解剖
| Coronary artery that supplies the diaphragmatic surface of the heart? | Left Ventricular Artery Right Marginal Artery Diagonal Artery Posterior Interventricular Artery |
| 3.Circumflex come from the? | left carotid artery |
| What coronary follows the course of great cardiac vein? | Coronary sinus |
| Where does the coronary sinus drain? | Right Atrium |
| Coronary sinus is formed by the union of great cardiac vein and? | Oblique vein of left atrium |
| Lymphatic System in cardiovascular system drains at | A. Bronchomediastinal B. Bronchopulmonary |
| What is the main tributary of coronary sinus? | Great Cardiac Vein |
| The coronary arteries arise from what specific part of the ascending aorta Hiatus Lunule Sinus Nodule | C. Sinus |
| Where is the SA node specifically located in the heart? | |
| The major blood supply of the SA (sinoatrial) node typically comes from | RCA |
| Location of AV node in the heart- posterior inferior of the interventricular septum | posterior inferior of the interventricular septum |
| Conduction pathway that distributes impulses from SA Node to AV Node | Internodal pathway |
| What structure in the RA separates the smooth muscle from its rough surface? | sulcus terminalis |
| Arterial blood supply sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes came from which sources? | Right Coronary Artery |
| Where do you usually locate the sympathetic cardiac plexus along the heart? | Arch of the aorta or ascending aorta? |
| Which of the following describes the cardiac plexus of the heart? | Both sympathetic and Parasympathetic |
| What level of spinal cord is the sympathetic innervation of the heart? | T1 &T4 |
| Which of the following branches is from the right coronary artery? a. Circumflex Artery | B. Posterior Interventricular Artery |
| b.Posterior Interventricular Artery c. Terminal Artery d. Diagonal Artery | |
| Which cardiac vein drains the right atrium? Anterior Cardiac and Small Vein Guys sorry ulit I forgot Middle and Small Cardiac Vein Posterior Interventricular and Oblique Vein | C. Middle and Small Cardiac Vein |
| Where does the anterior cardiac vein drain? A. Coronary sinus B. Left atrium C. Middle cardiac vein D. Right atrium | D. Right atrium |
| Which of the following structure is found at the posterior of the pulmonary trunk, ascending aorta and……? A. B.Vagus nerve C. D. Pericardiophrenic ligament | |
| where does the pericardiophrenic comes from? | c. Internal thoracic artery |
| What is the ventricular papillary muscle attached with septomarginal trabeculae? | Anterior papillary muscle of the right ventricle |
| Traverse through interventricular | Moderator band |
| septum | |
| What valve is located to the posterior of the sternum at the level of 3rd ICS? | Pulmonic valve Mitral valve C. Aortic D. Tricuspid valve |
| Chamber occupying majority of the diaphragmatic surface | Left ventricle |
| Chamber of the heart that constitute an impression on the inferior lobe of the left lung A. RA B. RV C. LA D. LV | D. LV |
| What vein enters the thorax at the 8th thoracic vertebral level and is considered the largest vein in the body? | Brachiocephalic Superior Vena Cava Inferior Vena Cava |
| Where does the right common carotid rise from | Brachiocephalic Trunk |
| Which chamber does embryologic remnant can be found (fossa ovale)? a.) Right Atrium | a. Right Atrium |
| b.) Right Ventricle c.) Left Atrium d.) Left ventricle | |
| What specific coronary branch determines whether the right and left are considered the dominant vessels? A. Posterior interventricular Branch B. Circumflex Artery C. Left Anterior Descending Branch D. M…… Artery | A. Posterior interventricular Branch |
| Left Coronary Artery passes between — | Left auricle and pulmonary trunk |
| Which coronaries travel inferolaterally and continue to the apex of the heart? | Anterior interventricular artery |
| Posterior Descending artery is supplying the Left Ventricle. If this branch is absent what branch will supply the LV? | anterior descending artery? Not sure |
| The right atrium is mainly supplied by what coronary branch? | SA Nodal Artery POsterior Interventricular Branch Right Marginal Artery AV Nodal Artery |
| Which cardiac chamber comprises mostly of its sternocostal surface? Right Atrium Right Ventricle Left Atrium Left Ventricle | B. Right Ventricle |
| What particular chamber or vessel of the heart form the inferior border of the heart? A. Right Ventricle only | B. Right Ventricle only |
| B. Right Atrium and Ventricle C. Right Atrium only D. Right Atrium and Superior Vena Cava |
組織
| A structure in the right ventricle that separates the inflow from the outflow tracts is called? | Supraventricular crest |
| This type of heart layer contains the coronary vessels and adipose tissue. Pericardium Myocardium Epicardium Endocardium | Epicardium- ditow ka.nlang mag type sorry my bad. |
| What structure lies between the tunica intima and tunica media in muscular arteries? External elastic lamina Internal elastic lamina Vasa vasorum Vessels | A. External elastic lamina |
| Is known as ventricular contraction | Systole |
| Function of carotid bodies | baroreceptors |
| It is known as elevated blood pressure a. Hypertension b. Hypotension c. Vertigo d. Dysuria | a. Hypertension |
| alternative microvascular pathway in which blood flows through two successive capillary beds separated by a vein | portal system |
| Which one of the ff comprises 90% body’s vasculature? Ans: capillaries A. Elastic arteries B. Medium arteries C. Capillaries D. Veins | C. Capillaries |
| Pre capillary sphincter muscle is | Metarterioles |
| present in? Veins Metarterioles Muscular artery Large artery | |
| What type of capillary is characterized by being discontinuous? | Sinusoidal |
| This type of capillaries have perforations in the endothelium which allows greater exchange in the endothelial cells? Fenestrated Continuous Sinosoidal Discontinuous | c. sinusoidal |
| These are long mesenchymal cells that surround the endothelial layer in long mitochondrial process | |
| Which layer is thick and well developed in veins Tunica media Tunica intima Tunica adventitia Stratum basale | Tunica adventitia |
| Type of capillary characterized with perforations: | Fenestrated Capillary |
| Where does the thoracic duct drain? a. RIght subclavian and | Left subclavian and left jugular vein |
| right jugular vein Left subclavian and left jugular vein Arch of aorta d. | |
| How does biologic oxidation primarily function in cells? A. It involves only transfer of electrons B. It always couples with ATP synthesis C. It occurs primarily in cytosol D. It involves the transfer of electrons to oxygen | D. It involves the transfer of electrons to oxygen |
| Creatinine to muscle | High-energy phosphate |
| What are the sources of electrons in the electro transport chain? | NADH and FADH2 |
| Coenzyme that serves as the mobile electron carrier from complex III to Complex IV | Ans: Cytochrome C |
| How does cyanide inhibit cellular respiration? | Inhibit the transport of oxygen by Complex IV |
| Which process produces the highest yield of ATP per mole of glucose during aerobic respiration? Glycolysis Citric Acid Cycle Oxidative Phosphorylation Fermentation | C. oxidative Phosphorylation |
| What molecule acts as the transfer electron acceptor in aerobic cellular respiration? | A. Oxygen |
| How is oxidative phosphorylation regulated in the mitochondria? I FORGOT Oxygen concentration Proton concentration NADH concentration | Oxygen concentration |
| For every NADH oxidized, Complex IV translocates how many protons? Select the correct response: a) three b) four c) one d) two | d) |
| What is the p/o ratio or nadh oxidation A. 1.5 B. 2.5 C. 3 D. 4 | B. 2.5 |
| A negative Gibbs energy in a biochemical reaction indicates that reaction is ______ | Exergonic |
| how is ΔG01 related to biochemical reaction a. direct proportional b. inversely proportional c. unrelated d. dependent on temperature only | Inversely proportional |
| Which enzyme transfers high energy phosphate? Pyruvate Kinase Phosphofructokinase Hexokinase Phosphoglycerate kinase | |
| Primary force(?) of oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria | Proton Motive Force |
| The amount of Gibbs free energy ‘ΔG′) released during the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi) | -7.5 k/cal |
| Which compound has the highest phosphoryl transfer potential in the body? A. Glucose-6-phosphate B. ATP C. Creatine Phosphate D. Phosphoenolypyruvate | D. Phosphoenolpyruvate |
| What is the primary role of thermodynamics in bioenergetics? Describes how energy is consumed Determines the rate of enzyme reactions Predicts the reaction and extent of chemical reactions Explains the mechanism of enzyme catalysis | C. Predicts the reaction and extent of chemical reactions |
| Function of proton gradient in ATP synthase? | Energy stored in the proton gradient (proton motive force ) is used by ATP synthase to drive the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP. (from study guide) |
生化
| How does complex 1in the ETC contribute to the process | NADH |
| 103. What molecule is not part of the etc | Glucose 6 phosphate |
| Cytochrome c is located in which part of the mitochondria? a. Inner mitochondria membrane b. Outer mitochondria membrane c. Mitochondrial matrix d. Intermembrane space | D. Intermembrane space |
| How does proton pumping contribute to ATP synthesis in the electron transport chain? a. Directly synthesizes ATP b. Establishes an electrochemical gradient c. Generate oxygen d. Transfers electron between complexes | b. Establishes an electrochemical gradient |
| What enzyme is responsible for ATP synthesis during oxidative phosphorylation? Cytochrome oxidase Ubiquinone (or Coenzyme Q) ATP synthase NADH dehydrogenase | C. ATP synthase |
| What is the another name for complex II in electron transport chain? A. Cytochrome c oxidase B. Succinate dehydrogenase C. NADH dehydrogenase D. Cytochrome a1 oxidase | B. Succinate dehydrogenase |
| Coenzyme that serves as the | B. Ubiquinone |
| mobile electron carrier in the inner mitochondrial membrane. A. NAD+ B. Ubiquinone C. Cytochrome A D. ….. | |
| How many proton molecules are used to generate ATP in oxidative phosphorylation? A. 2 B. 1 C. 3 D. 4 | C. 3 |
| Which enzymes conserve ADP to ATP in Oxidative phosphorylation | ATP Synthase Complex V |
| What is NOT a product of Electron Transport Chain | A. Water B. NADH C. ATP D. Proton Gradient |
| How is proton motive force generated in the electron transport chain? | |
| 116. Which complex facilitates transfer of electrons to oxygen? | a. Complex 1 b. Complex 2 c. Complex 3 d. Complex 4 |
| which molecules donates electrons directly at complex II? | FADH2 |
| How are electrons transferred between complexes | Direct chemical reaction Mobile electron carriers coenzyme Q and coenzyme c By ATP synthase Proton transfer |
| What best describes the process of oxidative phosphorylation ? |
生理
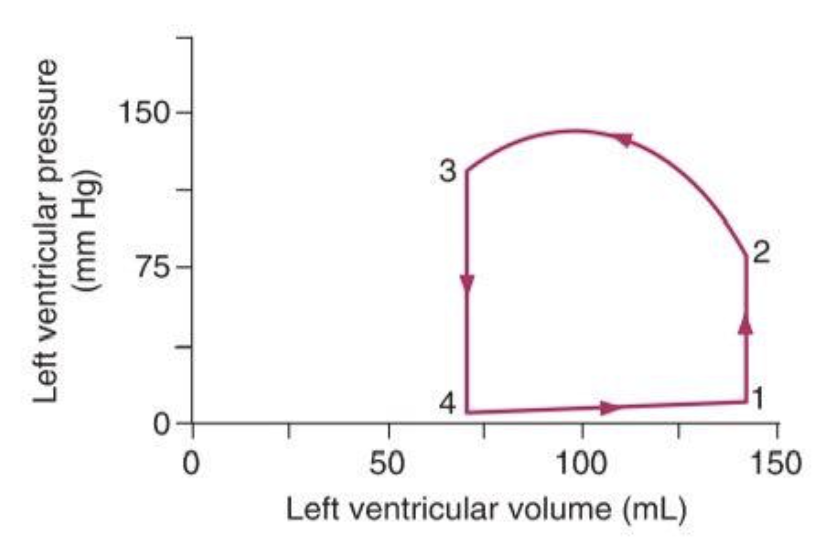 | |
| On the graph above showing isovolumetric contraction occurs between points A. 4to1 B. 1to2 C. 2to3 D. 3to4 | B. 1 to 2 |
| What is the patient’s ventricular ejection fraction? | 70% |
| Based on the graph in item 121, what is the end-systole volume? A. 140mL B. 100mL C. 70mL D. 0mL | C. 70mL |
| | |
| | |
| What does Ca+ does? a. Upstroke of SA node b. | |
| No P wave, normal QRS and normal T wave. Pacemaker is located in the? | AV node |
| 128. Which part of ECG corresponds to ventricular depolarization? A. P wave B. QRS duration C. U wave D. PR interval | |
| Axis of a normal heart (QRS Vector) | #ERROR! |
| Frank-Starling Mechanisms explains that | when the greater the Cardiac output, the greater the venous return |
| The physiologic function that is relatively slow conduction through AV node to allow sufficient time for: Runoff blood from the aorta to the arteriesVenous return to the atria | C. Filling of the ventricles |
| C. Filling of the ventricles D. Contraction of the ventricles | |
| | |
| A negative P wave in an AVR means A. Chamber enlargement of the atria B. Conducting abnormality from SA node to AV node C. Normal finding D. Echocardiogram to assess the valves and chambers | C. Normal finding |
| If all systemic vessel types were put side by side, which vessel type has the largest approximate totals cross sectional area? A. Arteries B. Arterioles C. Veins D. Capillaries | |
| Laminar flow in a blood vessel means: A. Each layer of blood remains the same distance from the walls B. Blood flows in layers creating sounds C. The central most portion of blood is the slowest D. . Blood flows in eddy currents | |
| during exercise | |
| Decreased Arteriolar resistance will produce: | Increase TPRIncrease AfterloadDecrease Arterial pressureDecrease Capillary blood flow |
| During exercise muscular movement increases, Arterioles (dilate?)increase 2 times, as a result blood flow resistance will be which of the following: | A. increase double B. Decreases in half C. Increases 16-folds D . Decreases 16- folds |
| | |
| Turbulence is caused by the increased of | Rate of blood flow becomes too greatwhen it passes by an obstruction in a resistance vessel |
| Case: 55% hematocrit, diagnosed With polycythemia. Decreases? | A. Reynold’s number B. Heheh C. Ish flow D. All of the above (?) |
| Which of the following has the highest vascular resistance? | vessels Blood flow Pressur e gradient A 1800 20 B 1600 40 C 1400 60 D 1200 80 |
| Last Ditch | CNS Ischemic |
| Repeated Question: A 30 year- old patient 55% hematocrit Diagnosed with polycythemia | Reynolds number |
| | |
| All veins in the neck are distended, the right atrial pressure will increase to? | 15 mmHg12 mmHg10 mmHg7 mmHg |
| What is the most important factor that regulates opening and closing of the metarterioles and capillary sphincter? | A. Degree of sympathetic stimulation B. Level of arterial pressure C. Tissue oxygen concentration D. Velocity of blood flow |
| regulates water and salt retention in the body | Aldosterone |
| Fainting caused by heavy emotions- vasovagal syncope | vasovagal syncope |
| atrial reflex control of heart rate | bainbridge reflex |


コメント