrapulmonary bronchi」と呼ばれます。
- 二次気管支(Secondary Bronchi):
- 一次気管支が左右の肺葉に分岐した後の「葉気管支(lobar bronchi)」もintrapulmonary bronchiの一部です。これらは肺の各葉に空気を供給します。
- 三次気管支(Tertiary Bronchi):
- 二次気管支がさらに細かく分岐し、各肺区域(bronchopulmonary segments)に空気を供給する部分で、これもintrapulmonary bronchiに含まれます。
Intrapulmonary bronchiの概要
- 位置: 肺の内部に位置し、肺の内部で次第に細かく分岐していく気管支系の一部です。
- 構造: 気管支の壁は滑らかな筋肉と軟骨に囲まれており、繊毛上皮や杯細胞が存在し、空気中の異物を除去し、粘液で保護します。ただし、末梢に向かうと杯細胞の数は減少します。
- 機能: 空気を肺胞に向かって効率よく運び、ガス交換が行われる場所へ供給する役割を果たしています。
Question 49:
Seromucous glands are found in which layer of the trachea?
- A) Epithelium
- B) Lamina propria
- C) Submucosa
- D) Adventitia
Answer: C) Submucosa
Explanation (日本語): 気管(trachea)の粘膜下層(submucosa)には、漿液粘液腺(seromucous glands)が存在し、粘液と漿液を分泌して気道を潤し、異物の排出を助けます。上皮や固有層(lamina propria)ではこれらの腺は見られません。粘膜下層は、気管の防御と湿潤のために重要な役割を果たしています。
Question 50:
Olfactory epithelium is characterized by which type of epithelium?
- A) Simple squamous epithelium
- B) Stratified squamous epithelium
- C) Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
- D) Simple cuboidal epithelium
Answer: C) Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Explanation (日本語): 嗅上皮(olfactory epithelium)は、鼻腔の嗅覚を司る部分で、多列線毛円柱上皮(pseudostratified columnar epithelium)で構成されています。嗅細胞(olfactory cells)、支持細胞(sustentacular cells)、基底細胞(basal cells)などの特殊な細胞が含まれており、これらの細胞が協力して匂いを感知します。嗅上皮は特定の鼻腔部分にのみ存在します。
PPTより自作(細胞障害、細胞死、適応)
Question 1:
What is the main feature of necrosis compared to apoptosis?
A) Cell shrinkage
B) Inflammation
C) Programmed cell death
D) Fragmentation into apoptotic bodies
Answer: B) Inflammation
解説: 壊死(Necrosis)は、細胞死に伴って炎症反応を引き起こす病的なプロセスです。一方、アポトーシス(Apoptosis)は計画的な細胞死で、炎症を伴わないのが特徴です。壊死では細胞内容物が漏れ出し、周囲の組織に影響を与えるため、炎症が頻繁に発生します。
Question 2:
Which type of necrosis is commonly seen in tuberculosis?
A) Liquefactive necrosis
B) Coagulative necrosis
C) Caseous necrosis
D) Fat necrosis
Answer: C) Caseous necrosis
解説: 結核(Tuberculosis)でよく見られるのは乾酪壊死(Caseous Necrosis)で、チーズ状の外観を持つことが特徴です。このタイプの壊死は、肉芽腫性炎症の一部として発生します。
Question 3:
What cellular adaptation involves an increase in cell number?
A) Hypertrophy
B) Hyperplasia
C) Atrophy
D) Metaplasia
Answer: B) Hyperplasia
解説: 過形成(Hyperplasia)は、細胞の数が増加する適応反応です。肥大(Hypertrophy)は細胞のサイズが増加することであり、萎縮(Atrophy)はサイズが減少すること、化生(Metaplasia)は細胞の表現型が変わることを指します。
Question 4:
Which of the following is a feature of reversible cell injury?
A) Karyolysis
B) Cellular swelling
C) Pyknosis
D) Karyorrhexis
Answer: B) Cellular swelling
解説: 可逆的損傷(Reversible injury)の特徴には、細胞膨潤(Cellular swelling)が含まれます。これは、細胞内に水が入り込むことによるものです。核の変化(Pyknosis, Karyorrhexis, Karyolysis)は不可逆的損傷の兆候です。
| 用語 | 説明 | 特徴 | 発生時期 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pyknosis(核濃縮, 核固縮) | 核が縮小し、クロマチンが凝集する現象 | 核が縮小して濃く染まる。染色性が増す。 | 細胞死の初期段階 |
| Karyorrhexis(核断片化) | 凝縮した核が断片化して崩壊する現象 | 核が小さな断片に分解される。 | Pyknosisの後に発生 |
| Karyolysis(核融解) | 核が溶解し、形態が消失する現象 | 核の染色性が低下し、最終的に核が消失する。 | 細胞死の最終段階 |
Question 5:
Which is NOT a cause of cell injury?
A) Oxygen deprivation
B) Physical agents
C) Overnutrition
D) Hyperplasia
Answer: D) Hyperplasia
解説: 過形成(Hyperplasia)は細胞の適応反応であり、損傷の原因ではありません。酸素欠乏(Oxygen deprivation)、物理的要因(Physical agents)、栄養の不均衡(Overnutrition)は、すべて細胞損傷の原因となることがあります。
Question 6:
Which giant cell is characterized by nuclei arranged in a horseshoe pattern?
A) Foreign body giant cell
B) Langhans giant cell
C) Reed-Sternberg cell
D) Epithelioid cell
Answer: B) Langhans giant cell
解説: ラングハンス型巨細胞(Langhans giant cell)は、結核やサルコイドーシスなどの肉芽腫性疾患で見られる細胞で、核が馬蹄形に配置されているのが特徴です。
Question 7:
Which form of cell death is considered a physiological process?
A) Necrosis
B) Apoptosis
C) Coagulative necrosis
D) Fat necrosis
Answer: B) Apoptosis
解説: アポトーシス(Apoptosis)は生理的なプロセスとして、不要な細胞を計画的に除去する役割を持っています。壊死(Necrosis)は病理的プロセスであり、不可逆的な細胞損傷によって引き起こされます。
Question 8:
Which pattern of tissue necrosis occurs due to the enzymatic digestion of fat?
A) Coagulative necrosis
B) Caseous necrosis
C) Liquefactive necrosis
D) Fat necrosis
Answer: D) Fat necrosis
解説: 脂肪壊死(Fat necrosis)は、膵臓酵素の活性化などによって脂肪組織が破壊されるプロセスです。これは主に膵炎や外傷などで見られます。
Question 9:
Which cellular adaptation involves a change in cell phenotype?
A) Hypertrophy
B) Hyperplasia
C) Atrophy
D) Metaplasia
Answer: D) Metaplasia
解説: 化生(Metaplasia)は、ある細胞のタイプが異なるタイプに変化する適応です。例えば、喫煙者の気管支で円柱上皮が扁平上皮に変わることが挙げられます。
Question 10:
What term describes the shrinkage of a cell during apoptosis?
A) Swelling
B) Hypertrophy
C) Atrophy
D) Shrinkage
Answer: D) Shrinkage
解説: アポトーシスでは細胞の縮小(Shrinkage)が起こり、細胞はコンパクトになります。これにより、細胞の内容物が周囲に漏れ出すことが防がれ、炎症が引き起こされないのが特徴です。
Question 11:
Which of the following is an example of dystrophic calcification?
A) Normal tissue calcification with high calcium levels
B) Calcification in necrotic tissue with normal calcium levels
C) Calcification in healthy tissues during hypercalcemia
D) Calcification in normal tissue without necrosis
Answer: B) Calcification in necrotic tissue with normal calcium levels
解説: 栄養障害性石灰化(Dystrophic calcification)は、壊死した組織にカルシウムが沈着する現象で、血清カルシウム濃度は通常正常です。一方、転移性石灰化(Metastatic calcification)は高カルシウム血症に伴って健康な組織にカルシウムが沈着する現象です。
Question 12:
Which nuclear change is a sign of irreversible cell injury?
A) Cellular swelling
B) Karyolysis
C) Mitochondrial swelling
D) Fatty change
Answer: B) Karyolysis
解説: 核融解(Karyolysis)は、不可逆的損傷の兆候であり、核の分解が進んでいることを示します。他の選択肢(細胞膨潤や脂肪変性)は可逆的損傷の特徴です。
Question 13:
What process results in the formation of apoptotic bodies?
A) Coagulative necrosis
B) Apoptosis
C) Fat necrosis
D) Caseous necrosis
Answer: B) Apoptosis
解説: アポトーシスの過程では、細胞が分解され、アポトーシス小体(Apoptotic bodies)と呼ばれる小さな断片が形成されます。これらは周囲の細胞やマクロファージによって処理され、炎症を引き起こしません。
Question 14:
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of necrosis?
A) Cell membrane rupture
B) Inflammation
C) Cell shrinkage
D) Enzymatic digestion of cellular contents
Answer: C) Cell shrinkage
解説: 細胞縮小(Cell shrinkage)はアポトーシスの特徴であり、壊死(Necrosis)では細胞が膨張し、膜が破れて炎症が引き起こされます。また、細胞内容物が酵素によって分解されるのも壊死の特徴です。
Question 15:
What type of necrosis is typically associated with abscess formation?
A) Coagulative necrosis
B) Liquefactive necrosis
C) Caseous necrosis
D) Fat necrosis
Answer: B) Liquefactive necrosis
解説: 融解壊死(Liquefactive necrosis)は、膿瘍(Abscess)の形成と関連しており、壊死した細胞が液化して粘稠な物質を形成します。この現象は、脳や化膿性感染でよく見られます。
Question 16:
Which term describes a decrease in cell size due to decreased workload or nutrition?
A) Hypertrophy
B) Hyperplasia
C) Atrophy
D) Metaplasia
Answer: C) Atrophy
解説: 萎縮(Atrophy)は、栄養不足や作業負荷の低下によって細胞のサイズが縮小する適応反応です。肥大(Hypertrophy)は細胞のサイズが増加し、過形成(Hyperplasia)は細胞の数が増加します。
Question 17:
Which form of necrosis results in a firm texture due to protein denaturation?
A) Liquefactive necrosis
B) Caseous necrosis
C) Fat necrosis
D) Coagulative necrosis
Answer: D) Coagulative necrosis
解説: 凝固壊死(Coagulative necrosis)は、タンパク質の変性によって細胞の構造が保存され、組織が硬くなるのが特徴です。これは心筋梗塞などの虚血性壊死でよく見られます。
Question 18:
Which of the following is the primary mechanism of fatty change in the liver?
A) Increased fatty acid synthesis
B) Impaired protein synthesis
C) Increased lipid breakdown
D) Impaired lipid export
Answer: D) Impaired lipid export
解説: 脂肪変性(Fatty change)は、特に肝臓でよく見られ、脂質の輸送障害(Impaired lipid export)によって中性脂肪が細胞内に蓄積します。アルコール性肝疾患などが原因で発生することがあります。
Question 19:
Which of the following is a hallmark of apoptosis but not necrosis?
A) Inflammation
B) Cell membrane disruption
C) Phagocytosis by neighboring cells
D) Release of cellular contents
Answer: C) Phagocytosis by neighboring cells
解説: アポトーシスでは、アポトーシス小体が形成され、周囲のマクロファージや隣接する細胞によって貪食されます。これにより炎症が引き起こされず、壊死とは異なります。
Question 20:
Which cellular organelle plays a key role in the initiation of apoptosis?
A) Lysosome
B) Mitochondria
C) Nucleus
D) Endoplasmic reticulum
Answer: B) Mitochondria
解説: ミトコンドリアは、アポトーシスの開始に重要な役割を果たします。特に、ミトコンドリアから放出されるシトクロムCがアポトーシス経路を活性化します。
アセス(呼吸)
Question 1:
Which of the following association is correct?
- A) Vestibule: sweat and sebaceous glands
- B) Larynx: purely serous glands
- C) Nasopharynx: Bowman’s gland
- D) Olfactory: mucous glands
Answer: A) Vestibule: sweat and sebaceous glands
Explanation (日本語): 鼻前庭(vestibule)は、鼻腔の外部に近い部分であり、皮膚に類似した構造を持っています。この部位には汗腺(sweat glands)と皮脂腺(sebaceous glands)が存在し、皮膚を潤滑し、保護します。他の選択肢はそれぞれ誤りです。Bowman腺は嗅覚領域に存在し、純粋な漿液腺(serous glands)です。
Question 2:
Which of the following parts of the respiratory system does not participate in gas exchange?
- A) Alveoli
- B) Terminal bronchiole
- C) Interalveolar septum
- D) Alveolar sac
Answer: B) Terminal bronchiole
Explanation (日本語): 終末細気管支(terminal bronchiole)は、気道の導管部分であり、ガス交換には直接関与していません。ガス交換が行われるのは肺胞(alveoli)や肺胞嚢(alveolar sac)、および肺胞中隔(interalveolar septum)です。終末細気管支は空気の通路として機能しますが、ガス交換には関与しません。
Question 3:
Which of the following structures are not seen in the supporting wall of the larynx?
- A) Elastic cartilage
- B) Hyaline cartilage
- C) Connective tissue
- D) Smooth muscle
Answer: D) Smooth muscle
Explanation (日本語): 喉頭(larynx)の支持壁には、弾性軟骨(elastic cartilage)と硝子軟骨(hyaline cartilage)が存在し、柔軟性と支持を提供します。また、結合組織(connective tissue)も喉頭の構造に含まれます。しかし、平滑筋(smooth muscle)は喉頭の壁の構成要素ではありません。
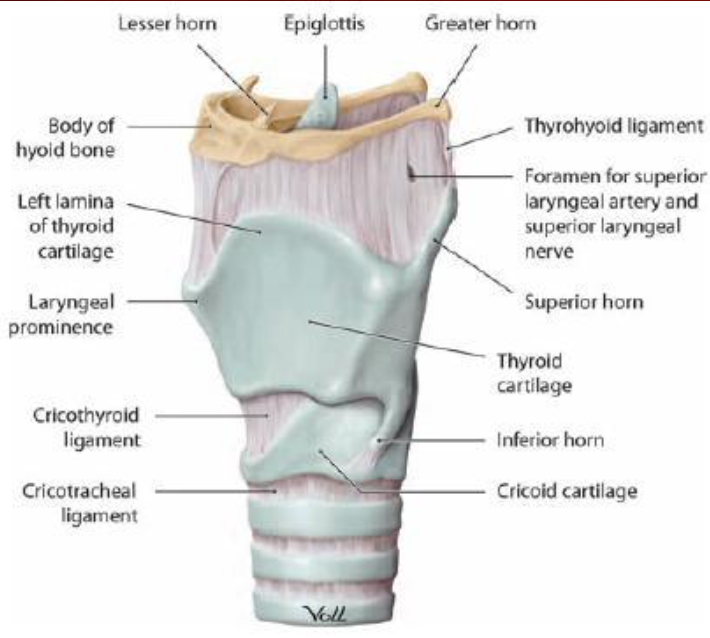
Question 4:
A 55-year-old man has experienced increasing respiratory difficulty for the past 18 months. A chest radiograph shows diffuse interstitial disease with no masses or hilar adenopathy. A biopsy shows a block on the vessel entering at the root of the lung and extending along the bronchial tree. Which major blood supply to the lung is affected?
- A) Pulmonary vein
- B) Pulmonary artery
- C) Pulmonary nerves
- D) Bronchial arteries and veins
Answer: B) Pulmonary artery
Explanation (日本語): 肺動脈(pulmonary artery)は、肺に静脈血を供給し、酸素化のために肺胞に到達します。このケースでは、肺門(root of the lung)に沿って動脈が塞がれているため、肺動脈が影響を受けている可能性が高いです。気管支動脈や静脈(bronchial arteries and veins)は肺の栄養供給を行う血管ですが、ガス交換には直接関与しません。
Question 5:
Which statement is histologically correct?
- A) The connective tissue layer contains several mucous glands
- B) The short basal cells resting on the basal lamina extend to the lumen
- C) The lamina propria consists of a thick layer of connective tissue beneath the basement membrane
- D) Intermittent longitudinal elastic fibers separate the lamina propria from the submucosa
Answer: A) The connective tissue layer contains several mucous glands
Explanation (日本語): 結合組織層には、多くの粘液腺(mucous glands)が存在し、気道を潤し、異物の除去を助けます。他の選択肢は誤りです。例えば、基底細胞は上皮の基底膜に接し、上皮の更新に関与しますが、全ての基底細胞が管腔まで伸びているわけではありません。
Question 6:
Lined by simple cuboidal epithelium ciliated with Clara cells:
- A) Terminal bronchioles
- B) Respiratory bronchioles
- C) Intrapulmonary bronchi
- D) Intrapulmonary bronchioles
Answer: A) Terminal bronchioles
Explanation (日本語): 終末細気管支(terminal bronchioles)は単層立方上皮(simple cuboidal epithelium)で覆われており、クララ細胞(Clara cells)が存在します。クララ細胞は防御物質を分泌し、気道を保護する役割を果たします。他の選択肢の構造では異なる種類の上皮が見られます。
Question 7:
Which of the following is the correct association?
- A) Primary bronchioles: simple cuboidal epithelium
- B) Intrapulmonary bronchi: pseudostratified columnar epithelium
- C) Respiratory bronchioles: simple squamous epithelium
- D) Primary bronchi: pseudostratified columnar ciliated
Answer: D) Primary bronchi: pseudostratified columnar ciliated
Explanation (日本語): 主気管支(primary bronchi)は、多列線毛円柱上皮(pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium)で覆われ、杯細胞(goblet cells)が存在します。これにより、粘液の分泌と線毛運動によって異物を捕捉し、気道から排除します。他の選択肢にある「一次細気管支」や「呼吸細気管支」は異なる上皮で覆われています。
Question 8:
The posterior continuation of the nasal cavity is lined by:
- A) Pseudostratified columnar
- B) Pseudostratified columnar ciliated with goblet cells
- C) Pseudostratified columnar ciliated
- D) Stratified squamous non-keratinized
Answer: B) Pseudostratified columnar ciliated with goblet cells
Explanation (日本語): 鼻腔の後続部は、多列線毛円柱上皮(pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium)で覆われ、杯細胞(goblet cells)が存在します。この上皮は、空気中の異物を捕捉し、線毛の動きによって気道外へと排出します。その他の選択肢では、正確な上皮の種類が示されていません。
Question 9:
An 82-year-old woman has had increasing difficulty in breathing without cough or increased sputum production for the past 5 months. A defective Clara cell is seen. Which is not true of Clara cells?
- A) Divide and some differentiate to form ciliated cells
- B) They metabolize airborne toxins by the P450 enzymes of the SER
- C) Secrete glycosaminoglycans
- D) Secrete pulmonary surfactant
Answer: D) Secrete pulmonary surfactant
Explanation (日本語): クララ細胞(Clara cells)は、P450酵素によって気道に侵入した有害物質を代謝し、また一部は線毛細胞に分化します。しかし、肺サーファクタントの分泌を行うのはII型肺胞上皮細胞(type II pneumocytes)です。したがって、クララ細胞がサーファクタントを分泌するという選択肢は誤りです。
Question 10:
Accommodates the blood-gas barrier:
- A) Terminal bronchioles
- B) Alveolar sac
- C) Interalveolar septum
- D) Alveoli
Answer: C) Interalveolar septum
Explanation (日本語): 肺胞中隔(interalveolar septum)は、肺胞と毛細血管の間でガス交換が行われる場所であり、血液-ガス障壁(blood-gas barrier)を形成します。この障壁は、酸素が肺胞から血液中へ、二酸化炭素が逆方向へと拡散することを可能にします。終末細気管支や肺胞嚢はガス交換には直接関与していません。
Question 11:
Which specific structure facilitates the surgical resection of lung tissue in disease?
- A) Intrapulmonary bronchi
- B) Segmental bronchi
- C) Lobar bronchi
- D) Secondary bronchi
Answer: B) Segmental bronchi
Explanation (日本語): 気管支肺区域(segmental bronchi)は肺の機能単位で、それぞれが独立した気管支と血管供給を持っています。このため、肺の一部に病変があっても、特定の気管支区域を切除することが可能です。この局在的な構造により、周囲の健常な肺組織を温存することができます。
Question 12:
Which of the following part of the pharynx is lined by respiratory epithelium?
- A) None of the above
- B) Nasopharynx
- C) Laryngopharynx
- D) Oropharynx
Answer: B) Nasopharynx
Explanation (日本語): 鼻咽頭(nasopharynx)は、呼吸器上皮(pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium with goblet cells)で覆われています。この上皮は、空気中の異物を捕捉し、線毛の動きによってそれを排出します。咽頭の他の部分である口咽頭(oropharynx)や喉頭咽頭(laryngopharynx)は、重層扁平上皮で覆われており、異なる機能を果たします。
鼻咽頭(nasopharynx)が呼吸上皮(pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium with goblet cells)で覆われている理由は、その解剖学的位置と機能に関連しています。鼻咽頭は呼吸器系の一部として、鼻から吸入された空気が通過する最初の領域です。そのため、以下の理由で呼吸上皮が最適とされています:
- 異物の捕捉と排出:
呼吸上皮には繊毛(cilia)があり、杯細胞(goblet cells)が粘液を分泌します。粘液は空気中の異物(ほこり、微生物など)を捕捉し、繊毛の動きによってそれらの異物を口の方向に移動させます。これにより、異物が気道の下部(肺など)に到達するのを防ぎ、呼吸器の保護機能を果たします。 - 湿度と温度の調整:
鼻咽頭は、吸入した空気を温め、加湿する役割も担っています。呼吸上皮は、この調整を助けるために、粘液を分泌して空気を適切な状態に保つことができます。粘液は湿度を保ち、乾燥した空気が直接肺に入るのを防ぎます。 - 効率的な空気の通過:
鼻咽頭は、空気がスムーズに通過するための通路でもあります。呼吸上皮は非常に薄く、空気の通過を阻害することなく異物の除去と空気の加湿を行うことができるため、鼻咽頭に適した組織です。
一方で、口咽頭(oropharynx)や喉頭咽頭(laryngopharynx)は食べ物や飲み物が通過する場所であり、物理的な摩擦が大きいです。そのため、これらの部分は保護機能が強い**重層扁平上皮(stratified squamous epithelium)**で覆われ、咽頭全体を保護しています。
Question 13:
Which of the following is true of alveolar cells?
- A) Thick cytoplasm
- B) Able to divide
- C) With phagocytic capabilities
- D) Forms loose junctions with adjacent cells
Answer: C) With phagocytic capabilities
Explanation (日本語): 肺胞マクロファージ(または「塵細胞」、「alveolar cells」)は、肺胞内に存在し、異物や細菌を貪食する能力を持っています。これにより、肺を清浄に保ち、感染を防ぐ役割を果たします。その他の選択肢は、肺胞上皮細胞の特性に当てはまらず、誤りです。
Question 14:
Which of the following is true of type II pneumocytes?
- A) Septal cells
- B) Not capable of mitosis
- C) Columnar in morphology
- D) Most often found near the alveolar space
Answer: A) Septal cells
Explanation (日本語): II型肺胞上皮細胞(type II pneumocytes)は「中隔細胞(septal cells)」とも呼ばれ、肺サーファクタントを分泌します。このサーファクタントは、肺胞の表面張力を低下させ、呼吸時に肺胞が潰れるのを防ぎます。また、II型肺胞上皮細胞は、肺胞損傷時にI型肺胞上皮細胞に分化する能力も持っています。
Question 15:
Synthesize pulmonary surfactants:
- A) Granular pneumocytes
- B) Type I pneumocytes
- C) Dust cells
- D) Alveolar macrophages
Answer: A) Granular pneumocytes
Explanation (日本語): II型肺胞上皮細胞は「顆粒肺胞細胞(granular pneumocytes)」とも呼ばれ、肺サーファクタントを合成・分泌します。サーファクタントは、肺胞の内側に薄く広がり、表面張力を低減させて呼吸時の肺胞の膨張を助けます。他の選択肢であるI型肺胞上皮細胞や肺胞マクロファージは、サーファクタントの分泌には関与していません。
Question 16:
What is the lining epithelium of the anterior part of the nasal cavity?
- A) Stratified squamous keratinized
- B) Stratified squamous non-keratinized
- C) Pseudostratified columnar
- D) Pseudostratified columnar ciliated
Answer: A) Stratified squamous keratinized
Explanation (日本語): 鼻腔の前方部分(鼻前庭)は、皮膚に近いため、角化重層扁平上皮(stratified squamous keratinized epithelium)で覆われています。この部分は外部環境にさらされるため、保護のために角化しています。一方、鼻腔の奥に進むと、非角化重層扁平上皮や多列線毛円柱上皮が見られます。
Question 17:
Hyaline cartilage is seen in the following areas, except:
- A) Corniculate
- B) Thyroid
- C) Cricoid
- D) Lower arytenoids
Answer: A) Corniculate
Explanation (日本語): 角軟骨(corniculate cartilage)は、弾性軟骨(elastic cartilage)で構成されており、柔軟性を持つ軟骨です。甲状軟骨(thyroid cartilage)、輪状軟骨(cricoid cartilage)、および下披裂軟骨(lower arytenoids)は硝子軟骨(hyaline cartilage)でできており、これらはより硬く、耐久性のある構造を提供します。
Question 18:
Alveolar macrophages are also known as:
- A) Endothelial cells
- B) Dust cells
- C) Kupffer cells
- D) Sinusoids
Answer: B) Dust cells
Explanation (日本語): 肺胞マクロファージは、「塵細胞(dust cells)」とも呼ばれ、肺胞内で異物や細菌を貪食し、肺を清浄に保つ役割を果たします。他の選択肢は異なる組織や臓器の細胞であり、Kupffer細胞は肝臓に存在し、内皮細胞は血管内を覆う細胞です。
Question 19:
The pharyngeal tonsil, which is a collection of lymphoid follicles, is seen in which layer of the organ?
- A) Lamina propria
- B) Submucosa
- C) Mucosa
- D) Epithelium
Answer: A) Lamina propria
Explanation (日本語): 咽頭扁桃(pharyngeal tonsil)は、リンパ濾胞が集まった構造で、粘膜固有層(lamina propria)に位置しています。この層には、免疫反応に関与する多くのリンパ球や免疫細胞が存在し、感染に対する防御を行います。その他の層は、扁桃の免疫機能には直接関与していません。
Question 20:
A 55-year-old woman goes to her family physician for an annual health maintenance examination. Her physician suggests a thorough check-up on the respiratory portion of her respiratory system. Which of the following would not be included in this check?
- A) Alveolar ducts
- B) Interalveolar septum
- C) Alveolar sacs
- D) Intrapulmonary bronchioles
Answer: D) Intrapulmonary bronchioles
Explanation (日本語): 呼吸部(respiratory portion)には、肺胞嚢(alveolar sacs)、肺胞導管(alveolar ducts)、および肺胞中隔(interalveolar septum)が含まれ、これらはガス交換に直接関与します。一方、肺内細気管支(intrapulmonary bronchioles)は、空気を導く役割を果たしますが、ガス交換には関与していません。そのため、呼吸部のチェックには含まれません。
Question 21:
A 78-year-old woman has had increasing dyspnea without cough or increased sputum production for the past 4 months. On physical examination, she is afebrile, and breath sounds are reduced in all lung fields. A defective Clara cell is observed. Which of the following is not true of Clara cells?
- A) They metabolize airborne toxins by the P450 enzymes of the SER
- B) Secrete glycosaminoglycans
- C) Secrete pulmonary surfactant
- D) Divide and some differentiate to form ciliated cells
Answer: C) Secrete pulmonary surfactant
Explanation (日本語): Clara細胞(またはクラブ細胞)は、主に有害物質を代謝するP450酵素を持つ滑面小胞体(SER)を含み、気道の修復や保護に関与します。また、グリコサミノグリカンを分泌し、部分的に線毛細胞に分化します。ただし、肺サーファクタントの分泌はII型肺胞上皮細胞(type II pneumocytes)の役割であり、Clara細胞の機能ではありません。
Question 22:
Which of the following does not contain goblet cells in their epithelium?
- A) Secondary bronchi
- B) Trachea
- C) Intrapulmonary bronchi
- D) Terminal bronchioles
Answer: D) Terminal bronchioles
Explanation (日本語): 杯細胞(goblet cells)は、気管(trachea)や二次気管支(secondary bronchi)、肺内気管支(intrapulmonary bronchi)で見られ、粘液を分泌して異物を捕捉します。しかし、終末細気管支(terminal bronchioles)には杯細胞は存在せず、代わりにClara細胞が見られ、気道の防御機能を果たします。
Question 23:
The walls consist of adjacent alveoli which are separated from one another by interalveolar septum:
- A) Alveolar ducts
- B) Alveolar sacs
- C) Terminal bronchioles
- D) Alveoli
Answer: A) Alveolar ducts
Explanation (日本語): 肺胞導管(alveolar ducts)は、隣接する肺胞の壁が肺胞中隔(interalveolar septum)によって区切られており、ガス交換が行われる場所です。肺胞嚢や肺胞自体は、ガス交換の主な部位ですが、肺胞導管はそれに至る通路として機能します。終末細気管支は空気の導管部であり、ガス交換には直接関与しません。
Question 24:
Which part of the respiratory system marks the transition from the conducting to the respiratory portion?
- A) Secondary bronchiole
- B) Terminal bronchiole
- C) Respiratory bronchiole
- D) Primary bronchi
Answer: C) Respiratory bronchiole
Explanation (日本語): 呼吸細気管支(respiratory bronchiole)は、呼吸器系の導管部(conducting portion)から呼吸部(respiratory portion)への移行点を示します。この部位から肺胞が現れ、ガス交換が可能になります。終末細気管支(terminal bronchioles)はまだ導管部に属し、ガス交換には関与しません。
Question 25:
Bowman’s glands are classified as:
- A) Mucous gland
- B) Mixed gland
- C) Serous gland
- D) Seromucous gland
Answer: C) Serous gland
Explanation (日本語): Bowman腺(Bowman’s glands)は、嗅覚系に関与する漿液腺(serous gland)であり、嗅上皮を洗い流し、匂い分子の新しい感知を可能にするための役割を果たします。他の選択肢の「粘液腺」や「混合腺」は、主に異なる部位で見られる腺の種類です。
A) Mucous gland(粘液腺):
粘液腺は、主に粘液(mucus)を分泌する腺です。粘液は厚く、粘性があり、保護や潤滑の役割を果たします。粘液は糖タンパク質を豊富に含み、分泌された際には水と結合して粘度が高くなります。呼吸器系や消化器系の内壁で見られ、異物の捕捉や組織の保護に重要な役割を果たします。例としては、**杯細胞(goblet cells)や気管腺(tracheal glands)**などが含まれます。
- 特徴: 粘液が粘性のため、保護や潤滑を必要とする領域に存在します。
- 例: 気管、食道、消化管の内壁
B) Mixed gland(混合腺):
混合腺は、粘液と漿液(serous)の両方を分泌する腺で、**粘液細胞(mucous cells)と漿液細胞(serous cells)**が共存しています。これにより、分泌物は粘液性と水分の多い漿液が混ざり合った性質を持ちます。唾液腺の多くがこのタイプに属し、食べ物を潤滑し、消化を助ける役割を果たします。
- 特徴: 粘液と漿液の混合分泌物を提供し、消化や保護に貢献します。
- 例: **顎下腺(submandibular gland)や舌下腺(sublingual gland)**など。
C) Serous gland(漿液腺):
漿液腺は、漿液(serous)、つまり水分が多く、タンパク質を含んだ透明でさらさらした液体を分泌する腺です。漿液は消化酵素を多く含んでおり、特に消化器系での消化作用を助けます。唾液腺の一部や膵臓の外分泌腺がこのタイプに属します。
- 特徴: 水分の多い分泌物を提供し、消化酵素の分泌が特徴的です。
- 例: 耳下腺(parotid gland)、**膵臓(pancreas)**の外分泌部。
D) Seromucous gland(漿液粘液腺):
漿液粘液腺は、粘液と漿液の両方を分泌する腺で、粘液腺と漿液腺が混合した構造です。これにより、粘性のある粘液と、水分を多く含んだ漿液が同時に分泌され、さまざまな役割を果たします。呼吸器系などでは、粘液で異物を捕捉し、漿液でそれを洗い流す役割を持ちます。
- 特徴: 粘液と漿液の両方の分泌が行われ、異物の捕捉と除去を助けます。
- 例: **気管支腺(bronchial glands)や鼻腺(nasal glands)**など。
自作問題(呼吸:ナバスカス)
Question 1:
Which of the following tissues is responsible for the strong contraction and movement of the body?
a. Epithelial tissue
b. Nervous tissue
c. Connective tissue
d. Muscular tissue
Answer: d. Muscular tissue
解説:
筋組織 (Muscular tissue) は、伸長した収縮性の細胞から構成され、強い収縮や体の運動を担います。したがって、この質問の正解は筋組織です。
他の選択肢が間違っている理由:
a. 上皮組織 (Epithelial tissue) は、表面を覆い、腺の分泌などに関与していますが、体の運動には直接関与しません。
b. 神経組織 (Nervous tissue) は、神経インパルスの伝達に関与し、運動の制御には関与しますが、収縮自体は行いません。
c. 結合組織 (Connective tissue) は、組織や臓器の支持と保護を行いますが、運動には直接関与していません。
Question 2:
Which type of epithelial tissue is found in the upper respiratory tract?
a. Simple squamous epithelium
b. Stratified cuboidal epithelium
c. Pseudostratified ciliated epithelium
d. Transitional epithelium
Answer: c. Pseudostratified ciliated epithelium
解説:
上気道の上皮は偽重層繊毛上皮 (Pseudostratified ciliated epithelium) で構成されており、異物を移動させる繊毛を持っています。したがって、上気道に見られる上皮は偽重層繊毛上皮です。
他の選択肢が間違っている理由:
a. 単層扁平上皮 (Simple squamous epithelium) は、肺胞のようなガス交換の場所で見られるもので、上気道ではありません。
b. 重層立方上皮 (Stratified cuboidal epithelium) は、主に汗腺の排出管で見られるもので、上気道には見られません。
d. 移行上皮 (Transitional epithelium) は、主に尿路に見られ、上気道には存在しません。
Question 3:
Which type of epithelial cell is primarily responsible for absorption in the intestines?
a. Stratified squamous epithelium
b. Simple cuboidal epithelium
c. Simple columnar epithelium
d. Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Answer: c. Simple columnar epithelium
解説:
小腸の吸収を担う上皮は単層円柱上皮 (Simple columnar epithelium) です。この細胞は高い吸収能力を持ち、多くの栄養素を取り込む役割を果たします。
他の選択肢が間違っている理由:
a. 重層扁平上皮 (Stratified squamous epithelium) は、皮膚や食道のような保護が重要な場所に存在しますが、吸収には関与しません。
b. 単層立方上皮 (Simple cuboidal epithelium) は、腺や小さな導管で見られるもので、腸では一般的ではありません。
d. 偽重層円柱上皮 (Pseudostratified columnar epithelium) は、主に呼吸器系に見られるもので、吸収機能は持っていません。
Question 4:
Which of the following tissues has the most abundant extracellular matrix?
a. Epithelial tissue
b. Nervous tissue
c. Muscular tissue
d. Connective tissue
Answer: d. Connective tissue
解説:
結合組織 (Connective tissue) は、非常に豊富な細胞外マトリックス (extracellular matrix) を持ち、組織や臓器を支持・保護する役割を果たします。このため、結合組織が最も細胞外マトリックスが豊富です。
他の選択肢が間違っている理由:
a. 上皮組織 (Epithelial tissue) は、細胞が密に集まっており、細胞外マトリックスはほとんどありません。
b. 神経組織 (Nervous tissue) も細胞外マトリックスが少なく、神経インパルスの伝達が主な機能です。
c. 筋組織 (Muscular tissue) も適度な細胞外マトリックスを持ちますが、結合組織ほど豊富ではありません。
Question 5:
Which component of epithelial cells is closest to the underlying connective tissue?
a. Apical pole
b. Lateral surfaces
c. Basal pole
d. Microvilli
Answer: c. Basal pole
解説:
上皮細胞の基底側 (Basal pole) は、基底膜 (basement membrane) に接し、その下にある結合組織と接触しています。これにより、基底側が結合組織に最も近い部分となります。
他の選択肢が間違っている理由:
a. 頂端側 (Apical pole) は、空間に面しており、結合組織とは逆の位置にあります。
b. 側面 (Lateral surfaces) は、隣接する細胞に接していますが、結合組織とは直接接触しません。
d. 微絨毛 (Microvilli) は、吸収面積を増やすための頂端部分の特殊化ですが、基底側とは関係ありません。
Question 6:
Which type of epithelial tissue lines the alveolar sacs?
a. Simple cuboidal epithelium
b. Pseudostratified ciliated epithelium
c. Simple squamous epithelium
d. Stratified columnar epithelium
Answer: c. Simple squamous epithelium
解説:
肺胞嚢 (Alveolar sacs) はガス交換を行うため、非常に薄い単層扁平上皮 (Simple squamous epithelium) で覆われています。この薄い構造により、酸素と二酸化炭素の迅速な拡散が可能です。
他の選択肢が間違っている理由:
a. 単層立方上皮 (Simple cuboidal epithelium) は、より厚い細胞層で、主に腺や導管で見られ、肺胞には適していません。
b. 偽重層繊毛上皮 (Pseudostratified ciliated epithelium) は、上気道で見られるものであり、ガス交換には不適です。
d. 重層円柱上皮 (Stratified columnar epithelium) は、特定の腺の導管などに見られるまれな上皮で、ガス交換部位では見られません。
Question 7:
Which of the following structures is responsible for increasing the surface area for absorption in the intestines?
a. Cilia
b. Microvilli
c. Goblet cells
d. Basal lamina
Answer: b. Microvilli
解説:
小腸の上皮細胞には微絨毛 (Microvilli) があり、これが表面積を増加させ、効率的な吸収を可能にします。
他の選択肢が間違っている理由:
a. 繊毛 (Cilia) は、主に呼吸器系で物質を移動させるために使用され、小腸での吸収には関与しません。
c. 杯細胞 (Goblet cells) は、粘液を分泌する細胞で、吸収機能には関与していません。
d. 基底板 (Basal lamina) は、基底膜の一部であり、吸収面積の増加には関与していません。
Question 8:
Which structure is responsible for producing mucus in the respiratory and digestive tracts?
a. Clara cells
b. Goblet cells
c. Microvilli
d. Fibroblasts
Answer: b. Goblet cells
解説:
杯細胞 (Goblet cells) は、呼吸器系および消化器系で粘液を分泌する単細胞腺 (unicellular glands) です。この粘液は表面を保護し、潤滑作用を持ちます。
他の選択肢が間違っている理由:
a. クララ細胞 (Clara cells) は、終末細気管支や呼吸細気管支で表面活性物質を分泌する細胞ですが、粘液の分泌は行いません。
c. 微絨毛 (Microvilli) は、主に吸収を助けるための構造であり、粘液の分泌には関与しません。
d. 線維芽細胞 (Fibroblasts) は、結合組織内でコラーゲンや他の細胞外マトリックス成分を生成する細胞であり、粘液の分泌には関与しません。
Question 9:
Which type of epithelium is typically found in the trachea?
a. Simple squamous epithelium
b. Pseudostratified ciliated epithelium
c. Stratified squamous epithelium
d. Simple cuboidal epithelium
Answer: b. Pseudostratified ciliated epithelium
解説:
気管 (Trachea) の上皮は、偽重層繊毛上皮 (Pseudostratified ciliated epithelium) であり、繊毛と杯細胞が含まれています。これにより、異物の除去と粘液の移動が行われます。
他の選択肢が間違っている理由:
a. 単層扁平上皮 (Simple squamous epithelium) は、肺胞のようなガス交換部位で見られるもので、気管には不適です。
c. 重層扁平上皮 (Stratified squamous epithelium) は、皮膚や食道で見られる保護的な上皮で、気管には見られません。
d. 単層立方上皮 (Simple cuboidal epithelium) は、腺や導管で見られるものであり、気管では一般的ではありません。
Question 10:
Which of the following cells is responsible for producing surfactant in the terminal bronchioles?
a. Clara cells
b. Goblet cells
c. Type II alveolar cells
d. Fibroblasts
Answer: a. Clara cells
解説:
クララ細胞 (Clara cells) は、終末細気管支や呼吸細気管支で表面活性物質を分泌し、気道の保護と修復を助ける機能を持ちます。
他の選択肢が間違っている理由:
b. 杯細胞 (Goblet cells) は、呼吸器系や消化器系で粘液を分泌しますが、表面活性物質の分泌は行いません。
c. II型肺胞細胞 (Type II alveolar cells) は、肺胞で表面活性物質を分泌しますが、終末細気管支では見られません。
d. 線維芽細胞 (Fibroblasts) は、結合組織内でコラーゲンを生成する細胞であり、表面活性物質の分泌には関与しません。
Question 11:
What type of cartilage is found in the trachea?
a. Elastic cartilage
b. Fibrocartilage
c. Hyaline cartilage
d. Reticular cartilage
Answer: c. Hyaline cartilage
解説:
気管 (Trachea) の軟骨はC字型の硝子軟骨 (Hyaline cartilage) で構成されており、気道を開いた状態に保つ役割を果たします。
他の選択肢が間違っている理由:
a. 弾性軟骨 (Elastic cartilage) は、耳介や喉頭蓋に見られるもので、気管には存在しません。
b. 線維軟骨 (Fibrocartilage) は、椎間板などの耐圧性が求められる部位に見られるもので、気管には存在しません。
d. 網状軟骨 (Reticular cartilage) という種類の軟骨は存在せず、この選択肢は誤りです。
Question 12:
Which type of epithelial tissue is found in smaller bronchioles?
a. Simple columnar epithelium
b. Stratified squamous epithelium
c. Simple cuboidal epithelium
d. Transitional epithelium
Answer: c. Simple cuboidal epithelium
解説:
小細気管支や終末細気管支は、単層立方上皮 (Simple cuboidal epithelium) で覆われています。この上皮は、気道が細くなるにつれて、ガス交換に備えるために厚さを減らします。
他の選択肢が間違っている理由:
a. 単層円柱上皮 (Simple columnar epithelium) は、腸などの吸収部位で見られ、細気管支には見られません。
b. 重層扁平上皮 (Stratified squamous epithelium) は、保護が必要な部位に見られますが、気道の細い部分ではありません。
d. 移行上皮 (Transitional epithelium) は、尿路に見られる特殊な上皮で、呼吸器系には存在しません。
Question 13:
Which type of epithelial tissue is responsible for secretion in glandular tissues?
a. Stratified squamous epithelium
b. Simple cuboidal epithelium
c. Simple squamous epithelium
d. Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Answer: b. Simple cuboidal epithelium
解説:
腺組織では、単層立方上皮 (Simple cuboidal epithelium) が一般的に分泌に関与しています。この上皮は、腺や導管で分泌物を生成・輸送する役割を担っています。
他の選択肢が間違っている理由:
a. 重層扁平上皮 (Stratified squamous epithelium) は、皮膚や食道など保護が必要な部位に見られるもので、分泌には関与しません。
c. 単層扁平上皮 (Simple squamous epithelium) は、ガス交換や物質の透過が重要な部位で見られるもので、分泌には関与しません。
d. 偽重層円柱上皮 (Pseudostratified columnar epithelium) は、主に呼吸器系で見られ、分泌に特化していません。
Question 14:
Which of the following is the primary function of epithelial tissue?
a. Support and protection of organs
b. Transmission of nerve impulses
c. Strong contraction for body movements
d. Lining of body surfaces and cavities
Answer: d. Lining of body surfaces and cavities
解説:
上皮組織 (Epithelial tissue) は、体表面や体腔を覆い、保護や分泌、吸収などの機能を果たします。このため、上皮組織の主な機能は体表面や体腔の裏打ちです。
他の選択肢が間違っている理由:
a. 結合組織 (Connective tissue) は、臓器の支持と保護に関与しますが、上皮組織ではありません。
b. 神経組織 (Nervous tissue) が神経インパルスの伝達を担っていますが、これは上皮組織の機能ではありません。
c. 筋組織 (Muscular tissue) が体の運動に関与していますが、上皮組織の機能ではありません。
Question 15:
Which of the following tissues is specialized for the transmission of electrical signals?
a. Epithelial tissue
b. Muscular tissue
c. Nervous tissue
d. Connective tissue
Answer: c. Nervous tissue
解説:
神経組織 (Nervous tissue) は、神経インパルスの伝達に特化しており、脳や脊髄、末梢神経に見られます。このため、電気信号の伝達に特化しています。
他の選択肢が間違っている理由:
a. 上皮組織 (Epithelial tissue) は、表面を覆い保護する機能がありますが、神経インパルスの伝達には関与していません。
b. 筋組織 (Muscular tissue) は、体の運動に関与しており、電気信号の伝達には関わりません。
d. 結合組織 (Connective tissue) は、組織や臓器の保護と支持に関与しますが、電気信号の伝達には関与していません。
Question 16:
Which layer of the basement membrane is closest to the epithelial cells?
a. Reticular lamina
b. Basal lamina
c. Apical pole
d. Lateral surfaces
Answer: b. Basal lamina
解説:
基底膜 (Basement membrane) のうち、基底板 (Basal lamina) は上皮細胞に最も近い部分です。この層は、上皮細胞と基底膜をつなぐ重要な役割を果たします。
他の選択肢が間違っている理由:
a. 網状板 (Reticular lamina) は、基底板の下にある拡散的で繊維性の層で、上皮細胞からはやや離れています。
c. 頂端側 (Apical pole) は、上皮細胞の空間に面した部分であり、基底膜とは反対の側に位置します。
d. 側面 (Lateral surfaces) は、隣接する細胞に接する部分であり、基底膜には接していません。
Question 17:
Which of the following structures is responsible for the filtration function of the basement membrane?
a. Microvilli
b. Type IV collagen
c. Goblet cells
d. Clara cells
Answer: b. Type IV collagen
解説:
基底膜 (Basement membrane) のフィルター機能は、主にIV型コラーゲン (Type IV collagen) によって提供されます。このコラーゲンは強固な構造を作り、上皮細胞と結合組織の間の選択的フィルターとして機能します。
他の選択肢が間違っている理由:
a. 微絨毛 (Microvilli) は、吸収面積を増加させるための構造であり、フィルター機能には関与していません。
c. 杯細胞 (Goblet cells) は、粘液を分泌する細胞で、基底膜のフィルター機能とは関係ありません。
d. クララ細胞 (Clara cells) は、終末細気管支や呼吸細気管支で表面活性物質を分泌する細胞で、基底膜の機能とは関係ありません。
Question 18:
Which type of epithelial cell surface specialization is responsible for moving particles across the respiratory tract?
a. Microvilli
b. Stereocilia
c. Cilia
d. Basal lamina
Answer: c. Cilia
解説:
繊毛 (Cilia) は、呼吸器系の上皮細胞の頂端部分に見られ、粘液や異物を移動させる役割を持っています。繊毛の動きによって、異物は体外へ排出されます。
他の選択肢が間違っている理由:
a. 微絨毛 (Microvilli) は、吸収面積を増加させるための構造であり、物質を移動させる機能はありません。
b. ステレオシリア (Stereocilia) は、主に精巣上体などに見られる突起で、繊毛ほど動的ではありません。
d. 基底板 (Basal lamina) は、上皮細胞の基底側にある構造で、物質の移動には関与していません。
Question 19:
Which type of epithelial tissue is specialized for rapid diffusion and filtration?
a. Simple cuboidal epithelium
b. Stratified squamous epithelium
c. Simple squamous epithelium
d. Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Answer: c. Simple squamous epithelium
解説:
単層扁平上皮 (Simple squamous epithelium) は、非常に薄く、拡散や濾過が迅速に行われるために特化しています。肺胞や血管内皮などで見られ、効率的なガス交換や物質の移動が行われます。
他の選択肢が間違っている理由:
a. 単層立方上皮 (Simple cuboidal epithelium) は、主に分泌や吸収を行う腺や導管で見られますが、拡散や濾過には適していません。
b. 重層扁平上皮 (Stratified squamous epithelium) は、保護が必要な部位で見られ、拡散や濾過には適していません。
d. 偽重層円柱上皮 (Pseudostratified columnar epithelium) は、呼吸器系に見られ、物質の拡散や濾過には適していません。
Question 20:
Which of the following structures provides structural support to epithelial tissues by anchoring them to underlying connective tissue?
a. Cilia
b. Goblet cells
c. Basement membrane
d. Microvilli
Answer: c. Basement membrane
解説:
基底膜 (Basement membrane) は、上皮組織を下層の結合組織にアンカーすることで、構造的な支持を提供しています。これにより、上皮細胞は安定して機能することができます。
他の選択肢が間違っている理由:
a. 繊毛 (Cilia) は、物質を移動させる役割を持つ上皮の頂端部分にある突起で、構造的な支持には関与しません。
b. 杯細胞 (Goblet cells) は、粘液を分泌する細胞で、支持機能には関与しません。
d. 微絨毛 (Microvilli) は、吸収面積を増やすための構造であり、支持機能には関与していません。


コメント